- 运行 SpringApplication
- StopWatch.start()
- createBootstrapContext();
- configureHeadlessProperty()
- getRunListeners(args)
- 监听器通知项目正在启动
- applicationArguments
- prepareEnvironment
- 创建IOC容器createApplicationContext
- 准备IOC容器上下文prepareContext
- refreshContext【核心源码】
- afterRefresh
- StopWatch.stop()
- listeners.started
- callRunners
- handleRunFailure
- listeners.running
- return context;
运行 SpringApplication
- StopWatch记录应用的启动时间
- 创建引导上下文(Context环境)createBootstrapContext()【bootstrappers 】
- 获取到所有之前的 bootstrappers 挨个执行 intitialize() 来完成对引导启动器上下文环境设置
- 让当前应用进入headless模式。java.awt.headless
- 获取所有 RunListener(运行监听器)【为了方便所有Listener进行事件感知】【SpringApplicationRunListener】
- getSpringFactoriesInstances 去spring.factories找 SpringApplicationRunListener.
- 遍历 SpringApplicationRunListener 调用 starting 方法;
- 相当于通知所有感兴趣系统正在启动过程的人,项目正在 starting
- 保存命令行参数;ApplicationArguments
- 准备环境 prepareEnvironment();
- 返回或者创建基础环境信息对象。StandardServletEnvironment
- 读取所有的配置源的配置属性值。得到所有的PropertySources,@PropertySources即加载外部所有的配置文件xxx.properties
- 配置激活环境Profile信息,configureProfiles(environment, args);
- 监听器调用 listener.environmentPrepared();通知所有的监听器当前环境准备完成
- 创建IOC容器(createApplicationContext())
- 根据项目类型(Servlet)创建容器,非Reactive
