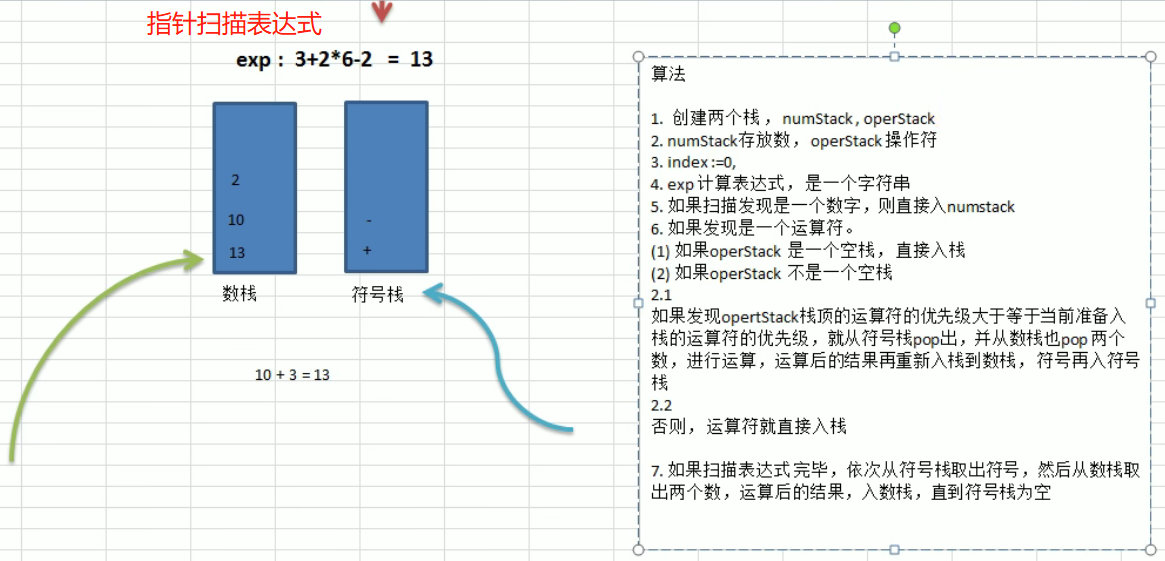
需求
输入一个表达式,返回计算结果。比如: 3 + 2 * 6 - 2 = 13
按照运算符的优先级进行正确的运算
思路
代码
// 栈的运用 - 计算表达式package mainimport ("errors""fmt""strconv")type Stack struct {MaxTop int // 栈的容量Top int // 栈顶下标 默认 -1arr [20]int // 数组模拟栈}// 入栈func (stack *Stack) Push(val int) (err error) {// 栈满if stack.Top == stack.MaxTop-1 {fmt.Println("stack full")return errors.New("stack full")}stack.Top++// 放入数据stack.arr[stack.Top] = valreturn}// 出栈func (stack *Stack) Pop() (val int, err error) {if stack.Top == -1 {fmt.Println("空栈")return 0, errors.New("空栈")}// 取出数据val = stack.arr[stack.Top]stack.Top--return val, nil}// 遍历栈func (stack *Stack) List() {if stack.Top == -1 {fmt.Println("空栈")return}for i := stack.Top; i >= 0; i-- {fmt.Printf("arr[%d] = %v \n", i, stack.arr[i])}}// 判断是运算符的函数 + - * / , 利用 ASCII 码func (stack *Stack) IsOper(val int) bool {if val == 42 || val == 43 || val == 45 || val == 47 {return true} else {return false}}// 运算的方法func (stack *Stack) Cal(num1 int, num2 int, oper int) int {// 注意运算的顺序res := 0switch oper {case 42:res = num2 * num1case 43:res = num2 + num1case 45:res = num2 - num1case 47:res = num2 / num1default:fmt.Println("运算符错误")}return res}// 返回运算符的优先级: * / => 1 ; + - => 0func (stack *Stack) Priority(oper int) int {res := 0if oper == 42 || oper == 47 {res = 1} else if oper == 43 || oper == 45 {res = 0}return res}func main() {// 数栈numStack := &Stack{MaxTop: 20,Top: -1,}// 符号栈operStack := &Stack{MaxTop: 20,Top: -1,}// 表达式exp := "33+2*6/1-2" // 字符串本身也是切片// 定义需要的变量num1 := 0num2 := 0oper := 0keepNum := "" // 字符串 用于拼接多位数// 定义索引,扫描表达式index := 0for {ch := exp[index : index+1] // 每次拿到一个字符, 如果数字大于1位就会出问题, 在非符号字符入栈时处理temp := int([]byte(ch)[0]) // 字符对应的 ASCII 码if operStack.IsOper(temp) {// 符号if operStack.Top == -1 {// 1. 符号栈为空operStack.Push(temp)} else {// 2. 符号栈不为空// 2.1 栈中的符号优先级大于等于即将入栈的符号if operStack.Priority(operStack.arr[operStack.Top]) >= operStack.Priority(temp) {num1, _ = numStack.Pop()num2, _ = numStack.Pop()oper, _ = operStack.Pop()result := operStack.Cal(num1, num2, oper)numStack.Push(result)operStack.Push(temp)} else {// 2.2 栈中的符号优先级小于即将入栈的符号operStack.Push(temp)}}} else {// 数字// 多位数拼接keepNum += ch// 判断扫描的下一位是不是运算符, 边界问题(表达式最后, 预防溢出)if index == len(exp)-1 {// 字符 转数字val, _ := strconv.Atoi(keepNum) // Atoi是ParseInt(s, 10, 0)的简写。 返回的就是 int 类型numStack.Push(val)} else {// 向后看一位if operStack.IsOper(int([]byte(exp[index+1 : index+2])[0])) {val, _ := strconv.Atoi(keepNum) // Atoi是ParseInt(s, 10, 0)的简写。 返回的就是 int 类型numStack.Push(val)keepNum = ""}// 其它情况不做处理,index++, 判断下一个字符}/*// 字符 转数字// val, _ := strconv.ParseInt(ch, 10, 0) // 返回 int64, 需要转 int(val)val, _ := strconv.Atoi(ch) // Atoi是ParseInt(s, 10, 0)的简写。 返回的就是 int 类型numStack.Push(val)*/}// 判断扫描位置if index+1 == len(exp) {fmt.Println("扫描到最后了")break}index++}// 扫描完毕,之后对数栈和符号栈剩余元素处理for {if operStack.Top == -1 {fmt.Println("没有运算符了, 数栈中的值就是计算结果")break}num1, _ = numStack.Pop()num2, _ = numStack.Pop()oper, _ = operStack.Pop()result := operStack.Cal(num1, num2, oper)numStack.Push(result)}// 如果计算正确,数栈中只剩下一个元素,就是计算结果res, _ := numStack.Pop()fmt.Printf("表达式: %s = %v \n", exp, res)}