机器学习视频 | 李宏毅 | 2019
课程相关
视频地址:
- B 站:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av46561029
- YouTube:https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLJV_el3uVTsOK_ZK5L0Iv_EQoL1JefRL4
课程主页:
The Next Step for Machine Learning
Meta-learning / Learn to learn
Few-shot learning / Zero-shot learning
Reinforcement Learning
强化学习,增强式学习
Network Compression
神经网络压缩
痛点
- 几乎所有的
Training Data和Testing Data一样,实际工程可能会有区别
总结

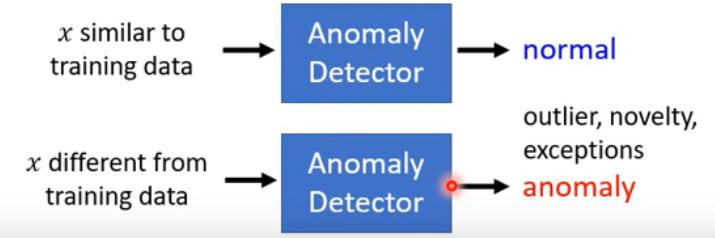
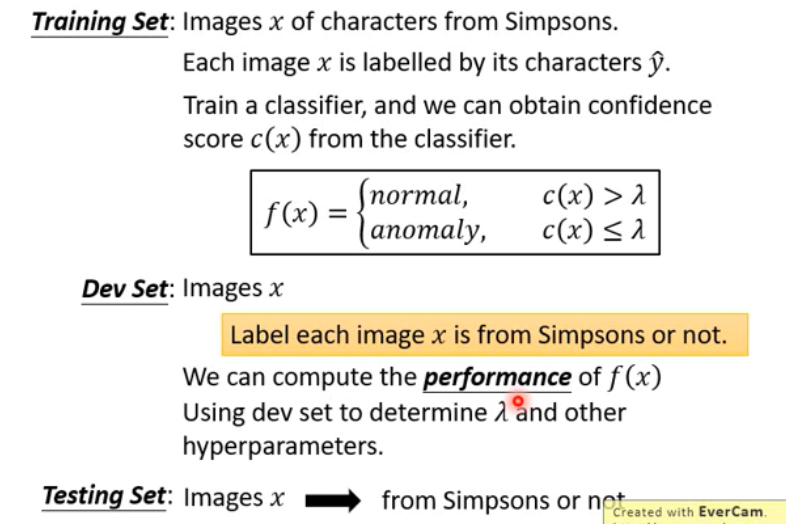
Anomaly Detection
解决问题:找出和训练数据不一样的输入
Applications
- Fraud Detection
- Network Intrusion Detection
- Cancer Detection
-
Binary Classification
No, “anomaly” is not easy to get and define.
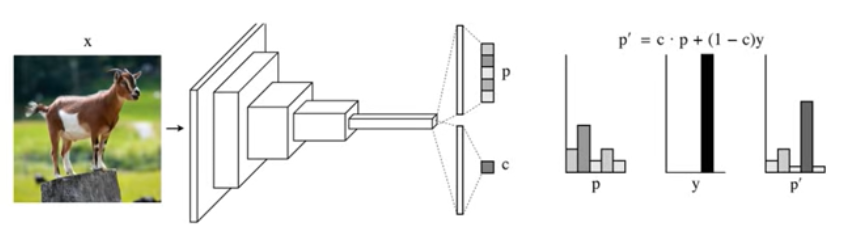
Label Case / With Classifier
先训练一个分类器,对已知类别进行分类。当应用于 Anomaly Detection 时,给出一个置信分数(confidence score,e.g. 取最大的概率),与一个门限进行比较。
Confidence Score
Framework
Evaluation
Accuracy Rate :√+1,X -1 —-> bad —-> 漏警代价比虚警概率代价更大
-
Novelty Detection with GAN
手动产生更多的样本(anomaly)同时训练分类和信心分数(confidence score)。

Twitch Plays Pokemon
Maximum Likelihood ( Estimate the
)
-
其中, 是
的均值(mean),
是 协方差矩阵(covariance matrix)
- More Features,使模型更加完善

- Auto-encoder
Attack and Defense
训练出来的模型不仅在模型中要强鲁棒性,在实际生活部署中也要可以应对(defense)各种情况(attack)。 Attack and Defense the Model.
Attack
通过给图片输入加噪使得
Loss Function变大。使得模型输出far from 目标输出

maybe 可以训练处来一种模型,这种模型的输入是各种被 attack 的图片,通过不断训练,使模型可以对图片中决定性元素的权值进行加重,比如通过给一张猫的图片中改变猫的颜色,使颜色的权值降低,从而使其他判断这张图片为猫的权值升高,可能这就是一种简单的增强数据集的方法?但是这种方法对于大规模的图片无法进行处理,可能需要一个新的方法处理数据?
Loss Function
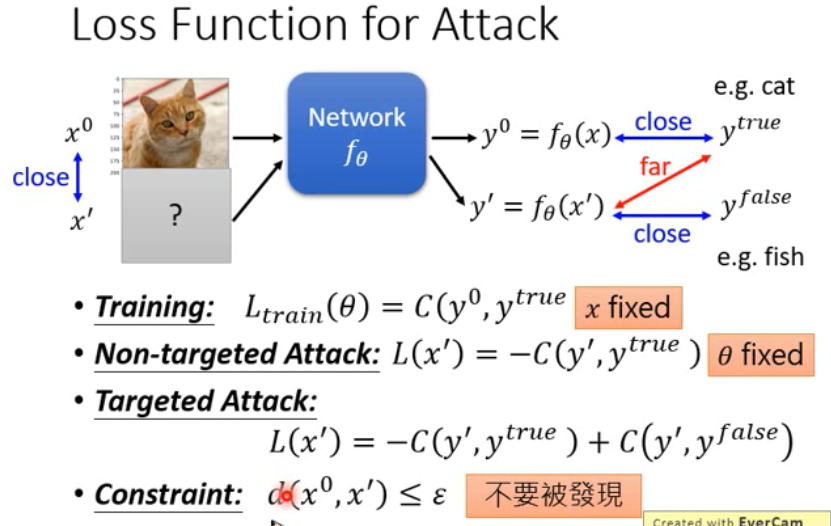
- 训练模型时是调整模型参数
- Attack 时是调整给输入加的噪声(即输入)
初始化时 就是原始图片,采取GD(Gradient Descent)
更新方法:类似于自适应滤波中的更新权值的方法,逐步逼近最优点,步长可调。
Example
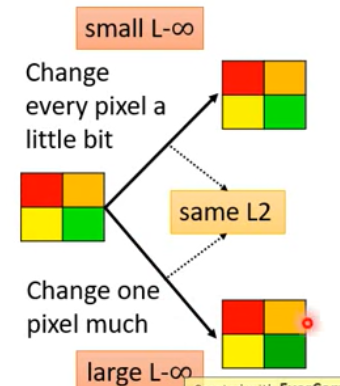
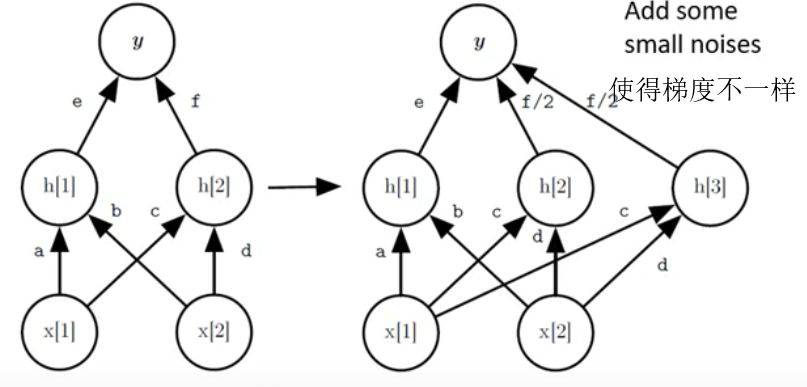
试图解释:在某些维度上, 和
在输入稍微改变一点时,输出就会发生很大的变化。
Approaches
- 采用不用的优化方法(different optimization methods)
使用不同的约束方法(different constraints)
类似于拉格朗日乘子法
e.g.
