一、简介
- 数据结构:计算机存储、组织数据的方式,就像锅碗瓢盆
- 算法:一系列解决问题的清晰指令,就像食谱
- 程序 = 数据结构 + 算法
数据结构**
- 栈、队列、链表
- 集合、字典
- 树、堆、图
算法
- 链表:遍历链表、删除链表节点
- 树、图:深度/广度优先遍历
- 数组:冒泡/选择/插入/归并/快速排序、顺序/二分搜索
算法设计思想
- 分而治之
- 动态规划
- 贪心算法
- 回溯算法
算法解题四步分析法
- 模拟:模拟题目的运行
- 规律:尝试总结出题目的一般规律和特点
- 匹配:找到符合这些特点的数据结构与算法
- 边界:考虑特殊情况
二、时间复杂度与空间复杂度
1、时间复杂度
- 一个函数,用大O表示,比如O(1)、O(n)、O(logN)
- 定性描述该算法的运行时间(执行次数)
2、空间复杂度
- 一个函数,用大O表示,比如O(1)、O(n)、O(n ^ 2)
- 算法在运行过程中临时占用存储空间大小的量度(占用的内存单元)
三、栈
一个后进先出的数据结构
1、使用场景例子
- 十进制转二进制
- 有效的括号(LeetCode-20)
- js函数调用堆栈
2、常用操作方式
- push、pop、stack[stack.length - 1]
四、队列
一个先进先出的数据结构
1、使用场景例子
- 食堂排队打饭
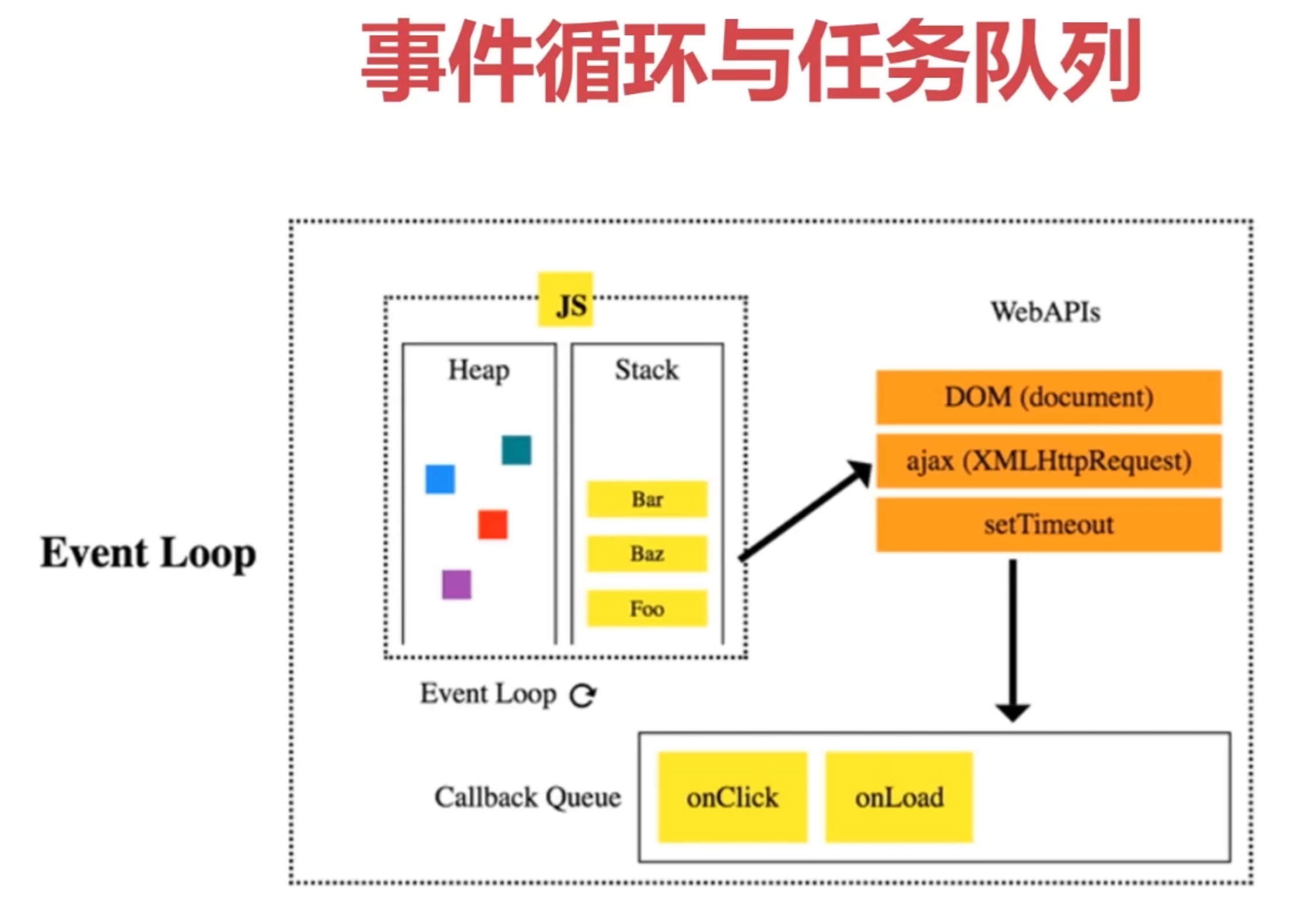
- JS异步中的任务队列
- 计算最近请求次数(LeetCode-933)
2、常用操作方式
- push、shift、queue[0]
五、链表
- 多个元素组成的列表
- 元素存储不连续,用 next 指针连在一起
- 在 js 中使用 Object 实现链表
1、链表和数组的区别
- 数组:增删非首尾元素时往往需要移动元素
- 链表:增删非首尾元素,不需要移动元素,只需要更改 next 的指向即可
2、链表创建方法及操作
const a = { val: 'a' };const b = { val: 'b' };const c = { val: 'c' };const d = { val: 'd' };a.next = b;b.next = c;c.next = d;// 遍历链表let p = a;while (p) {console.log(p.val);p = p.next;}// 插入const e = { val: 'e' };c.next = e;e.next = d;// 删除c.next = d;
3、算法场景
- 删除链表中的节点(LeetCode-237)
- 反转链表(LeetCode-206)
- 两数相加(LeetCode-2)
- 删除排序链表中的重复元素(LeetCode-83)
- 环形链表(LeetCode-141)
4、JS 中的链表 — 原型链
- 原型链的本质是链表
- 原型链上的节点是各种原型对象,比如 Function.prototype、Object.prototype
- 原型链通过
__proto__属性链接各种原型对象
4.1 常见原型链
- obj -> Object.prototype -> null
- func -> Function.prototype -> Object.prototype -> null
- arr -> Array.prototype -> Object.prototype -> null
4.2 原型链知识点
- 如果 A 沿着原型链能找到 B.prototype,那么 A instanceof B 为 true
// 手动实现 instanceofconst instanceof = (A, B) => {let p = Awhile (p) {if (p === B.prototype) {return true}p = p.__proto__}return false}
- 如果在 A 对象上没有找到 x 属性,那么会沿着原型链找 x 属性(如 toString)
5、JS 中的链表 — 使用链表指针获取 JSON 的节点值
const json = {a: { b: { c: 1 } },d: { e: 2 },}const path = ['a', 'b', 'c']let p = jsonpath.forEach(k => {p = p[k]})