- 当前会创建 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
- 准备ApplicationContext IOC容器的基本信息 prepareContext()
- 保存环境信息
- IOC容器的后置处理流程。
- 应用初始化器;applyInitializers;
- 遍历所有的 ApplicationContextInitializer 。调用 initialize.。来对ioc容器进行初始化扩展功能【initialize】
- 遍历所有的 listener 调用 contextPrepared。EventPublishRunListenr;通知所有的监听器contextPrepared【无处不在的listener】
- 所有的监听器 调用 contextLoaded。通知所有的监听器 contextLoaded;
- 刷新IOC容器。refreshContext【核心源码】
- 创建容器中的所有组件(Spring注解)
- 容器刷新完成后工作?afterRefresh
- 所有监听器 调用 listeners.started(context); 通知所有的监听器 started
- 调用所有runners;callRunners()
- 获取容器中的ApplicationRunner
- 获取容器中的 CommandLineRunner
- 合并所有runner并且按照@Order进行排序
- 遍历所有的runner。先ApplicationRunner 后CommandLineRunner调用 run 方法
- 如果以上有异常,
- 调用Listener 的 failed
- 调用所有监听器的 running 方法 listeners.running(context); 通知所有的监听器 running
- running如果有问题。继续通知 failed 。调用所有 Listener 的 failed;通知所有的监听器 failed
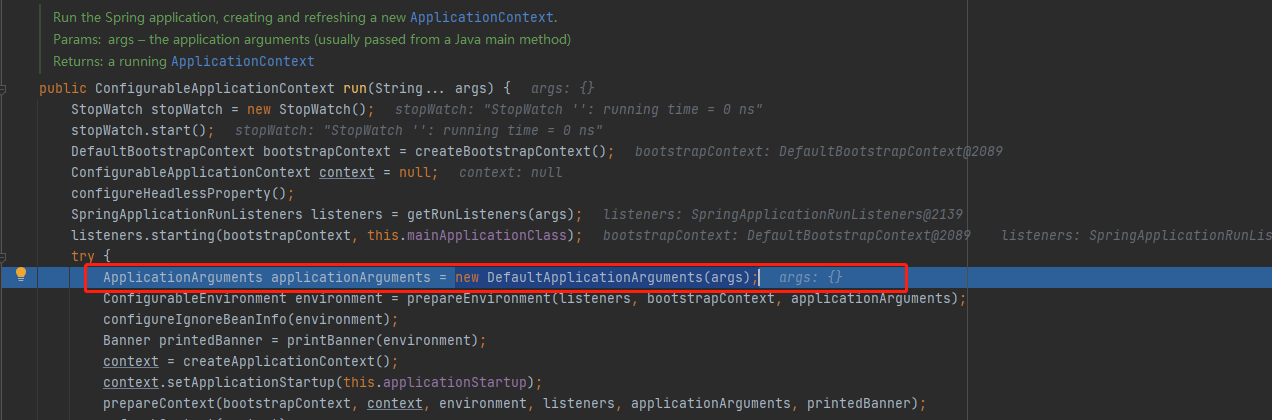
Run the Spring application来到了SpringApplication的这里,run方法参数String... args指的是命令行运行Java程序传入的命令行参数
传入的命令行参数可以在idea里面传Edit Configuration