FGSM(Fast Gradient Sign Method)
相当于只在意梯度的方向而不在意梯度的大小,用sign函数(+1,-1)来表示方向,一次得出,
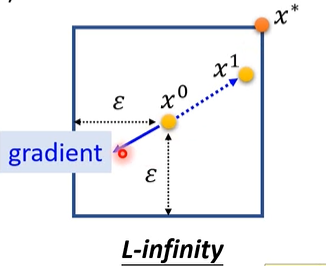
在二维中,相当于通过更新将拉到(
)上。
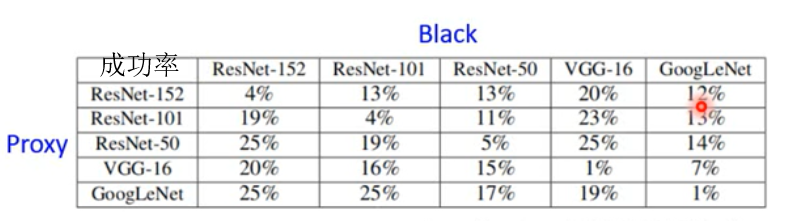
Black Box Attack v.s. White Box Attack
已知训练数据,通过训练数据来进行训练模型(Proxy)并攻击黑箱(Black)
Universal Adversarial Attack
找到一个 Attack SIgnal,可以用它来攻击所有类别
Adversarial Reprogramming
Adversarial Reprogramming of Neural Network (ICLR,2019)
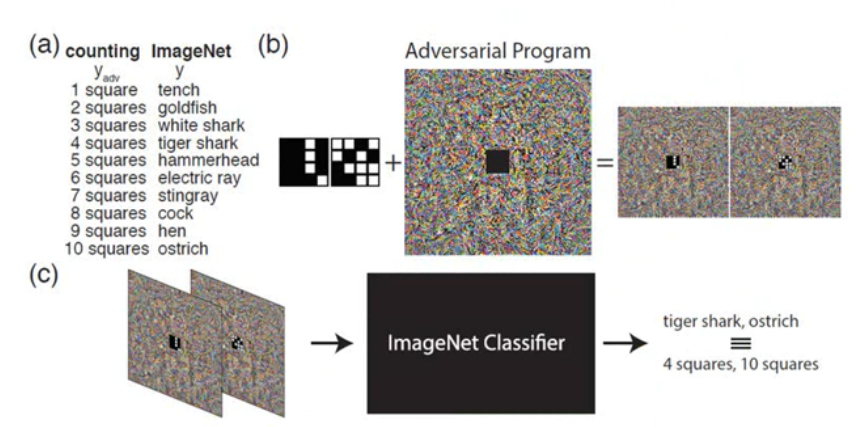
Attack in the Real World
maybe we can use a pair of glasses to attack face-recognition
limits
Beyond Images
Defense
- Passive Defense
被动防御,给已经训练好的模型增加防御。
- Feature Defense
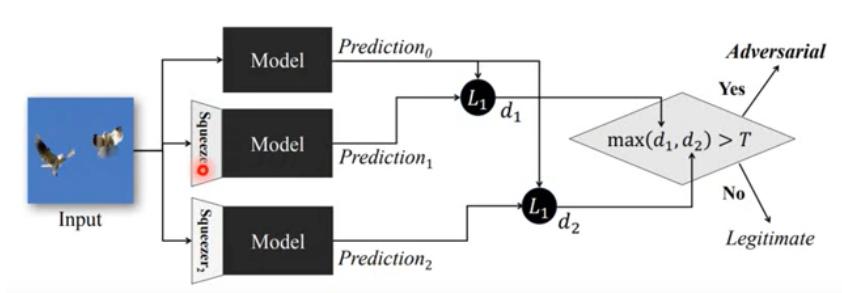
- Randomization at Inference Phase
图片进行缩放(resize)之后在周围加上 padding
- 缺点
- 当前面加的 filter 泄露之后,attack 时把这个 filter 当做一个 layer 来进行训练
- Proactive Defense
- 当前面加的 filter 泄露之后,attack 时把这个 filter 当做一个 layer 来进行训练
主动防御,在训练时考虑这种情况。(在训练时,找出漏洞,然后把这些漏洞数据作为训练资料,再训练模型,补起来漏洞。注意:补齐一个漏洞之后可能会有新的漏洞,要进行多次的训练)
Explainable ML
- Local Explanation
为什么你认为这张图片是猫
- Global Explanation
你认为猫是什么样子的
Author’s view
Application
- 判别履历
- 判断罪犯是否可以假释
- 模型诊断:机器学到了什么,可解释性深度学习
- 经济机器学习
-
Interpretable v.s. Powerful
Local Explanation
基本思想:
观察一个输入(e.g. 图片)的某些特征(pixel,component…)对模型的决策影响的大小。
通过改变(e.g. 掩盖)这些特征观察模型输出和 ground truth 的差别,从而得出那些特征对判断类别是重要的。(saliency map) gradient
- intergrated gradient
- deep lift
Global Explanation
基本思想:
找一个图片,使得某一类的输出最大(),要画出人可是别的 saliency map 还需要很多调整。
Image Generator
- GAN
- VAE
- …….
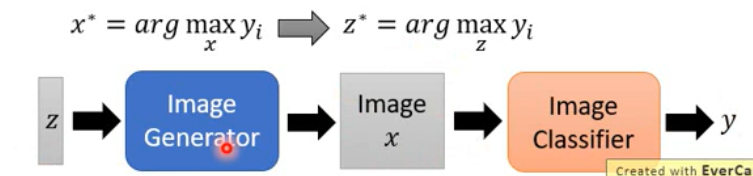
与 GAN 不同的是,这里的 Generator 和 Classifier 是固定的。
Using a model to explain another
类似于自适应滤波里面的应用,用一个模型(e.g. linear)去预测一个模型,可以只去预测某些特征
LIME
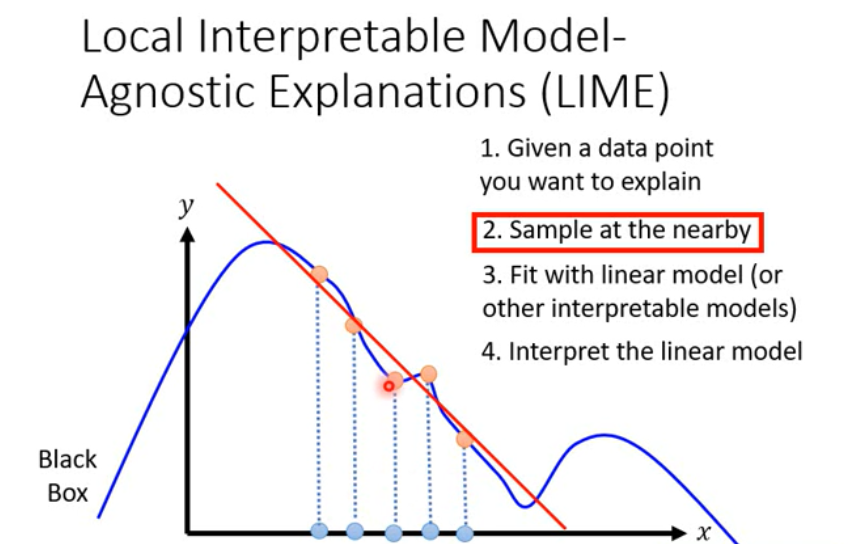
Steps:


Decision Tree
In order to make the tree not too large, we can train a network that is easy to be interpreted by decision tree.
