- SlowFast Networks for Video Recognition
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/SlowFast
https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorchvideo/blob/main/pytorchvideo/models/slowfast.py
一、要解决什么问题?
1.1 视频中的时空信息是否需要对称的处理?
相较于二维图像的宽和高,两者具有相同的可能性,因此一般采用对称处理的方式。而视频则是在二维的空间维度上增加了一个时间维度,在一段视频中,大部分内容都处于静止状态,慢动作发生的可能性比快动作更高,是否还有必要对称的处理时间和空间这两个维度?
二、如何解决的,效果怎么样?
2.1 双分支
文中使用了双分支的方式分别去捕获视频中的空间信息和运动信息。在一段时间内,对于空间信息,一个动作的主体他不会变化,比如这个“挥手的人”、“跑步的人”、“静置的沙发”,它们经过多帧也还是人、沙发,所以对于这些类别的识别,是可以用一个较低的帧率刷新的。而运动信息可能就不是,这一帧还是挥手下一帧可能就是拍手,所以需要一个较高的帧率进行获取。
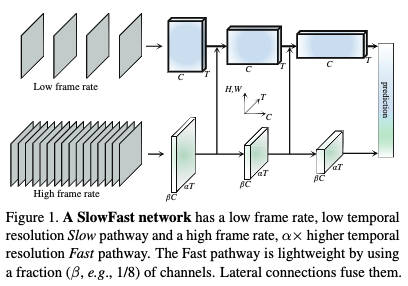
如图中所示,两个分支,Slow分支以较低的帧率运行获取空间信息。Fast分支则是以较高的帧率运行获取运动信息。比如slow每16帧采样1帧,fast每2帧采样1帧,对于32FPS的视频,slow可以采样两帧,而Fast分支则是采样16帧。在论文中,两者之间的帧率比。
两个分支除采样的帧率不同以外,通道数也是完全不同。其中,Fast分支的通道数是Slow分支通道数的1/8,使用进行表示。
2.2 Fusion
对于两个分支,采用每个Stage融合一次的方式,将两个分支的信息进行融合。总的来说可以使用三种融合方式:
1. Fast to Slow1. Slow to Fast1. Fast to Slow and Slow to Fast
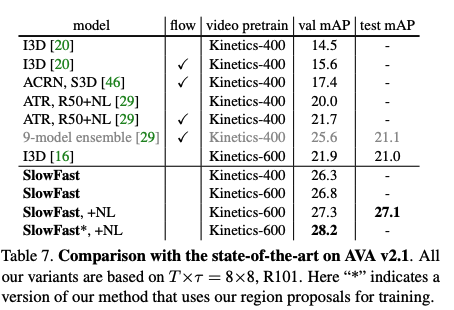
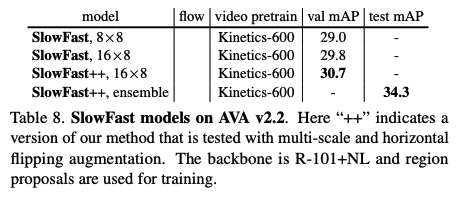
2.3 效果
三、实现细节
论文以及实现细节以Pytorch Video的官方源码为准。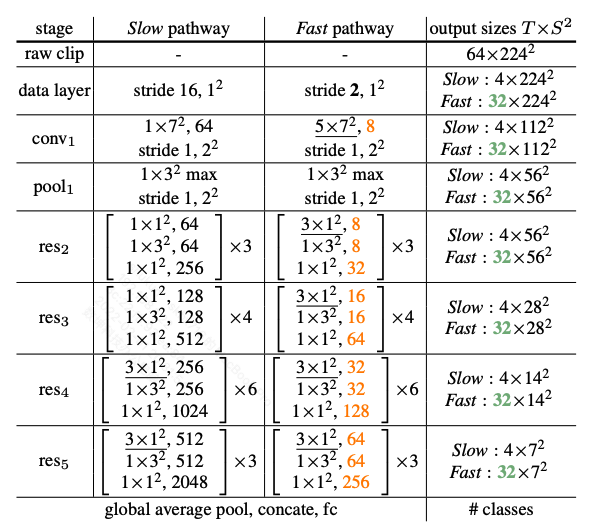
- 绿色与橙色分别表示两者通道和帧率的区别。
- stride 16,1*1表示以16帧取1帧,
分别表示
,下划线则表示进行了时间下采样,但是实现的时候使用了padding保证了时间维度不发生变化,因此实际上并没有进行时间下采样。
这部分的设置我们可以通过pytorchvideo/pytorchvideo/models/slowfast.py中的create_slowfast看到。
def create_slowfast(
*,
# SlowFast configs. fast和slow通道的比率,论文中的$\beta$,论文中为1/8。
# 可以很方便的扩展每个分支之间的比率,同时这个参数用于后续Fusion时的尺寸调整
slowfast_channel_reduction_ratio: Union[Tuple[int], int] = (8,),
# Fusion使用的是3D卷积进行尺寸的调整与匹配
slowfast_conv_channel_fusion_ratio: int = 2,
slowfast_fusion_conv_kernel_size: Tuple[int] = (
7,
1,
1,
), # deprecated, use fusion_builder
slowfast_fusion_conv_stride: Tuple[int] = (
4,
1,
1,
), # deprecated, use fusion_builder
fusion_builder: Callable[
[int, int], nn.Module