六、集合
- 一种无序且唯一的数据结构
- ES6 中有集合,名为 Set
- 集合的常用操作:去重、判断某元素是否在集合中、求交集
// 去重const arr = [1, 1, 2, 2]const arr2 = [...new Set(arr)]// 判断元素是否在集合中const set = new Set(arr)const has = set.has(1)// 求交集const set2 = new Set([2, 3])const set3 = new Set([...set].filter(v => set2.has(v)))
1、算法场景
- 两个数组的交集(LeetCode-349)
2、ES6 的 Set
- 使用 Set 对象:new、add、delete、has、size
let mySet = new Set();mySet.add(1);mySet.add(5);mySet.add(5);mySet.add('some text');let o = { a: 1, b: 2 };mySet.add(o);mySet.add({ a: 1, b: 2 });const has = mySet.has(o);mySet.delete(5);console.log(mySet.size)
- 迭代 Set:多种迭代方法、Set 与 Array 互转、求交集/差集
// 三种迭代方法,其中第一、第二种等价for(let item of mySet.keys()) console.log(item)for(let item of mySet.values()) console.log(item)for(let [key, value] of mySet.entries()) console.log(key, value);mySet.forEach((value, key, current) => {})// Set 与 Array 互转const myArr = Array.from(mySet);const myArr2 = [...mySet]const mySet2 = new Set([1,2,3,4]);// 求交集/差集const intersection = new Set([...mySet].filter(x => mySet2.has(x)));const difference = new Set([...mySet].filter(x => !mySet2.has(x)));
七、字典
- 与集合类似,也是存储唯一值的数据结构,但它是以键值对的形式来存储
- ES6 中有字典,名为 Map
- 常用操作:键值对的增删改查
const m = new Map();// 增m.set('a', 'aa');m.set('b', 'bb');// 删m.delete('b');// m.clear();// 改m.set('a', 'aaa');// 查m.get('a')// 遍历和与数组互转,方法同集合(set)
1、算法场景
- 两个数组的交集(LeetCode-349)
- 有效的括号(LeetCode-20)
- 两数之和(LeetCode-1)
- 无重复字符的最长子串(LeetCode-3)
- 最小覆盖子串(LeetCode-76)
八、树
- 一种分层数据的抽象模型
- 前端工作中常见的树包括:DOM树、级联选择、树形控件
- JS中没有树,但是可以用 Object 和 Array 构建树
- 常用操作:深度/广度优先遍历、先中后序遍历
1、深度/广度优先遍历
- 深度优先遍历:尽可能深的搜索树的分支
- 广度优先遍历:先访问离根节点最近的节点
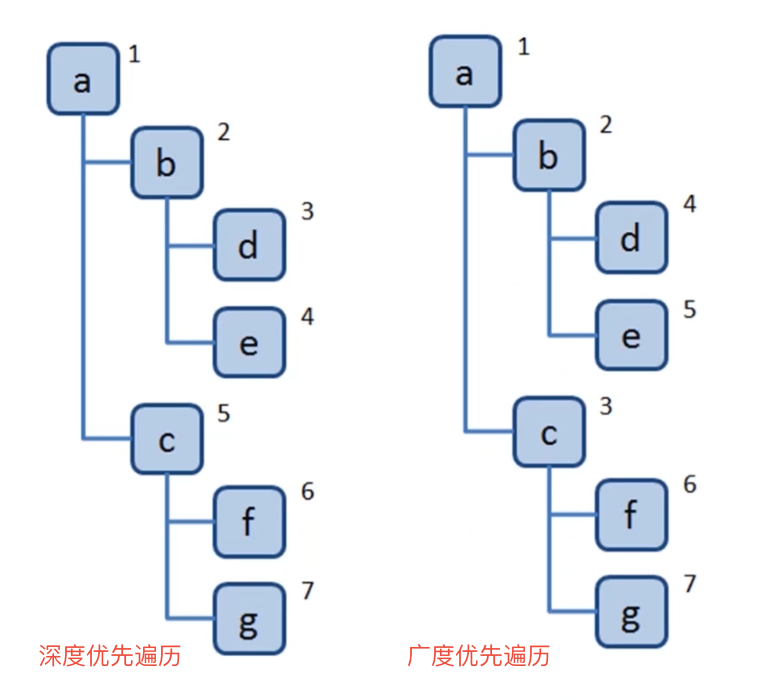
1.1 深度优先遍历口诀
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的 children 挨个进行深度优先遍历
