16.4版本以上的生命周期 react-lifecycle-methods-diagram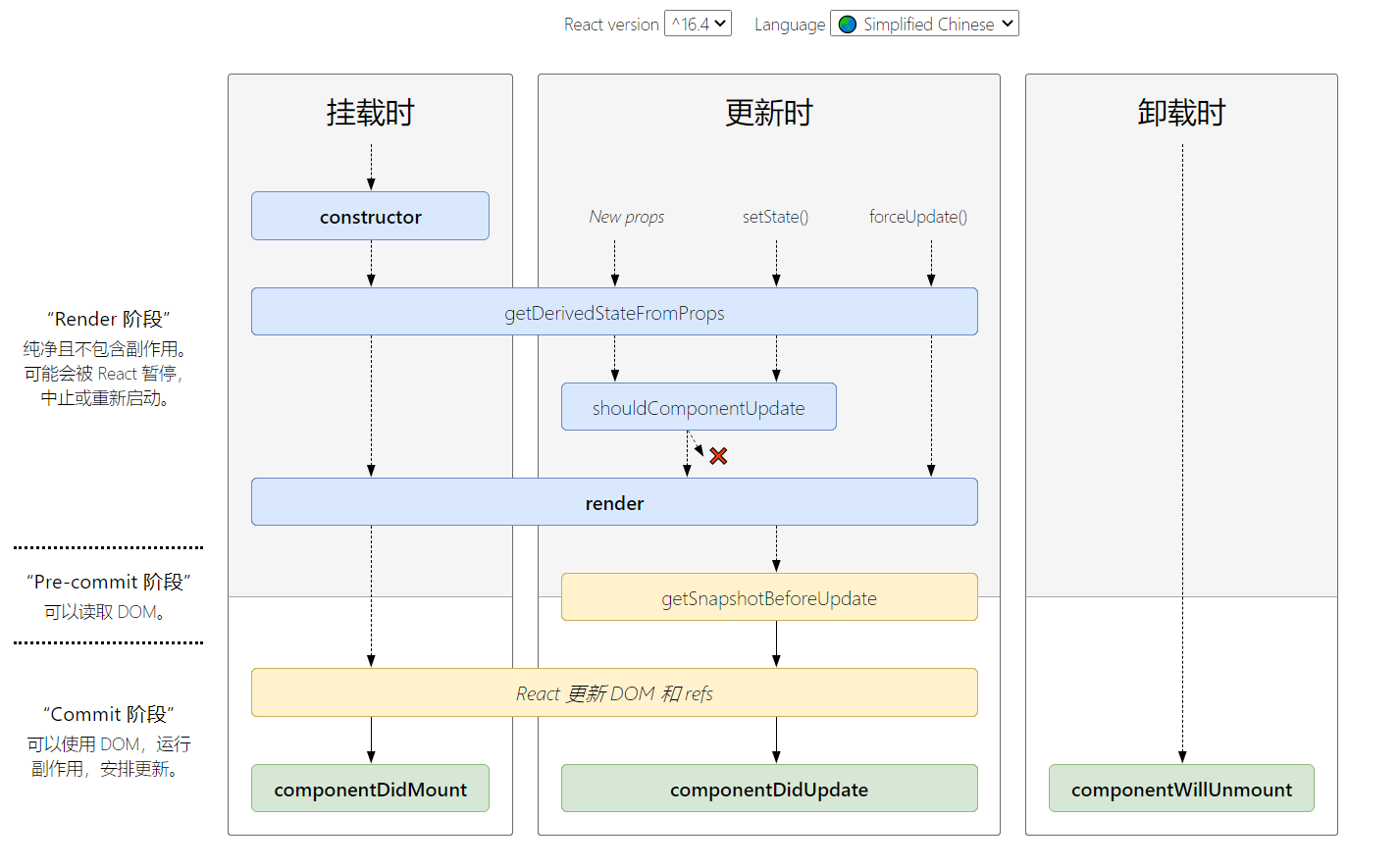
*16.3版本 getDerivedStateFormProps 不会被setState() 和 forceUpdate触发。
为什么要废弃 willmount willupdate willreceiveprops?
