附近含有 m6A 修饰的 Stop Codon 序列提取
背景
m6A 修饰存在于 RNA 上,在 RNA 的出生,转运和成熟、降解、翻译等过程发挥着重要的作用。
m6A 修饰分布于 RNA 上的 5’UTR、CDS、3’UTR、Exon 和 Intron 里,主要富集在 stop codon 附近,那么 stop codon 附近的 m6A 修饰具体发挥着怎样的功能和分子机制研究的不是很清楚,在不同物种间的、不同组织间和不同生理状态下 m6A 修饰的水平也会随之动态变化。
AI 画个示意图如下:
m6A 位点的预测和实验研究验证的信息都有很多在线数据库可以查询,对于数据库里数据的分析可以是多样化和个性化的,讲述一个合理的生物学过程,结合实验验证,是文章的主题框架和思路。
人生和生命科学一样,在不断折腾和求真知的路途中找到真理和生命的本质!
准备
整合实验数据的 m6A 修饰位点注释信息的数据库有好几个,如 RMBase、RNAmod、REPIC 和 m6A-atals 等,可以查询单个基因的 m6A 位点信息或者直接下载全部的信息。此外还可查询下载其它 RNA 修饰的信息。
1、数据下载
直接去数据库下载,我下载了 m6A-atals 数据库的 Human 的 m6A 的 Basic_Site_Information 信息,下载方法是进入网址后点击 Download 进入下载界面,下载相应文件即可。
或者 linux 里下载
$ wget http://180.208.58.66/m6A-Atlas/Download/m6A_Human_Basic_Site_Information.txt
下载好后的文件打开长这样:
包括染色体、起始位置、终止位置、分布区域、数据来源、实验类型等等
$ less -S m6A_Human_Basic_Site_Information.txtchr start end pos strand name gene_id dist type seq data exper cellhuman_m6A_1 chr1 564474 564474 1 + LOC101928626 ENSG00000225972 ncRNA_exonic unprocessed_pseudogene CAAGGTCAAAGGGAGTCCGAACTAGTCTCAGGCTTCAACAT No 25491922 GSE54921 PA-m6A-seq HeLa Controlhuman_m6A_2 chr1 564545 564545 1 + LOC101928626 ENSG00000225972 ncRNA_exonic unprocessed_pseudogene CTTCATAGCCGAATACACAAACATTATTATAATAAACACCC No 30867593 GSE121942 miCLIP HepG2 Control|25491922human_m6A_3 chr1 564560 564560 1 + LOC101928626 ENSG00000225972 ncRNA_exonic unprocessed_pseudogene CACAAACATTATTATAATAAACACCCTCACCACTACAATCT No 30867593 GSE121942 miCLIP HepG2 SETD2 knockdown|25491922
然后在 excel 里打开对数据进行筛选,假如筛选细胞系 cell 为 CD8T、type 为 protein coding、dist 为 exonic,intronic 和 3UTR,然后提取 chr、start、end、strand、name、dist 列:
$ less m6a.txtchr start end strand name distchr1 949587 949587 + ISG15 exonicchr1 1168512 1168512 + B3GALT6 exonicchr1 1169034 1169034 + B3GALT6 UTR3
2、提取 stop codon 信息
要提取 stop codon 信息首先得知道数据库用的注释文件或基因组版本是哪有个,不然序列位置和注释信息是对不上的。去 m6A-atals 找了一下也没看到有写,那就先下一个 hg38 的 gtf 文件看看,结果发现序列位置差的太远了,肯定不是,于是又下载了 hg19 的才对的上,毕竟早期的文献数据分析都是用的较早的基因组和注释文件,hg19 基因组是 2009 年出来的。
下载 UCSC hg19 注释文件:
$ wget https://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg38/bigZips/genes/hg38.ncbiRefSeq.gtf.gz
我们需要提取 stop codon 的位置信息:
chr、stop_codon、start、end、strand、gene_name 这么几列
$ zless -S hg19.ncbiRefSeq.gtf.gz | grep -w 'stop_codon' |sed 's/"/\t/g' |sed 's/;/\t/g' |awk '{print $1"\t"$3"\t"$4"\t"$5"\t"$7"\t"$18}' | wc -l67419