] = None, # Args: fusion_dim_in, stage_idx
# Input clip configs.
# 输入的通道,分别对应slow和fast分支,同样方便后续的扩展
input_channels: Tuple[int] = (3, 3),
# Model configs.
model_depth: int = 50,
model_num_class: int = 400,
dropout_rate: float = 0.5,
# Normalization configs.
norm: Callable = nn.BatchNorm3d,
# Activation configs.
activation: Callable = nn.ReLU,
# Stem configs.
stem_function: Tuple[Callable] = (
create_res_basic_stem,
create_res_basic_stem,
),
# 分别对应对应论文中slow与fast分支的conv1,pool1.
stem_dim_outs: Tuple[int] = (64, 8),
stem_conv_kernel_sizes: Tuple[Tuple[int]] = ((1, 7, 7), (5, 7, 7)),
stem_conv_strides: Tuple[Tuple[int]] = ((1, 2, 2), (1, 2, 2)),
stem_pool: Union[Callable, Tuple[Callable]] = (nn.MaxPool3d, nn.MaxPool3d),
stem_pool_kernel_sizes: Tuple[Tuple[int]] = ((1, 3, 3), (1, 3, 3)),
stem_pool_strides: Tuple[Tuple[int]] = ((1, 2, 2), (1, 2, 2)),
# Stage configs.
# stage_conv_a_kernel_sizes[pathway][i],
# con_b_kernel_sizes[pathwayidx][i]
# con_dilations[pathwayidx][i]
# 这三个一起是一个res的
stage_conv_a_kernel_sizes: Tuple[Tuple[Tuple[int]]] = (
((1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1), (3, 1, 1), (3, 1, 1)),
((3, 1, 1), (3, 1, 1), (3, 1, 1), (3, 1, 1)),
),
stage_conv_b_kernel_sizes: Tuple[Tuple[Tuple[int]]] = (
((1, 3, 3), (1, 3, 3), (1, 3, 3), (1, 3, 3)),
((1, 3, 3), (1, 3, 3), (1, 3, 3), (1, 3, 3)),
),
stage_conv_b_num_groups: Tuple[Tuple[int]] = ((1, 1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1, 1)),
stage_conv_b_dilations: Tuple[Tuple[Tuple[int]]] = (
((1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1)),
((1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1)),
),
stage_spatial_strides: Tuple[Tuple[int]] = ((1, 2, 2, 2), (1, 2, 2, 2)),
stage_temporal_strides: Tuple[Tuple[int]] = ((1, 1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1, 1)),