// dfsconst tree = {val: 'a',children: [{val: 'b',children: [{val: 'd',children: [],},{val: 'e',children: [],}],},{val: 'c',children: [{val: 'f',children: [],},{val: 'g',children: [],}],}],};const dfs = (root) => {console.log(root.val);root.children.forEach(dfs);};dfs(tree);
1.2 广度优先遍历口诀
- 新建一个队列,把根节点入队
- 把队头出队并访问
- 把队头的 children 挨个入队
- 重复第二、三步,直到队列为空
// bfsconst tree = {val: 'a',children: [{val: 'b',children: [{val: 'd',children: [],},{val: 'e',children: [],}],},{val: 'c',children: [{val: 'f',children: [],},{val: 'g',children: [],}],}],};const bfs = (root) => {const q = [root];while (q.length > 0) {const n = q.shift();console.log(n.val);n.children.forEach(child => {q.push(child);});}};bfs(tree);
2、二叉树先中后序遍历
- 树中每个节点最多只能有两个子节点
- 在 JS 中通常用 Object 来模拟二叉树
const binaryTree = {val: 1,left: {val: 2,left: null,right: null},right: {val: 3,left: null,right: null}}
2.1 先序遍历算法口诀
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的左子树进行先序遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行先序遍历
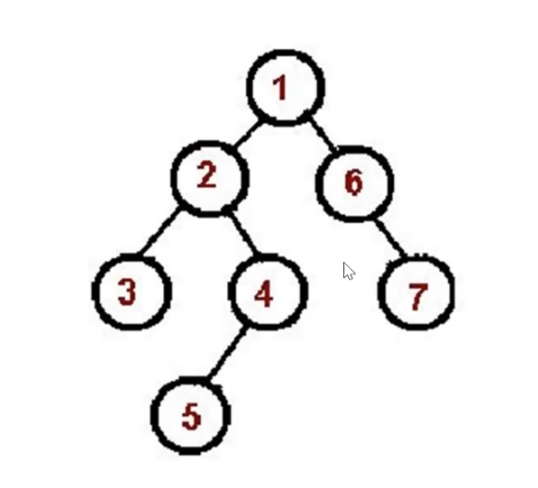
// preorderconst bt = {val: 1,left: {val: 2,left: {val: 4,left: null,right: null,},right: {val: 5,left: null,right: null,},},right: {val: 3,left: {val: 6,left: null,right: null,},right: {val: 7,left: null,right: null,},},};// 递归版const preorder = (root) => {if (!root) { return; }console.log(root.val);preorder(root.left);preorder(root.right);};// 非递归版const preorder = (root) => {if (!root) { return; }const stack = [root]while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop()console.log(n.val)if (n.right) stack.push(n.right)if (n.left) stack.push(n.left)}};preorder(bt);
2.2 中序遍历算法口诀
- 对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历
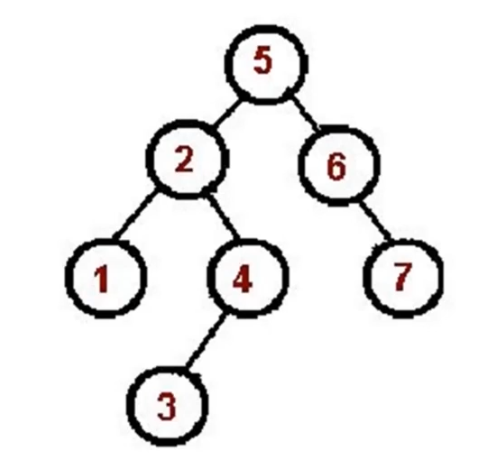
