I/O流的作用
I 就是输入流(读数据),O就是输出流(写数据)。当我们需要从硬盘,内存或者网络中读写数据时,数据的传输量可能很大,而我们的内存和带宽有限,无法一次性获取大数据量时,就可以通过IO流来解决问题。而流,就像河流中的水一样,缓缓的流入大海。(PS:IO流让我们在各种环境下更好的读写数据。)
**
I/O流的分类
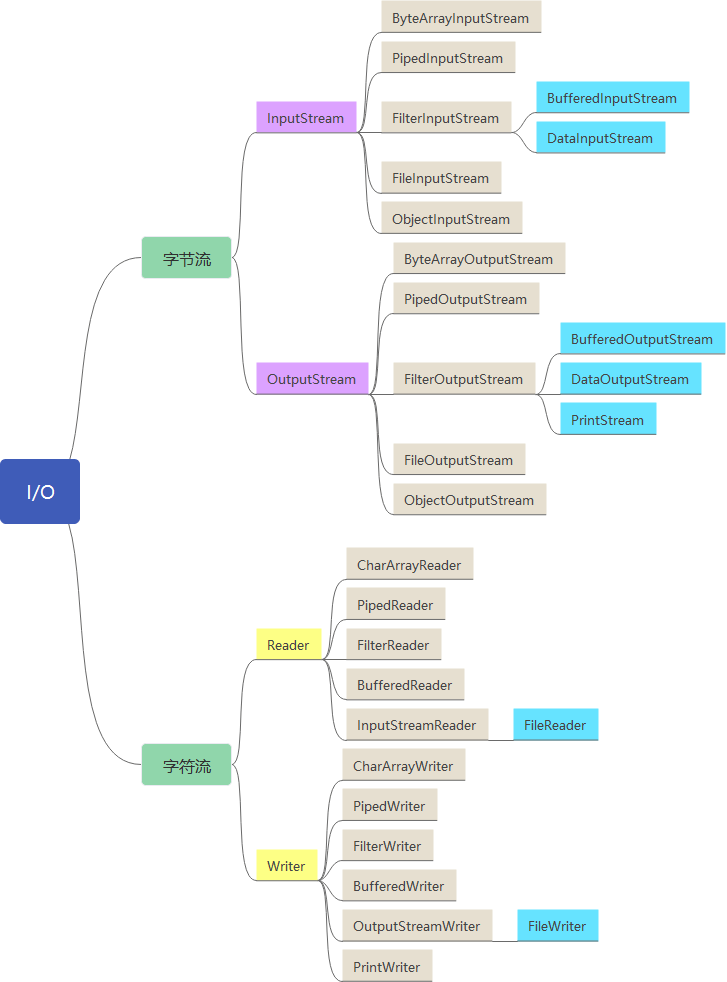
- 从传输数据类型分为:字节流和字符流
- 从传输方向分为:输入流和输出流
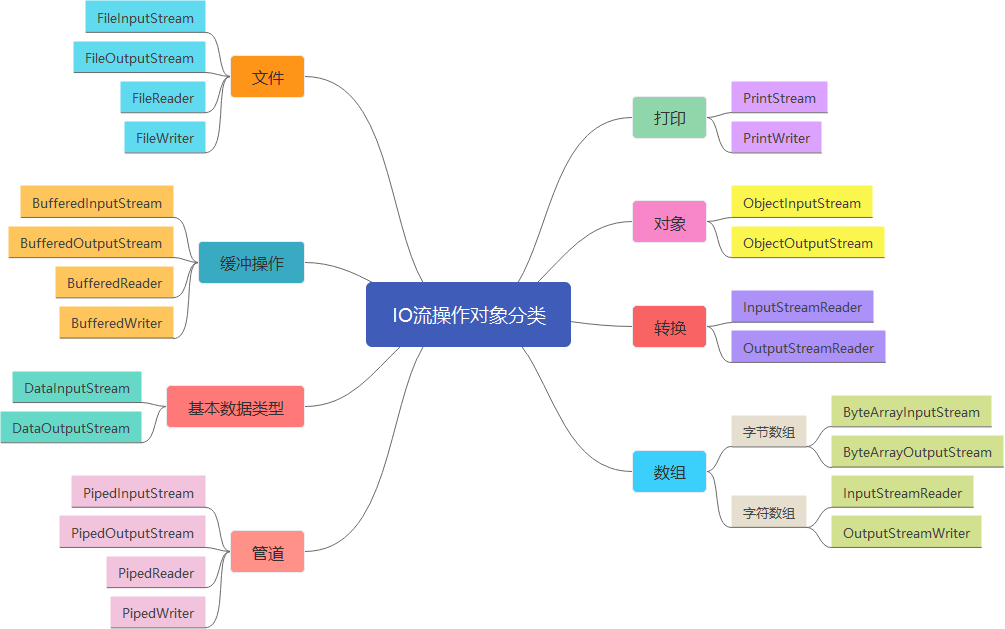
- 从IO操作对象划分:
如何更好的使用IO流
我们在使用IO流的时候,我们要明确,是读数据还是写数据,传输的数据时字节还是字符,数据所在的设备等问题,决定我们应该用什么IO流,具体情况具体分析,举个例子我们来了解一下。
序列化,就是将Java对象以字节流的方式存入硬盘中,分析一下,操作的是对象,字节流,写数据,我们就可判断用的是ObjectOutputStream,则反序列化用的ObjectInputStream读数据。
public class test{public static void main(String[] arg) throws CloneNotSupportedException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, ClassNotFoundException {String fileUrl = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\person.txt";try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(fileUrl))) {//序列化Person person = new Person();person.setName("小张");person.setAge(18);oos.writeObject(person);//反序列化ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(fileUrl));Person person1 = (Person) ois.readObject();System.out.println(person1.getName() +"," + person1.getAge());//输出:小张,18oos.close();ois.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
当我们需要把数据暂存内存时,可以用ByteArrayOutputStream,因为ByteArrayOutputStream创建实例对象的时候,程序内部创建一个byte型别数组的缓冲区,然后利用ByteArrayOutputStream和ByteArrayInputStream的实例向数组中写入或读出byte型数据,在网络传输中我们往往要传输很多变量,我们可以利用ByteArrayOutputStream把所有的变量收集到一起,然后一次性把数据发送出去。
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//将a.txt中的内容,放入缓冲区String fileUrl = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\a.txt";FileInputStream in = null;try {in = new FileInputStream(fileUrl);} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}ByteArrayOutputStream byteOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len=0;while ((len=in.read(bytes))!=-1){byteOutputStream.write(bytes,0,len);}System.out.println(byteOutputStream.toString());}}

当我们要得到某个文件的内容的时候,我们就可以用FileInputStream来得到文件中的内容
public class test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {String fileUrl = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\a.txt";try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(fileUrl)) {//用于声明文件读取到那里int len;// 建立缓冲字节数组,大小一般用1024倍数,理论上越高效率越高byte bur[] = new byte[1024];// 如果使用read传入字节数组,那么数据是存储到字节数组的,// 返回值是存储到缓冲数组中字节个数,-1为结束while ((len = fis.read(bur)) != -1) {System.out.println(new String(bur, 0, len));}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}

从以上三个例子,其实想说不同场景下,需要用到不同的IO流,我们现在只是简单的了解了一下Java的IO流,对于后端的开发同学来说,熟练的掌握IO流是极其重要的,我们可以通过网络,文件,内存对数据进行读写操作,后面我们继续深入的分析IO流的源码,到时候发出来供大家参考。

