概念
Annotation(注解)是 Java 提供的一种对元程序中元素关联信息和元数据(metadata)的途径 和方法。Annatation(注解)是一个接口,程序可以通过反射来获取指定程序中元素的 Annotation 对象,然后通过该 Annotation 对象来获取注解中的元数据信息。
4 种标准元注解
@Target 修饰的对象范围
@Target说明了Annotation所修饰的对象范围: Annotation可被用于 packages、types(类、 接口、枚举、Annotation 类型)、类型成员(方法、构造方法、成员变量、枚举值)、方法参数 和本地变量(如循环变量、catch 参数)。在Annotation 类型的声明中使用了target可更加明晰其修饰的目标
@Retention 定义 被保留的时间长短
Retention 定义了该 Annotation 被保留的时间长短:表示需要在什么级别保存注解信息,用于描述注解的生命周期(即:被描述的注解在什么范围内有效),取值(RetentionPoicy)由:
- SOURCE:在源文件中有效(即源文件保留)
- CLASS:在 class 文件中有效(即 class 保留)
- RUNTIME:在运行时有效(即运行时保留)
@Documented 描述-javadoc
@ Documented 用于描述其它类型的 annotation 应该被作为被标注的程序成员的公共 API,因此可以被例如 javadoc 此类的工具文档化。 标记这些注解是否包含在用户文档中。@Inherited 阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的
@Inherited 元注解是一个标记注解,@Inherited 阐述了某个被标注的类型是被继承的。如果一 个使用了@Inherited 修饰的 annotation 类型被用于一个 class,则这个 annotation 将被用于该class 的子类。标记这个注解是继承于哪个注解类(默认 注解并没有继承于任何子类)作用在代码的注解
- @Override - 检查该方法是否是重写方法。如果发现其父类,或者是引用的接口中并没有该方法时,会报编译错误。
- @Deprecated - 标记过时方法。如果使用该方法,会报编译警告。
- @SuppressWarnings - 指示编译器去忽略注解中声明的警告。
- @SafeVarargs - Java 7 开始支持,忽略任何使用参数为泛型变量的方法或构造函数调用产生的警告。
- @FunctionalInterface - Java 8 开始支持,标识一个匿名函数或函数式接口。
@Repeatable - Java 8 开始支持,标识某注解可以在同一个声明上使用多次。
Annotation 架构
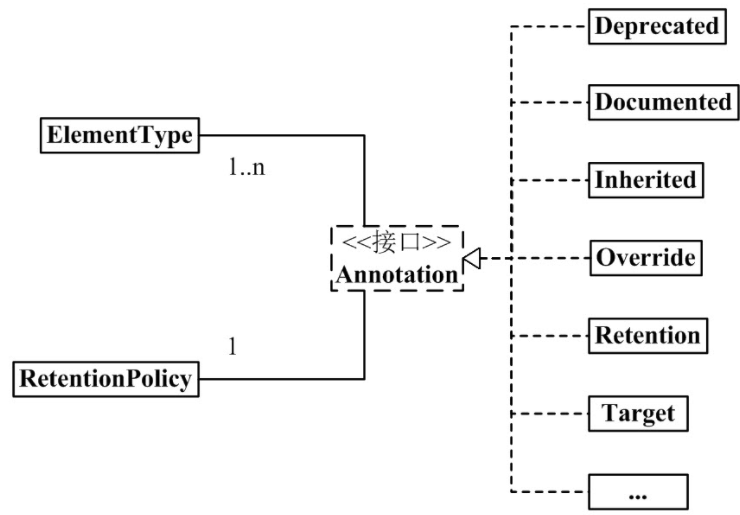
从中,我们可以看出:
1 个 Annotation 和 1 个 RetentionPolicy 关联。
可以理解为:每1个Annotation对象,都会有唯一的RetentionPolicy属性。
1 个 Annotation 和 1~n 个 ElementType 关联。
可以理解为:对于每 1 个 Annotation 对象,可以有若干个 ElementType 属性。
Annotation 有许多实现类,包括:Deprecated, Documented, Inherited, Override 等等。
Annotation 的每一个实现类,都 “和 1 个 RetentionPolicy 关联” 并且 “ 和 1~n 个 ElementType 关联”。
Annotation 组成部分
Annotation
package java.lang.annotation;public interface Annotation {boolean equals(Object obj);int hashCode();String toString();Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType();}
ElementType
```java package java.lang.annotation;
public enum ElementType { TYPE, / 类、接口(包括注释类型)或枚举声明 /
FIELD, /* 字段声明(包括枚举常量) */
METHOD, /* 方法声明 */
PARAMETER, /* 参数声明 */
CONSTRUCTOR, /* 构造方法声明 */
LOCAL_VARIABLE, /* 局部变量声明 */
ANNOTATION_TYPE, /* 注释类型声明 */
PACKAGE /* 包声明 */
}
<a name="RpgTT"></a>
## RetentionPolicy
```java
package java.lang.annotation;
public enum RetentionPolicy {
SOURCE, /* Annotation信息仅存在于编译器处理期间,编译器处理完之后就没有该Annotation信息了 */
