构造函数和实例化原理
function Car(color,brand) {// var this = {// 隐式定义了this;// }this.color = color;this.brand = brand;//return this;隐式返回了this}var car = new Car('red','BMW');console.log(car.color);GO = {car:undefined,Car :function(){....}}AO = {this:{color:color,brand:brand}//实例化的时候产生了this;}
- new 改变了this指向,将this 指向改为指向实例化对象。
模拟构造函数
function Car(color,brand){var me = {};//类似 this;me.color = color;me.brand = brand;return me;//这里显示返回me 构造函数是隐式返回this;}
构造函数中的return引用值类型就会覆盖原来的this,return 原始值类型则不会覆盖
function Test(opt){this.name =opt.name;return undefined;//无效return null;//无效return 1,//无效return false,//无效return '1'//无效}var t = new Test({name:1})console.log(t.name)//1function Test(opt){this.name =opt.name;return {};//有效return [];//有效return /{abc}/g//有效return new Date();//有效}var t = new Test({name:1})console.log(t.name)//undefined
JS包装类
- 原始值没有自己的属性和方法
new Number() new String() new Boolean();
var a = 1;var b = new Number(a);b.len = 3;b.add = function(){console.log(1);}console.log(b);//{len:3,add:function(){...}}
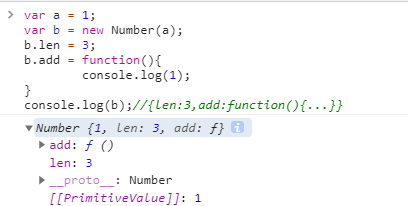
例子2var a = 123;a.len = 3;console.log(a.len)//undefined/**系统操作* //new Number(123).len = 3; delete a.len;* 类似于* var obj={};* obj.name=3;* delete obj.name;* console.log(obj.name);*/
一个数字经过new Number()之后就变成数字对象。数字对象参与运算之后又回归的原始值。
- undefined,null 不能有属性和方法 undefined.len=3;null.len=3???//报错、
字符串包装类有length 属性。原型值是没有方法和属性的
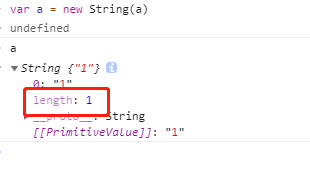
undefined.length//报错。null.length//报错var a = new String('123');
当给原始值添加属性或者方法的时候,系统会使用js包装类.但是系统无法保存 这个属性或方法。所以就删除了这个属性。
- 字符串的length ```javascript var str = ‘abc’; console.log(str.length);//3 console.log(new String(str).length);//3
var str = ‘abc’; str.length=1;//new String(str).length=1; delete new String(str).length console.log(str.length);//再次new String(str).length 3
- 数组的截断```javascriptvar arr = [1,2,3,4,5];//length 5arr.length =2;console.log(arr)//[1,2]arr.length = 6;console.log(arr) //[1,2,3,4,5,empty];
题目
第一题
var name = 'languiji';name += 10;//'languiji10'var type = typeof (name);//'string'if (type.length === 6) {//true// type = new String(type);type.text = 'string';//new String('string').text ='string' delete new String('string').text;//或者}console.log(type.text)//undefined
第二题
function Test(a, b, c) {var d = 1;this.a = a;this.b = b;this.c = c;function f() {d++;console.log(d)}this.g = f;//return this; 隐式返回this;形成了闭包。}var t1 = new Test(1, 2, 3);t1.g();//2t1.g();//3var test = new Test();test.g();//2
第三题
/*go{x:undefined,1,y:undefined,0,4,z:undefined,0,4add:function(n){return n=n+3;}}*/// 阿里面试题。var x = 1,y = z = 0;function add(n) {return n=n+1;}y = add(x);function add(n) {return n=n+3}z = add(x);console.log(x, y, z);
第四题
下列那几个能输出1,2,3,4,5
function foo(x) {console.log(arguments);return x;}foo(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);function foo(x) {console.log(arguments);return x;} (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)//(1,2,3,4,5)被理解成了表达式 返回了最后的5(function foo(x) {console.log(arguments);})(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
第五题
//原题function b(x,y,a) {a = 10;console.log(arguments[2]);//10}b(1, 2, 3);//变形式function b(x,y,a) {arguments[2] = 10;console.log(a);//10}b(1, 2, 3);//自己写的function b(x,y,a) {a = 10;console.log(arguments[2]);//undefined、因为实参没有传值,所以a=10;不能赋值}b(1, 2);
作业_
//ASCII 码 表一0-127 表二 128-255/*** UNICODE码 0-255占一个字节、涵盖ASCII码,256以后 占2个字节.*/// 写一个函数 接收任意一个字符串。算出这个字符串的总字节数。function getBytes(str) {var len = str.length;console.log(str.length);var bytes = 0;for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {var item = str[i];//字符串当前值。if (item.charCodeAt(0) > 255) {bytes += 2;} else {bytes += 1;}}return bytes;}//优化function getBytes(str){var bytes = str.length;for(var i = 0;i<str.length;i++){if(str.charCodeAt(i)>255){bytes++;}}return bytes;}

