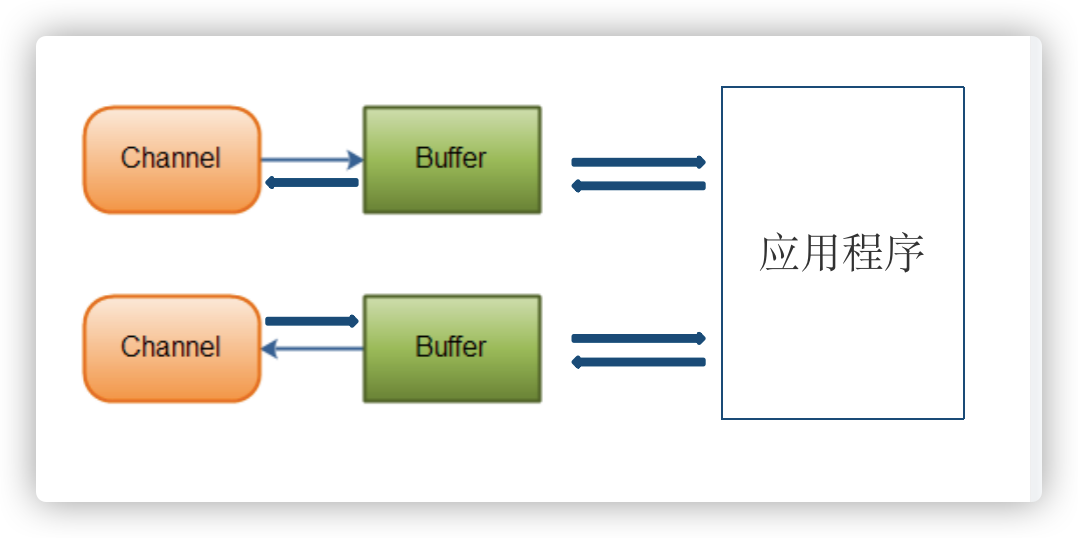
1.向 Buffer 中写数据
public static void writeBuffer() {ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);// byte 范围是多少? byte 由8bit表示,2^8=256,范围[-128~127]byte b = 127;// 填充一个 byte 值byteBuffer.put(b);// 在指定位置填充一个 byte 值byteBuffer.put(20, b);// 将一个数组中的值填充进去byte[] byteArray = "something".getBytes();byteBuffer.put(byteArray);// 在指定位置填充一个 byte 数组//参数一:byte数组 参数二:src开始位置 参数三:有效数据长度byteBuffer.put(byteArray, 0, byteArray.length);//上述这些方法需要自己控制 Buffer 大小,不能超过 capacity,超过会抛 java.nio.BufferOverflowException 异常。// 对于 Buffer 来说,另一个常见的操作中就是,我们要将来自 Channel 的数据填充到 Buffer 中,// 在系统层面上,这个操作我们称为读操作,因为数据是从外部(文件或网络等)读到内存中。// ps:伪代码,这段代码无法正常运行..try {SocketChannel socketChannel = socketChannel();//read方法会返回读取的数据量num,相对于buffer来说,channel读取 对应 buffer 写操作。int num = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);} catch (IOException e) {}}
2.flip()方法
flip方法将 Buffer 从写模式切换到读模式。
调用flip()方法会将 position 设回0,并将 limit 设置成之前 position 的值。
换句话说,position 现在用于标记读的位置,limit 表示之前写进了多少个 byte、char 等, 现在就能读取多少个 byte、char 等。
3.从 Buffer 中读取数据
public static void readBuffer(ByteBuffer byteBuffer) {// 1. 按照position顺序读取,每get一次,position + 1byte val1 = byteBuffer.get();// 2. 获取指定位置的数据byte val2 = byteBuffer.get(10);// 3. 将buffer中的数据,拷贝到一个指定的数组中byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];byteBuffer.get(bytes);// 4. 另一个经常使用的方法,直接返回Buffer内部的byte[]数组String str = new String(byteBuffer.array());// 5.// 网络编程中,我们将数据发送至对端 或者 使用FileChannel将内存中的数据写入到硬盘// 这种操作,我们通常称之为 Channel 的写操作,与之对应的 Buffer 就是 读操作。// ps:伪代码,这段代码无法正常运行..try {SocketChannel socketChannel = socketChannel();// byteBuffer.flip(); 一定要注意!socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);} catch (IOException e) {}}
