介绍
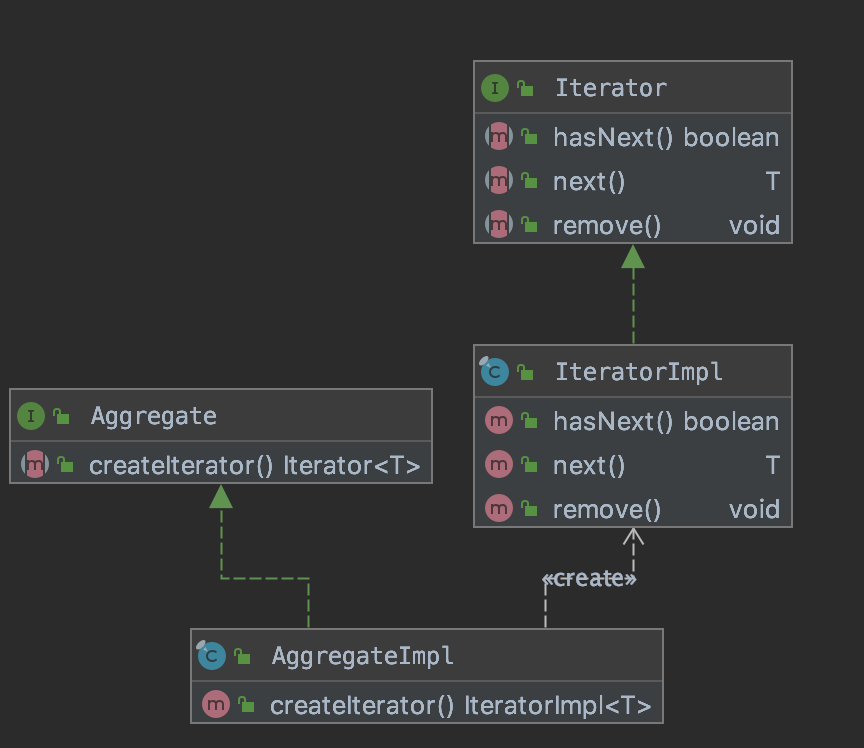
定义:迭代器模式提供一种方法顺序访问一个集合对象中的各个元素,而不暴露该对象的内部表示。
适用场景:
- 访问一个集合对象的内容而无序暴露它的内部表示。
- 为遍历不同的集合提供一个统一个接口。
优点:
- 分离了集合对象的遍历行为。
- 数组、列表遍历比较简单,但是树、图遍历复杂且遍历方式多样(中序、前序、后序;BFS、DFS),若由客户端遍历,则易错且成本高。
- 每个迭代器独享游标信息,所以可以创建多个迭代器,同时遍历而不相互影响。
- 迭代器提供了抽象接口,当客户端切换新的遍历算法时,只需要获取不同的迭代器实现类。如 DFS 改成 BFS。
缺点:类的个数成对增加,每增加一种集合,就需要增加响应的迭代器实现。
类图
源码
JDK 的 ArrayList 实现了 Iterator 接口。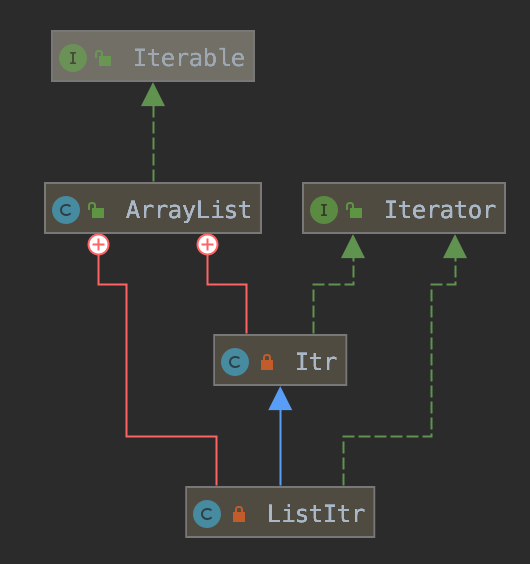
下面代码说明:
- 迭代过程中不能直接通过 List 的方法增加或删除元素。
- 可以通过迭代器的 remove 方法删除元素。
- 迭代器每次访问 next 方法,只能调用一次 remove 方法,连续调用两次会报错。
- 若两个迭代器同时在用,其中一个调用 remove 方法后,另一个再调用 next 或 remove 方法都会报错。
public class ArrayList
transient Object[] elementData;
private int size;
public Iterator
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”)
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
}