// inorder// 递归版const inorder = (root) => {if (!root) { return; }inorder(root.left);console.log(root.val);inorder(root.right);};// 非递归版const inorder = (root) => {if (!root) { return; }const stack = []let p = rootwhile (stack.length || p) {while (p) {stack.push(p)p = p.left}const n = stack.pop()console.log(n.val)p = n.right}};inorder(bt);
2.3 后序遍历算法口诀
- 对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历
- 访问根节点
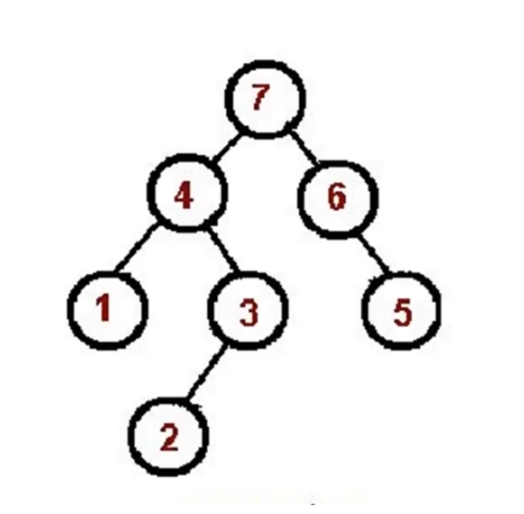
// postorder// 递归版const inorder = (root) => {if (!root) { return; }inorder(root.left);inorder(root.right);console.log(root.val);};// 非递归版// 逆序思考,类似先序遍历(根右左)const postorder = (root) => {if (!root) { return; }const stack = [root]const outputStack = []while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop()outputStack.push(n)if (n.left) stack.push(n.left)if (n.right) stack.push(n.right)}while (outputStack.length) {const n = outputStack.pop()console.log(n.val)}};postorder(bt);
3、算法场景
- 二叉树的最大深度(LeetCode-104)
- 二叉树的最小深度(LeetCode-111)
- 二叉树的层序遍历(LeetCode-102)
- 二叉树的中序遍历(LeetCode-94)
- 路径总和(LeetCode-112)
4、前端与树
- 遍历 JSON 的所有节点值
const json = {a: { b: { c: 1 } },d: [1, 2],};const dfs = (n, path) => {console.log(n, path);Object.keys(n).forEach(k => {dfs(n[k], path.concat(k));});};dfs(json, []);
- 渲染 Antd 的树组件
九、图
- 图是网络结构的抽象,是一组由边连接的节点
- 图可以表示任何二元关系,比如道路、航班等
- JS 中没有图,但是可以用 Object 和 Array 构建图
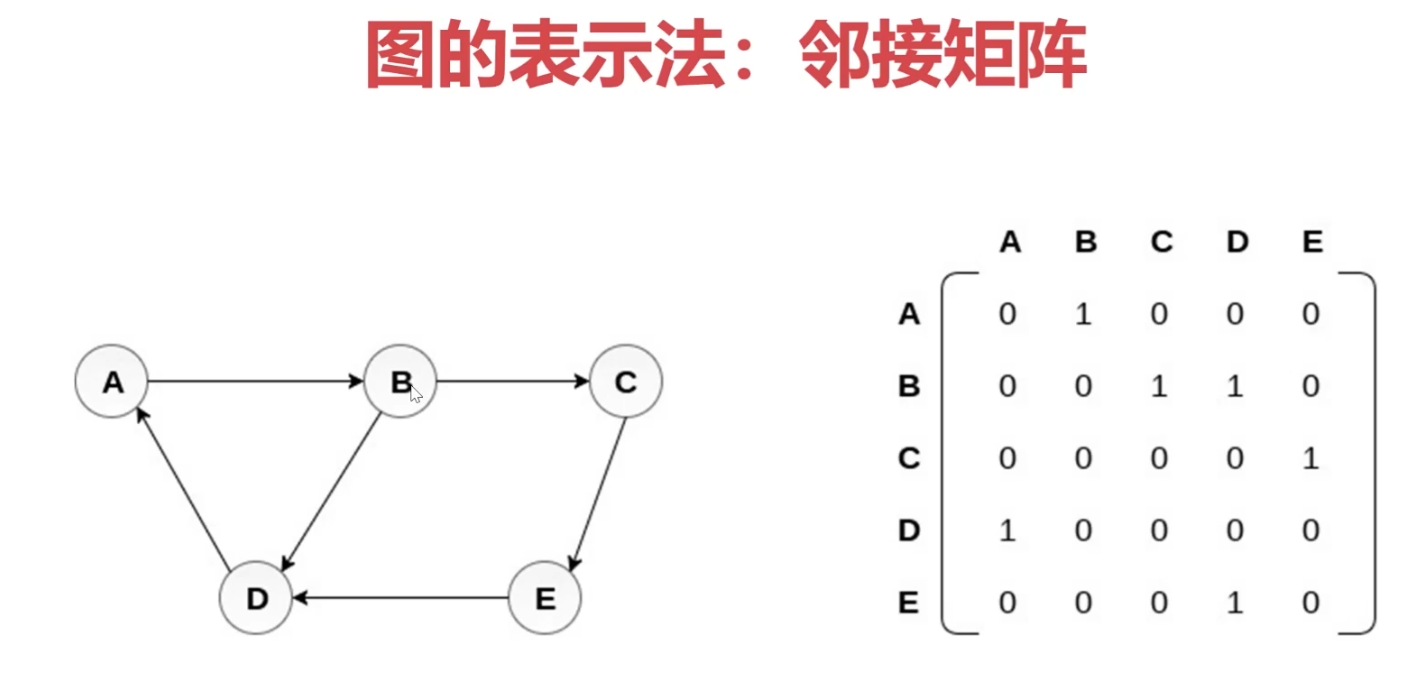
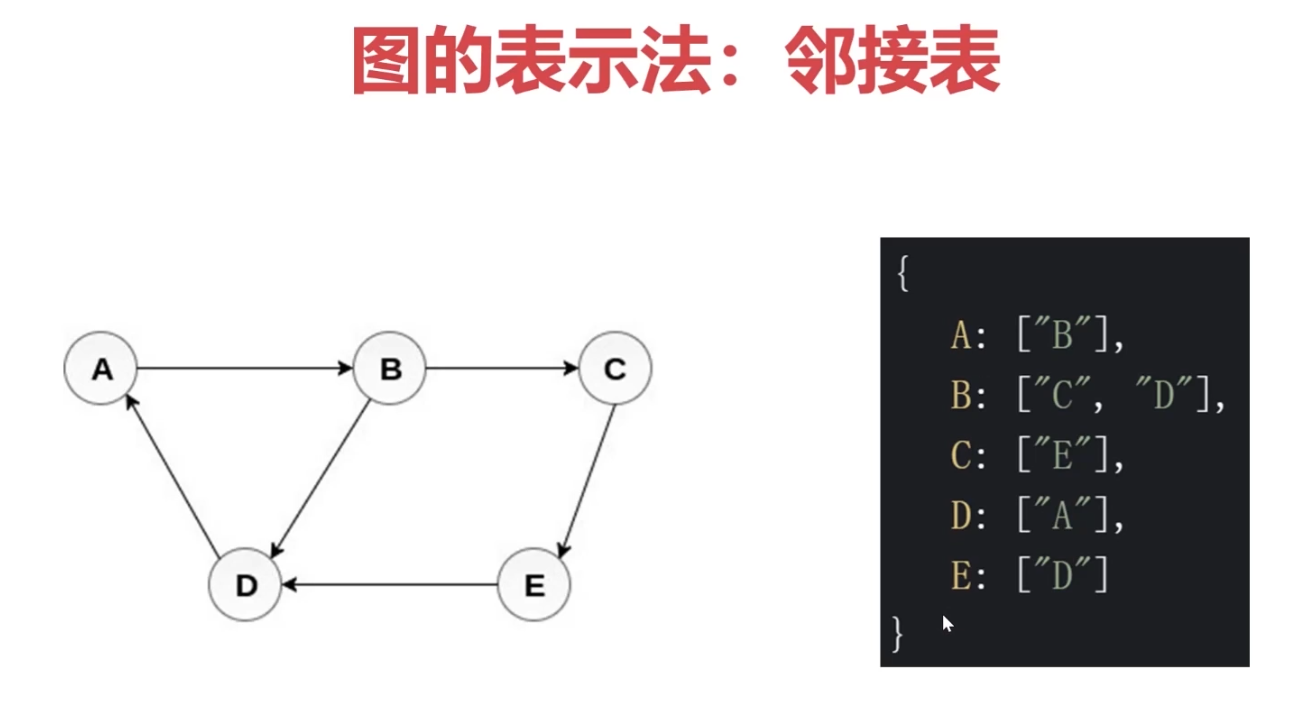
- 图的表示法:邻接矩阵、邻接表、关联矩阵等
- 常用操作:深度/广度优先遍历
1、图的深度/广度优先遍历
- 深度优先遍历:尽可能深的搜索图的分支
- 广度优先遍历:先访问离根节点最近的节点
1.1 深度优先遍历口诀
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的没访问过的相邻节点挨个进行深度优先遍历
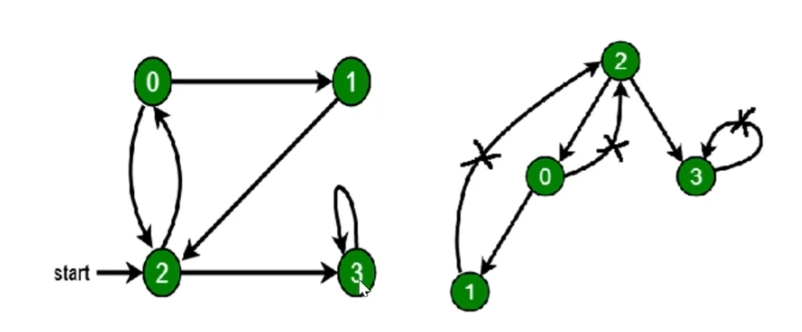
const graph = {0: [1, 2],1: [2],2: [0, 3],3: [3]};const visited = new Set()const dfs = (n) => {console.log(n)visited.add(n)graph[n].forEach(c => {if (!visited.has(c)) {dfs(c)}})}
1.2 广度优先遍历口诀
- 新增一个队列,把根节点入队
- 把队头出队并访问
- 把队头的没访问过的相邻节点入队
- 重复第二、三步直到队列为空
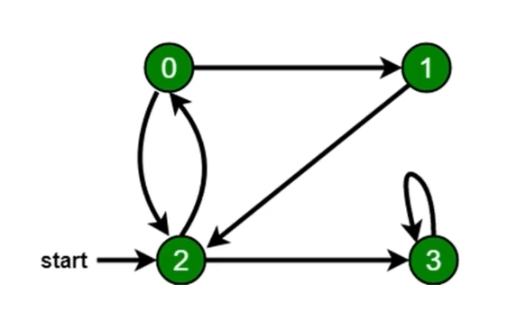
