动态语言
动态语言,是指程序在运行时可以改变其结构:新的函数可以引进,已有的函数可以被删除等结
构上的变化。比如常见的 JavaScript 就是动态语言,除此之外 Ruby,Python 等也属于动态语言,
而 C、C++则不属于动态语言。从反射角度说 JAVA 属于半动态语言。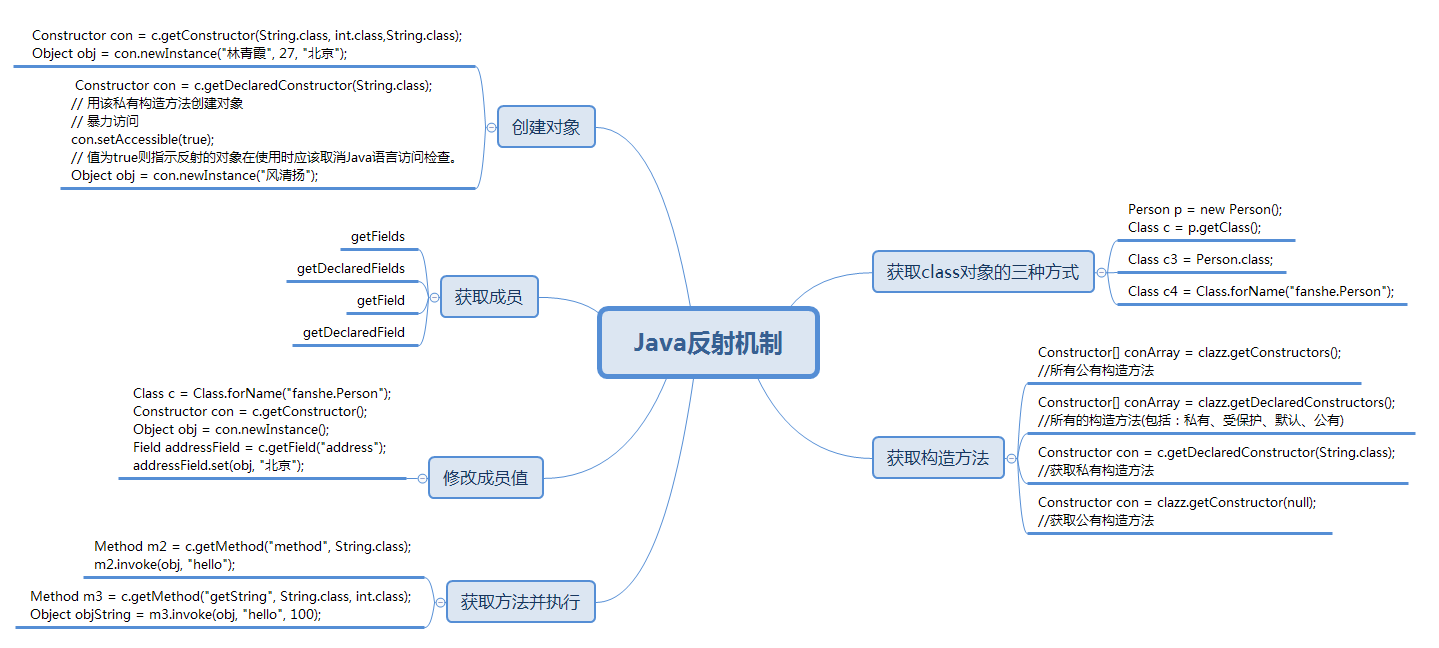
反射机制概念 (运行状态中知道类所有的属性和方法)
Class对象
在你想检查一个类的信息之前,你首先需要获取类的Class对象。Java中的所有类型包括基本类型(int, long, float等等),即使是数组都有与之关联的Class类的对象。如果你在编译期知道一个类的名字的话,那么你可以使用如下的方式获取一个类的Class对象。
Class testClass = Test.class;//或//在运行期获取的类名字符串String className = "com.springboot.learn.Test" ;Class class = Class.forName(className);
在使用Class.forName()方法时,你必须提供一个类的全名,这个全名包括类所在的包的名字。例如MyObject类位于com.springboot.learn包,那么他的全名就是com.springboot.learn.Test。
如果在调用Class.forName()方法时,没有在编译路径下(classpath)找到对应的类,那么将会抛出ClassNotFoundException。
类名
通过getName() 方法返回类的全限定类名(包含包名)
//获取Class对象Class aClass = Test.class;String className = aClass.getName();
如果你仅仅只是想获取类的名字(不包含包名),那么你可以使用getSimpleName()方法
//获取Class对象Class aClass = Test.class;String simpleClassName = aClass.getSimpleName();
修饰符
可以通过Class对象来访问一个类的修饰符,即public,private,static等等的关键字,你可以使用如下方法来获取类的修饰符。
//获取Class对象,具体方式可见Class对象小节Class aClass = Test.class;int modifiers = aClass.getModifiers();
修饰符都被包装成一个int类型的数字,这样每个修饰符都是一个位标识(flag bit),这个位标识可以设置和清除修饰符的类型。可以使用java.lang.reflect.Modifier类中的方法来检查修饰符的类型。
Modifier.isAbstract(int modifiers);Modifier.isFinal(int modifiers);Modifier.isInterface(int modifiers);Modifier.isNative(int modifiers);Modifier.isPrivate(int modifiers);Modifier.isProtected(int modifiers);Modifier.isPublic(int modifiers);Modifier.isStatic(int modifiers);Modifier.isStrict(int modifiers);Modifier.isSynchronized(int modifiers);Modifier.isTransient(int modifiers);Modifier.isVolatile(int modifiers);
包信息
可以使用Class对象通过如下的方式获取包信息
//获取Class对象Class aClass = Test.class;Package package = aClass.getPackage();
通过Package对象你可以获取包的相关信息,比如包名,你也可以通过Manifest文件访问位于编译路径下jar包的指定信息,比如你可以在Manifest文件中指定包的版本编号。
父类
Class superclass = aClass.getSuperclass();
superclass对象其实就是一个Class类的实例,所以可以继续在这个对象上进行反射操作。
接口
由于一个类可以实现多个接口,因此getInterfaces();方法返回一个Class数组,在Java中接口同样有对应的Class对象。
注意:getInterfaces()方法仅仅只返回当前类所实现的接口。当前类的父类如果实现了接口,这些接口是不会在返回的Class集合中的,尽管实际上当前类其实已经实现了父类接口。
//获取接口Class[] interfaces = aClass.getInterfaces();
构造器
获取Constructor对象
//获取对象Class aClass = Test.class;Constructor[] constructors = aClass.getConstructors();
返回的Constructor数组包含每一个声明为公有的(Public)构造方法。如果你知道你要访问的构造方法的方法参数类型,你可以用下面的方法获取指定的构造方法,这例子返回的构造方法的方法参数为String类型
Constructor constructor = aClass.getConstructor(new Class[]{String.class});
如果没有指定的构造方法能满足匹配的方法参数则会抛出:NoSuchMethodException
构造方法参数
Class[] parameterTypes = constructor.getParameterTypes();
利用Constructor对象实例化一个类
Constructor constructor =Test.class.getConstructor(String.class);Test myObject = (Test)constructor.newInstance("constructor-arg1");
constructor.newInstance()方法的方法参数是一个可变参数列表,但是当你调用构造方法的时候你必须提供精确的参数,即形参与实参必须一一对应。在这个例子中构造方法需要一个String类型的参数,那我们在调用newInstance方法的时候就必须传入一个String类型的参数。
方法
获取Method对象
