1. 官方介绍
- Allure Framework 是一种灵活的轻量级多语言测试报告工具,不仅可以以简洁的 Web 报告形式非常简洁地显示已测试的内容,也允许参与开发过程的每个人从日常测试中提取最大程度的有用信息
- 从开发/质量保证的角度来看,Allure 报告可以缩短常见缺陷的生命周期:可以将测试失败划分为bug和损坏的测试,还可以配置 log,step,fixture,attachments,timings,历史记录以及与TMS的集成以及Bug跟踪系统,因此负责任的开发人员和测试人员将掌握所有信息
- 从管理人员的角度来看,Allure 提供了一个清晰的“全局”,涵盖了已涵盖的功能,缺陷聚集的位置,执行时间表的外观以及许多其他方便的事情
- Allure 的模块化和可扩展性确保您始终能够微调某些东西,以使 Allure 更适合您
2. 个人介绍
- 对于管理层来说,测试报告当然是越直观、简洁、数据清晰越好,而 Allure 就满足以上这么多点,而且很好的和 pytest 集成了
- 相比于 pytest-html 来说,Allure 的报告真的更加完美鸭!!
- 唯一不足的就是,拓展功能需要在测试用例集上加装饰器
3. 环境配置
看上一篇文章
18. allure 环境准备
4. 安装插件
pip3 install allure-pytest -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com
5. 快速入门
这是运行代码的包结构
# 是项目文件夹名称15allure│ conftest.py│ test_1.py│ __init__.py│├─test_51job│ │ conftest.py│ │ test_case1.py│ │ __init__.py│├─test_toutiao│ │ test_case2.py│├─test_weibo│ │ conftest.py│ │ test_case3.py│ │ __init__.py│
5.1 最外层的 conftest.py
# 外层conftest.py@pytest.fixture(scope="session")def login():print("====登录功能,返回账号,token===")name = "testyy"token = "npoi213bn4"yield name, tokenprint("====退出登录!!!====")
5.2 最外层的 test_1.py
import pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize("n", list(range(5)))def test_get_info(login, n):sleep(1)name, token = loginprint("***基础用例:获取用户个人信息***", n)print(f"用户名:{name}, token:{token}")
5.3 test_51job 包下的 conftest.py
import pytest@pytest.fixture(scope="module")def open_51(login):name, token = loginprint(f"###用户 {name} 打开51job网站###")
5.4 test_51job 包下的 test_case1.py
from time import sleepimport pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize("n", list(range(5)))def test_case2_01(open_51, n):sleep(1)print("51job,列出所有职位用例", n)@pytest.mark.parametrize("n", list(range(5)))def test_case2_02(open_51, n):sleep(1)print("51job,找出所有python岗位", n)
