Vue响应式原理
Vue 使用 Object.defineProperty 定义 setter/getter 函数对数据进行劫持,实现数据的响应式。在 getter 函数中进行依赖收集,在 setter 函数中触发更新操作。
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" /><title>Document</title></head><body><div id="app"><p>你好,<span id="name"></span></p></div><script>var obj = {};Object.defineProperty(obj, "name", {get() {console.log("获取name");return document.querySelector("#name").innerHTML;},set(nick) {console.log("设置name");document.querySelector("#name").innerHTML = nick;}});obj.name = "Jerry";console.log(obj.name);</script></body></html>
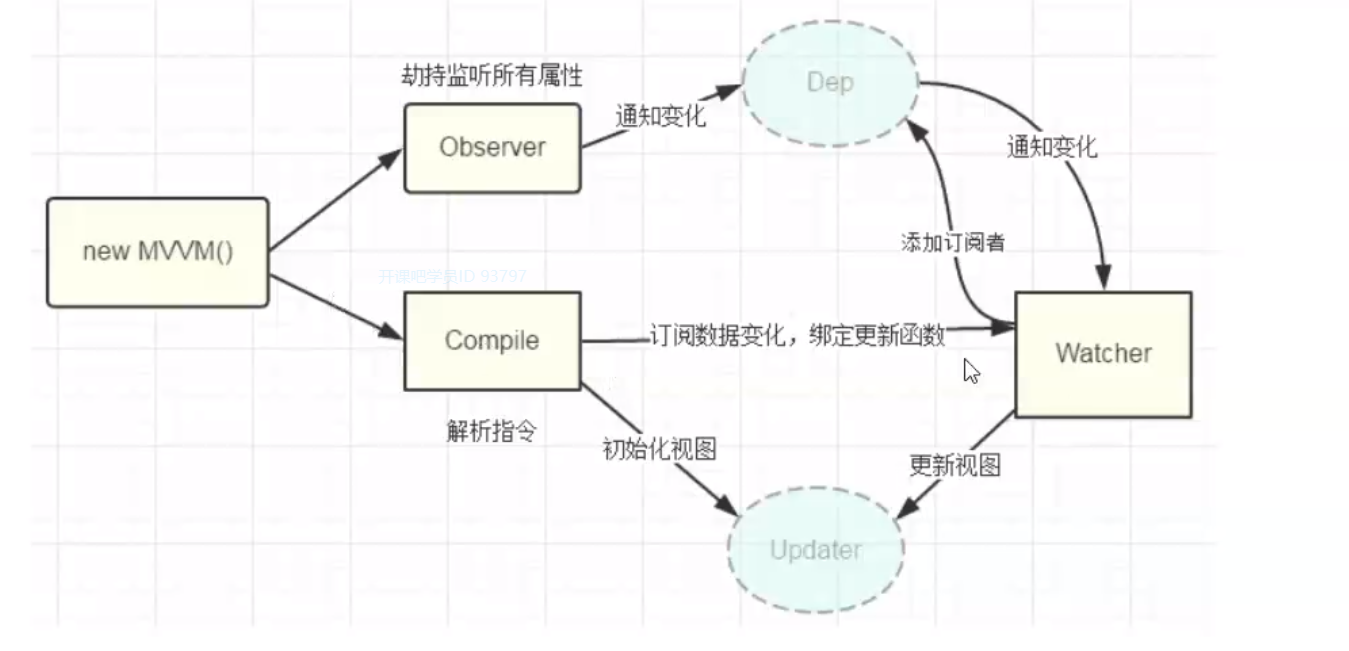
Vue工作机制(简化版)
Vue源码实现(简化版)
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset="utf-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><title>Page Title</title><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"></head><body><div>{{name}}</div><script>// 递归遍历,使传递进来的对象响应化function observe(obj) {// 判断类型if (!obj || typeof obj !== 'object') {return}Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => {defineReactive(obj, key, obj[key])})}function defineReactive(obj, key, val) {// 递归子属性observe(val)let dp = new Dep()Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {enumerable: true,configurable: true,get: function reactiveGetter() {console.log('get value')// 将Dep.target指向的Watcher实例加入到Dep中if (Dep.target) {dp.addSub(Dep.target)}return val},set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {console.log('change value')val = newVal// 执行 watcher 的 update 方法dp.notify()}})}// 通过 Dep类 解耦属性的依赖收集和更新操作(Dep 类是一个简单的观察者模式的实现)class Dep {constructor() {this.subs = []}// 添加依赖addSub(sub) {this.subs.push(sub)}// 更新notify() {this.subs.forEach(sub => {sub.update()})}}// 全局属性,通过该属性配置 WatcherDep.target = nullclass Watcher {constructor(obj, key, cb) {this.obj = objthis.key = keythis.cb = cbDep.target = this // 将 Dep.target 指向自己obj[key] // 读一次key触发getterDep.target = null // 最后将 Dep.target 置空}update() {// 获得新值this.value = this.obj[this.key]// 调用 update 方法更新 DOMthis.cb(this.value)}}// 组件初始化的时候执行 observe 方法var data = { name: 'yck' }observe(data)// 编译器工作:解析模板,收集依赖,创建 Watcher 和 update 函数(这里的 update 函数会在 Watcher 执 行自身的 update 函数时被调用,从而更新 DOM)// 完整的编译器再执行 更新DOM 操作之前,会有一个 patch 过程,该过程会执行 diff算法, 进行虚拟DOM的比对,然后再更新 DOMfunction update(value) {document.querySelector('div').innerText = value}// 模拟解析到 `{{ name }}` 触发的操作let watch = new Watcher(data, 'name', update)// update Dom innerTextdata.name = 'yyy'</script></body></html>