使用 Buffer 读写数据步骤
- 写入数据到 Buffer
- 调用 flip()方法
- 从 Buffer 中读取数据
- 调用 clear()方法或者 compact()方法,准备下一次的写入
当向 buffer 写入数据时,buffer 会记录下写了多少数据。一旦要读取数据,需要通过 flip()方法将 Buffer 从写模式切换到读模式。在读模式下,可以读取之前写入到 buffer 的所有数据。
一旦读完了所有的数据,就需要清空缓冲区,让它可以再次被写入。
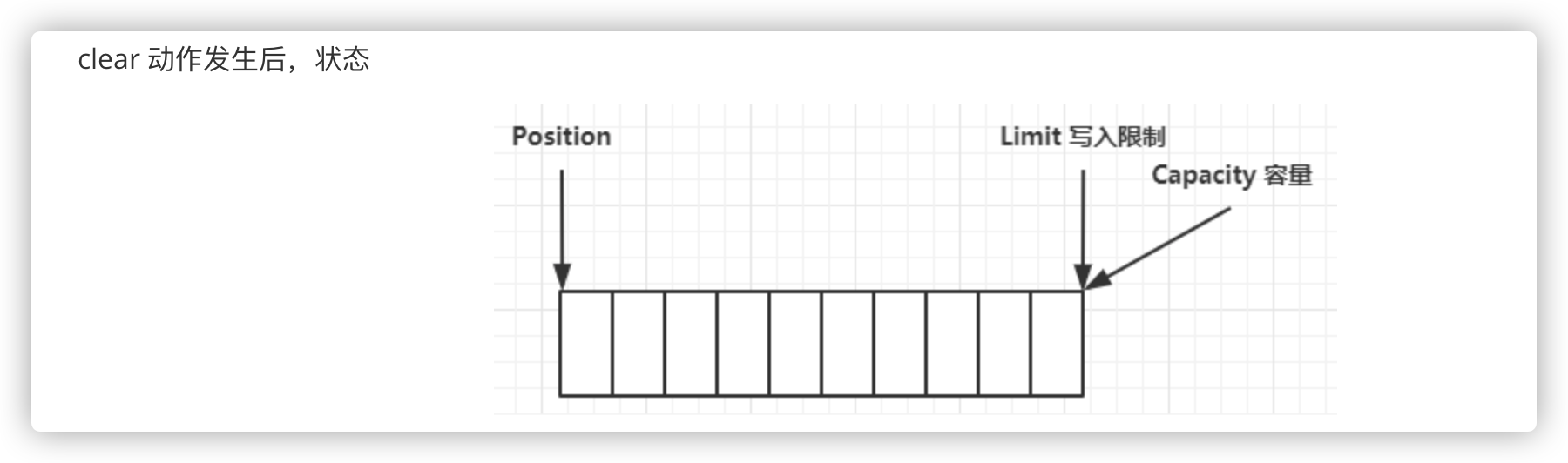
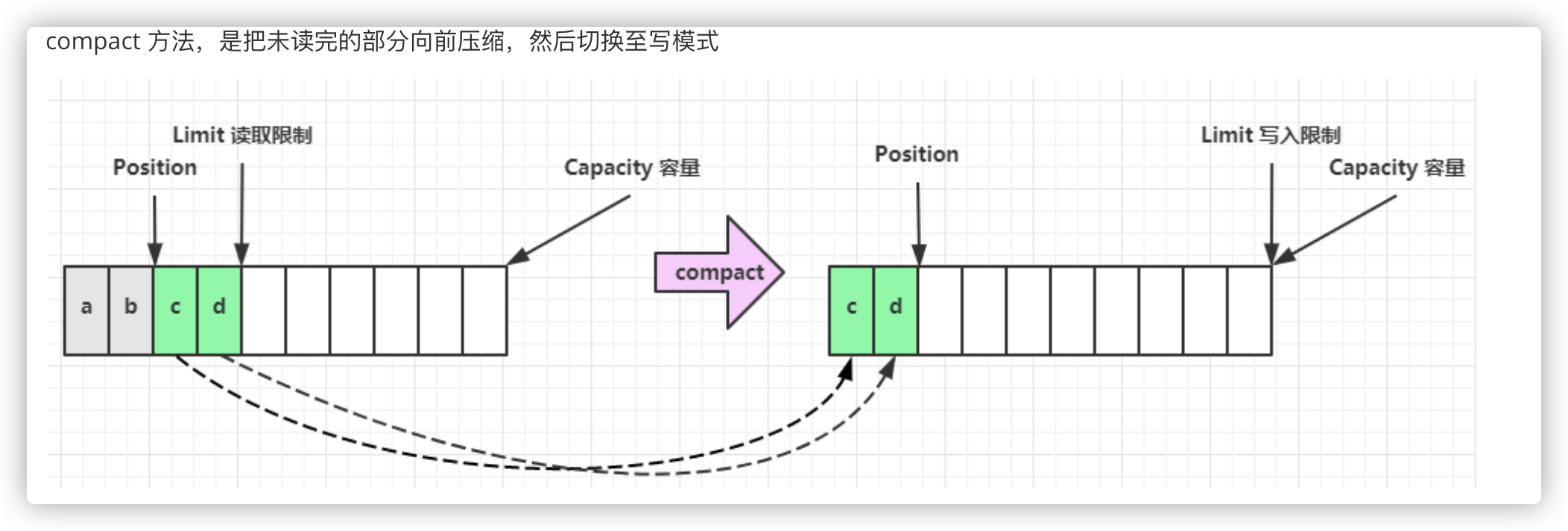
有两种方式能清空缓冲区:调用 clear()或 compact()方法。
- clear()方法会清空整个缓冲区。(没有真的清除数据,只是重置了指针)
- compact()方法只会清除已经读过的数据。(会删除已读的数据,把剩余的未读数据挪到开始的地方)
public class BufferMethod {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("------Test get and put-------------");ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);buffer.put((byte) 'a')//0.put((byte) 'b')//1.put((byte) 'c')//2.put((byte) 'd')//3.put((byte) 'e')//4.put((byte) 'f');//5System.out.println("before flip()" + buffer);/* 转换为读取模式*/buffer.flip();System.out.println("before get():" + buffer);System.out.println((char)buffer.get());System.out.println("after get():" + buffer);/* position移动两位*/byte[] dst = new byte[10];buffer.get(dst, 0, 2);System.out.println("after get(dst, 0, 2):" + buffer);System.out.println("dst:" + new String(dst));/*绝对读写*/System.out.println("--------Test 绝对读写-------");ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);System.out.println("before put(byte):" + bb);System.out.println("after put(byte):" + bb.put((byte) 'z'));/* put(2,(byte) 'c')不改变position的位置*/bb.put(2, (byte) 'c');System.out.println("after put(2,(byte) 