//获取对象Class aClass = Test.class;//获取方法Method[] method = aClass.getMethods();
返回的Method对象数组包含了指定类中声明为公有的(public)的所有变量集合。
如果你知道你要调用方法的具体参数类型,你就可以直接通过参数类型来获取指定的方法,下面这个例子中返回方法对象名称是“test”,它的方法参数是String类型。
Method method = aClass.getMethod("test", new Class[]{String.class});
如果根据给定的方法名称以及参数类型无法匹配到相应的方法,则会抛出NoSuchMethodException。
如果你想要获取的方法没有参数,那么在调用getMethod()方法时第二个参数传入null即可。
Method method = aClass.getMethod("test", null);
方法参数以及返回类型
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();//获取指定方法的返回类型Method method =aClass.getMethod("test", null);Class returnType = method.getReturnType();
通过Method对象调用方法
//获取一个方法名为doSomesthing,参数类型为String的方法Method method = MyObject.class.getMethod("test",String.class);Object returnValue = method.invoke(null, "parameter-value1");
传入的null参数是你要调用方法的对象,如果是一个静态方法调用的话则可以用null代替指定对象作为invoke()的参数,如果“test”不是静态方法的话,你就要传入有效的Test实例而不是null。
Method.invoke(Object target, Object … parameters)方法的第二个参数是一个可变参数列表,但是你必须要传入与你要调用方法的形参一一对应的实参。方法需要String类型的参数,那我们必须要传入一个字符串。
变量
获取Field对象
//获取对象Class aClass = Test.class;//变量Field[] method = aClass.getFields();
返回的Field对象数组包含了指定类中声明为公有的(public)的所有变量集合。
Class aClass = Test.class;//如果知道要访问的变量名称,可以根据变量名称获取Field field = aClass.getField("name");
返回的Field类的实例对应的就是在Test类中声明的名为name的成员变量
public class Test{public String name = null;public void test(){System.out.println("你好世界!");}}
在调用getField()方法时,如果根据给定的方法参数没有找到对应的变量,那么就会抛出NoSuchFieldException。
Field field = aClass.getField("name");//变量名称Object fieldName = field.getName();//变量类型Object fieldType = field.getType();
获取或设置(get/set)变量值
Class aClass = Test.classField field = aClass.getField("name");Test objectInstance =(Test)aClass.getConstructors().newInstance("constructor-arg1");Object value = field.get(objectInstance);field.set(objetInstance, value);
传入Field.get()/Field.set()方法的参数objetInstance应该是拥有指定变量的类的实例。
如果变量是静态变量的话(public static)那么在调用Field.get()/Field.set()方法的时候传入null做为参数而不用传递拥有该变量的类的实例。
如果传入拥有该变量的类的实例也可以得到相同的结果。
注解
什么是注解
注解是Java 5的一个新特性。注解是插入你代码中的一种注释或者说是一种元数据(meta data)。这些注解信息可以在编译期使用预编译工具进行处理(pre-compiler tools),也可以在运行期使用Java反射机制进行处理。
@MyAnnotation(name="test", value = "Hello World")public class Test {}
在Test类定义的上面有一个@MyAnnotation的注解。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.TYPE)public @interface MyAnnotation {public String name();public String value();}
在interface前面的@符号表名这是一个注解,一旦你定义了一个注解之后你就可以将其应用到你的代码中,就像之前我们的那个例子那样。
在注解定义中的两个指示
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)和@Target(ElementType.TYPE),说明了这个注解该如何使用。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)表示这个注解可以在运行期通过反射访问。如果你没有在注解定义的时候使用这个指示那么这个注解的信息不会保留到运行期,这样反射就无法获取它的信息。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) 表示这个注解只能用在类型上面(比如类跟接口)。你同样可以把Type改为Field或者Method,或者你可以不用这个指示,这样的话你的注解在类,方法和变量上就都可以使用了。
类注解
使用方法1