Vue工作机制
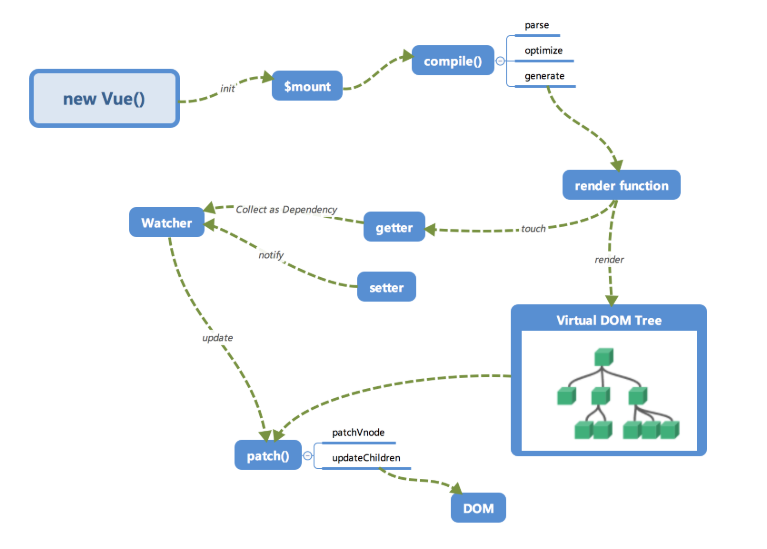
- 在 new Vue() 之后。 Vue 会调用 init 函数进行初始化,其中最重要的是通过 Object.defineProperty 设置 setter 与 getter 函数,实现数据的响应式。
- 初始化之后调用 $mount 挂载组件,进行编译操作,对 template 进行解析,编译可以分成parse、optimize 与 generate 三个阶段,最终得到 render function string:
- parse:生成 AST(抽象语法树)
- optimize:优化,判断标签中是否绑定了数据等
- generate:AST —> renderStr(渲染函数字符串),通过 new Function(renderStr) 最终得到 render function
- 执行 render 方法生成虚拟DOM,在虚拟 DOM 映射到真实 DOM 之前有一个 patch 过程,该过程会执行 diff 算法进行优化,减少重复的操作。最后生成真实 DOM。
diff 算法
diff 算法可以比对出两颗树的「差异」,我们来看一下,假设我们现在有如下两颗树,它们分别是新老 VNode 节点,这时候到了 patch 的过程,我们需要将他们进行比对,diff 算法是通过同层的树节点进行比较而非对树进行逐层搜索遍历的方式,所以时间复杂度只有 O(n),是一种相当高效的算法,如下图。
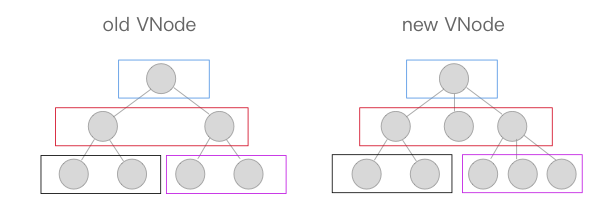
这张图中的相同颜色的方块中的节点会进行比对,比对得到「差异」后将这些「差异」更新到视图上。因为只进行同层级的比对,所以十分高效。
function patch (oldVnode, vnode, parentElm) {if (!oldVnode) {addVnodes(parentElm, null, vnode, 0, vnode.length - 1);} else if (!vnode) {removeVnodes(parentElm, oldVnode, 0, oldVnode.length - 1);} else {if (sameVnode(oldVNode, vnode)) {patchVnode(oldVNode, vnode);} else {removeVnodes(parentElm, oldVnode, 0, oldVnode.length - 1);addVnodes(parentElm, null, vnode, 0, vnode.length - 1);}}}
首先在 oldVnode(老 VNode 节点)不存在的时候,相当于新的 VNode 替代原本没有的节点,所以直接用 addVnodes 将这些节点批量添加到 parentElm 上。
然后同理,在 vnode(新 VNode 节点)不存在的时候,相当于要把老的节点删除,所以直接使用 removeVnodes 进行批量的节点删除即可。
最后一种情况,当 oldVNode 与 vnode 都存在的时候,需要判断它们是否属于 sameVnode(相同的节点)。如果是则进行patchVnode(比对 VNode )操作,否则删除老节点,增加新节点。
Vue 源码实现
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" /><title>Document</title></head><body><div id="app"><p>{{ name }}</p><p k-text="name"></p><p>{{ age }}</p><p>{{ doubleAge }}</p><input type="text" k-model="name" /><button @click="changeName">测试</button><div k-html="html"></div></div><script src="./compile.js"></script><script src="./kvue.js"></script><script>const vm = new KVue({el: "#app",data: {name: "I am test.",age: 12,html: "<button>这是一个按钮</button>"},created () {console.log("开始啦");setTimeout(() => {this.name = "我是测试";}, 1500);},methods: {changeName () {this.name = "哈喽,开课吧";this.age = 1;}}});</script></body></html>
