prototype(显式原型)
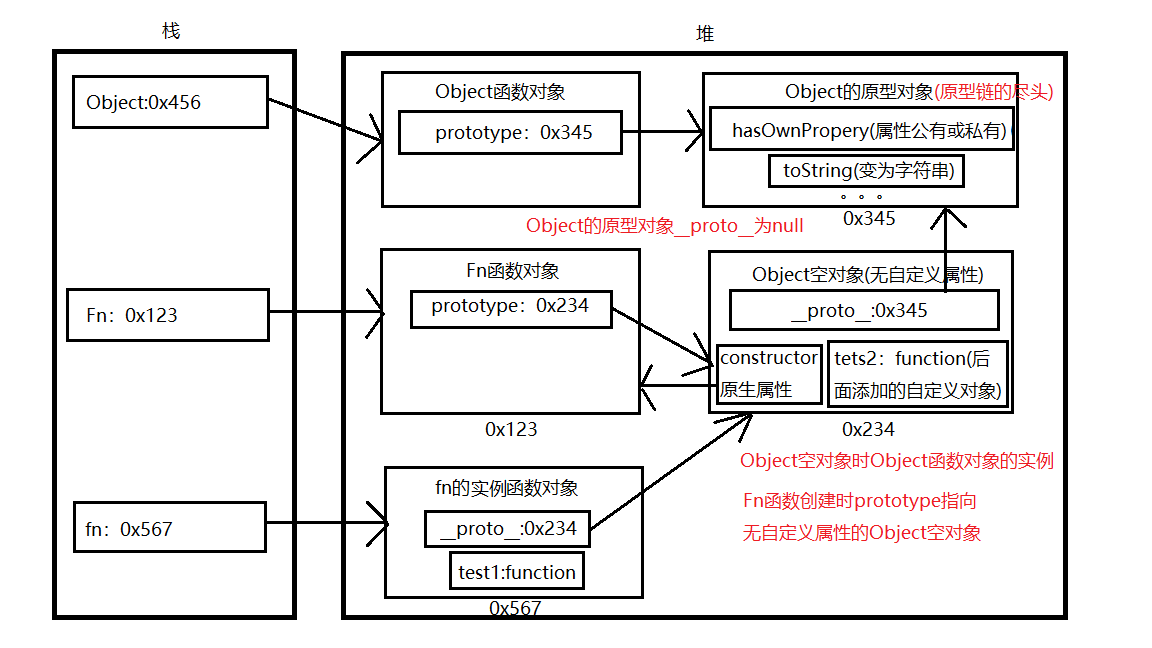
每个函数(构造函数)都有一个prototype属性,它默认指向一个Object空对象
原型对象的constructor属性指向它本身
var Person = function(){}var p = new Person;console.log(Person.prototype)
作用:给原型对象添加属性(一般是方法)
var Person = function(name,age){this.name = name;this.age = age;this.see = function(){console.log(this.name+"爱看片")}}var chengchao = new Person("程超",18)chengchao.see();
这样相当于给每一个示例对象添加了see方法,非常占用内存
var Person = function(name,age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}Person.prototype.see = function(){console.log(this.name+"爱看片")}var chengchao = new Person("程超",18)chengchao.see(); //程超爱看片console.log(Person.prototype)
 给Person的prototype中添加see。每一个Person的示例都可以调用
给Person的prototype中添加see。每一个Person的示例都可以调用
proto(隐式原型)
每一个示例对象都有一个proto属性
对象的隐式原型的值与其对应构造函数的显式原型的值相等,对象创建时其对应构造函数将其prototype的地址值赋给对象的proto
var Person = function(name,age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}Person.prototype.see = function(){console.log(this.name+"爱看片")}var chengchao = new Person("程超",18)console.log(chengchao.__proto__ == Person.prototype)//true
原型链(隐式原型链)
作用:查找对象的属性
当我们去访问一个对象的属性时
现在自身属性中查找,
如果没有,再沿着proto这条链向上查找,找到返回,
如果任未找到,则返回undefind
function Fn(){this.test1 = function(){console.log('test1()')}}Fn.prototype.test2 = function (){console.log('test2()')}var fn = new Fn();fn.test1();fn.test2();console.log(fn.toString())fn.test3();