1) 完全可以转移到其他生命周期(尤其是 componentDidxxx)里去做。
2)在 Fiber 带来的异步渲染机制下,可能会导致非常严重的 Bug。
比如如果用户在willxxx里发起付款请求,由于处于render阶段,可能会被打断或者重启,这样会导致灾难性的后果
3)即使你没有开启异步,React 15 下也有不少人能把自己“玩死”。
在willxx里滥用setState 导致死循环
React 16 改造生命周期的主要动机是为了配合 Fiber 架构带来的异步渲染机制。在这个改造的过程中,React 团队精益求精,针对生命周期中长期被滥用的部分推行了具有强制性的最佳实践。这一系列的工作做下来,首先是确保了 Fiber 机制下数据和视图的安全性,同时也确保了生命周期方法的行为更加纯粹、可控、可预测。
挂载阶段 Mounting
constructor()
构造器,用于初始化组件的状态和方法,使用super(props)初始化父类。
如果没有初始化状态也不需要绑定handle函数的this,可以省略constructor函数。constructor(props) {super(props);this.state = {color: '#fff'};this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps)
derived v. 派生, 导源
该方法会在render函数被调用之前调用,包括第一次初始化组件以及后续的更新过程中,每次接收新props之后都会返回一个对象作为新的state,也可以返回null不对state进行更新。
该方法主要用于替换UNSAFE_componentWillReceiveProps()(将在17版本废弃)。 // 为什么替换
getDerivedStateFromProps是一个static方法,意味着拿不到实例的this。- render()
该方法在react组建中是必须实现的。
这是React组件的核心方法,用于根据状态state和属性props渲染一个React组件。我们应该保持该方法的纯洁性,这会让我们的组件更易于理解,只要state和props不变,每次调用render返回的结果应当相同,所以请不要在render方法中改变组件状态,也不要在在这个方法中和浏览器直接交互。 - componentDidMount()
componentDidMount方法会在render方法之后立即被调用,该方法在整个React生命周期中只会被调用一次。React的组件树是一个树形结构,此时你可以认为这个组件以及他下面的所有子组件都已经渲染完了,所以在这个方法中你可以调用和真实DOM相关的操作了。
有些组件的启动工作是依赖 DOM 的,例如动画的启动,而componentWillMount的时候组件还没挂载完成,所以没法进行这些启动工作,这时候就可以把这些操作放在componentDidMount当中。
我们推荐可以在这个函数中发送异步请求,在回调函数中调用setState()设置state,等数据到达后触发重新渲染。但注意尽量不要在这个函数中直接调用setState()设置状态,这会触发一次额外的重新渲染,可能造成性能问题。
下面的代码演示了如何在componentDidMount加载数据并设置状态:componentDidMount() {console.log('componentDidMount');fetch("https://api.github.com/search/repositories?q=language:java&sort=stars").then(res => res.json()).then((result) => {this.setState({ // 触发renderitems: result.items});}).catch((error) => { console.log(error)});// this.setState({color: xxx}) // 不要这样做}
更新阶段 Updating
- static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps)
同 ↑ - shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
通过此方法告诉react是否要进行下一次render(),默认返回为true,即每次更新状态和属性的时候都进行组件更新。此函数返回false并不会导致子组件不更新。
一般不需要实现,除非遇到了性能问题。 - render()
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState)
该方法的触发时间为update发生的时候,在render之后dom渲染之前返回一个值,作为componentDidUpdate的第三个参数。该函数与 componentDidUpdate 一起使用可以取代 componentWillUpdate 的所有功能,比如以下是官方的例子:class ScrollingList extends React.Component {constructor(props) {super(props);this.listRef = React.createRef();}getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {// Are we adding new items to the list?// Capture the scroll position so we can adjust scroll later.if (prevProps.list.length < this.props.list.length) {const list = this.listRef.current;return list.scrollHeight - list.scrollTop;}return null;}componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {// If we have a snapshot value, we've just added new items.// Adjust scroll so these new items don't push the old ones out of view.// (snapshot here is the value returned from getSnapshotBeforeUpdate)if (snapshot !== null) {const list = this.listRef.current;list.scrollTop = list.scrollHeight - snapshot;}}render() {return (<div ref={this.listRef}>{/* ...contents... */}</div>);}}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot)
该方法会在更新完成后被立即调用,你可以在这个方法中进行DOM操作,或者做一些异步调用。这个和首次装载过程后调用componentDidMount是类似的,不一样的是你可能需要判断下属性是否变化了再发起网络请求,如:componentDidUpdate(prevProps) { // 来自网络if(prevProps.myProps !== this.props.myProp) {// this.props.myProp has a different value// we can perform any operations that would// need the new value and/or cause side-effects// like AJAX calls with the new value - this.props.myProp}}
卸载阶段 Unmounting
componentWillUnmout()
该方法会在组件被卸载之前被调用,可以在这个函数中进行相关清理工作,比如删除定时器之类的操作。错误捕获
componentDidCatch(error, info)
在react组件中如果产生的错误没有被被捕获会被抛给上层组件,如果上层也不处理的话就会抛到顶层导致浏览器白屏错误,在React16中我们可以实现这个方法来捕获子组件产生的错误,然后在父组件中妥善处理,比如搞个弹层通知用户网页崩溃等。
在这个函数中请只进行错误恢复相关的处理,不要做其他流程控制方面的操作。比如:componentDidCatch(error, info) { // from react.org// Display fallback UIthis.setState({ hasError: true });// You can also log the error to an error reporting servicelogErrorToMyService(error, info);}

