堆排序(Heapsort)是指利用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法。堆积是一个近似完全二叉树的结构,并同时满足堆积的性质:即子结点的键值或索引总是小于(或者大于)它的父节点。堆排序可以说是一种利用堆的概念来排序的选择排序。分为两种方法:
- 大顶堆:每个节点的值都大于或等于其子节点的值,在堆排序算法中用于升序排列;
- 小顶堆:每个节点的值都小于或等于其子节点的值,在堆排序算法中用于降序排列;
1. 算法步骤
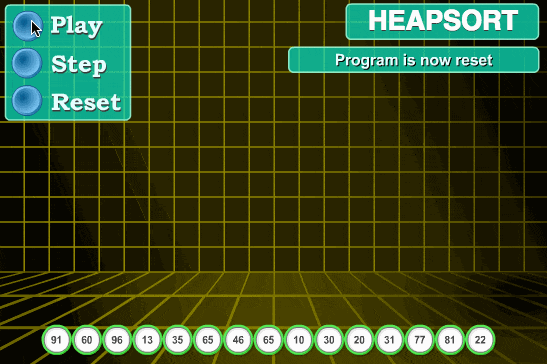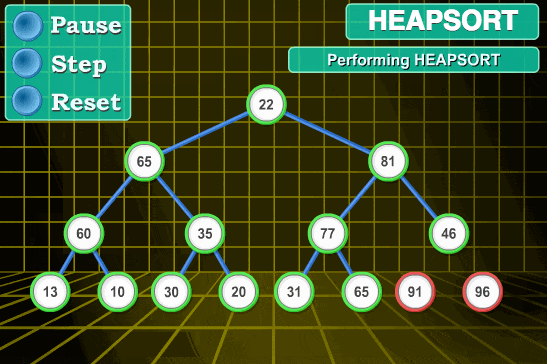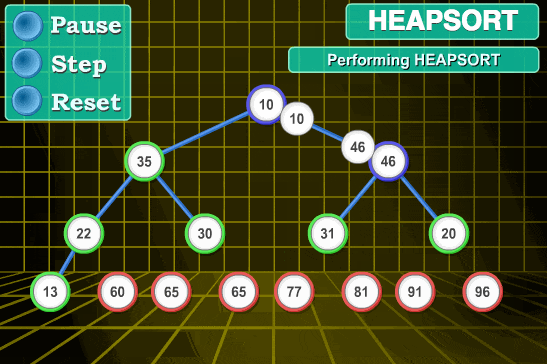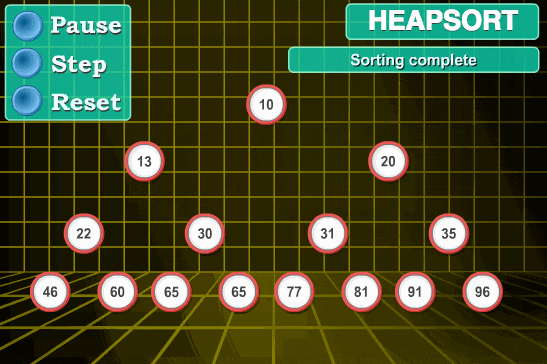
- 将待排序序列构建成一个堆 H[0……n-1],根据(升序降序需求)选择大顶堆或小顶堆;
- 把堆首(最大值)和堆尾互换;
- 把堆的尺寸缩小 1,并调用 shift_down(0),目的是把新的数组顶端数据调整到相应位置;
-
2. 动图演示
3. Java 代码实现
private static void heapSort(int[] arr) {// 原地建堆int heapSize = arr.length;for (int i = (heapSize >> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {siftDown(arr, i, heapSize);}while (heapSize > 1) {//交换堆顶元素和尾部元素,heapSize--swap(arr, 0, --heapSize);//对0位置siftDown,恢复堆的性质siftDown(arr, 0, heapSize);}}private static void siftDown(int[] array, int index, int heapSize) {Integer element = array[index];int half = heapSize >> 1;// index必须是非叶子节点while (index < half) {// 默认是左边跟父节点比int childIndex = (index << 1) + 1;Integer child = array[childIndex];int rightIndex = childIndex + 1;// 右子节点比左子节点大if (rightIndex < heapSize && array[rightIndex] > child) {child = array[childIndex = rightIndex];}// 大于等于子节点if (element >= child) {break;}array[index] = child;index = childIndex;}array[index] = element;}