CLASS, /* 编译器将Annotation存储于类对应的.class文件中。默认行为 */
RUNTIME /* 编译器将Annotation存储于class文件中,并且可由JVM读入 */
}
- Annotation 就是个接口。
“每 1 个 Annotation” 都与 “1 个 RetentionPolicy” 关联,并且与 “1~n 个 ElementType” 关联。可以通俗的理解为:每 1 个 Annotation 对象,都会有唯一的 RetentionPolicy 属性;至于 ElementType 属性,则有 1~n 个。
- ElementType 是 Enum 枚举类型,它用来指定 Annotation 的类型。
“每 1 个 Annotation” 都与 “1~n 个 ElementType” 关联。当 Annotation 与某个 ElementType 关联时,就意味着:Annotation有了某种用途。例如,若一个 Annotation 对象是 METHOD 类型,则该 Annotation 只能用来修饰方法。
- RetentionPolicy 是 Enum 枚举类型,它用来指定 Annotation 的策略。通俗点说,就是不同 RetentionPolicy 类型的 Annotation 的作用域不同。
“每 1 个 Annotation” 都与 “1 个 RetentionPolicy” 关联。
- 若 Annotation 的类型为 SOURCE,则意味着:Annotation 仅存在于编译器处理期间,编译器处理完之后,该 Annotation 就没用了。 例如,” @Override” 标志就是一个 Annotation。当它修饰一个方法的时候,就意味着该方法覆盖父类的方法;并且在编译期间会进行语法检查!编译器处理完后,”@Override” 就没有任何作用了。
- 若 Annotation 的类型为 CLASS,则意味着:编译器将 Annotation 存储于类对应的 .class 文件中,它是 Annotation 的默认行为。
- 若 Annotation 的类型为 RUNTIME,则意味着:编译器将 Annotation 存储于 class 文件中,并且可由JVM读入。
这时,只需要记住”每 1 个 Annotation” 都与 “1 个 RetentionPolicy” 关联,并且与 “1~n 个 ElementType” 关联。学完后面的内容之后,再回头看这些内容,会更容易理解。
java 自带的 Annotation
Annotation 通用定义
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation1 {
}
上面的作用是定义一个 Annotation,它的名字是 MyAnnotation1。定义了 MyAnnotation1 之后,我们可以在代码中通过 “@MyAnnotation1” 来使用它。 其它的,@Documented, @Target, @Retention, @interface 都是来修饰 MyAnnotation1 的。
@interface:使用 @interface 定义注解时,意味着它实现了java.lang.annotation.Annotation 接口,即该注解就是一个Annotation。定义 Annotation 时,@interface 是必须的。
注意:它和我们通常的 implemented 实现接口的方法不同。Annotation 接口的实现细节都由编译器完成。通过 @interface 定义注解后,该注解不能继承其他的注解或接口。
@Documented
类和方法的 Annotation 在缺省情况下是不出现在 javadoc 中的。如果使用 @Documented 修饰该 Annotation,则表示它可以出现在 javadoc 中。
定义 Annotation 时,@Documented 可有可无;若没有定义,则 Annotation 不会出现在 javadoc 中。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
前面我们说过,ElementType 是 Annotation 的类型属性。而 @Target 的作用,就是来指定 Annotation 的类型属性。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) 的意思就是指定该 Annotation 的类型是 ElementType.TYPE。这就意味着,MyAnnotation1 是来修饰”类、接口(包括注释类型)或枚举声明”的注解。
定义 Annotation 时,@Target 可有可无。若有 @Target,则该 Annotation 只能用于它所指定的地方;若没有 @Target,则该 Annotation 可以用于任何地方。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