# 两个分支
bottleneck: Union[Callable, Tuple[Tuple[Callable]]] = (
(
create_bottleneck_block,
create_bottleneck_block,
create_bottleneck_block,
create_bottleneck_block,
),
(
create_bottleneck_block,
create_bottleneck_block,
create_bottleneck_block,
create_bottleneck_block,
),
),
# Head configs.
head: Callable = create_res_basic_head,
head_pool: Callable = nn.AvgPool3d,
head_pool_kernel_sizes: Tuple[Tuple[int]] = ((8, 7, 7), (32, 7, 7)),
head_output_size: Tuple[int] = (1, 1, 1),
head_activation: Callable = None,
head_output_with_global_average: bool = True,
) -> nn.Module:
3.1 分支的创建方法
Pytorch Video使用了每个Stage同时创建两个分支的方案,并在每个Stage添加完双分支的卷积层之后,添加Fusion层对信息进行融合。
# Slow Input Fast Input
# ↓ ↓
# Stem Stem
# ↓ ⭠ Fusion- ↓
# Stage 1 Stage 1
# ↓ ⭠ Fusion- ↓
# . .
# ↓ ↓
# Stage N Stage N
# ↓ ⭠ Fusion- ↓
# ↓
# Head
# Build stem blocks.
# 同时建立两个分支
# conv和pool部分的建立
_num_pathway = len(input_channels)
stems = []
for pathway_idx in range(_num_pathway):
stems.append(
stem_function[pathway_idx](
in_channels=input_channels[pathway_idx],
out_channels=stem_dim_outs[pathway_idx], # #(64, 8)
conv_kernel_size=stem_conv_kernel_sizes[pathway_idx], # ((1, 7, 7), (5, 7, 7))
conv_stride=stem_conv_strides[pathway_idx], # ((1, 2, 2), (1, 2, 2))
conv_padding=[
size // 2 for size in stem_conv_kernel_sizes[pathway_idx]
], # 填充一下保证尺寸不变
pool=stem_pool[pathway_idx],
pool_kernel_size=stem_pool_kernel_sizes[pathway_idx], # ((1, 3, 3), (1, 3, 3))
pool_stride=stem_pool_strides[pathway_idx], # ((1, 2, 2), (1, 2, 2))
pool_padding=[
size // 2 for size in stem_pool_kernel_sizes[pathway_idx]
],
norm=norm,
activation=activation,
)
)
# 添加完两个分支的卷积层后做一下第一阶段的横向连接
stages = []
stages.append(
MultiPathWayWithFuse(
multipathway_blocks=nn.ModuleList(stems),
multipathway_fusion=fusion_builder(
fusion_dim_in=stem_dim_outs[0],
stage_idx=0,
),
)
)
3.2 Slow分支
- 可以是任意一个将视频片段作为输入的卷积模型,比如I3D、Non-local等等。
Slow分支并没有全部使用3D卷积,而是先2D后3D的策略,可能是因为浅层网的咯的感受也不够大,运动速度过快的时候,两帧的语义相关性不大。
3.3 Fast分支
全部使用3D卷积
-
3.4 Fusion
对于Fusion,需要注意的是分支之间的尺寸是不相同的,需要先进行尺寸上的调整,才可以与Slow分支进行拼接。文中提供了三种调整尺寸的方式,均是以Slow分支的尺寸为基准去调整Fast分支。
- Time-to-channel: We reshape and transpose {αT, S 2 , βC} into {T, S 2 , αβC}, meaning that we pack all α frames into the channels of one frame.
- Time-strided sampling: We simply sample one out of every α frames, so {αT, S 2 , βC} becomes {T, S 2 , βC}.
- Time-strided convolution: We perform a 3D convolution of a 5×1 2 kernel with 2βC output channels and stride = α. The output of the lateral connections is fused into the Slow pathway by summation or concatenation.
代码中则是用了第一种方式。
# 会首先创建一个fusion块会用到的尺寸调整层,这个层根据通道数比率和采样的比率进行设置。
if fusion_builder is None:
fusion_builder = FastToSlowFusionBuilder(
slowfast_channel_reduction_ratio=slowfast_channel_reduction_ratio[0],
conv_fusion_channel_ratio=slowfast_conv_channel_fusion_ratio,
conv_kernel_size=slowfast_fusion_conv_kernel_size,
conv_stride=slowfast_fusion_conv_stride,
norm=norm,
activation=activation,
max_stage_idx=len(stage_depths) - 1,
).create_module
class FastToSlowFusionBuilder:
...