kvue.js
class KVue {constructor(options) {this.$options = options;this.$data = options.data;// 响应化this.observe(this.$data);// 创建编译器new Compile(options.el, this);// 执行 created 函数if (options.created) {options.created.call(this);}}// 递归遍历,使传递进来的对象响应化observe(value) {if (!value || typeof value !== "object") {return;}// 遍历Object.keys(value).forEach(key => {// 对 key 做响应式处理this.defineReactive(value, key, value[key]);this.proxyData(key);});}defineReactive(obj, key, val) {// 递归this.observe(val);// 创建Dep实例:Dep 和 key 一对一对应const dep = new Dep();// 给obj定义属性Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {get() {// 将 Dep.target 指向的 Watcher 实例加入到 Dep 中Dep.target && dep.addDep(Dep.target);return val;},set(newVal) {if (newVal !== val) {val = newVal;dep.notify();}}});}// 在 Vue 实例上定义属性,代理data中的数据proxyData(key) {Object.defineProperty(this, key, {get() {return this.$data[key];},set(newVal) {this.$data[key] = newVal;}});}}// Dep:管理若干 Watcher 实例,它和key一对一关系class Dep {constructor() {this.deps = [];}addDep(watcher) {this.deps.push(watcher);}notify() {this.deps.forEach(watcher => watcher.update());}}// 保存 ui 中依赖,通过 update 函数可以更新class Watcher {constructor(vm, key, cb) {this.vm = vm;this.key = key;this.cb = cb;// 将当前实例指向Dep.targetDep.target = this;this.vm[this.key]; // 读一次key触发getterDep.target = null;}update() {this.cb.call(this.vm, this.vm[this.key]);// console.log(`${this.key}属性更新了`);}}
compile.js
// 遍历模板,处理插值表达式// 另外如果发现k-xx, @xx做特别处理class Compile {constructor(el, vm) {this.$vm = vm;this.$el = document.querySelector(el);if (this.$el) {// 1.$el中的内容 暂时存放 到一个fragment,提高操作效率this.$fragment = this.node2Fragment(this.$el);// 2.编译 fragmentthis.compile(this.$fragment);// 3.将编译结果插入到 挂载元素 下面this.$el.appendChild(this.$fragment);}}// 遍历el,把里面的内容 暂时存放 到新创建 fragment 中,这个操作会删除页面的 DOM 节点node2Fragment(el) {const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment();let child;while ((child = el.firstChild)) {// appenChild 是移动操作fragment.appendChild(child);}return fragment;}// 编译模板,替换动态值,处理指令和事件compile(el) {// 遍历elconst childNodes = el.childNodes;Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node => {if (this.isElement(node)) {// console.log("编译元素:" + node.nodeName);// 如果是元素节点,我们要处理指令k-xx,事件@xxthis.compileElement(node);} else if (this.isInterpolation(node)) {// console.log("编译文本:" + node.textContent);this.compileText(node);}// 递归子元素if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length > 0) {this.compile(node);}});}// 判断是否是元素isElement(node) {return node.nodeType === 1;}// 判断是否是插值表达式判断isInterpolation(node) {// 需要满足{{ xx }}return node.nodeType === 3 && /\{\{(.*)\}\}/.test(node.textContent);}compileElement(node) {// 查看node的特性中是否有k-xx,@xxconst nodeAttrs = node.attributes;Array.from(nodeAttrs).forEach(attr => {// 获取属性名称和值 k-text="abc"const attrName = attr.name; // k-textconst exp = attr.value; // abc// 指令:k-xxif (attrName.indexOf("k-") === 0) {const dir = attrName.substring(2); // text// 执行指令this[dir] && this[dir](node, this.$vm, exp);} else if(attrName.indexOf('@') === 0) {// 事件 @click="handlClick"const eventName = attrName.substring(1); // clickthis.eventHandler(node, this.$vm, exp, eventName);}});}// 处理 k-model 双向数据绑定指令model(node, vm, exp) {// update是数据变了改界面this.update(node, vm, exp, "model");// 界面变了改数值node.addEventListener("input", e => {vm[exp] = e.target.value;});}modelUpdator(node, value) {node.value = value;}// 处理 k-html 指令html(node, vm, exp) {this.update(node, vm, exp, "html");}htmlUpdator(node, value) {node.innerHTML = value;}// 处理 @ 指令eventHandler(node, vm, exp, eventName){// 获取回调函数const fn = vm.$options.methods && vm.$options.methods[exp];if(eventName && fn) {node.addEventListener(eventName, fn.bind(vm))}}// 把插值表达式替换为实际内容compileText(node) {console.log(node)// {{xxx}}// RegExp.$1是匹配分组部分// console.log(RegExp.$1);const exp = RegExp.$1;this.update(node, this.$vm, exp, "text");}// 处理 k-text 指令text(node, vm, exp) {this.update(node, vm, exp, "text");}textUpdator(node, value) {node.textContent = value;}// 编写update函数,它可复用// exp是表达式, dir是具体操作:text,html,modelupdate(node, vm, exp, dir) {const fn = this[dir + "Updator"];fn && fn(node, vm[exp]);// 创建Watcher// new Vue({// data: {// xxx: 'bla'// }// })// exp 就是 xxxnew Watcher(vm, exp, function() {fn && fn(node, vm[exp]);});}}