const graph = {0: [1, 2],1: [2],2: [0, 3],3: [3]};const bfs = (root) => {const visited = new Set()visited.add(root)const q = [root]while(q.length) {const n = q.shift()console.log(n)graph[n].forEach(c => {if (!visited.has(c)) {q.push(c)visited.add(c)}})}}
2、算法场景
- 有效数字(LeetCode-65)
- 太平洋大西洋水流问题(LeetCode-417)
- 克隆图(LeetCode-133)
十、堆
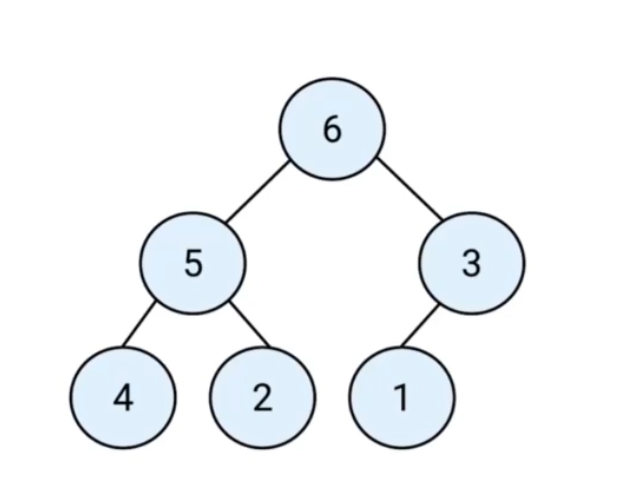
- 堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树(节点完全填满,只能剩余右侧的节点)
- 所有的节点都大于等于(最大堆)或小于等于(最小堆)它的子节点
1、JS 中的堆
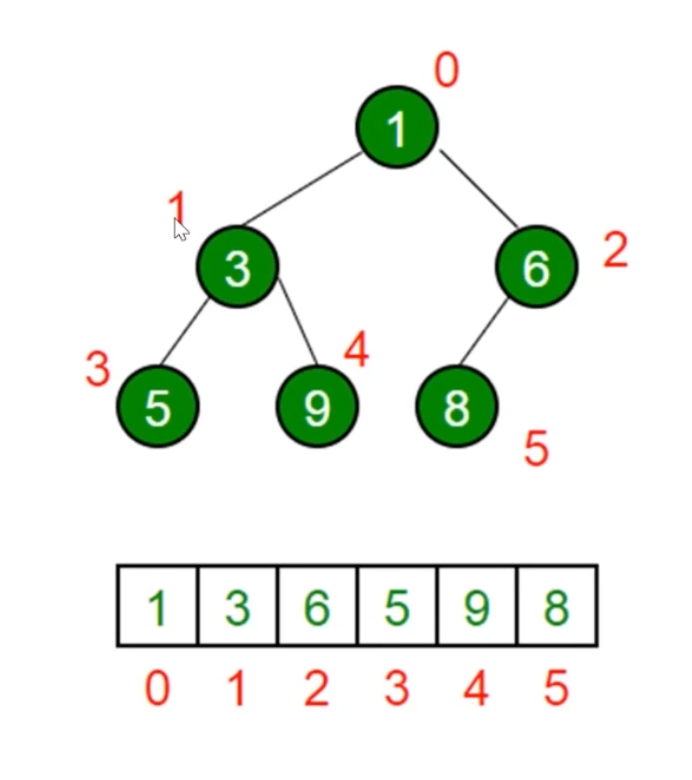
- JS 中通常用数组来表示堆
- 左侧子节点的位置是2 * index + 1
- 右侧子节点的位置是2 * index + 2
- 父节点的位置是 (index - 1) / 2
2、堆的应用
- 堆能高效、快速地找出最大/最小值,时间复杂度是 O(1)
- 找出第 k 个最大(小)元素
2.1 找出第 k 个最大(小)元素
2.2 最小堆类实现
- 在类中,声明一个数组,用来装元素
- 主要方法:插入、删除堆顶、获取堆顶、获取堆大小
插入
- 将值插入堆的底部,即数组的尾部
- 然后上移:将这个值和它的父节点进行交换,直到父节点小于等于这个插入的值
删除堆顶
- 用数组尾部元素替换堆顶(直接删除堆顶会破坏堆结构)
- 然后下移:将新堆顶和它的子节点进行交换,直到子节点大于等于这个新堆顶
获取堆顶和堆的大小
- 获取堆顶:返回数组的头部
获取堆的大小:返回数组的长度 ```javascript class MinHeap { constructor() { this.heap = [] }
swap(i1, i2) { const temp = this.heap[i1] this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2] this.heap[i2] = temp }
getParentIndex(i) { return (i - 1) >> 1 // return Math.floor((i - 1) / 2) }
getLeftIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 1 }
getRightIndex(i) { return i * 2 + 2 }
shiftUp(index) { if (index === 0) return const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index) if (this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]) {
this.swap(parentIndex, index)this.shiftUp(parentIndex)
} }
shiftDown(index) { const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index) const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index)
if (this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[index]) {
this.swap(leftIndex, index)this.shiftDown(leftIndex)
