数据结构:堆
- 完全二叉树
- parent >= children(大顶堆)、parent <= children(小顶堆)
堆排序平均时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
1-保证一个父节点是其子节点的最大值
完全二叉树可以由数组表示,坐标从0开始,对应树从上到下,从左往右
完全二叉树在数组中的特性,节点下标为 i,则:
- 父节点在 (i - 1)/2 只保留整数部分
- 左子节点 2i + 1
- 右子节点 2i + 2
由此节点可构建一个小堆,这个过程可以称为 heapify
public static void heapify(int[] tree, int length, int i) {if (i >= length) {return;}// 左子节点int c1 = 2 * i + 1;// 右子节点int c2 = 2 * i + 2;// 假设该父节点临时是最大值int max = i;// c1,c2 有可能不存在,也就是下标溢出if (c1 < length && tree[c1] > tree[max]) {max = c1;}if (c2 < length && tree[c2] > tree[max]) {max = c2;}// 如果该父节点不是最大值,最大值与其交换位置,从而构建一个局部堆if (max != i) {swap(tree, i, max);}}
2-将乱序完全二叉树构建成堆
从倒数第二层开始构建局部堆,由下至上,能够保证其子节点就是以下最大的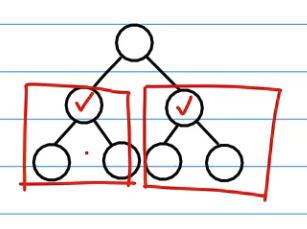
根据父节点的下标规律可知,某个父节点的上一个父节点在数组中的下标是 i—
由以上特性构建一个大顶堆
public static void buildHeap(int[] tree, int length) {// 最后一个节点int lastNode = length - 1;// 最后一个父节点int parent = (lastNode - 1) / 2;while (parent >= 0) {// 保证与其子节点构成堆结构heapify(tree, length, parent);// 上一个父节点是 index--parent--;}}
3-堆顶与最后一个节点交换位置,截掉最后节点,重新构建堆
截取到最后一个节点,数组就有序了
public static void heapSort(int[] tree) {buildHeap(tree, tree.length);for (int i = tree.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {swap(tree, i, 0);buildHeap(tree, i);}}
堆排序完整代码
public class HeapSort {public static void swap(int[] tree, int a, int b) {int temp = tree[a];tree[a] = tree[b];tree[b] = temp;}public static void heapify(int[] tree, int length, int i) {if (i >= length) {return;}int c1 = 2 * i + 1;int c2 = 2 * i + 2;int max = i;if (c1 < length && tree[c1] > tree[max]) {max = c1;}if (c2 < length && tree[c2] > tree[max]) {max = c2;}if (max != i) {swap(tree, i, max);}}public static void buildHeap(int[] tree, int length) {// 从最底层父节点 heapify,最底层父节点也是 index 最大的父节点,上一个父节点是 index--int lastNode = length - 1;int parent = (lastNode - 1) / 2;while (parent >= 0) {heapify(tree, length, parent);parent--;}}public static void heapSort(int[] tree) {buildHeap(tree, tree.length);for (int i = tree.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {swap(tree, i, 0);buildHeap(tree, i);}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {4, 9, 3, 5, 1, 2, 12, 5, 11, 44, 55, 13, 6};HeapSort.heapSort(arr);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}}
满二叉树、完全二叉树、平衡二叉树、最优二叉树
满二叉树
一棵二叉树的结点要么是叶子结点,要么它有两个子结点
(如果一个二叉树的层数为K,且结点总数是(2^k) -1,则它就是满二叉树。)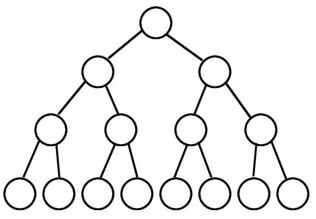
完全二叉树
若设二叉树的深度为k,除第 k 层外,其它各层 (1~k-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,
第k 层所有的结点都 连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。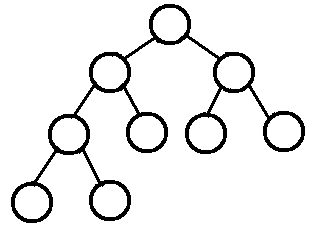
平衡二叉树
它或者是一颗空树,或它的左子树和右子树的深度之差(平衡因子)的绝对值不超过1,且它的左子树和右子树都是一颗平衡二叉树。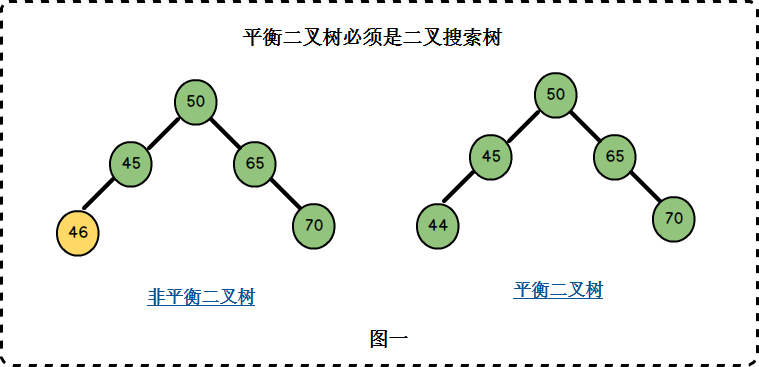
最优二叉树(哈夫曼树)
树的带权路径长度达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)。哈夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。

