Overview
Datasets
Dataframes
SQL tables and views
Dataframes and Datasets
Definition
Table-like collections with well-defined rows and columns
Each column must have the same number of rows as all the other columns
Immutable, lazily evaluated plans that specify what operations to apply to data residing as a location to generate some output
Schemas
defined the column names and types of a Dataframe
Overview of Structured Spark Types
Def
Spark types map directly to the different language APIs through a lookup table
Spark uses an engine called Catalyst that maintains its own type information through the planning and processing of work
Example

This addition happens because Spark will convert an expression written in an input language to Spark’s internal Catalyst representation of that same type information
Dataframes Versus Datasets
检查类型的时间点
Compile Time(Datasets)
Run Time(Dataframe)
检查类型的时间点
JVM Types(Datasets)
Datasets of Row Type-Optimized internal format (Dataframe)
Both can benefit from the Catalyst Engine
Columns
simple type like an integer or string
complex type like an array or map
null value
Rows
Each record in a Dataframe must be of type Row
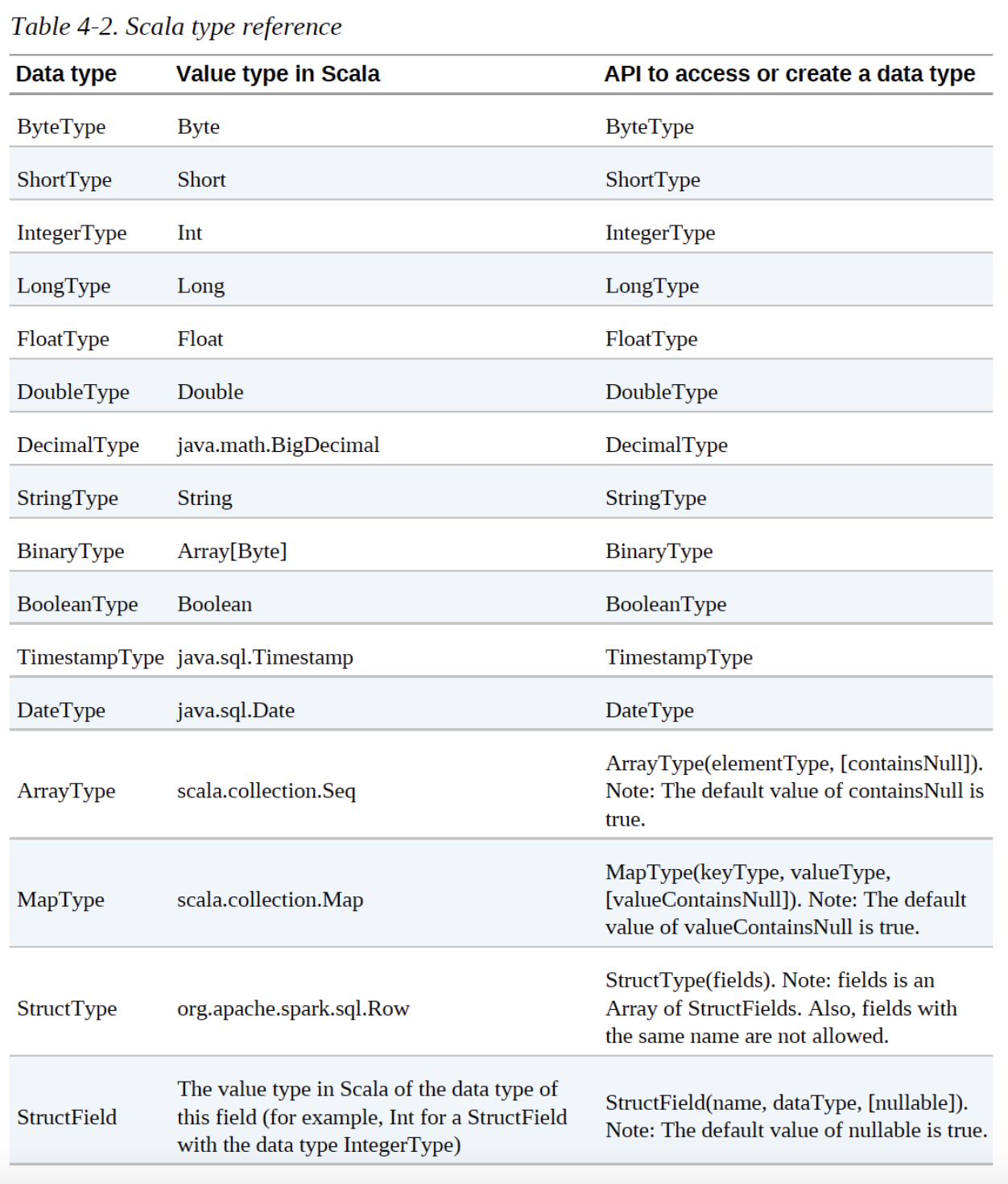
Spark Types
Scala type reference
Overview of Structured API Execution