/*** Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new* {@link ApplicationContext}.* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}*/public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();stopWatch.start();DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;configureHeadlessProperty();SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);try {ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);context = createApplicationContext();context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);refreshContext(context);afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);stopWatch.stop();if (this.logStartupInfo) {new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);}listeners.started(context);callRunners(context, applicationArguments);}catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}try {listeners.running(context);}catch (Throwable ex) {handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);throw new IllegalStateException(ex);}return context;}
StopWatch.start()
进入StopWatch的start()方法
public void start() throws IllegalStateException {this.start("");}
stepinto,给StopWatch类的this.currentTaskName和this.startTimeNanos赋值,记录程序启动的当前时间
public void start(String taskName) throws IllegalStateException {if (this.currentTaskName != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("Can't start StopWatch: it's already running");} else {this.currentTaskName = taskName;this.startTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();}}
createBootstrapContext();
stepinto进去DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();,为我们创建了默认的引导启动器上下文DefaultBootstrapContext
private List<Bootstrapper> bootstrappers;//size=0...private DefaultBootstrapContext createBootstrapContext() {DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();this.bootstrappers.forEach((initializer) -> initializer.intitialize(bootstrapContext));return bootstrapContext;}
虽然我们的this.bootstrappers.size=0,先不管,这也是在spring.factories里面配置的。如果我们配置了引导启动器,spring会帮我们把每一个引导启动器遍历出来,然后调用引导启动器的intitialize方法,来完成对引导启动器上下文环境设置,最后返回一个默认的上下文bootstrapContext
引导启动器Bootstrapper的源码如下:
/** Copyright 2012-2020 the original author or authors.** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.* You may obtain a copy of the License at** https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and* limitations under the License.*/package org.springframework.boot;/*** Callback interface that can be used to initialize a {@link BootstrapRegistry} before it* is used.