什么是反射
程序在运行中,对任意一个类都能获取其所有的属性和方法,并且对任意一个对象都能调用其任意一个方法,这种机制被称为Java的反射机制。
反射的作用
我们自己写代码的时候,当对一个对象的类型不确定的时候,我们就用反射的机制,来获取这个对象的信息,我们看下面这个例子。
public class Person {public void show(){System.out.println("show");}}public class Student extends Person{public void play(){System.out.println("play");}}public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {Person person = new Student();//person.play(); 无法获取到play方法}}
我们测试的时候,person对象是无法获取到play方法的,因为在编译时person对象的类型是Person,而在运行时,person对象的类型就是Student了,如果想在编译时期,在这段代码里,运行play()方法,则就需要用到反射机制, 在运行时,获取这个对象的属性和放方法。
反射的主要作用还是,对于一些对象在编译时期不清楚类型信息的,我们都可以在运行时期获取到,以便我们更好的操作对象。
Class对象
只要运行在内存的类,都会有Class对象的,Class对象包含了这个类的所有信息。
public static void main(String[] args) {Person person = new Student();String name = person.getClass().getName();System.out.println(name);//输出:demo.a8.Student}
可以用Class对象,在运行中获取对象的具体类型。
获取Class对象的三种方式
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {//第一种:通过类名 . 的方式获取Class clazz = Student.class;System.out.println(clazz.getName());//输出:demo.a8.Student//第二种:通过对象的getClass方法获取Person person = new Student();System.out.println(person.getClass().getName());//输出:demo.a8.Student//第三种:通过Class类的forName方法,加路径参数获取Class clazz3 = null;try {clazz3 = Class.forName("demo.a8.Student");System.out.println(clazz3.getName());//输出:demo.a8.Student} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
通过Class对象获取属性,所有构造方法,所有方法
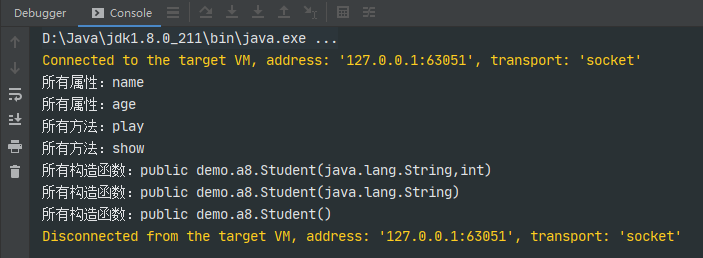
public class Student{String name;int age;public Student(){}public Student(String name){this.name = name;}public Student(String name, int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}public void play(){System.out.println("play");}public void show(String str){System.out.println(str);}}public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {Student student = new Student();Class studentClass = student.getClass();Field[] fields = studentClass.getDeclaredFields();for (Field field : fields) {System.out.println("所有属性:"+field.getName());}Method[] methods = studentClass.getDeclaredMethods();for (Method method : methods) {System.out.println("所有方法:"+method.getName());}Constructor[] constructors = studentClass.getDeclaredConstructors();for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {System.out.println("所有构造函数:"+constructor.toString());}}}
通过反射调用方法
调用方法是通过Method对象的invoke方法调用。
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) {Student student = new Student();//1.获Student的实例对象try {Method show = studentClass.getMethod("show", String.class);//2.获取show方法的Method类实例对象show.invoke(student, "aaaa");//3.调用method实例对象的invoke方法,传入参数student实例对象,和show方法参数} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//输出:aaa}
常见反射应用场景
- 许多Java框架中大量用到了反射,例如Spring框架的通过 XML 配置模式装载 Bean 的过程
- JDBC连接数据库
反射的优点与缺点
- 优点
使程序更加灵活,增加扩展性,降低代码耦合度
- 缺点
性能问题,反射操作的效率要比正常操作效率低很多,如果程序对安全性要求很高,则不建议使用反射;破坏了类的封装性,通过反射能够访问,类的私有属性和方法。