前面我们说过,RetentionPolicy 是 Annotation 的策略属性,而 @Retention 的作用,就是指定 Annotation 的策略属性。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 的意思就是指定该 Annotation 的策略是 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME。这就意味着,编译器会将该 Annotation 信息保留在 .class 文件中,并且能被虚拟机读取。
定义 Annotation 时,@Retention 可有可无。若没有 @Retention,则默认是 RetentionPolicy.CLASS。
java自带的Annotation
@interface 用来声明 Annotation,@Documented 用来表示该 Annotation 是否会出现在 javadoc 中, @Target 用来指定 Annotation 的类型,@Retention 用来指定 Annotation 的策略。
java 常用的 Annotation
@Deprecated -- @Deprecated 所标注内容,不再被建议使用。
@Override -- @Override 只能标注方法,表示该方法覆盖父类中的方法。
@Documented -- @Documented 所标注内容,可以出现在javadoc中。
@Inherited -- @Inherited只能被用来标注“Annotation类型”,它所标注的Annotation具有继承性。
@Retention -- @Retention只能被用来标注“Annotation类型”,而且它被用来指定Annotation的RetentionPolicy属性。
@Target -- @Target只能被用来标注“Annotation类型”,而且它被用来指定Annotation的ElementType属性。
@SuppressWarnings -- @SuppressWarnings 所标注内容产生的警告,编译器会对这些警告保持静默。
@Deprecated
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Deprecated {
}
- @interface — 它的用来修饰 Deprecated,意味着 Deprecated 实现了 java.lang.annotation.Annotation 接口;即 Deprecated 就是一个注解。 (02) @Documented — 它的作用是说明该注解能出现在 javadoc 中。
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) — 它的作用是指定 Deprecated 的策略是 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME。这就意味着,编译器会将Deprecated 的信息保留在 .class 文件中,并且能被虚拟机读取。
- @Deprecated 所标注内容,不再被建议使用。
若某个方法被 @Deprecated 标注,则该方法不再被建议使用。如果有开发人员试图使用或重写被 @Deprecated 标示的方法,编译器会给相应的提示信息。
/**
* TODO
*
* @author lijun
* @date 2022/4/19 17:04
*/
public class DeprecatedTest {
// @Deprecated 修饰 getString1(),表示 它是建议不被使用的函数
@Deprecated
private static void getString1(){
System.out.println("Deprecated Method");
}
private static void getString2(){
System.out.println("Normal Method");
}
// Date是日期/时间类。java已经不建议使用该类了
private static void testDate() {
Date date = new Date(113, 8, 25);
System.out.println(date.getYear());
}
// Calendar是日期/时间类。java建议使用Calendar取代Date表示"日期/时间"
private static void testCalendar() {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.YEAR));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
getString1();
getString2();
testDate();
testCalendar();
}
}
比较类中 “getString1() 和 getString2()” 以及 “testDate() 和 testCalendar()” 。
(01) getString1() 被 @Deprecated 标注,意味着建议不再使用 getString1(); 所以 getString1() 的定义和调用时,都会一横线。这一横线是eclipse() 对 @Deprecated 方法的处理。