** @author Phillip Webb* @since 2.4.0* @see SpringApplication#addBootstrapper(Bootstrapper)* @see BootstrapRegistry*/public interface Bootstrapper {/*** Initialize the given {@link BootstrapRegistry} with any required registrations.* @param registry the registry to initialize*/void intitialize(BootstrapRegistry registry);}
configureHeadlessProperty()
stepinto进去configureHeadlessProperty();
让当前应用进入headless模式。java.awt.headless
getRunListeners(args)
stepinto进SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);,
获取所有运行监听器RunListener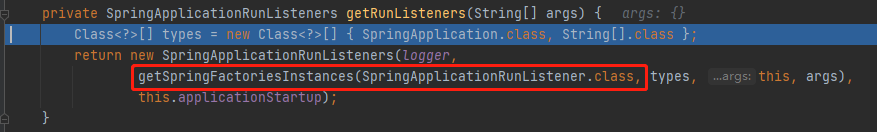
getSpringFactoriesInstances去META-INF/spring.factories找 SpringApplicationRunListener.
监听器通知项目正在启动
stepinto进listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);,来到SpringApplicationRunListener类,有如下两个方法:
- starting方法
- doWithListeners方法
其中start方法调用doWithListeners方法。
遍历 SpringApplicationRunListener 调用 starting 方法:意思是通知所有感兴趣系统正在启动过程的人,项目正在 starting。
其中this.listeners.size=1,是EventPublishingRunListener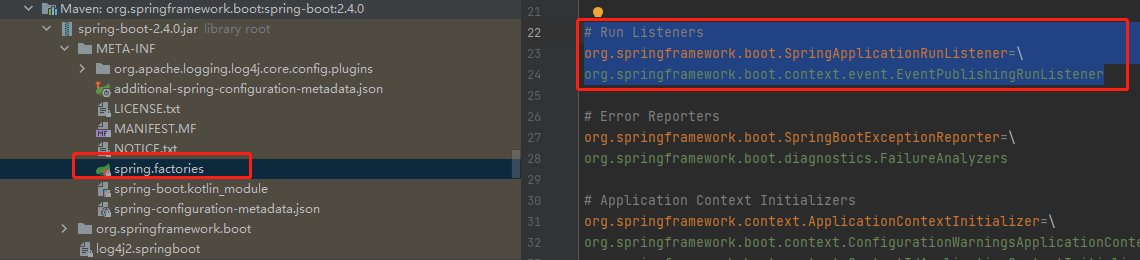
starting
我们进入starting之后在,stepinto进入doWithListeners,
来到this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction);这一行我们接着stepinto,发现又回到了start方法的(listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext),为什么呢?