Life Long Learning
Difficulties
- Knowledge Retention
- Knowledge Transfer
-
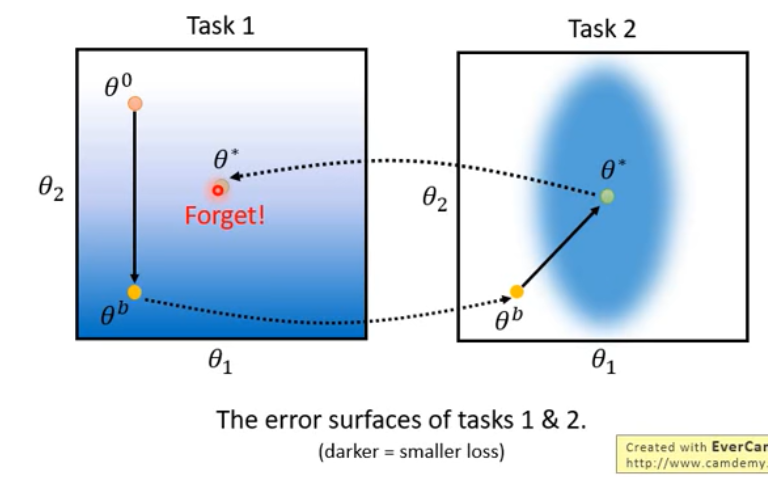
Knowledge Retention
catastrophic forgetting
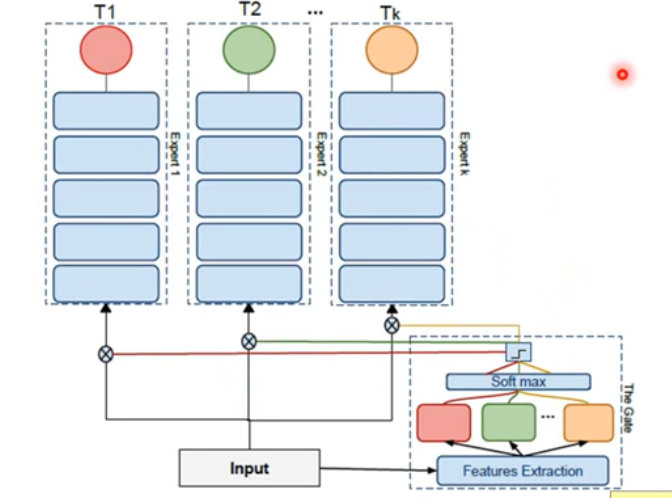
- multi-task learning
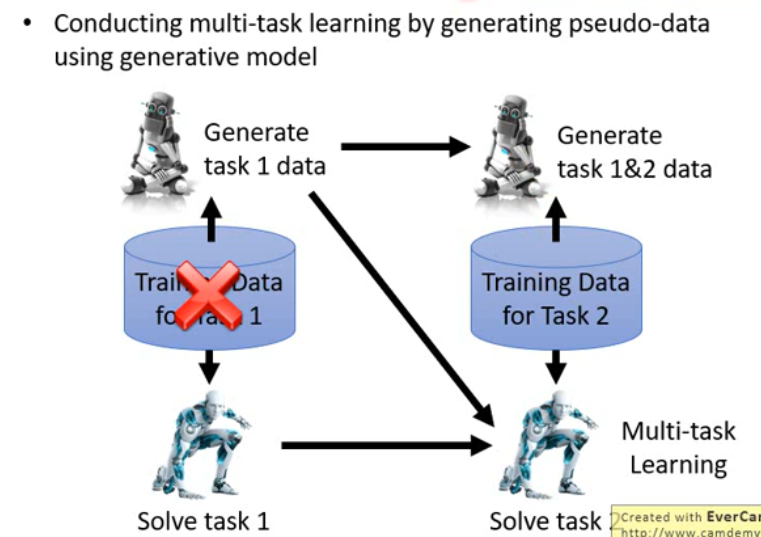
- Generating Data
基本思想:
再次训练时,只改变不重要的参数
具体方法:
给每一个参数增加一个 guard , 给损失函数加上新的一项。
e.g. the 2nd derivative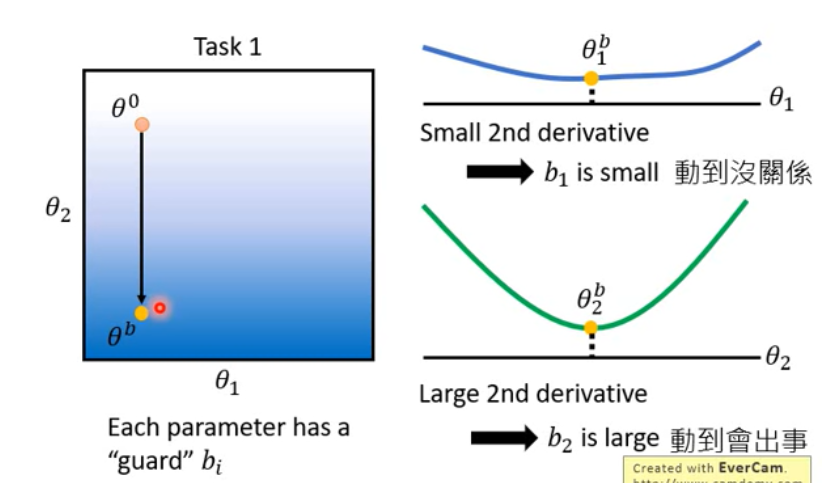
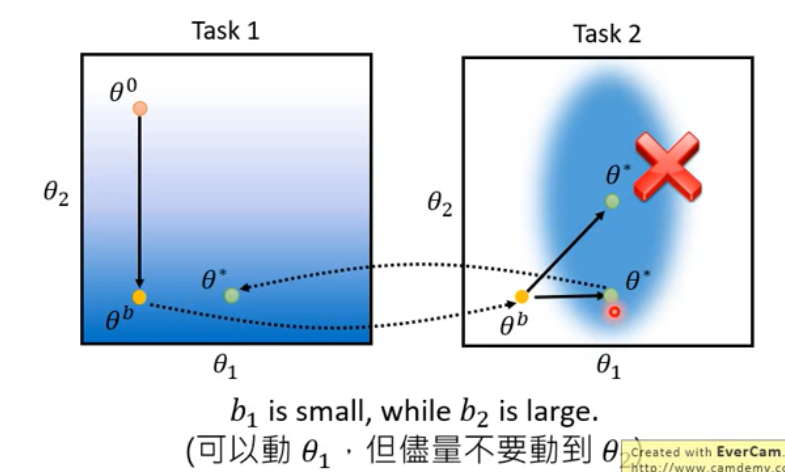
Different methods(different way to calculate )
Knowledge Transfer
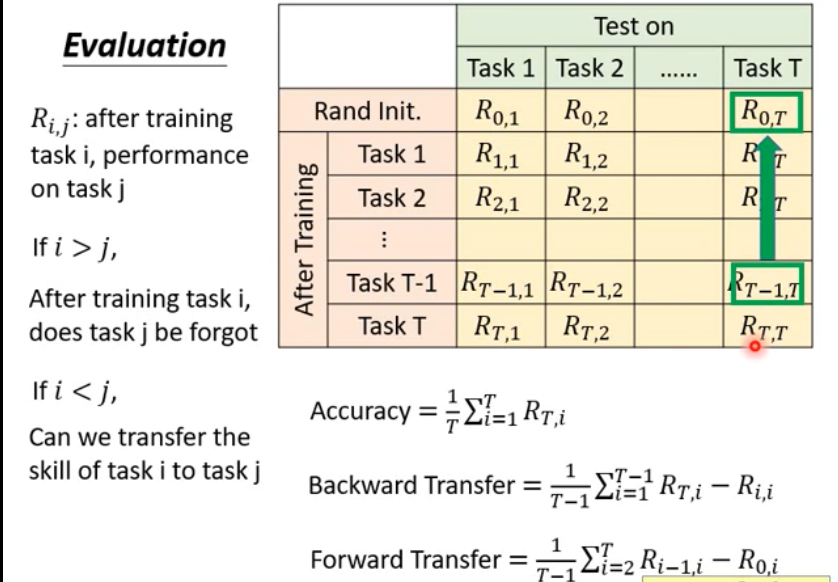
How to evaluate
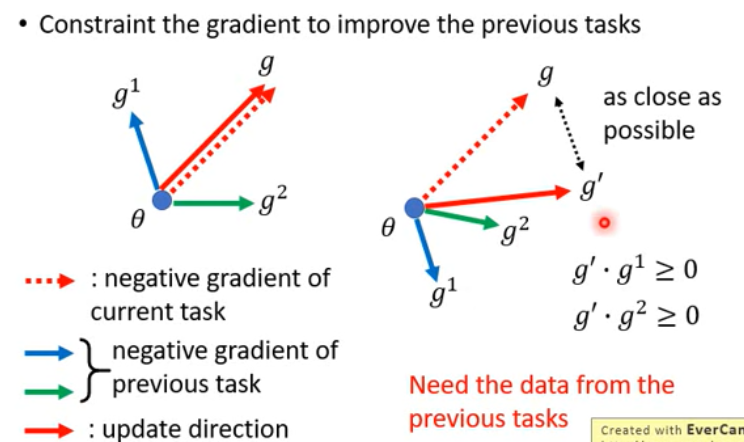
GEM
A-GEM
Model Expansion
Expand with Parameter Efficiency
Progressive Neural Network
Expert Gate
Net2Net
Curriculum Learning (the Proper Learning Order)
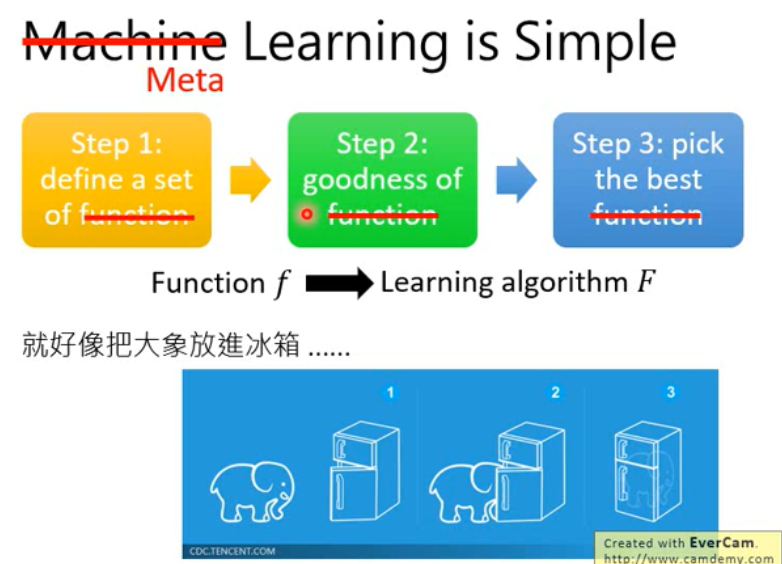
Meta Learning (MAML)
Make the machine learn to learn ( a better learner )
Difference
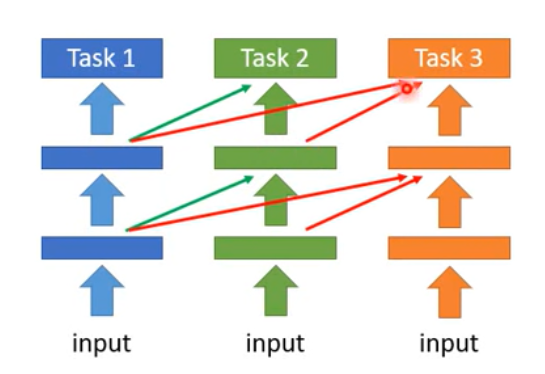
- life-long: 一个模型适应所有的 task
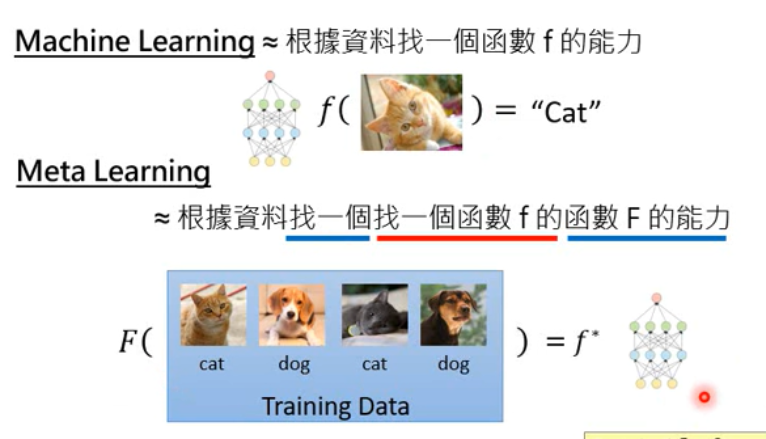
- meta-learning: 根据资料找一个 找一个函数f的 函数F的能力
Steps
- Define a set of learning algorithm
- 如CNN的网络架构
- 让机器去设计网络架构中某些结构.