'c'):" + bb);System.out.println(new String(bb.array()));/* get(index)不影响position的值*/System.out.println((char) buffer.get(2));System.out.println("after get(index):" + buffer);System.out.println("--------Test Clear And Compact--------");ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);buffer2.put((byte) 'x');System.out.println("before clear:" + buffer2);buffer2.clear();System.out.println("after clear:" + buffer2);System.out.println(new String(buffer2.array()));/*放入4个字节,position移动到下个可写入的位置,也就是4*/buffer2.put("abcd".getBytes());System.out.println("before compact:" + buffer2);buffer2.flip();//将position设回0,并将limit设置成之前position的值*/System.out.println("after flip:" + buffer2);/*compact()方法将所有未读的数据拷贝到Buffer起始处。*//* 然后将position设到最后一个未读元素正后面。*/System.out.println("还有数据未读,个数:" + buffer2.remaining());buffer2.compact();System.out.println("after compact:" + buffer2);System.out.println(new String(buffer2.array()));System.out.println("--------Test rewind--------");buffer.clear();buffer.position(10);/*移动position到10*/buffer.limit(15);/*限定最大可写入的位置为15*/System.out.println("before rewind:" + buffer);buffer.rewind();/*将position设回0*/System.out.println("before rewind:" + buffer);System.out.println("--------Test mark AND reset----------");buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(20);System.out.println("buffer = " + buffer);buffer.clear();buffer.position(5);/*移动position到5*/buffer.mark();/*记录当前position的位置*/buffer.position(10);/*移动position到10*/System.out.println("before reset:" + buffer);buffer.reset();/*复位position到记录的地址*/System.out.println("after reset:" + buffer);}}