有 67419 个 stop codon,一个基因有多个转录本,如果这多个转录本的 stop codon 位置不一样的话那么一个基因就会有多个不一样的 stop codon,但是这多个转录本的 stop codon 位置也可能是一样,所以这 67419 个终止密码子是有冗余或者重复的,我们需要去一下重复。
查看重复的 stop codon:
$ zless -S hg19.ncbiRefSeq.gtf.gz | grep -w 'stop_codon' |sed 's/"/\t/g' |sed 's/;/\t/g' |awk '{print $1"\t"$3"\t"$4"\t"$5"\t"$7"\t"$18}' |lesschr22 stop_codon 38689293 38689295 - CSNK1Echr22 stop_codon 38689293 38689295 - CSNK1Echr22 stop_codon 38689293 38689295 - TPTEP2-CSNK1Echr22 stop_codon 38617476 38617478 - TMEM184Bchr22 stop_codon 38617476 38617478 - TMEM184Bchr22 stop_codon 38617476 38617478 - TMEM184Bchr22 stop_codon 38610883 38610885 + MAFFchr22 stop_codon 38610883 38610885 + MAFFchr22 stop_codon 38610883 38610885 + MAFFchr22 stop_codon 38610883 38610885 + MAFF
去除重复:
$ zless -S hg19.ncbiRefSeq.gtf.gz | grep -w 'stop_codon' |sed 's/"/\t/g' |sed 's/;/\t/g' |awk '{print $1"\t"$3"\t"$4"\t"$5"\t"$7"\t"$18}' |sort -k3,3n |uniq |wc -l27734# 输出到文件保存结果$ zless -S hg19.ncbiRefSeq.gtf.gz | grep -w 'stop_codon' |sed 's/"/\t/g' |sed 's/;/\t/g' |awk '{print $1"\t"$3"\t"$4"\t"$5"\t"$7"\t"$18}' |sort -k3,3n |uniq > stopc.txt
最后我们把 stopc.txt 第二列放到最后一列,给它加上和 m6a.txt 一样的列名就可以了。
$ less stopc.txtchr start end strand name distchr1 70006 70008 + OR4F5 stop_codonchr1 368595 368597 + OR4F29 stop_codonchr1 879531 879533 + SAMD11 stop_codon
算法思路
计算每个 m6A 修饰位点距离 stop codon 的距离,满足一定距离(100bp)的保存对应的 stop codon 位置信息。
分析:
1、m6A 修饰位点可位于 stop codon 上游也能是下游
2、一个基因存在多个 stop codon 位点 (一样位置的stop codon已经去除)
3、一个基因存在多个 m6A 修饰位点
YTHDF3 有 8 个转录本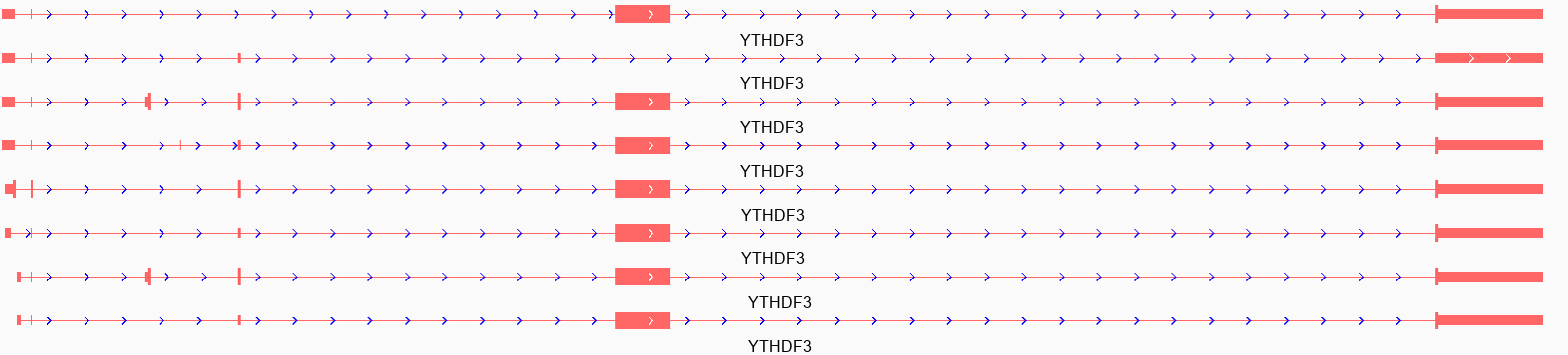
要是一个个去 excel 里找到每个基因对应的 m6A 位点和 stop codon 位点再互相减,挑选出在 100bp 以内的 stop codon 位点信息。如果有多个 stop codon 得更加多次的相减,几万个基因得减到猴年马月!此时对于这样一次次条件判断的重复过程我们可以使用编程的循环语句就能轻松实现。
解决思路
1、循环每个基因,取出相应的 m6A 和 stop codon 信息
2、判断该基因的 stop codon 的数量
3、如果 stop codon ==1,则与每个 m6A 位置相减,取出绝对值小于 100bp 的 stop codon
3、如果 stop codon >1,循环该基因每个 stop codon,与每个 m6A 位置相减,取出绝对值小于 100bp 的 stop codon
和师妹共同讨论了文件和解决思路,一起完成了一个循环。以下是代码部分:
# 加载R包library(tidyverse)# 1、读取筛选过后的m6a文件和stop codon信息文件stopcodon <- read.delim("C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\stopc.txt")m6A_293 <- read.delim("C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\m6a.txt")# 2、取共有基因交集m6A_gene <- unique(m6A_293$name)stop_gene <- unique(stopcodon$name)oveloap <- intersect(m6A_gene,stop_gene)# 3、去除没有m6a或者stop codon信息的基因m6A_gene_clean <- m6A_293[which(m6A_293$name %in% oveloap ),]stopcodon_clean <-stopcodon[which(stopcodon$name %in% oveloap),]# 4、在stop codon clean信息文件添加一列,为终止密码子中间位置stopcodon_clean$pos <- stopcodon_clean$start+1# 5、循环筛选符合m6a位点在密码子上下游15nt 以内符合条件的stop codon信息for(i in oveloap){temp_m6A <- m6A_gene_clean %>% filter(name == i)temp_stop <- stopcodon_clean %>% filter(name == i)if(length(temp_stop$pos) == 1){test_16 <- abs(temp_m6A$start - temp_stop$pos) <= 100if("TRUE" %in% test_16){tar_stop1 <- temp_stopfile1 <- paste(i,'s_tar_stop',sep="_")assign(file1,temp_stop)}else {}}else{for(m in temp_stop$pos){test_16m <- abs(temp_m6A$start - m) <= 100# print(test_16m)# print(i)if("TRUE" %in% test_16m){tar_stop2 <- temp_stop %>% filter(pos == m)file2 <- paste(i,'m_tar_stop',sep="_")assign(file2,tar_stop2)}else{}}}}# 6、查看含有单个密码子和多个密码子的筛选结果数量length(ls(pattern = '*s_tar_stop'))[1] 725length(ls(pattern = '*m_tar_stop'))[1] 279# 7、储存总的结果变量名res_name <- ls(pattern ='*_[s,m]_tar_stop' )# 8、结果数量length(res_name)[1] 1004# 9、合并所有结果到一个数据表里nm <- map(res_name,as.name)final_res <- do.call('rbind',nm)# 10、整理成bed格式的文件便于提取序列final_res_bed <- final_res[,c(1,2,3,5,6,4,7)]# 11、提取stop codon序列的文件final_res_bed2fa <- final_res_bedfinal_res_bed2fa$start <- final_res_bed2fa$start-1head(final_res_bed)chr start end name dist strand pos1 chr10 101611386 101611388 ABCC2 stop_codon + 1016113872 chr21 43716500 43716502 ABCG1 stop_codon + 437165013 chr3 52015032 52015034 ABHD14A stop_codon + 520150334 chr6 24701841 24701843 ACOT13 stop_codon + 247018425 chr4 2930248 2930250 ADD1 stop_codon + 29302496 chr2 228419209 228419211 AGFG1 stop_codon + 228419210# 12、保存结果文件write.table(final_res,file="C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\final_res.csv",quote = F,sep=",",row.names = F)write.table(final_res_bed2fa,file="C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\final_res_bed2fa.csv",quote = F,sep=",",row.names = F)
这里产生的结果文件会以单个文件保存在环境变量中,环境变量会生成很多文件名。
代码优化:
想了一下其实不用分 stop codon 的数量,不管有几个,直接与每个 m6A 位置相减,取出绝对值小于 100bp 的 stop codon 就行了,其次把每次循环产生的结果保存追加到一个 list 中,这样环境变量就不会生成很多文件了。
以下是优化后的代码部分,循环前的代码是一样的,就不放了,这里放循环及后面代码:
###################################################代码优化# 6、新建一个空列表用来储存结果数据mylst <- list()# 7、分析循环for(my_gene in oveloap){# a、提取基因的m6a 和 stop codon信息temp_m6A <- m6A_gene_clean %>% filter(name == my_gene)temp_stop <- stopcodon_clean %>% filter(name == my_gene)# 遍历每个stop codon位点信息for(sp in temp_stop$pos){# b、设定筛选条件test_16 <- abs(temp_m6A$start - sp) <= 100# c、挑选符合条件的stop codon位置信息if("TRUE" %in% test_16){# d、将结果保存到列表里mylst[[my_gene]] <- temp_stop %>% filter(pos == sp)}else{}}}# 8、查看筛选结果数量,数量和原来的是一样的length(mylst)[1] 1004# 9、合并输出到data.framesp_results <- do.call('rbind',mylst)# 10、调整列顺序,整理为bed格式final_res_bed <- sp_results[,c(1,2,3,5,6,4,7)]# 11、制作提取stop codon序列的文件final_res_bed2fa <- final_res_bedfinal_res_bed2fa$start <- final_res_bed2fa$start-1# 12、保存结果文件write.table(final_res,file="C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\final_res.csv",quote = F,sep=",",row.names = F)write.table(final_res_bed2fa,file="C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\final_res_bed2fa.csv",quote = F,sep=",",row.names = F)
可以看到循环每次输出的结果依次保存到 list 里了
序列提取
序列提取首先获得对应基因组的文件,去 UCSC 数据库下载 hg19 的基因组序列:
$ wget https://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg19/bigZips/hg19.fa.gz$ gunzip hg19.fa.gz
使用 bedtools getfasta 命令提取序列,安装查看帮助文档:
$ conda install -y bedtools# 查看帮助文档$ bedtools getfastaTool: bedtools getfasta (aka fastaFromBed)Version: v2.30.0Summary: Extract DNA sequences from a fasta file based on feature coordinates.Usage: bedtools getfasta [OPTIONS] -fi <fasta> -bed <bed/gff/vcf>Options:-fi Input FASTA file-fo Output file (opt., default is STDOUT-bed BED/GFF/VCF file of ranges to extract from -fi-name Use the name field and coordinates for the FASTA header-name+ (deprecated) Use the name field and coordinates for the FASTA header-nameOnly Use the name field for the FASTA header-split Given BED12 fmt., extract and concatenate the sequencesfrom the BED "blocks" (e.g., exons)-tab Write output in TAB delimited format.-bedOut Report extract sequences in a tab-delimited BED format instead of in FASTA format.- Default is FASTA format.-s Force strandedness. If the feature occupies the antisense,strand, the sequence will be reverse complemented.- By default, strand information is ignored.-fullHeader Use full fasta header.- By default, only the word before the first space or tabis used.-rna The FASTA is RNA not DNA. Reverse complementation handled accordingly.