# 论文lateral中的time-to-channel
# 使用alpha和beta将fast的尺寸调整为论文中要求的尺寸,{αT, S^2,βC} into {T, S^2, αβC}
# 好像有差异,这个时间维度没有对齐?
# 设fast =[1,8,32,56,56] BCTWH->[1,64,8,56,56]
conv_dim_in = fusion_dim_in // self.slowfast_channel_reduction_ratio
conv_fast_to_slow = nn.Conv3d(
conv_dim_in,
int(conv_dim_in * self.conv_fusion_channel_ratio),
kernel_size=self.conv_kernel_size,
stride=self.conv_stride,
padding=[k_size // 2 for k_size in self.conv_kernel_size],
bias=False,
)
...
class FuseFastToSlow(nn.Module):
"""
Given a list of two tensors from Slow pathway and Fast pathway, fusion information
from the Fast pathway to the Slow on through a convolution followed by a
concatenation, then return the fused list of tensors from Slow and Fast pathway in
order.
"""
def __init__(
self,
conv_fast_to_slow: nn.Module,
norm: Optional[nn.Module] = None,
activation: Optional[nn.Module] = None,
) -> None:
"""
Args:
conv_fast_to_slow (nn.module): convolution to perform fusion.
norm (nn.module): normalization module.
activation (torch.nn.modules): activation module.
"""
super().__init__()
set_attributes(self, locals())
def forward(self, x):
x_s = x[0]
x_f = x[1]
# 首先使用一个3D卷积调整一下尺寸
fuse = self.conv_fast_to_slow(x_f)
if self.norm is not None:
fuse = self.norm(fuse)
if self.activation is not None:
fuse = self.activation(fuse)
# slow分支和调整后的Fast进行拼接,然后将拼接后的的结果以及原来的Fast返回
x_s_fuse = torch.cat([x_s, fuse], 1)
return [x_s_fuse, x_f]
四、非官方源码
可以帮助理解
源自:https://github.com/r1c7/SlowFastNetworks 来自知乎用户@渔舟唱晚
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
__all__ = ['resnet50', 'resnet101','resnet152', 'resnet200']
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, head_conv=1):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
if head_conv == 1:
self.conv1 = nn.Conv3d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes)
elif head_conv == 3:
self.conv1 = nn.Conv3d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=(3, 1, 1), bias=False, padding=(1, 0, 0))
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes)
else:
raise ValueError("Unsupported head_conv!")
self.conv2 = nn.Conv3d(
planes, planes, kernel_size=(1, 3, 3), stride=(1,stride,stride), padding=(0, 1, 1), bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv3d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm3d(planes * 4)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class SlowFast(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block=Bottleneck, layers=[3, 4, 6, 3], class_num=10, dropout=0.5 ):
super(SlowFast, self).__init__()
self.fast_inplanes = 8
self.fast_conv1 = nn.Conv3d(3, 8, kernel_size=(5, 7, 7), stride=(1, 2, 2), padding=(2, 3, 3), bias=False)
self.fast_bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(8)
self.fast_relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.fast_maxpool = nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size=(1, 3, 3), stride=(1, 2, 2), padding=(0, 1, 1))
self.fast_res2 = self._make_layer_fast(block, 8, layers[0], head_conv=3)
self.fast_res3 = self._make_layer_fast(
block, 16, layers[1], stride=2, head_conv=3)
self.fast_res4 = self._make_layer_fast(
block, 32, layers[2], stride=2, head_conv=3)
self.fast_res5 = self._make_layer_fast(
block, 64, layers[3], stride=2, head_conv=3)
self.lateral_p1 = nn.Conv3d(8, 8*2, kernel_size=(5, 1, 1), stride=(8, 1 ,1), bias=False, padding=(2, 0, 0))
self.lateral_res2 = nn.Conv3d(32,32*2, kernel_size=(5, 1, 1), stride=(8, 1 ,1), bias=False, padding=(2, 0, 0))
self.lateral_res3 = nn.Conv3d(64,64*2, kernel_size=(5, 1, 1), stride=(8, 1 ,1), bias=False, padding=(2, 0, 0))
self.lateral_res4 = nn.Conv3d(128,128*2, kernel_size=(5, 1, 1), stride=(8, 1 ,1), bias=False, padding=(2, 0, 0))
self.slow_inplanes = 64+64//8*2
self.slow_conv1 = nn.Conv3d(3, 64, kernel_size=(1, 7, 7), stride=(1, 2, 2), padding=(0, 3, 3), bias=False)
self.slow_bn1 = nn.BatchNorm3d(64)
self.slow_relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.slow_maxpool = nn.MaxPool3d(kernel_size=(1, 3, 3), stride=(1, 2, 2), padding=(0, 1, 1))