Steps
1. Write Dataframe/Dataset/SQL Code
2. If valid code, Spark converts this to a Logical Plan
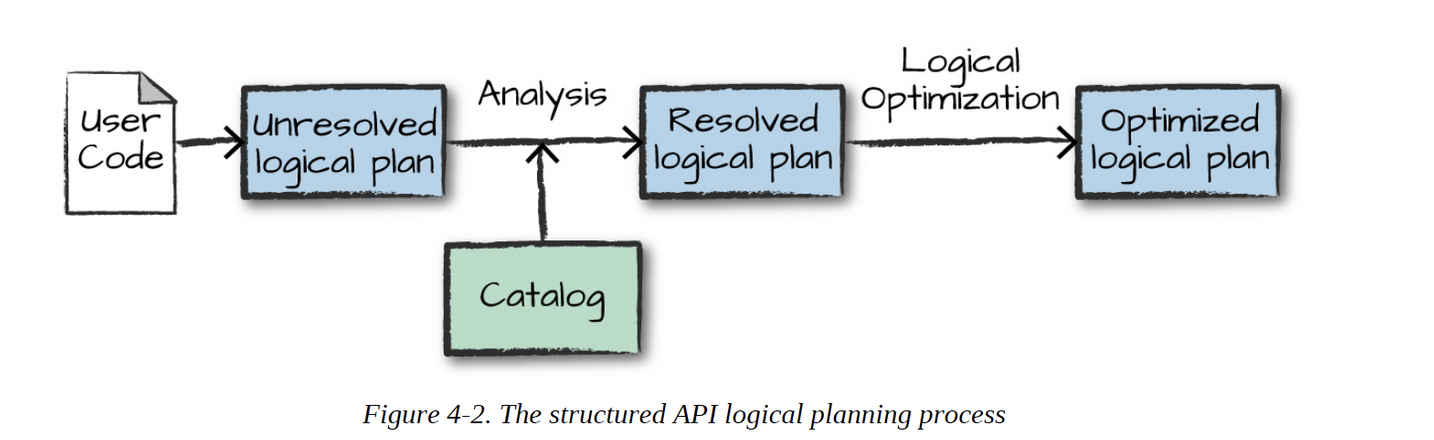
Unresolved Logical Plan
Resolved Logical Plan
- Spark use the catalog, a repository of all table and Dataframe information, to resolve columns and tables in the analyzer
- Optimized Logical Plan
- pushing down predicates or selections
3. Spark transforms this Logical Plan to a Physical Plan, checking for optimizations along the way
generating different physical plan
compare through a cost model
choose best physical plan
an Example of the cost comparison might be choosing how to perform a given join by looking at the physical attributes of a given table(how big the table is or how big its partitions are
- results in a series of RDDS and transformations
4. Spark then executes this Physical Plan(RDD manipulations) on the cluster
Runs all of this code over RDDs, the lower-level programming interfave of Spark
Spark performs further optimizations at runtime, generating native Java bytecode that can remove entire tasks or stages during execution
Attachments:
 image-20210113-063736.png
image-20210113-063736.png image-20210113-063814.png
image-20210113-063814.png image-20210113-063834.png
image-20210113-063834.png