参数详解:
- -fi 输入 fasta 文件
- -fo 输出文件
- -bed 需要提取序列的位置信息,bed、gff、vcf 格式
- -name 使用 bed 的第四列和 start-end 信息作为提取出 fasta 的名字
- -name+ 和 name 参数一样,应该废弃了
- -nameOnly 只使用第四列内容作为 fasta 序列的名字
- -split 对 bed12 格式的文件切分内含子整合外显子,提取外显子序列
- -tab 输出以 tab 分割符格式
- -bedOut 输出 bed 格式结果代替 fasta 格式,默认时输出 fasta 格式
- -s 区分正负链,根据正负链提取相应序列
- -fullHeader 使用完整名作为序列名,默认是空格或者 tab 键前第一个单词
- -rna 输入 fasta 序列为 RNA 序列,加上这个参数后会进行反向互补
注意:
bedtools 提取序列不是从第一个位点提取的,而是从第二个位点往后提取,假如你的位点信息是 1-3,提取的序列应该是 2 和 3 两个碱基:
$ cat test.fa>chr1AGCTGGG$ cat test.bedchr1 1 3$ bedtools getfasta -fi test.fa -bed test.bed>chr1:1-3GC
所以提取 stop codon 时应该将 start 位点减 1,之前代码里已经做过了,保存在 final_res_bed2fa 结果文件里:
head(final_res_bed2fa)chr start end name dist strand pos1 chr20 34843664 34843667 AAR2 stop_codon + 348436662 chr19 1065421 1065424 ABCA7 stop_codon + 10654233 chr16 16235135 16235138 ABCC1 stop_codon + 162351374 chr10 101611385 101611388 ABCC2 stop_codon + 1016113875 chr17 48768558 48768561 ABCC3 stop_codon + 487685606 chr3 183911483 183911486 ABCF3 stop_codon + 183911485# 保存为txt格式write.table(final_res_bed2fa,file="C:\\Users\\admin\\Desktop\\final_res_bed2fa.txt",quote = F,sep="\t",row.names = F)
提取 stop codon 序列,输出 tab 格式的 RNA 序列:
# 去掉第一行,取前面6列$ awk 'NR>1 {print $0}' final_res_bed2fa.txt | cut -f 1-6 > sp_seq.bed# 提取序列$ bedtools getfasta -fi hg19.fa \-bed sp_seq.bed \-fo sp_seqinfo.txt \-name \-tab \-sindex file hg19.fa.fai not found, generating...# 查看结果$ head -4 sp_seqinfo.txtAAR2::chr20:34843664-34843667(+) TAAABCA7::chr19:1065421-1065424(+) TGAABCC1::chr16:16235135-16235138(+) TGAABCC2::chr10:101611385-101611388(+) TAG# 查看第二列序列类型统计个数$ cut -f 2 sp_seqinfo.txt | sort | uniq -c1 A398 TAA212 TAG385 TGA3 taa5 tga
为什么还有终止密码子只有一个碱基的?查看 stop codon 位置信息也是:
MRPL35::chr2:86439548-86439549(+) A
原因:
stop codon 位置信息的注释是基于基因组的,我们知道,成熟 mRNA 是没有内含子的,但是在基因组序列上,在外显子的序列间保留了内含子的序列,如果存在可变剪接的话,stop codon 位置就可能不是连续的,不过这种情况很少,大部分的终止密码子 3 个碱基都是在一起的。
下面画个示意图表示:
提取到一个碱基的应该是图里的第 1 个图的情况,提取了 stop codon 的第三个碱基,如果是第 2 个图的话,提取到的碱基应该是 T 。那么有没有可能 stop codon 被分成了 3 个碱基呢?
如果终止密码子里存在两个可变剪接位点,它就会被剪切成三部分,那么就会有一个碱基充当一个外显子。所以有有外显子是一个碱基这么短的吗?应该是没有的。
至于提取的还有是小写的终止密码子序列是因为这几个终止密码子序列可能位于基因组的重复序列中,但不影响结果,直接变成大写就可以。基因组序列大部分是大写字母的,重复序列会用小写表示。
下面是官网说明:
- hg19.fa.gz:”Soft-masked” assembly sequence in one file.
- Repeats from RepeatMasker and Tandem Repeats Finder (with period of 12 or less) are shown in lower case; non-repeating sequence is shown in upper case. Again, the most current version of this file is latest/hg19.fa.gz. For many types of analysis that include sequence comparisons,the files in the directory analysisSet are recommended, as these include fewer duplicates.

