线程与进程的区别
进程是一个运行程序的实例,例如我们打开一个视频软件就是一个进程;
线程就是进程中的一个执行流程,例如我们在视频软件中看视频,又点击了下载,播放视频是一个线程,下载视频又是一个线程。
- 进程是资源(包括内存、打开的文件等)分配的单位,线程是 CPU 调度的单位;
- 进程拥有一个完整的资源平台,而线程只独享必不可少的资源,如寄存器和栈;
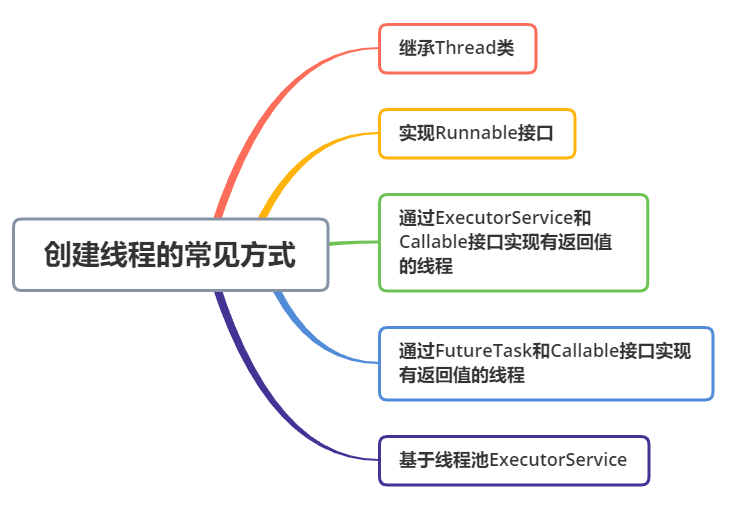
创建线程的5种方法
1.继承Thread类
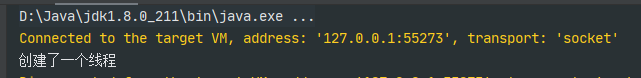
继承Thread类之后,重写run方法,把你需要执行的代码写在run方法中(如果不重写的话,继承父类的run方法,空输出),测试的话,实例化一个MyThread实例对象,实行start()方法,执行线程,输出“创建一个线程”。
public class MyThread extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("创建了一个线程");}}public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyThread thread = new MyThread();thread.start();}}
2.实现Runnable接口
我们先看下Thread类的源码实现,发现其实Thread类也是实现了Runnable接口。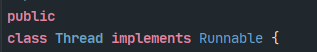
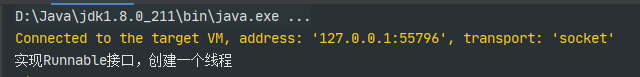
实现Runnable接口创建线程和直接继承Thread类创建线程,不一样。创建的线程类实现Runnable接口必须重写run()方法,否则编译报错。在测试这个创建线程的时候,也有点不一样,先实例化一个实现Runnable接口的线程对象thread2,将thread2作为Thread类实例化对象的参数创建对象thread,然后调用thread对象的run方法,执行thread2的run方法具体逻辑代码。
为什么thread2不能直接调用start方法,因为实现的Runnable接口,而Runnable接口中只有一个抽象方法run()。
public class MyThread2 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("实现Runnable接口,创建一个线程");}}public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyThread2 thread2 = new MyThread2();Thread thread = new Thread(thread2);thread.start();}}
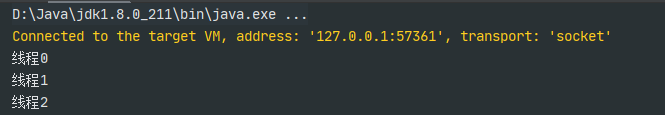
3.通过ExecutorService和Callable
实现Callable接口,重写call方法。(PS:call方法是有返回值的,而run方法是没有返回值的)
public class CallableTest implements Callable {private String threadName;public CallableTest(String threadName){this.threadName = threadName;}@Overridepublic Object call() throws Exception {return threadName;}}public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//1.创建线程池ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);List<Future> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {//2.实例化CallableTestCallable callable = new CallableTest("线程"+i);//3.获取执行结果(Future是一个接口,代表了一个异步计算的结果)Future future = threadPool.submit(callable);list.add(future);}//4.关闭线程池threadPool.shutdown();for (Future future : list) {//5.输出执行结果System.out.println(future.get().toString());}}}
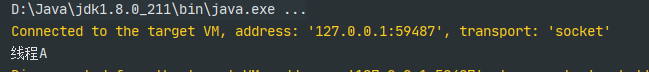
4.通过FutureTask和Callable接口
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//1.实例化CallableTest对象Callable callable = new CallableTest("线程A");//2.实例化FutureTask对象,callable作为参数FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(callable);//3.实例化Thread对象,futureTask作为参数Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask);//4.执行线程thread.start();//5.输出结果:线程ASystem.out.println(futureTask.get());}}
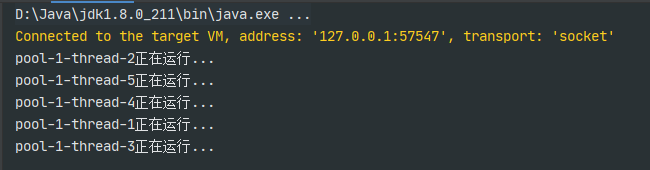
5.通过线程池ExecutorService
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//1.创建线程ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {//2.执行线程threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在运行...");}});}}}