getString2() 没有被 @Deprecated 标注,它的显示正常。
(02) testDate() 调用了 Date 的相关方法,而 java 已经建议不再使用 Date 操作日期/时间。因此,在调用 Date的API 时,会产生警告信息,途中的 warnings。
testCalendar() 调用了 Calendar 的 API 来操作日期/时间,java 建议用 Calendar 取代 Date。因此,操作 Calendar 不会产生 warning。
@Inherited
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Inherited {
}
- @interface — 它的用来修饰 Inherited,意味着 Inherited 实现了 java.lang.annotation.Annotation 接口;即 Inherited 就是一个注解。
- @Documented — 它的作用是说明该注解能出现在 javadoc 中。
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) — 它的作用是指定 Inherited 的策略是 RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME。这就意味着,编译器会将 Inherited 的信息保留在 .class 文件中,并且能被虚拟机读取。
- @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) — 它的作用是指定 Inherited 的类型是 ANNOTATION_TYPE。这就意味着,@Inherited 只能被用来标注 “Annotation 类型”。
- @Inherited 的含义是,它所标注的Annotation将具有继承性。
假设,我们定义了某个 Annotaion,它的名称是 MyAnnotation,并且 MyAnnotation 被标注为 @Inherited。现在,某个类 Base 使用了
MyAnnotation,则 Base 具有了”具有了注解 MyAnnotation”;现在,Sub 继承了 Base,由于 MyAnnotation 是 @Inherited的(具有继承性),所以,Sub 也 “具有了注解 MyAnnotation”。
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 自定义的Annotation。
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@interface Inheritable {
}
/**
* @author lijun
* @date 2022/4/19 17:06
*/
@Inheritable
class InheritableFather {
public InheritableFather() {
// InheritableBase是否具有 Inheritable Annotation
System.out.println("InheritableFather:" + InheritableFather.class.isAnnotationPresent(Inheritable.class));
}
}
/**
* InheritableSon 类只是继承于 InheritableFather,
*/
public class InheritableSon extends InheritableFather {
public InheritableSon() {
super(); // 调用父类的构造函数
// InheritableSon类是否具有 Inheritable Annotation
System.out.println("InheritableSon:" + InheritableSon.class.isAnnotationPresent(Inheritable.class));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InheritableSon is = new InheritableSon();
}
}
运行结果: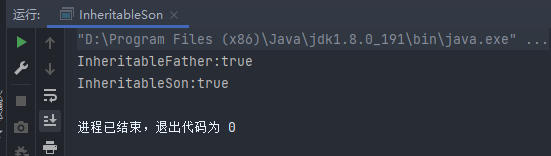
注释掉 “Inheritable 的 @Inherited 注解”。再执行程序
运行结果: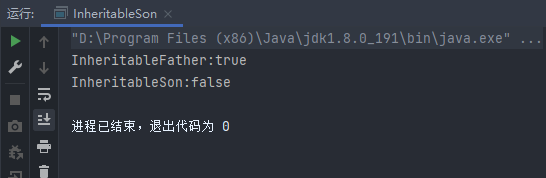
对比两个结果发现,当注解 Inheritable 被 @Inherited 标注时,它具有继承性。否则,没有继承性。
@SuppressWarnings
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface SuppressWarnings {
String[] value();
}