- Define the goodness of a function F
- Loss function
, 其中
是不同task的loss function
- FInd the best function
Omniglot
Few-shot Classification N-ways K-shots

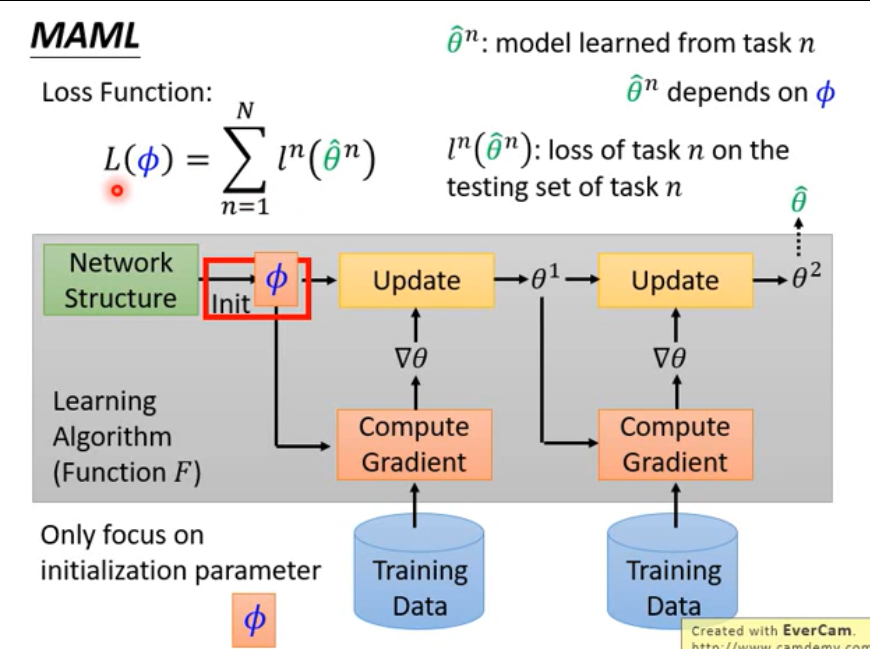
MAML
Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks 学习一个好的初始化参数
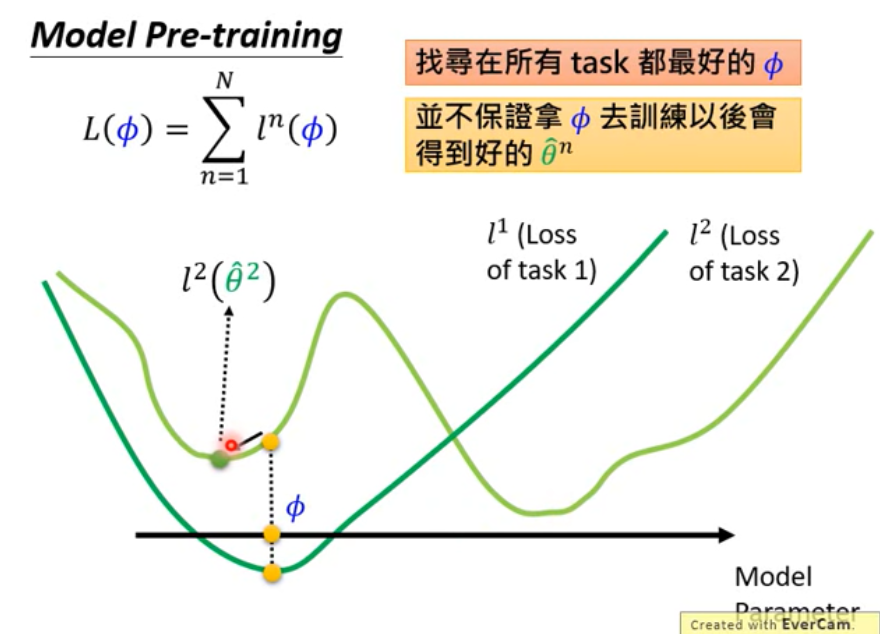
Different from Model Pre-training
- MAML (之后的Model)
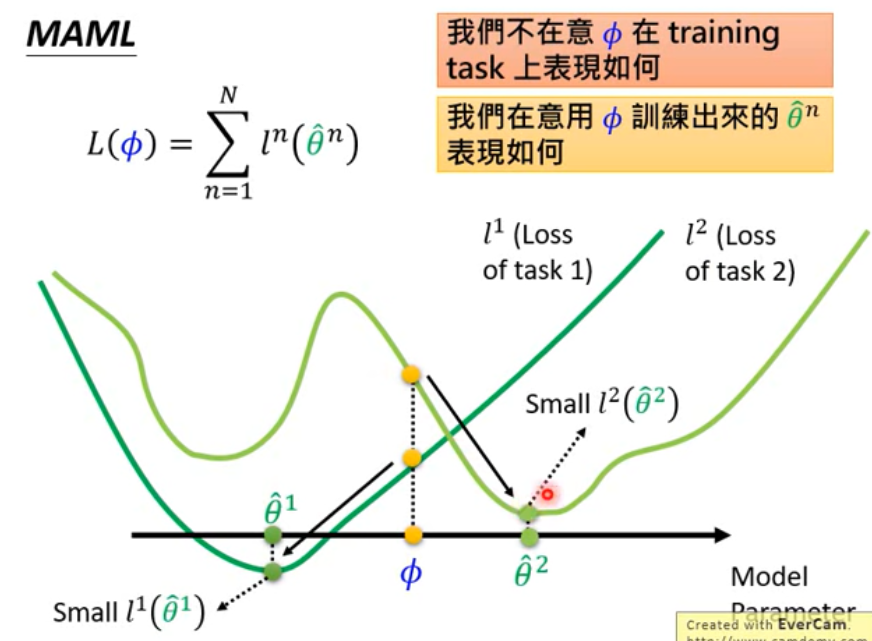
- MAML

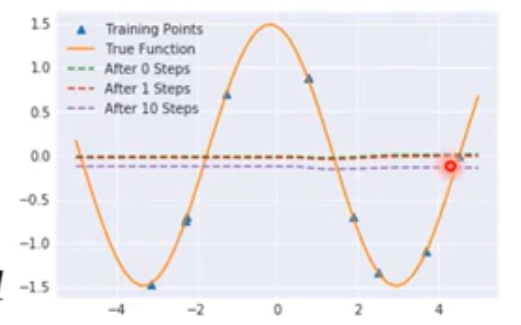
Real Implementation
MAML : 取第二次的gradient来更新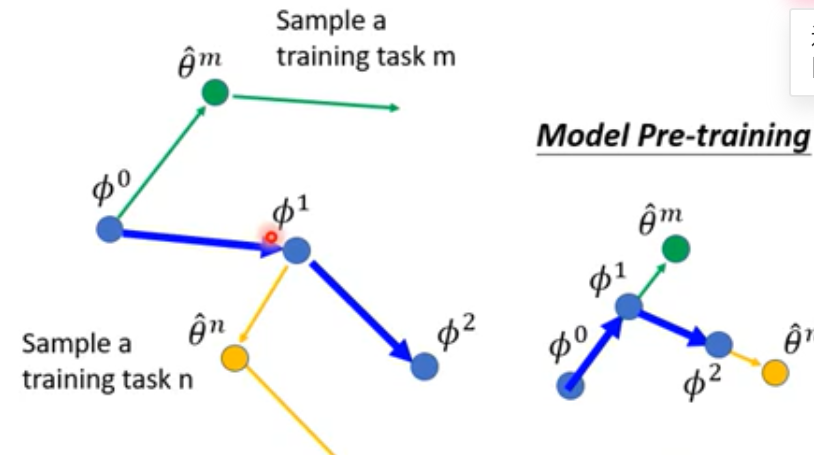