5.5 test_toutiao 包下的 test_case2.py
from time import sleepimport pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize("n", list(range(5)))def test_no_fixture(login, n):sleep(1)print("==没有__init__测试用例,我进入头条了==", login)
5.6 test_weibo 包下的 conftest.py
import pytest@pytest.fixture(scope="function")def open_weibo(login):name, token = loginprint(f"&&& 用户 {name} 返回微博首页 &&&")
5.7 test_weibo 包下的 test_case3.py
from time import sleepimport pytest@pytest.mark.parametrize("n", list(range(5)))class TestWeibo:def test_case1_01(self, open_weibo, n):sleep(1)print("查看微博热搜", n)def test_case1_02(self, open_weibo, n):sleep(1)print("查看微博范冰冰", n)
5.8 执行命令
要使 Allure 能够在测试执行期间收集测试结果,只需添加 —alluredir 选项,并提供指向应存储结果的文件夹的路径
pytest -n auto --alluredir=allure
5.9 生成出来的结果
可以看到,这不是我们想要的结果,一堆json、txt文件….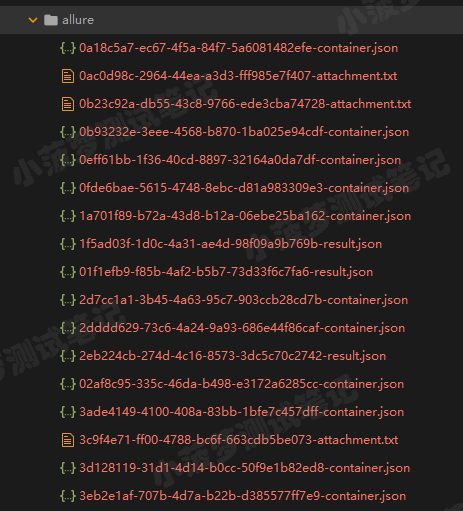
5.10 生成报告
要在测试完成后查看实际报告,需要使用Allure命令行来让测试结果生成报告
allure serve allure
然后就会自动在默认浏览器中显示生成的报告
6. 查看suites(函数级别的测试用例)
从包名-模块名-测试用例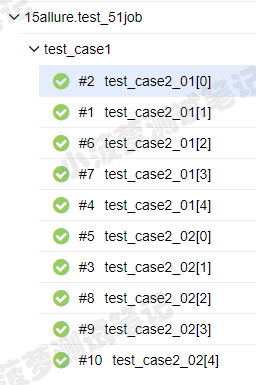
7. 查看suites(类级别的测试用例)
从包名-模块名-类名-测试用例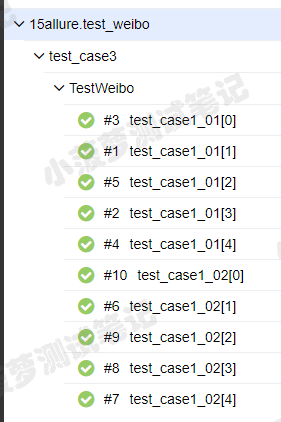
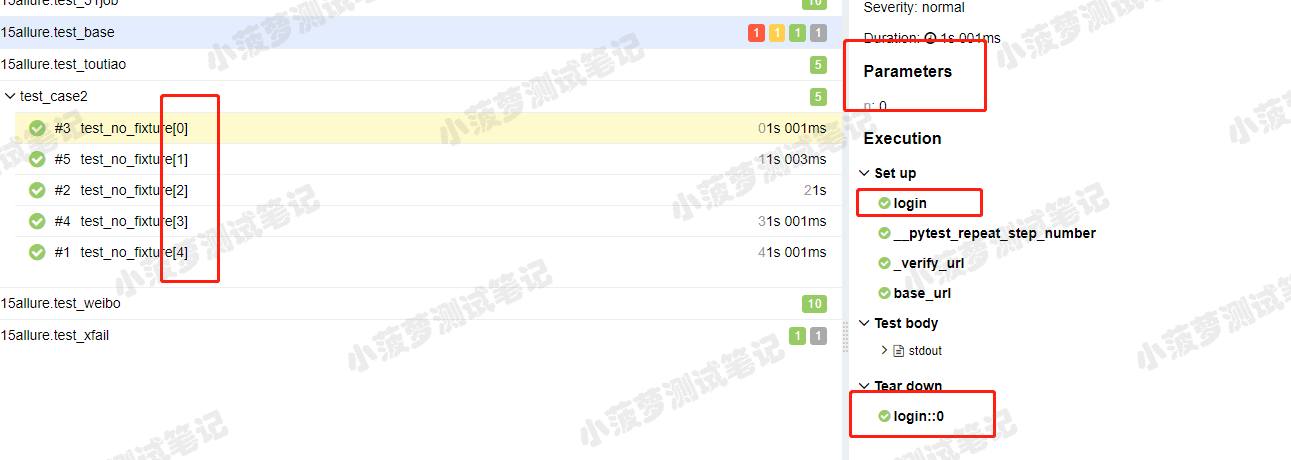
8. 查看测试用例详情
- parameters:如果用了 @pytest.mark.parametrize ,在右侧的 parameters 是可以看到传了什么参数和对应的值
- set up:调用 fixture 的前置操作
- tear down:调用 fixture 的后置操作
9. Allure报告结构
- Overview:总览
- Categories:类别,默认是分了 failed 和 error,凡是执行结果是其中一个的都会被归到类里面,可以通过这里快捷查看哪些用例是 failed 和 error 的
- Suites:测试套件,就是所有用例的层级关系,可以根据package、module、类、方法来查找用例
- Graphs:测试结果图形化,包括用例执行结果的分布图,优先级,耗时等
- Timeline:可以看到测试用例精确的测试时序(执行顺序),包括执行时间
- Behaviors:行为驱动,根据 epic、feature、story 来分组测试用例(后面会讲到)
- Packages:这就是按照 package、module 来分组测试用例了