- @interface — 它的用来修饰 SuppressWarnings,意味着 SuppressWarnings 实现了 java.lang.annotation.Annotation 接口;即 SuppressWarnings 就是一个注解。
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) — 它的作用是指定 SuppressWarnings 的策略是 RetentionPolicy.SOURCE。这就意味着,SuppressWarnings 信息仅存在于编译器处理期间,编译器处理完之后 SuppressWarnings 就没有作用了。
- @Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE}) — 它的作用是指定 SuppressWarnings 的类型同时包括TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE。
- TYPE 意味着,它能标注”类、接口(包括注释类型)或枚举声明”。
- FIELD 意味着,它能标注”字段声明”。
- METHOD 意味着,它能标注”方法”。
- PARAMETER 意味着,它能标注”参数”。
- CONSTRUCTOR 意味着,它能标注”构造方法”。
- LOCAL_VARIABLE 意味着,它能标注”局部变量”。
- String[] value(); 意味着,SuppressWarnings 能指定参数。
- SuppressWarnings 的作用是,让编译器对”它所标注的内容”的某些警告保持静默。例如,”@SuppressWarnings(value={“deprecation”, “unchecked”})” 表示对”它所标注的内容”中的 “SuppressWarnings 不再建议使用警告”和”未检查的转换时的警告”保持沉默。 ```java import java.util.Date;
/**
- TODO *
- @author lijun
@date 2022/4/19 17:13 */ public class SuppressWarningTest {
/**
- 没有使用 @SuppressWarnings(value={“deprecation”}) , 而 Date 属于 java 不再建议使用的类。
因此,调用 Date 的 API 时,会产生警告。 **/ // @SuppressWarnings(value={“deprecation”}) public static void doSomething(){
Date date = new Date(113, 8, 26); System.out.println(date); }
/**
- 使用了 @SuppressWarnings(value={“deprecation”})。
因此,编译器对”调用 Date 的 API 产生的警告”保持沉默。 **/ @SuppressWarnings(value={“deprecation”}) public static void doSomething1(){ //没有使用 @SuppressWarnings(value={“deprecation”}) , 而 Date 属于 java 不再建议使用的类。因此,调用 Date 的 API 时,会产生警告。 Date date = new Date(113, 8, 26); System.out.println(date); }
public static void main(String[] args) { doSomething(); }
}
**SuppressWarnings 常用的关键字的表格**
```java
deprecation -- 使用了不赞成使用的类或方法时的警告
unchecked -- 执行了未检查的转换时的警告,例如当使用集合时没有用泛型 (Generics) 来指定集合保存的类型。
fallthrough -- 当 Switch 程序块直接通往下一种情况而没有 Break 时的警告。
path -- 在类路径、源文件路径等中有不存在的路径时的警告。
serial -- 当在可序列化的类上缺少 serialVersionUID 定义时的警告。
finally -- 任何 finally 子句不能正常完成时的警告。
all -- 关于以上所有情况的警告。
Annotation 的作用
Annotation 是一个辅助类,它在 Junit、Struts、Spring 等工具框架中被广泛使用。
编译检查
Annotation 具有”让编译器进行编译检查的作用”。
@SuppressWarnings, @Deprecated 和 @Override 都具有编译检查作用。
方法被 @Override 的标注,则意味着该方法会覆盖父类中的同名方法。
如果有方法被 @Override 标示,但父类中却没有”被 @Override 标注”的同名方法,则编译器会报错。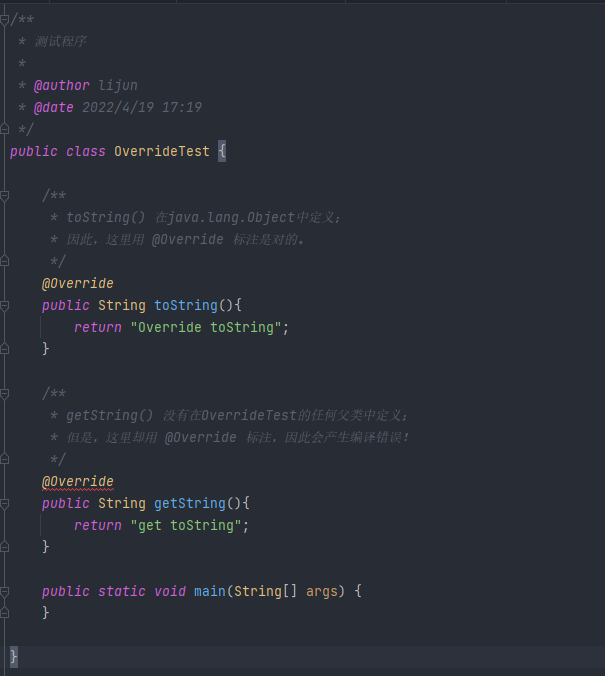
从中,我们可以发现 “getString()” 函数会报错。这是因为 “getString() 被 @Override 所标注,但在OverrideTest 的任何父类中都没有定义 getString1() 函数”。