} if (this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[index]) {
this.swap(rightIndex, index)this.shiftDown(rightIndex)
} }
// 插入方法 insert(value) { this.heap.push(value) this.shiftUp(this.heap.length - 1) }
// 删除方法 pop() { this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop() this.shiftDown(0) }
// 获取堆顶 top() { return this.heap[0] }
// 获取堆大小 size() { return this.heap.length } }
// 示例 const h = new MinHeap() h.insert(3) h.insert(2) h.insert(1) h.pop()
<a name="GlNGh"></a>### 3、算法场景- 数组中的第 K 个最大元素(LeetCode-215)- 前 K 个高频元素(LeetCode-347)- 合并 K 个排序链表(LeetCode-23)<a name="uVEvR"></a>## 十一、搜索排序<a name="WWed6"></a>### 1、排序把某个乱序的数组变成升序或者降序的数组,JS 中的排序如 sort 方法,常见排序算法如下:<a name="swz6I"></a>#### 1.1 冒泡排序**思路:**1. 比较所有相邻元素,如果第一个比第二个大,则交换它们2. 一轮下来可以保证最后一个数是最大的3. 执行 n - 1 轮,就可以完成排序**<br />**代码实现:**```javascript// 时间复杂度 O(n^2)// 升序Array.prototype.bubbleSort = function () {for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i += 1) {for (let j = 0; j < this.length - 1 - i; j += 1) {if (this[j] > this[j + 1]) {const temp = this[j]this[j] = this[j + 1]this[j + 1] = temp}}}}const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]arr.bubbleSort()console.log(arr)
1.2 选择排序
思路:
- 找到数组中的最小值,选中它并将其放置在第一位
- 接着找到第二小的值,选中它并将其放置在第二位
- 以此类推,执行 n - 1 轮
代码实现:**
// 时间复杂度 O(n^2)// 升序Array.prototype.selectionSort = function () {for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i += 1) {let minIndex = ifor (let j = i + 1; j < this.length; j += 1) {if (this[minIndex] > this[j]) {minIndex = j}}if (i !== minIndex) {const temp = this[i]this[i] = this[minIndex]this[minIndex] = temp}}}const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]arr.selectionSort()console.log(arr)
1.3 插入排序
思路:
- 从第二个数开始,将其“提取”往前比
- 比它大就往后移一格,否则将其插入
- 以此类推进行到最后一个数
代码实现:**