void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, Class<?> mainApplicationClass) {doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.starting", (listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext),(step) -> {if (mainApplicationClass != null) {step.tag("mainApplicationClass", mainApplicationClass.getName());}});}private void doWithListeners(String stepName, Consumer<SpringApplicationRunListener> listenerAction,Consumer<StartupStep> stepAction) {StartupStep step = this.applicationStartup.start(stepName);this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction);if (stepAction != null) {stepAction.accept(step);}step.end();}
doWithListeners
private void doWithListeners(String stepName, Consumer<SpringApplicationRunListener> listenerAction,Consumer<StartupStep> stepAction) {StartupStep step = this.applicationStartup.start(stepName);this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction);if (stepAction != null) {stepAction.accept(step);}step.end();}
因为forEach是Iterable接口的方法,传入的是Consumer函数式接口,上面的listenerAction就是该Consumer函数式接口的形参,lambda表达式就是listenerAction的实参,lambda表达式是匿名内部类的语法糖,匿名内部类就是对接口当中特定函数的实现,所以隐含了一个接口方法,stepinto就是进入这个Consumer函数式接口内部方法的实现,就回到了(listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext)这行。
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);for (T t : this) {action.accept(t);}}
其中EventPublishingRunListener源码如下: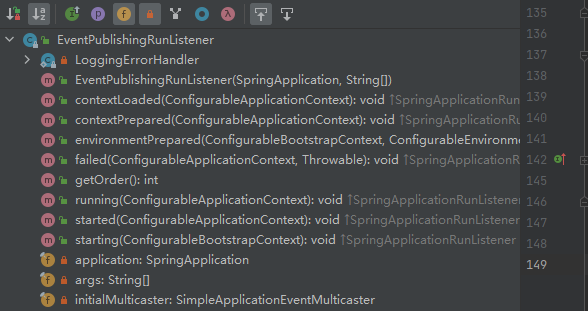
applicationArguments
prepareEnvironment
stepinto进ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);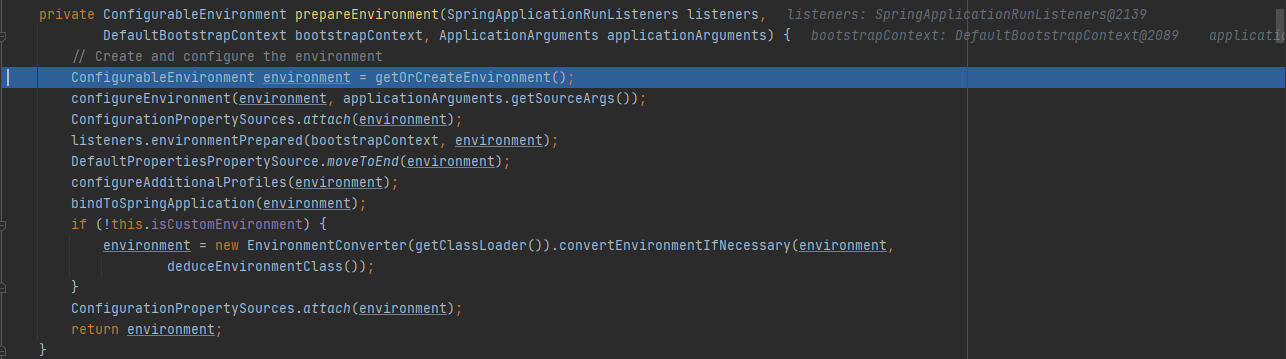
getOrCreateEnvironment
stepinto进ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();,为我们装载一个SERVLET环境StandardServletEnvironment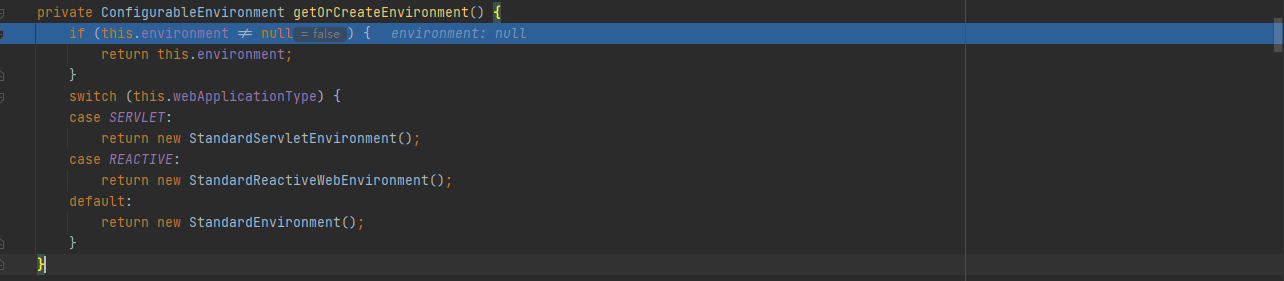
返回到上一级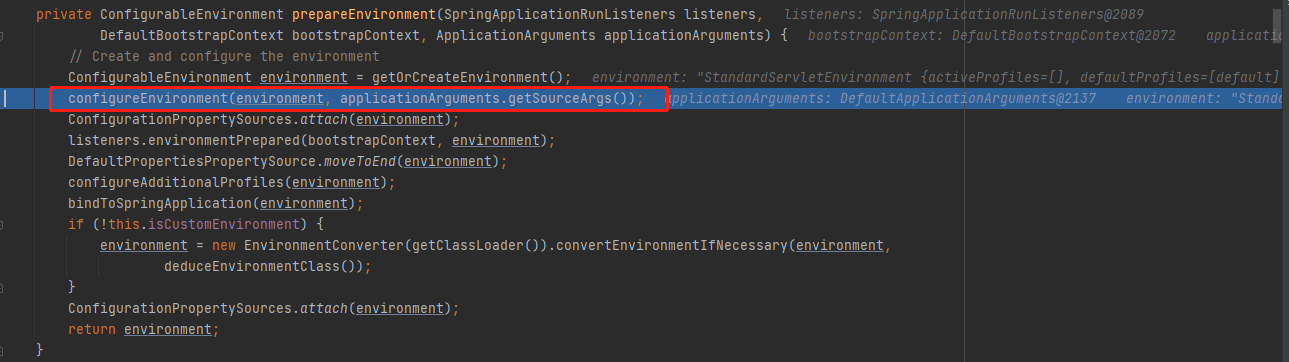
configureEnvironment
stepinto进configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());,为我们配置类型转换器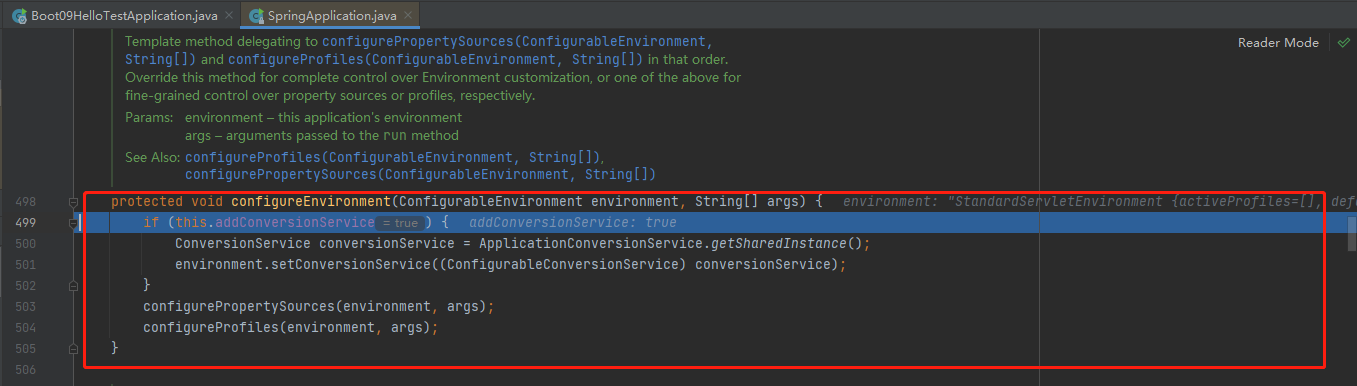
stepinto进去configurePropertySources(environment, args);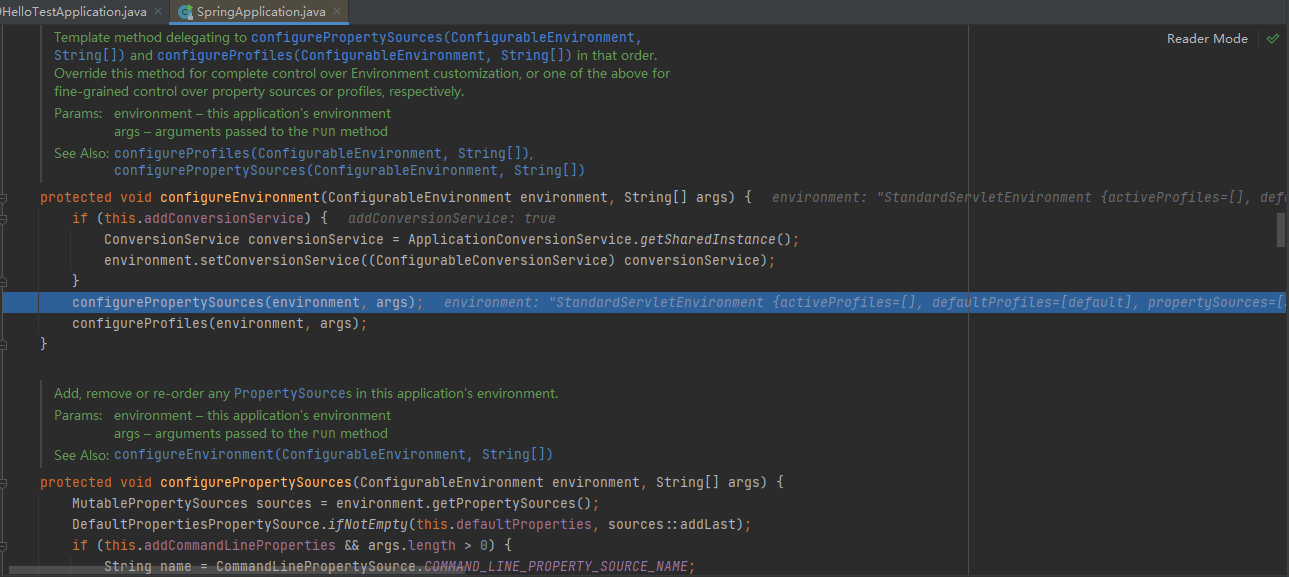
environment.getPropertySources();得到所有的PropertySources,@PropertySources即加载外部所有的配置文件xxx.properties
Spring Boot 官网使用的是application.properties文件来实现文件的配置。但是实际情况下一个配置文件是不够用的,比如项目集成redis,mq,以及数据库比如mysql的时候,redis.properties,mq.properties,mysql.properties多个配置文件有利于开发及维护的管理。Spring Boot是通过@PropertySource或者@PropertySources来实现多配置文件的。
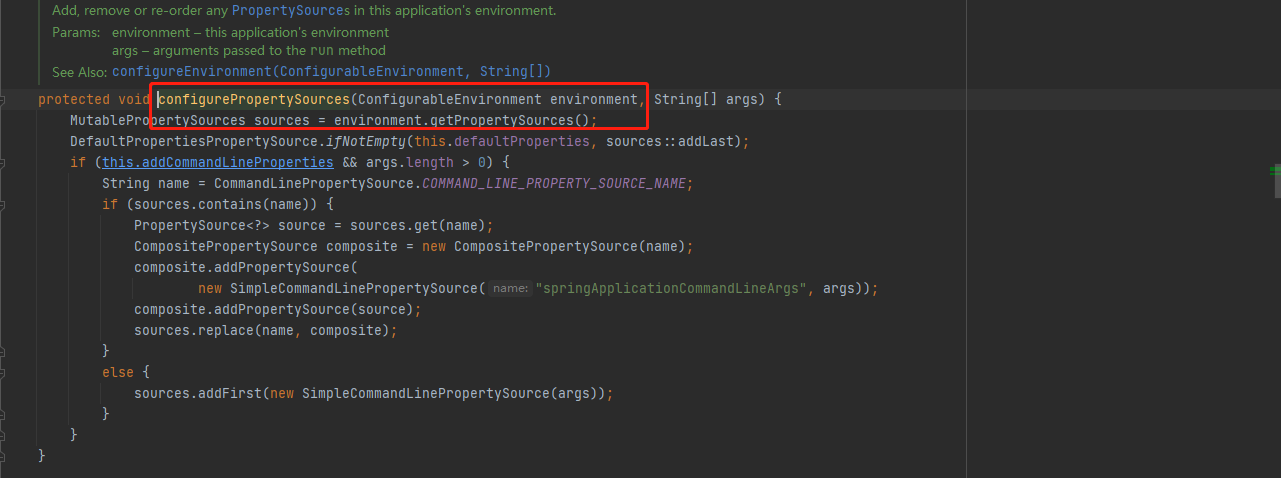