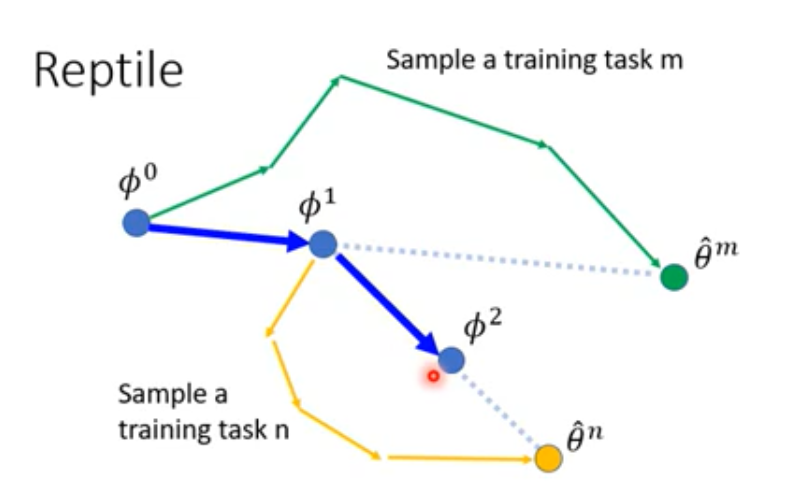
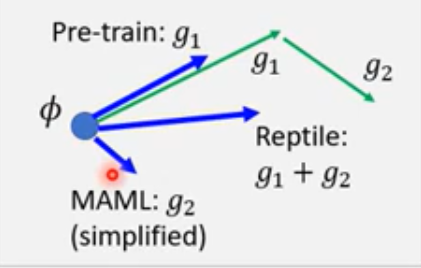
Reptile
Different from others
Meta Learning (Gradient Descent as LSTM)
RNN
LSTM
Meta Learning (Metric-based)
同时输入一个训练和一个侧式, 网络会给出结果
Siamese Network
类似于一个二分类问题, 输入两张图片, 判断两种图片是否是一个人.
不同于Auto-Encoder的是可能Siamese Network可能会忽略一些东西 (如背景) 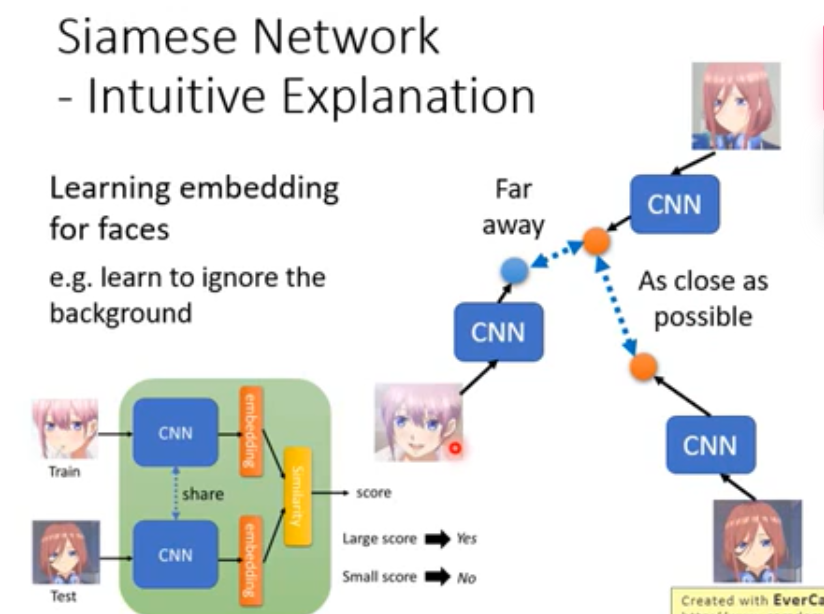
N-way Few/One-shot Learning
- Prototypical Network ( https: //arxiv.org/abs/1703.05175 )
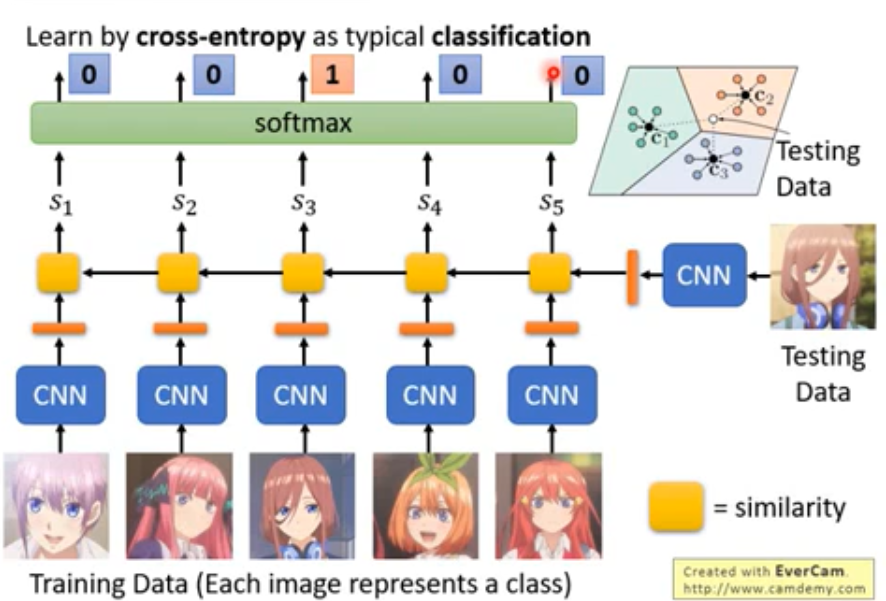
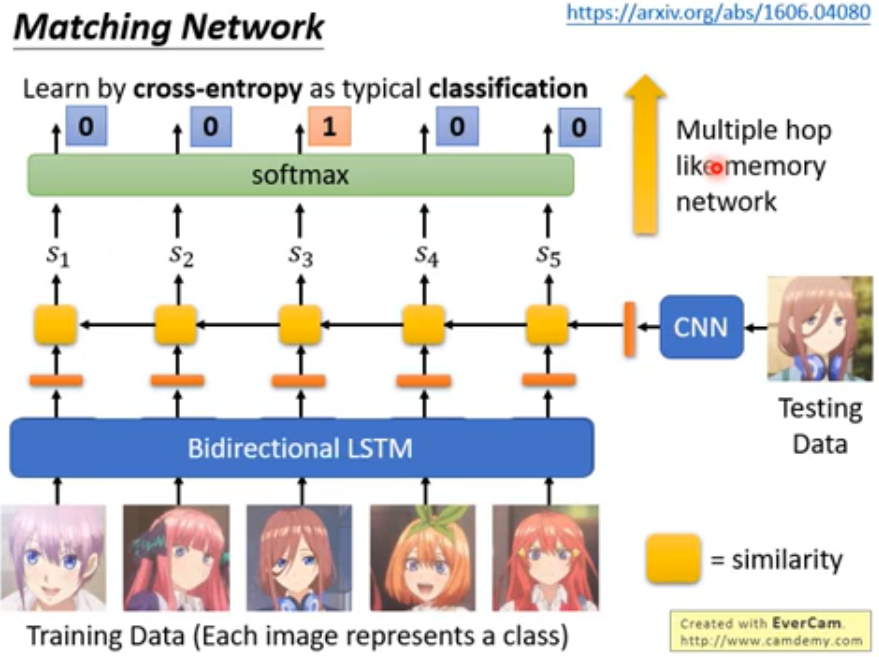
- Matching Network
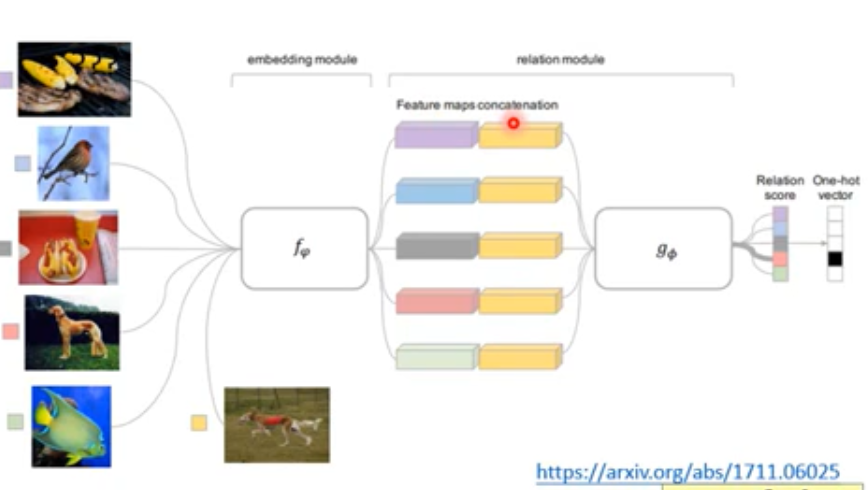