// 时间复杂度 O(n^2)// 升序Array.prototype.insertSort = function () {for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i += 1) {const temp = this[i]for (let j = i - 1; j >= 0; j -= 1) {if (this[j] > temp) {this[j + 1] = this[j]this[j] = temp} else {break}}}}const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]arr.insertSort()console.log(arr)
1.4 归并排序
思路:
- 分:把数组劈成两半,再递归地对子数组进行“分”操作,直到分成一个个单独的数
- 合:把两个数合并为有序数组,再对有序数组进行合并,直到全部子数组合并为一个完整数组
合并两个有序数组:
- 新建一个空数组 res,用于存放最终排序后的数组
- 比较两个有序数组的头部,较小者出队并推入 res 中
- 如果两个数组还有值,就重复第二步
代码实现:**
// 时间复杂度 O(nlogn)// 升序Array.prototype.mergeSort = function () {const rec = (arr) => {if (arr.length === 1) return arrconst mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2)const left = arr.slice(0, mid)const right = arr.slice(mid, arr.length)const orderLeft = rec(left)const orderRight = rec(right)const res = []while (orderLeft.length || orderRight.length) {if (orderLeft.length && orderRight.length) {res.push(orderLeft[0] < orderRight[0] ? orderLeft.shift() : orderRight.shift())} else if (orderLeft.length) {res.push(orderLeft.shift())} else if (orderRight.length) {res.push(orderRight.shift())}}return res}const res = rec(this)res.forEach((v, i) => {this[i] = v})}const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]arr.mergeSort()console.log(arr)
1.5 快速排序
思路:
- 分区:从数组中任意选择一个“基准”,所有比基准小的元素放在基准前面,比基准大的元素放在基准的后面
- 递归:递归地对基准前后的子数组进行分区
代码实现:**
// 时间复杂度 O(nlogn)// 升序Array.prototype.quickSort = function () {const rec = (arr) => {if (arr.length <= 1) return arrconst left = []const right = []const mid = arr[0]for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i += 1) {if (arr[i] < mid) {left.push(arr[i])} else {right.push(arr[i])}}return [...rec(left), mid, ...rec(right)]}const res = rec(this)res.forEach((v, i) => {this[i] = v})}const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]arr.quickSort()console.log(arr)
2、搜索