“将 getString() 上面的 @Override注释掉”,即可解决该错误。
在反射中使用 Annotation
在反射的 Class, Method, Field 等函数中,有许多于 Annotation 相关的接口。
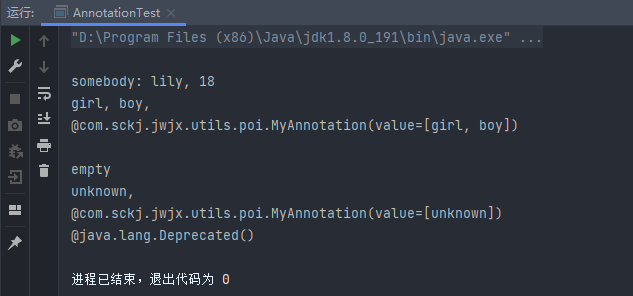
AnnotationTest
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Annotation在反射函数中的使用示例
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation {
String[] value() default "unknown";
}
/**
* Person类。它会使用MyAnnotation注解。
*/
class Person {
/**
* empty()方法同时被 "@Deprecated" 和 "@MyAnnotation(value={"a","b"})"所标注
* (01) @Deprecated,意味着empty()方法,不再被建议使用
* (02) @MyAnnotation, 意味着empty() 方法对应的MyAnnotation的value值是默认值"unknown"
*/
@MyAnnotation
@Deprecated
public void empty(){
System.out.println("\nempty");
}
/**
* sombody() 被 @MyAnnotation(value={"girl","boy"}) 所标注,
* @MyAnnotation(value={"girl","boy"}), 意味着MyAnnotation的value值是{"girl","boy"}
*/
@MyAnnotation(value={"girl","boy"})
public void somebody(String name, int age){
System.out.println("\nsomebody: "+name+", "+age);
}
}
public class AnnotationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 新建Person
Person person = new Person();
// 获取Person的Class实例
Class<Person> c = Person.class;
// 获取 somebody() 方法的Method实例
Method mSomebody = c.getMethod("somebody", new Class[]{String.class, int.class});
// 执行该方法
mSomebody.invoke(person, new Object[]{"lily", 18});
iteratorAnnotations(mSomebody);
// 获取 somebody() 方法的Method实例
Method mEmpty = c.getMethod("empty", new Class[]{});
// 执行该方法
mEmpty.invoke(person, new Object[]{});
iteratorAnnotations(mEmpty);
}
public static void iteratorAnnotations(Method method) {
// 判断 somebody() 方法是否包含MyAnnotation注解
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)){
// 获取该方法的MyAnnotation注解实例
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
// 获取 myAnnotation的值,并打印出来
String[] values = myAnnotation.value();
for (String str:values)
System.out.printf(str+", ");
System.out.println();
}
// 获取方法上的所有注解,并打印出来
Annotation[] annotations = method.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation annotation : annotations){
System.out.println(annotation);
}
}
}
根据 Annotation 生成帮助文档
通过给 Annotation 注解加上 @Documented 标签,能使该 Annotation 标签出现在 javadoc 中。
能够帮忙查看查看代码
通过 @Override, @Deprecated 等,我们能很方便的了解程序的大致结构。
另外,我们也可以通过自定义 Annotation 来实现一些功能。