- Relation Network
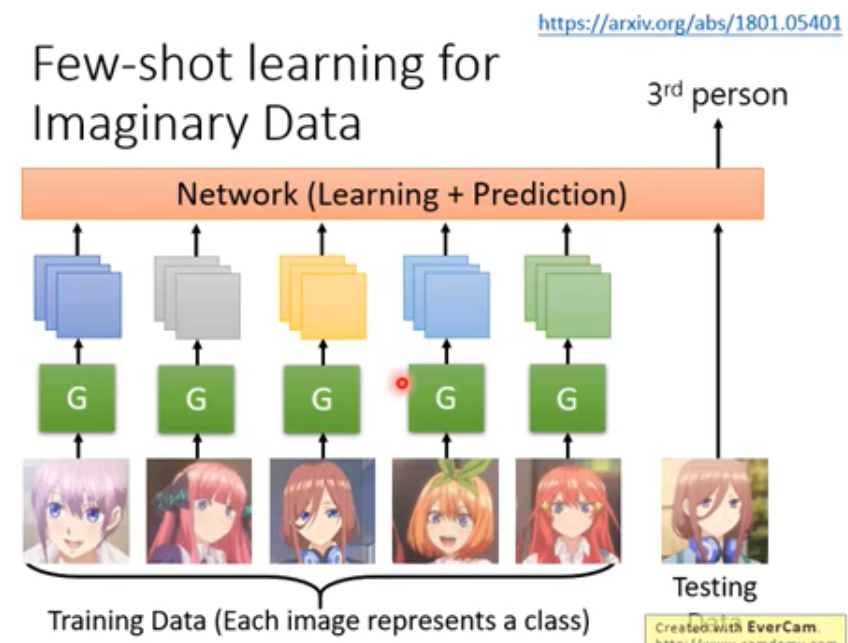
Few-shot Learning for Imaginary Data
Train and Test as RNN
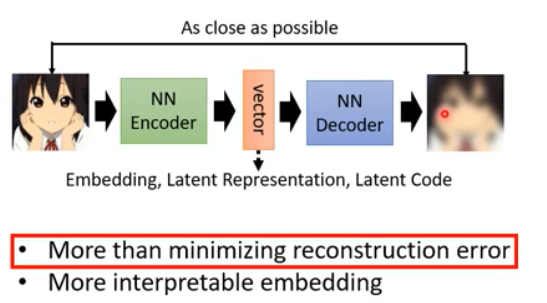
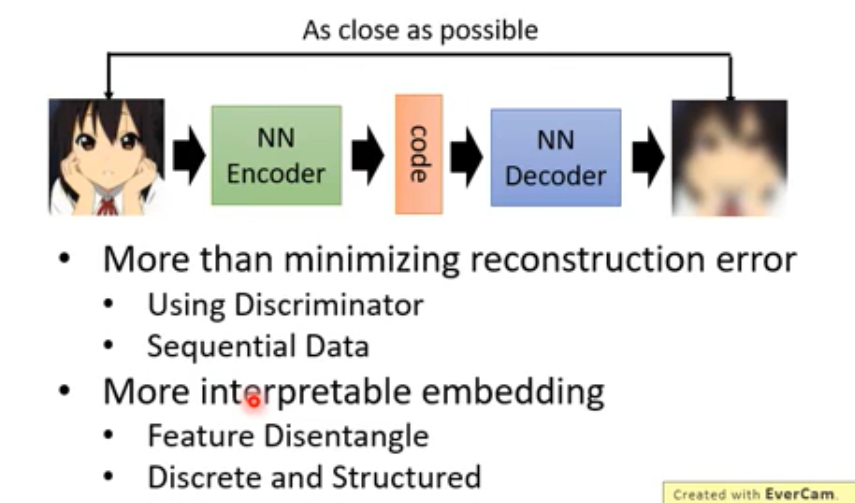
Auto-encoder
More than minimizing reconstruction error
Embedding : Beyond Reconstruction, 将一种将源数据映射到另外一个空间.
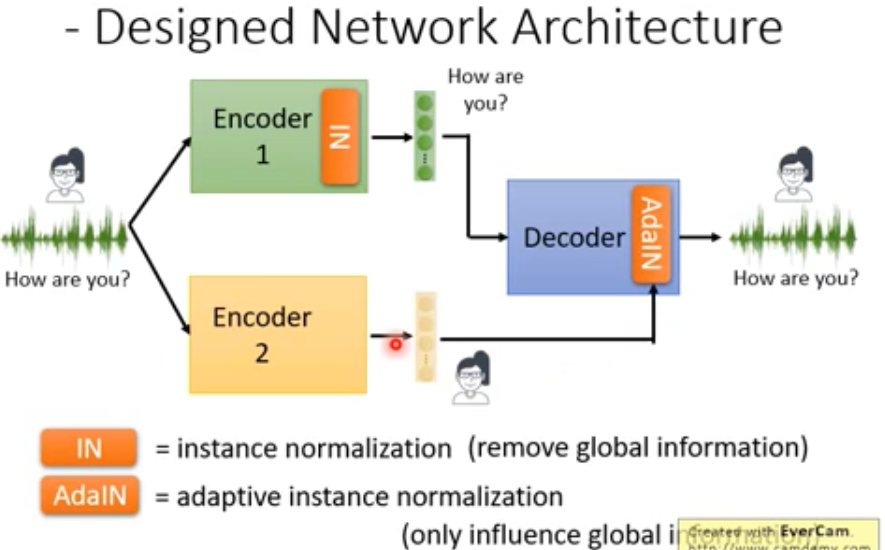
将向量中特征分开 (内容,音色…) , 之后可以重组 (变声)
e.g.1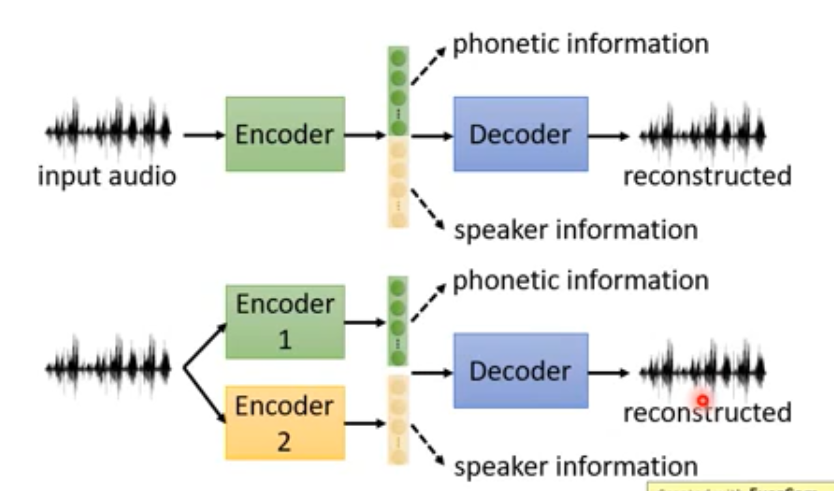

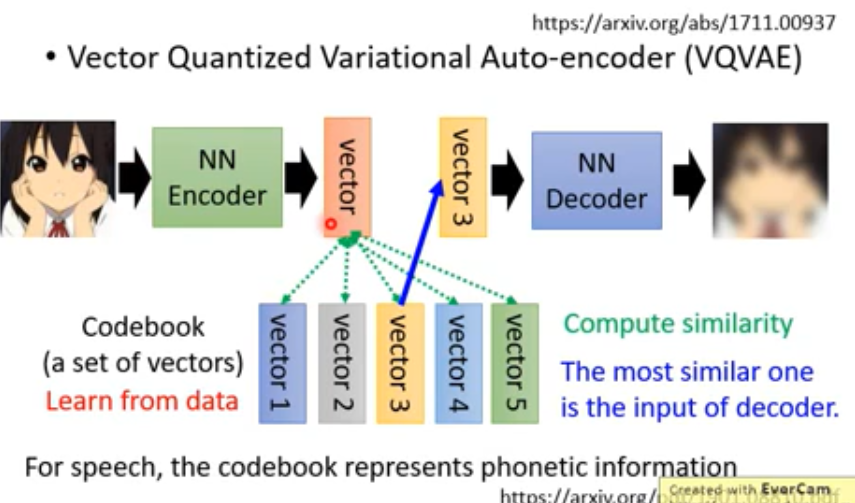
VQVAE
Sequence as Embedding
总结
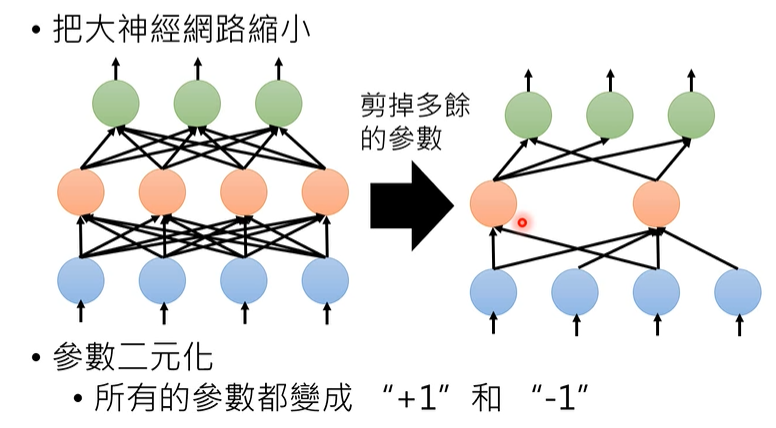