找出数组中某个元素的下标,JS 中的搜索如 indexOf、findIndex等方法,常见搜索算法如下:
2.1 顺序搜索
思路:
- 遍历数组
- 找到跟目标值相等的元素,就返回它的下标
- 遍历结束后,如果没找到,就返回 -1
代码实现:**
// 时间复杂度 O(n)Array.prototype.sequentialSearch = function (target) {for(let i = 0; i < this.length; i += 1) {if (this[i] === target) return i}return -1}const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]const index = arr.sequentialSearch(2)console.log(index)
2.2 二分搜索
必须有序
思路:
- 从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是目标值,则搜索结束
- 如果目标值大于或小于中间元素,则在大于或小于中间元素的那一半数组中搜索
代码实现:**
// 时间复杂度 O(logn)Array.prototype.binarySearch = function (target) {let begin = 0let end = this.length - 1while (begin <= end) {const mid = Math.floor((end + begin) / 2)if (this[mid] === target) {return mid} else if (this[mid] < target) {begin = mid + 1} else if (this[mid] > target) {end = mid - 1}}return -1}const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]const index = arr.binarySearch(2)console.log(index)
3、算法场景
- 合并两个有序链表(LeetCode-21)
- 猜数字大小(LeetCode-374)
十二、分而治之
- 分而治之是算法设计中的一种方法,是一种思想
- 它将一个问题分成多个和原问题相似的小问题,递归解决小问题,再将结果合并以解决原来的问题
1、场景一:归并排序
- 分:把数组从中间一分为二
- 解:递归地对两个子数组进行归并排序
- 合:合并有序子数组
2、场景二:快速排序
- 分:选基准,按基准把数组分成两个子数组
- 解:递归地对两个子数组进行快速排序
- 合:对两个子数组进行合并
3、算法场景
- 猜数字大小(LeetCode-374)
- 翻转二叉树(LeetCode-226)
- 相同的树(LeetCode-100)
- 对称二叉树(LeetCode-101)
十三、动态规划
- 动态规划是算法设计中的一种方法,是一种思想
- 它将一个问题分解为相互重叠的子问题,通过反复求解子问题,来解决原来的问题
1、动态规划 vs 分而治之
- 相同点:动态规划和分而治之都是将一个问题分解为子问题
- 不同点:动态规划是相互重叠的子问题,子问题之间有关联关系;分而治之的子问题彼此相互独立
2、算法场景
- 爬楼梯(LeetCode-70)
- 打家劫舍(LeetCode-198)
十四、贪心算法
- 贪心算法是算法设计中的一种方法,是一种思想
- 期盼通过每个阶段的局部最优选择,从而达到全局的最优
- 结果并不一定是最优
1、算法场景
- 分饼干(LeetCode-455)
- 买卖股票的最佳时机(LeetCode-122)
十五、回溯算法
- 回溯算法是算法设计中的一种方法,是一种思想
- 回溯算法是一种渐进式寻找并构建问题解决方式的策略
- 回溯算法会先从一个可能的动作开始解决问题,如果不行,就回溯并选择另一个动作,直到将问题解决
1、适用场景
- 有很多路
- 这些路里,有死路,也有出路
- 通常需要递归来模拟所有的路
2、算法场景
- 全排列(LeetCode-46)
- 子集(LeetCode-78)