一、ThreadLocal介绍
1、官方介绍
- 从Java官方文档中的描述:ThreadLocal类用来提供线程内部的局部变量。这种变量在多线程环境下访问(通过get和set方法访问)时能保证各个线程的变量相对独立于其他线程内的变量。ThreadLocal实例通常来说都是private static类型的,用于关联线程和线程上下文。
- 我们可以得知 ThreadLocal 的作用是:提供线程内的局部变量,不同的线程之间不会相互干扰,这种变量在线程的生命周期内起作用,减少同一个线程内多个函数或组件之间一些公共变量传递的复杂度。
2、总结:
- 线程并发: 在多线程并发的场景下
- 传递数据: 我们可以通过ThreadLocal在同一线程,不同组件中传递公共变量
-
3、基本使用
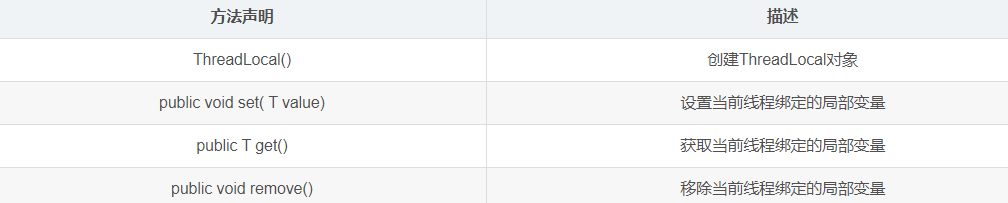
3.1 常用方法
在使用之前,我们先来认识几个ThreadLocal的常用方法
、
3.2 使用案例
我们来看下面这个案例 , 感受一下ThreadLocal 线程隔离的特点:
public class MyDemo {private String content;private String getContent() {return content;}private void setContent(String content) {this.content = content;}public static void main(String[] args) {MyDemo demo = new MyDemo();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {demo.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据");System.out.println("-----------------------");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + demo.getContent());}});thread.setName("线程" + i);thread.start();}}}
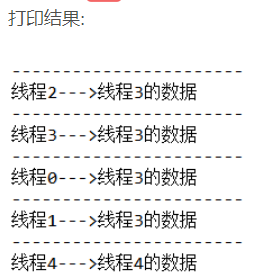
从结果可以看出多个线程在访问同一个变量的时候出现的异常,线程间的数据没有隔离。下面我们来看下采用 ThreadLocal 的方式来解决这个问题的例子。
public class MyDemo1 {private static ThreadLocal<String> tl = new ThreadLocal<>();private String content;private String getContent() {return tl.get();}private void setContent(String content) {tl.set(content);}public static void main(String[] args) {MyDemo demo = new MyDemo();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {demo.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据");System.out.println("-----------------------");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + demo.getContent());}});thread.setName("线程" + i);thread.start();}}}
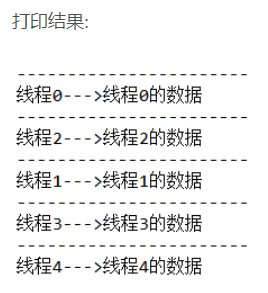
从结果来看,这样很好的解决了多线程之间数据隔离的问题,十分方便。二、ThreadLocal类与synchronized关键字
1 synchronized同步方式
这里可能有的朋友会觉得在上述例子中我们完全可以通过加锁来实现这个功能。我们首先来看一下用synchronized代码块实现的效果:
public class Demo02 {private String content;public String getContent() {return content;}public void setContent(String content) {this.content = content;}public static void main(String[] args) {Demo02 demo02 = new Demo02();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Thread t = new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (Demo02.class){demo02.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据");System.out.println("-------------------------------------");String content = demo02.getContent();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + content);}}};t.setName("线程" + i);t.start();}}}

从结果可以发现, 加锁确实可以解决这个问题,但是在这里我们强调的是线程数据隔离的问题,并不是多线程共享数据的问题, 在这个案例中使用synchronized关键字是不合适的。2、ThreadLocal与synchronized的区别
虽然ThreadLocal模式与synchronized关键字都用于处理多线程并发访问变量的问题, 不过两者处理问题的角度和思路不同。
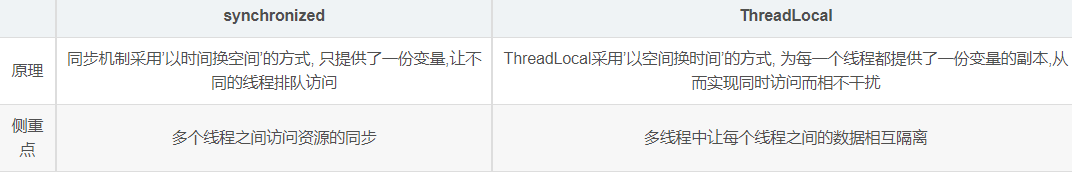
总结:
在刚刚的案例中,虽然使用ThreadLocal和synchronized都能解决问题,但是使用ThreadLocal更为合适,因为这样可以使程序拥有更高的并发性。