Network Compression
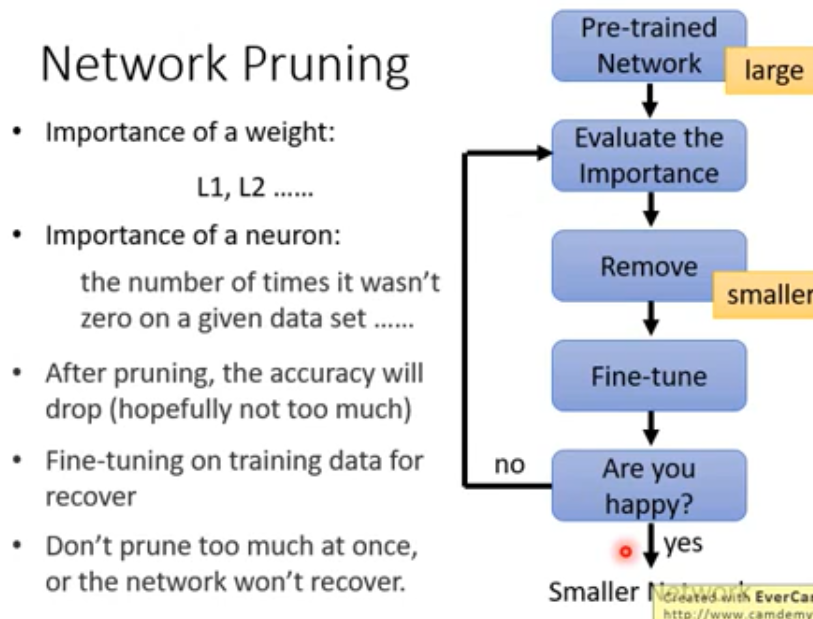
Network Pruning
原因 : 网络中很多参数是有多余的, 彼此之间不是正交 ?
- 评价权值是否很重要
- 评价神经元是否很重要
- 移除不重要的部分
Why Pruning
大的网络比较容易训练,所以先训练大的网络,之后才Pruning,而不是直接训练小的模型
- Lottery Ticket Hypothesis
Rethinking the Value of Network Pruning
Practical Issue
不是真正移除 而是将要移除的变为0
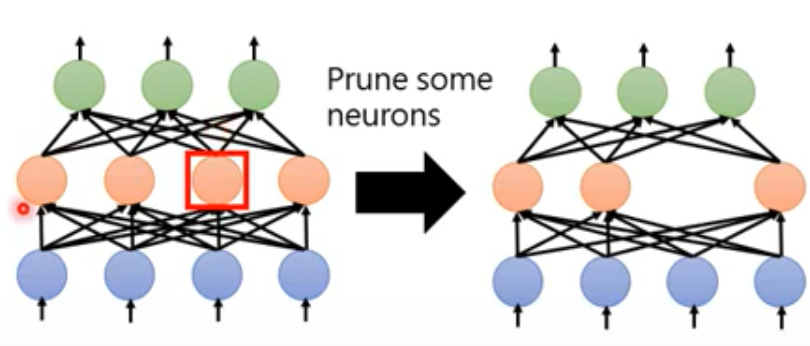
Weight pruning
- Neuron pruning (easy to implement)
Knowledge Distillation
先train一个大的network 然后train一个小的network去学习这个大的
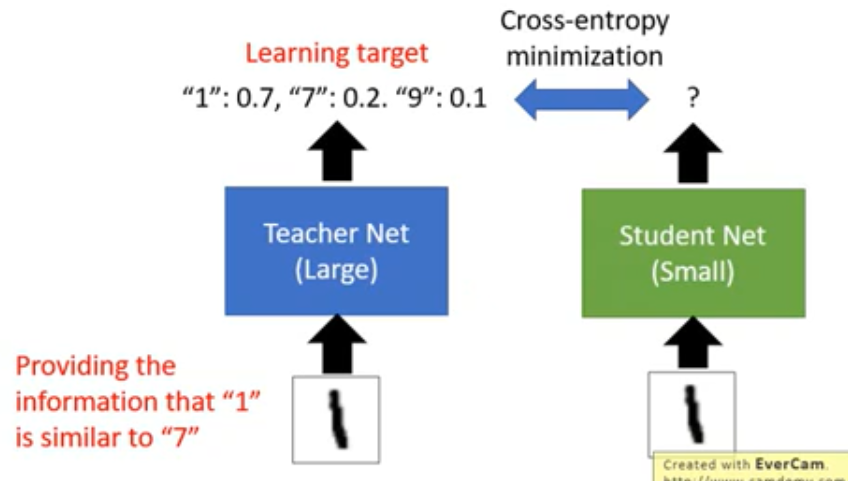
Ensemble