self.slow_res2 = self._make_layer_slow(block, 64, layers[0], head_conv=1)
self.slow_res3 = self._make_layer_slow(
block, 128, layers[1], stride=2, head_conv=1)
self.slow_res4 = self._make_layer_slow(
block, 256, layers[2], stride=2, head_conv=3)
self.slow_res5 = self._make_layer_slow(
block, 512, layers[3], stride=2, head_conv=3)
self.dp = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.fc = nn.Linear(self.fast_inplanes+2048, class_num, bias=False)
def forward(self, input):
fast, lateral = self.FastPath(input[:, :, ::2, :, :])
slow = self.SlowPath(input[:, :, ::16, :, :], lateral)
x = torch.cat([slow, fast], dim=1)
x = self.dp(x)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def SlowPath(self, input, lateral):
x = self.slow_conv1(input)
x = self.slow_bn1(x)
x = self.slow_relu(x)
x = self.slow_maxpool(x)
x = torch.cat([x, lateral[0]],dim=1)
x = self.slow_res2(x)
x = torch.cat([x, lateral[1]],dim=1)
x = self.slow_res3(x)
x = torch.cat([x, lateral[2]],dim=1)
x = self.slow_res4(x)
x = torch.cat([x, lateral[3]],dim=1)
x = self.slow_res5(x)
x = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d(1)(x)
x = x.view(-1, x.size(1))
return x
def FastPath(self, input):
lateral = []
x = self.fast_conv1(input)
x = self.fast_bn1(x)
x = self.fast_relu(x)
pool1 = self.fast_maxpool(x)
lateral_p = self.lateral_p1(pool1)
lateral.append(lateral_p)
res2 = self.fast_res2(pool1)
lateral_res2 = self.lateral_res2(res2)
lateral.append(lateral_res2)
res3 = self.fast_res3(res2)
lateral_res3 = self.lateral_res3(res3)
lateral.append(lateral_res3)
res4 = self.fast_res4(res3)
lateral_res4 = self.lateral_res4(res4)
lateral.append(lateral_res4)
res5 = self.fast_res5(res4)
x = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool3d(1)(res5)
x = x.view(-1, x.size(1))
return x, lateral
def _make_layer_fast(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, head_conv=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.fast_inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3d(
self.fast_inplanes,
planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1,
stride=(1,stride,stride),
bias=False), nn.BatchNorm3d(planes * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.fast_inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, head_conv=head_conv))
self.fast_inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.fast_inplanes, planes, head_conv=head_conv))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _make_layer_slow(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, head_conv=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.slow_inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv3d(
self.slow_inplanes,
planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1,
stride=(1,stride,stride),
bias=False), nn.BatchNorm3d(planes * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.slow_inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, head_conv=head_conv))
self.slow_inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.slow_inplanes, planes, head_conv=head_conv))
self.slow_inplanes = planes * block.expansion + planes * block.expansion//8*2
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def resnet50(**kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-50 model.
"""
model = SlowFast(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
return model
def resnet101(**kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
"""
model = SlowFast(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], **kwargs)
return model
def resnet152(**kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
"""
model = SlowFast(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], **kwargs)
return model
def resnet200(**kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
"""
model = SlowFast(Bottleneck, [3, 24, 36, 3], **kwargs)
return model
if __name__ == "__main__":
num_classes = 101
input_tensor = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.rand(1, 3, 64, 224, 224))
model = resnet50(class_num=num_classes)
output = model(input_tensor)
print(output.size())