Class aClass = Test.class;Annotation[] annotations = aClass.getAnnotations();for(Annotation annotation : annotations){if(annotation instanceof MyAnnotation){MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;System.out.println("name: " + myAnnotation.name());System.out.println("value: " + myAnnotation.value());}}
使用方法2
Class aClass = Test.class;Annotation annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);if(annotation instanceof MyAnnotation){MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;System.out.println("name: " + myAnnotation.name());System.out.println("value: " + myAnnotation.value());}
方法注解
方法注解实例
public class Test {@MyAnnotation(name="someName", value = "Hello World")public void test(){}}
使用方法1(访问方法注解)
//获取方法对象Method method = Test.class.getMethod("someName", String.class);Annotation[] annotations = method.getDeclaredAnnotations();for(Annotation annotation : annotations){if(annotation instanceof MyAnnotation){MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;System.out.println("name: " + myAnnotation.name());System.out.println("value: " + myAnnotation.value());}}
使用方法2(访问指定的方法注解)
//获取方法对象
Method method = Test.class.getMethod("someName", null);
Annotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
if(annotation instanceof MyAnnotation){
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;
System.out.println("name: " + myAnnotation.name());
System.out.println("value: " + myAnnotation.value());
}
参数注解
public class Test {
public static void someName(@MyAnnotation(name="aName", value="aValue")String parameter){
}
}
通过Method对象来访问方法参数注解
Method method = Test.class.getMethod("someName", null);
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
int i=0;
for(Annotation[] annotations : parameterAnnotations){
Class parameterType = parameterTypes[i++];
for(Annotation annotation : annotations){
if(annotation instanceof MyAnnotation){
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;
System.out.println("param: " +parameterType.getName());
System.out.println("name : " + myAnnotation.name());
System.out.println("value: " + myAnnotation.value());
}
}
}
需要注意的是Method.getParameterAnnotations()方法返回一个注解类型的二维数组,每一个方法的参数包含一个注解数组。
变量注解
public class Test {
@MyAnnotation(name="someName", value = "Hello World")
public String myField = null;
}
访问变量的注解
////获取方法对象
Field field = Test.class.getField("myField");
Annotation[] annotations = field.getDeclaredAnnotations();
for(Annotation annotation : annotations){
if(annotation instanceof MyAnnotation){
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;
System.out.println("name: " + myAnnotation.name());
System.out.println("value: " + myAnnotation.value());
}
}
访问指定的变量注解
////获取方法对象
Field field = Test.class.getField("myField");
Annotation annotation = field.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
if(annotation instanceof MyAnnotation){
MyAnnotation myAnnotation = (MyAnnotation) annotation;
System.out.println("name: " + myAnnotation.name());
System.out.println("value: " + myAnnotation.value());
}