为了区别pruning 采用(可能实用不是有用)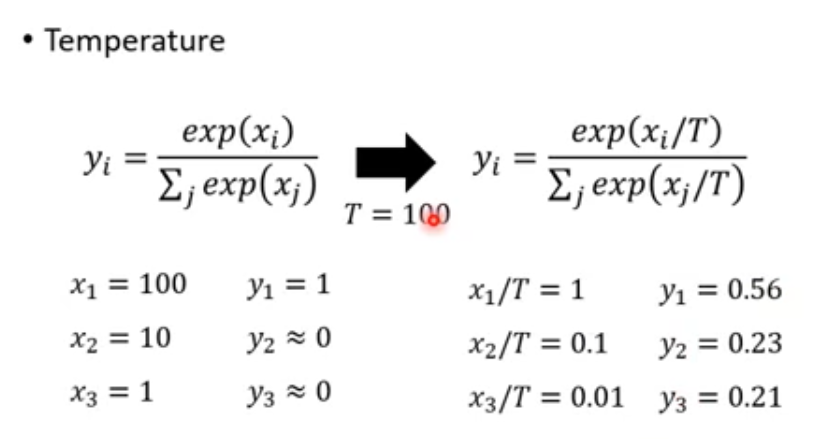
Parameter Quantization
类似于编码 Huffman编码之类balabala
Architecture Design
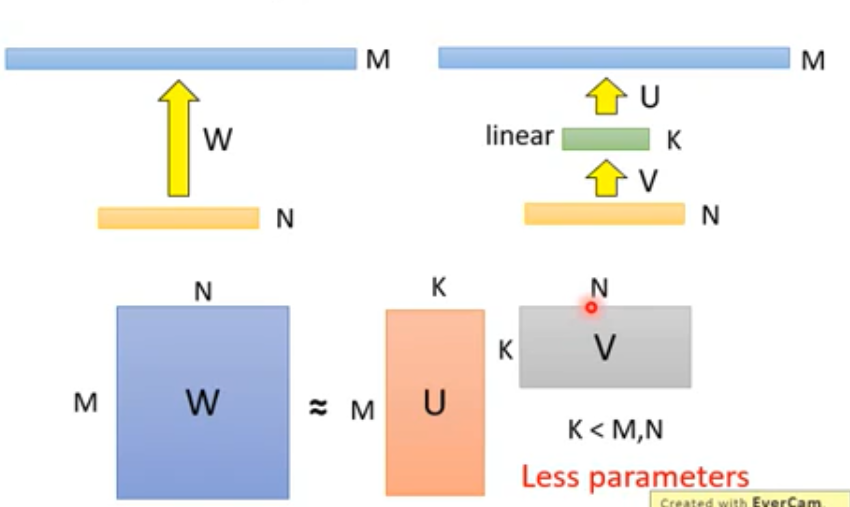
Low rank approximation
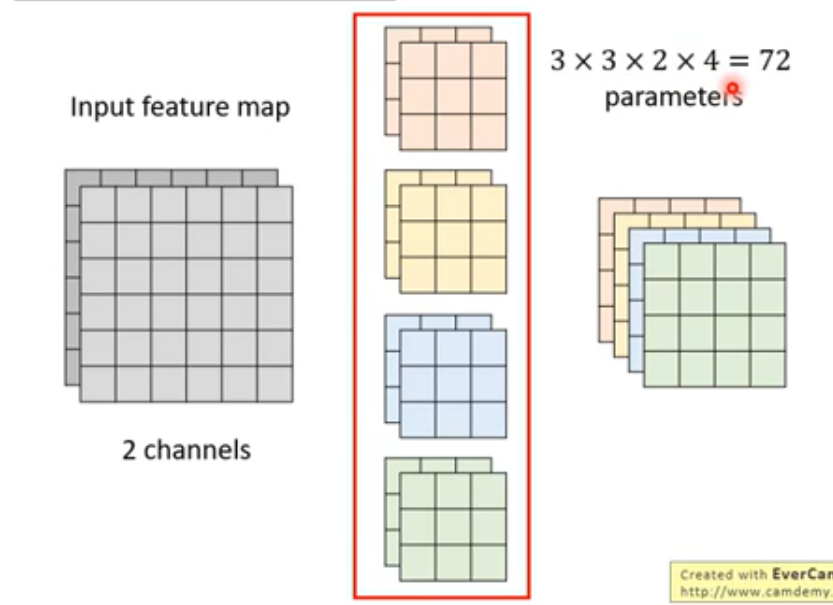
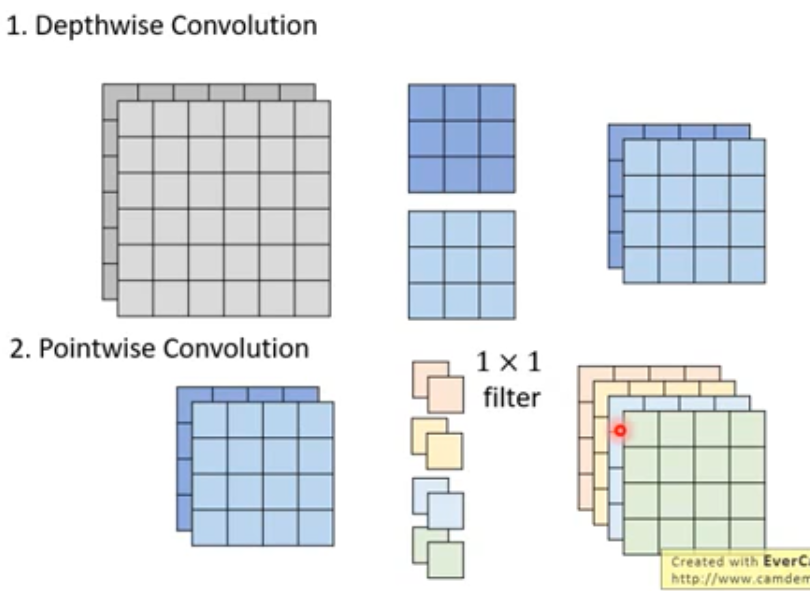
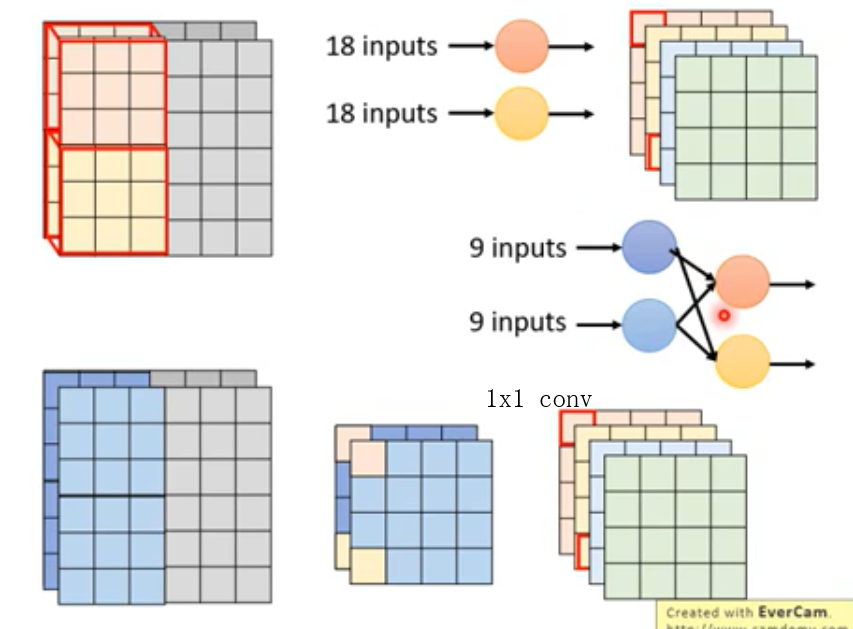
Depthwise Separable Convolution
不同于CNN(左), 其(右)先在每个channel上分别做局部卷积, 之后用1x1的卷积层进行通道信息的融合
Details
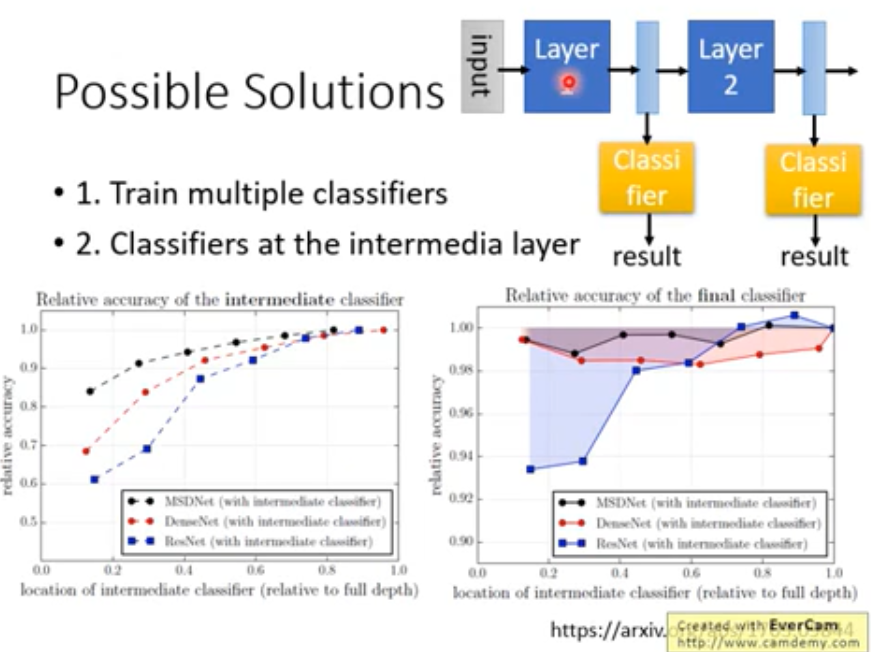
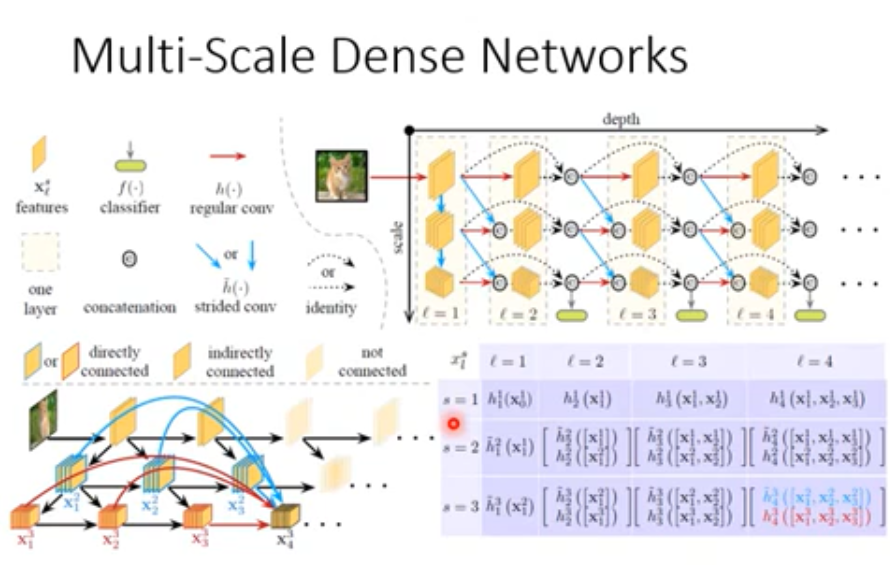
Dynamic Computation
根据device的当前状态(computation)来进行不同的计算方式(e.g. nums_layers)
OVER !