返回上级,配置激活环境Profile信息,configureProfiles(environment, args);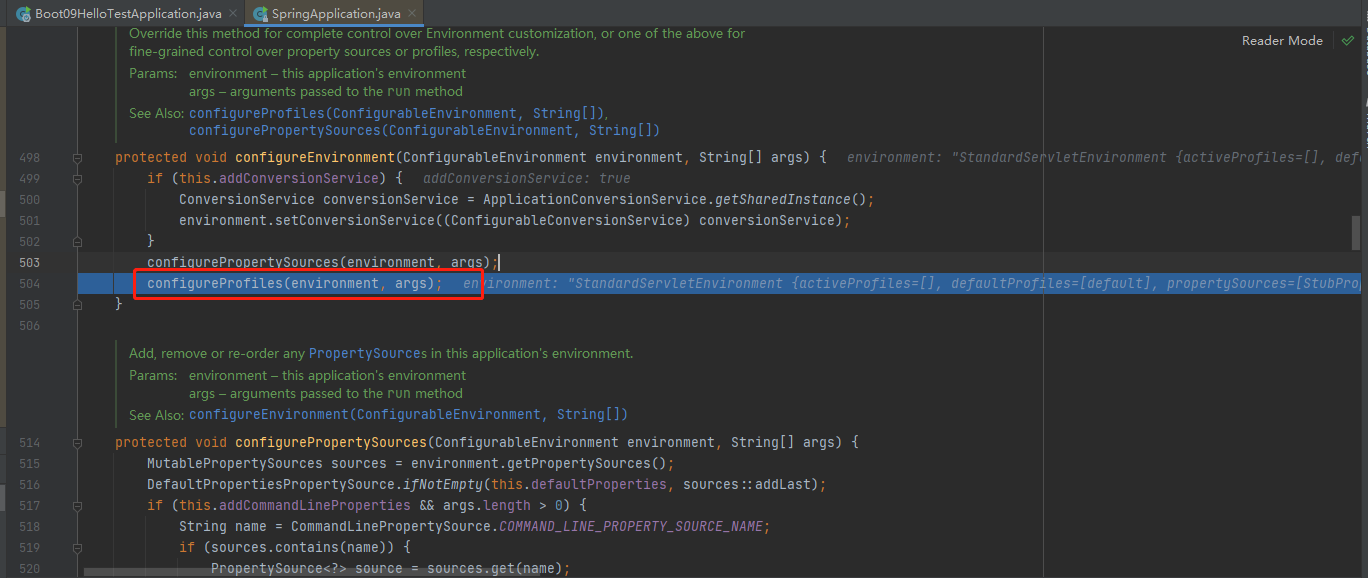
listeners.environmentPrepared
stepinto进去listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);,遍历每一个Listener监听器,通知我们的应用环境已经准备好了。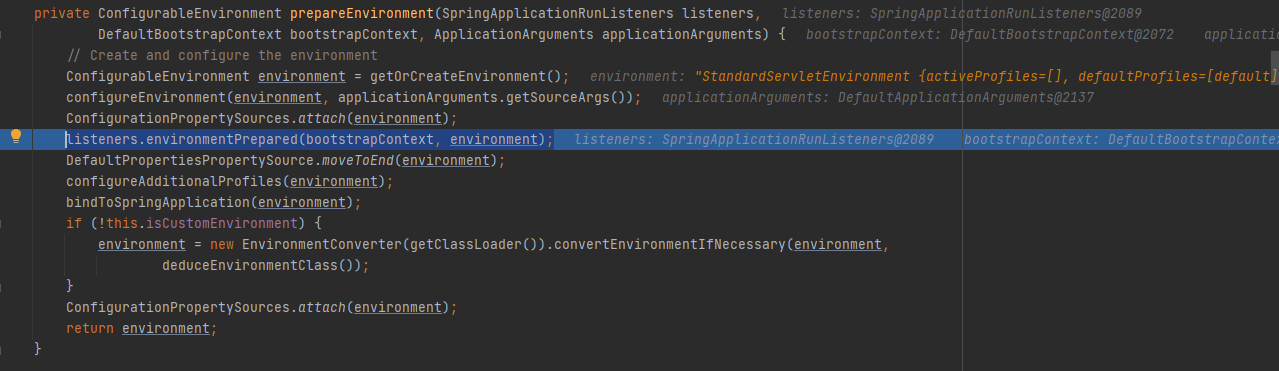
监听器调用 listener.environmentPrepared();通知所有的监听器当前环境准备完成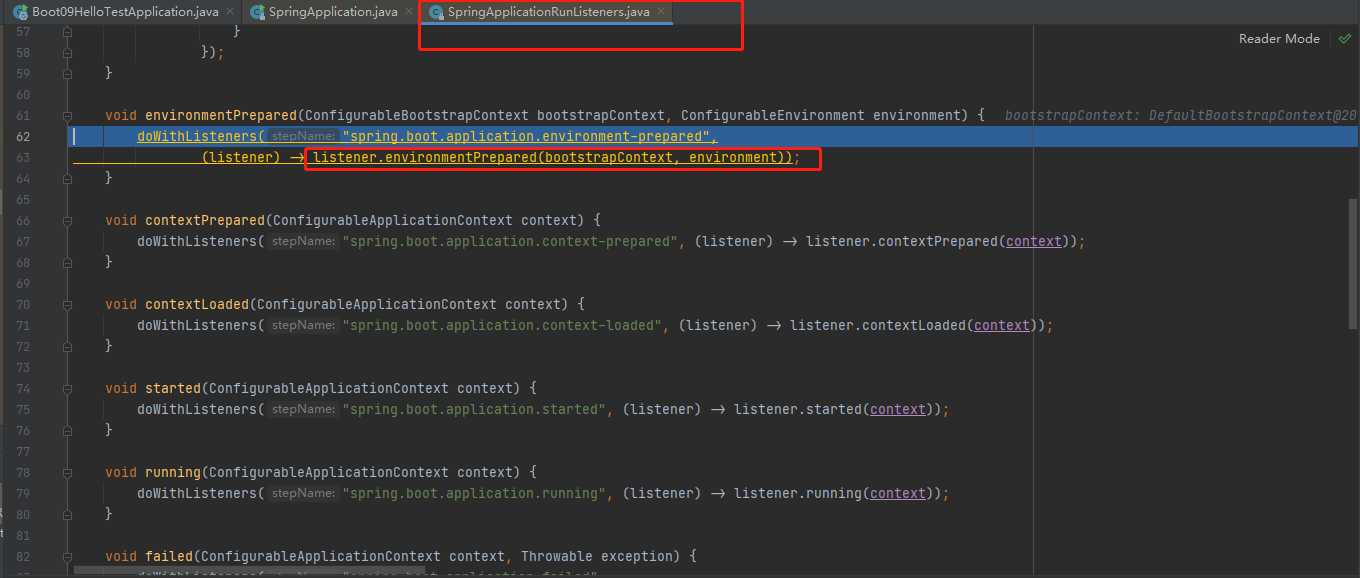
看下SpringApplicationRunListener源码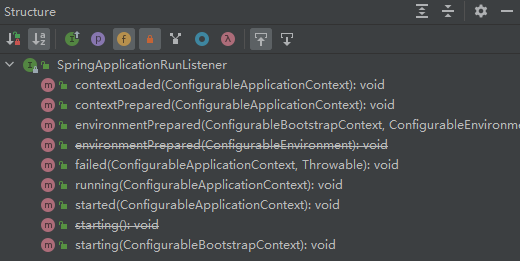
创建IOC容器createApplicationContext
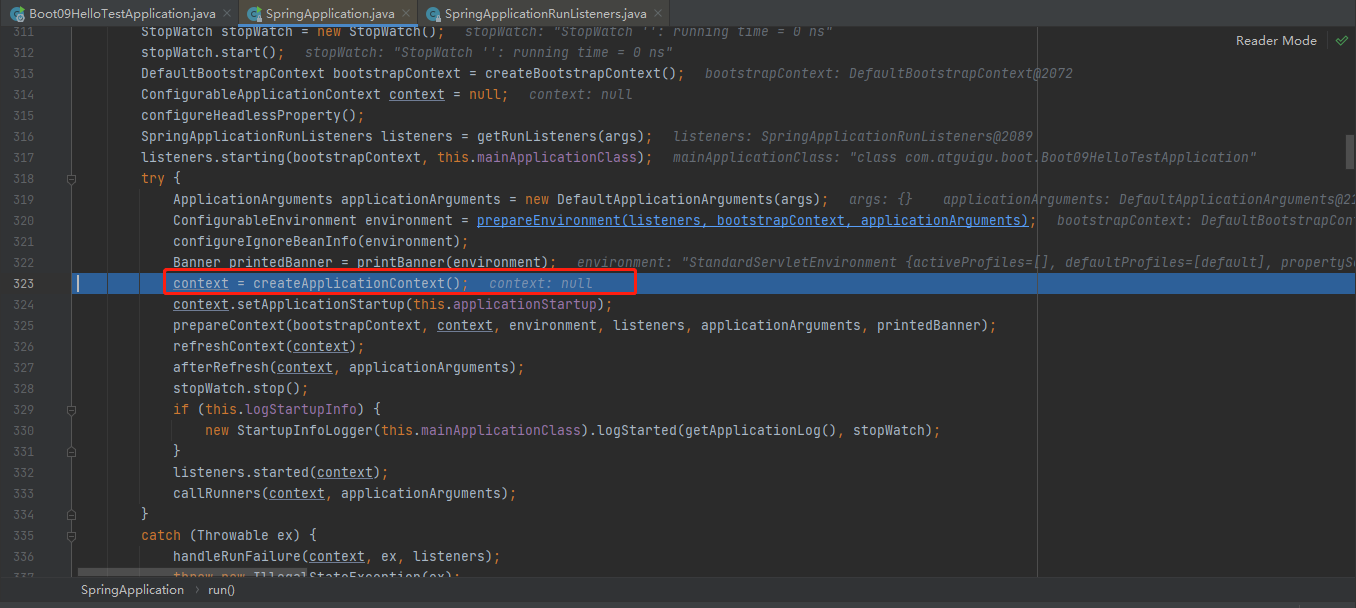
stepinto进去context = createApplicationContext();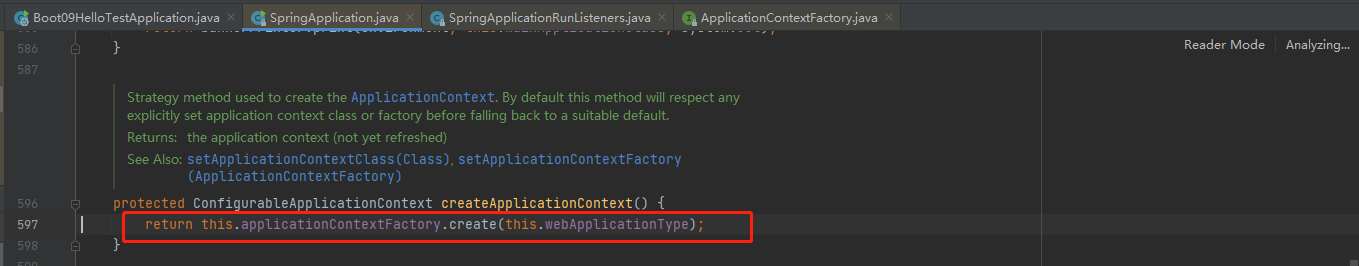
stepinto进去return this.applicationContextFactory.create(this.webApplicationType);,最终默认给我们创建了个SERVLET容器
返回AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext这个IOC容器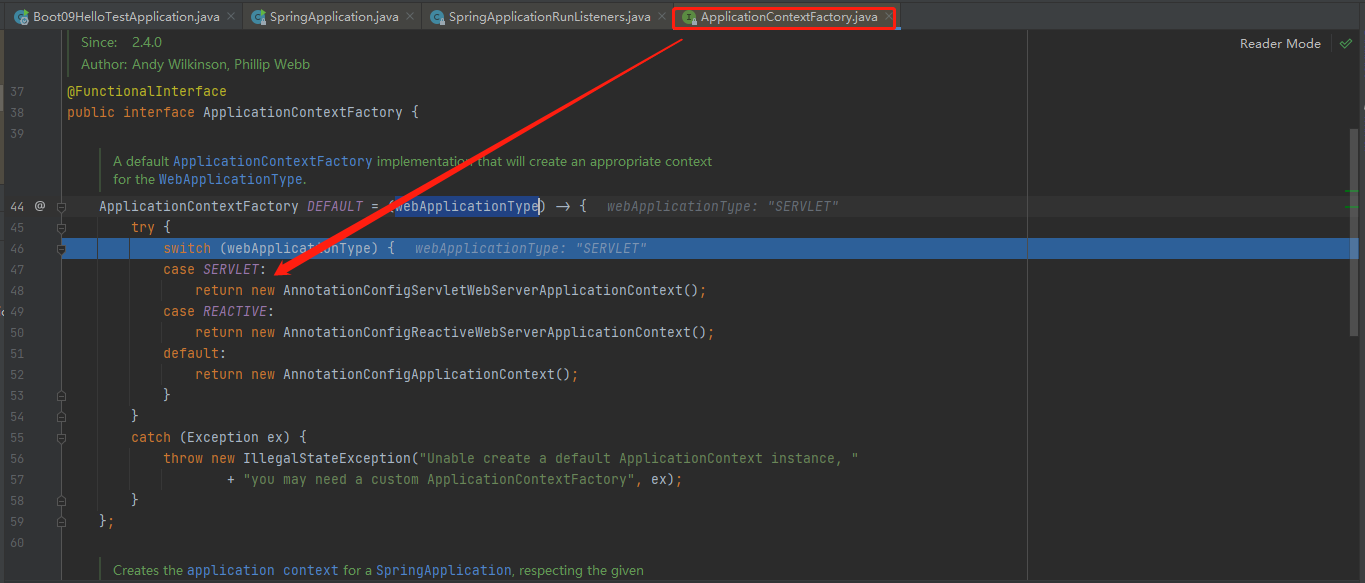
准备IOC容器上下文prepareContext
stepinto进入prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);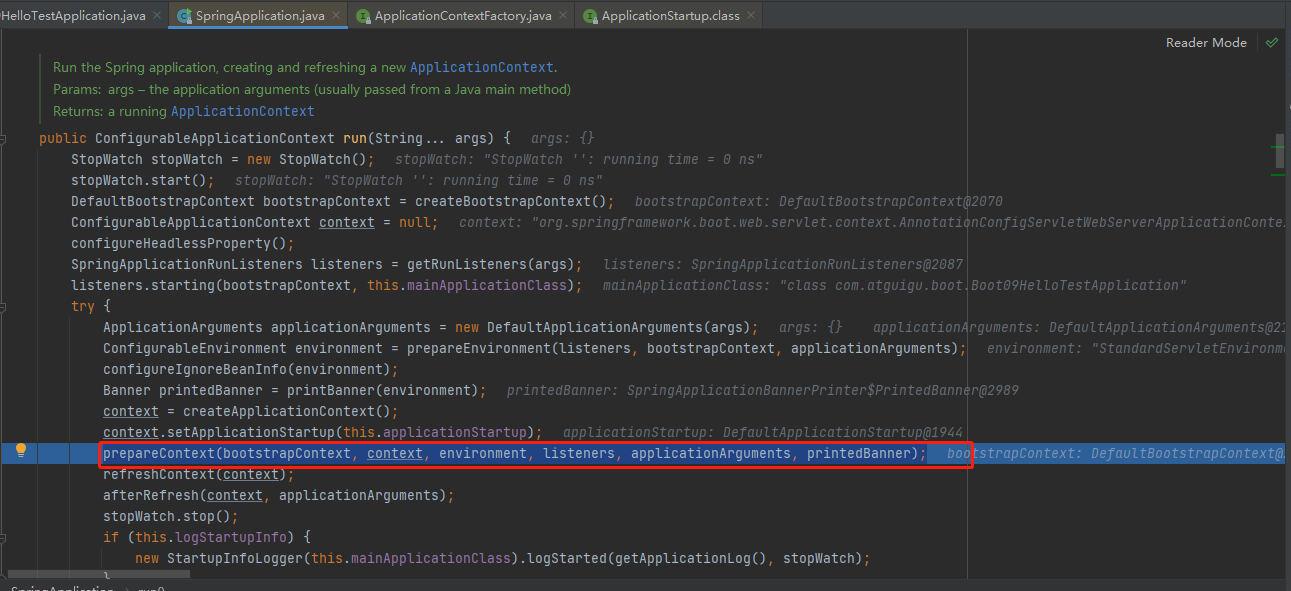
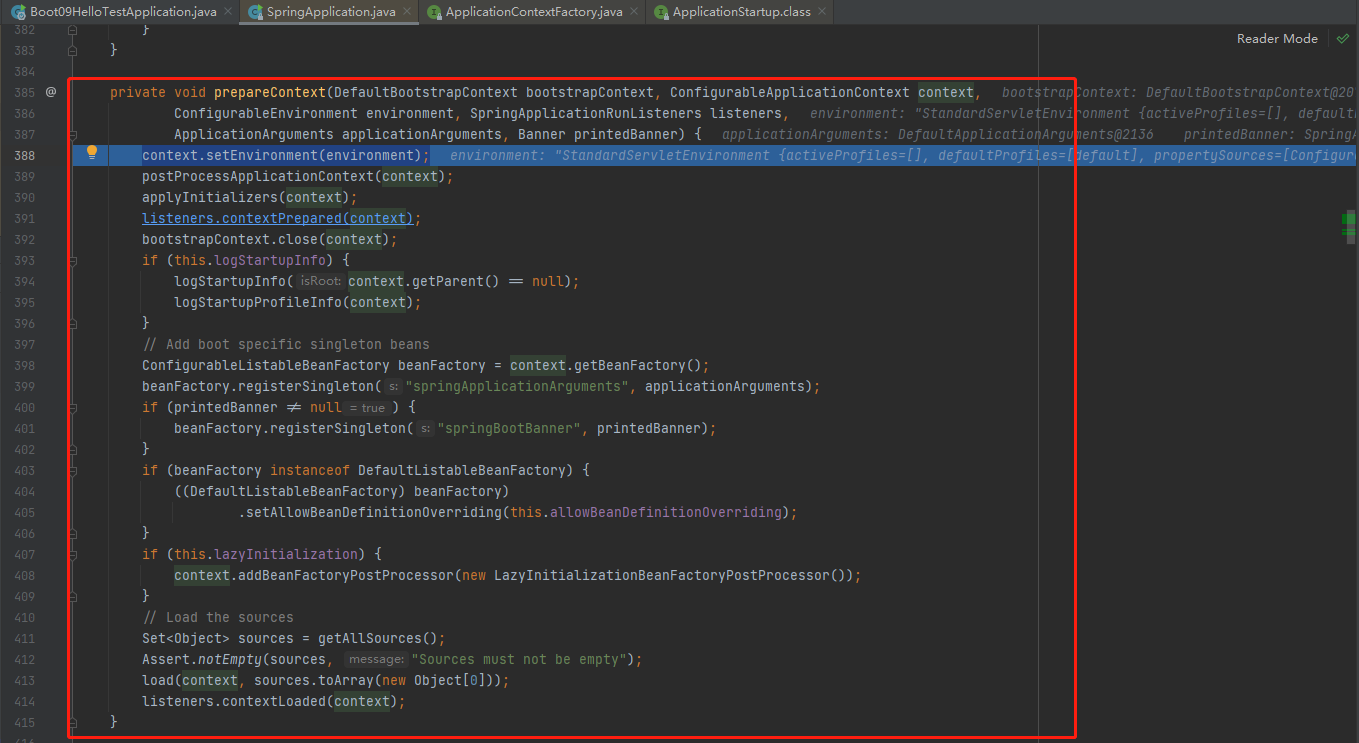
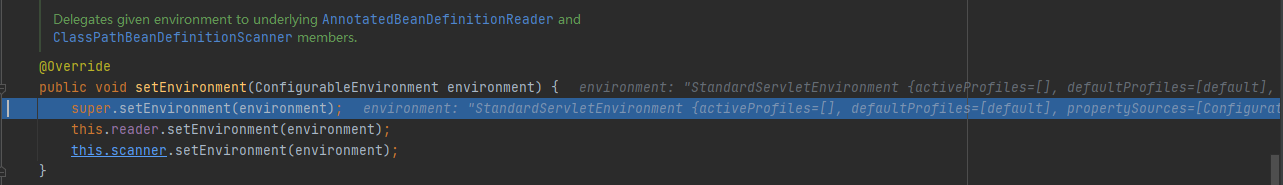
context.setEnvironment
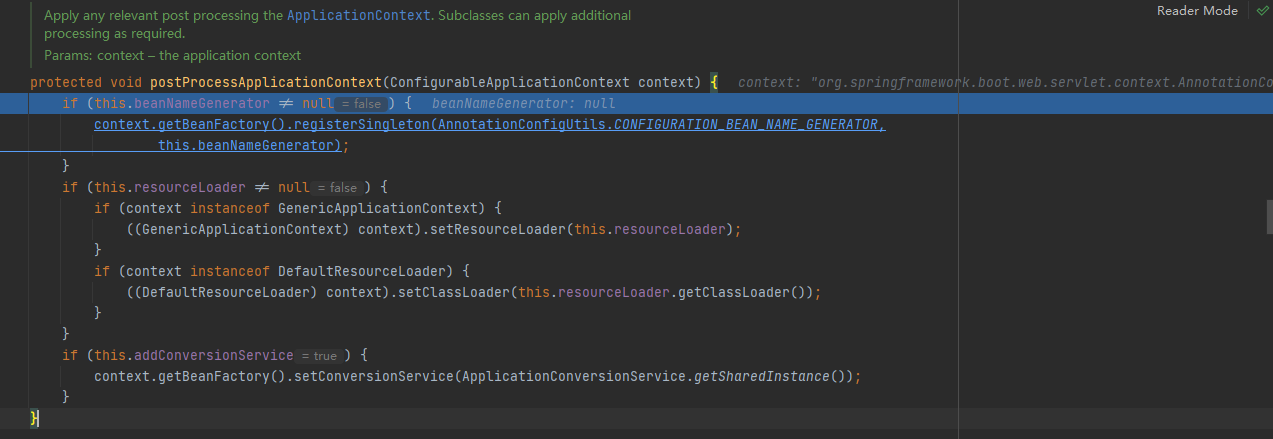
postProcessApplicationContext
applyInitializers
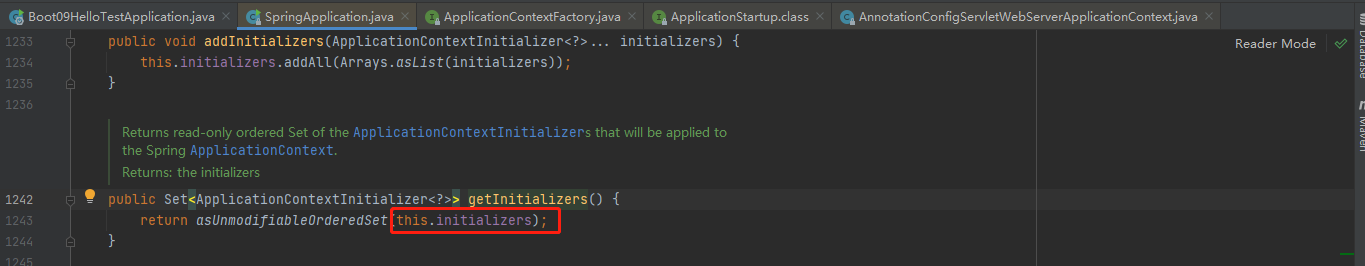
getInitializers()就是我们在创建SpringApplication的时候存进去的8个Initializers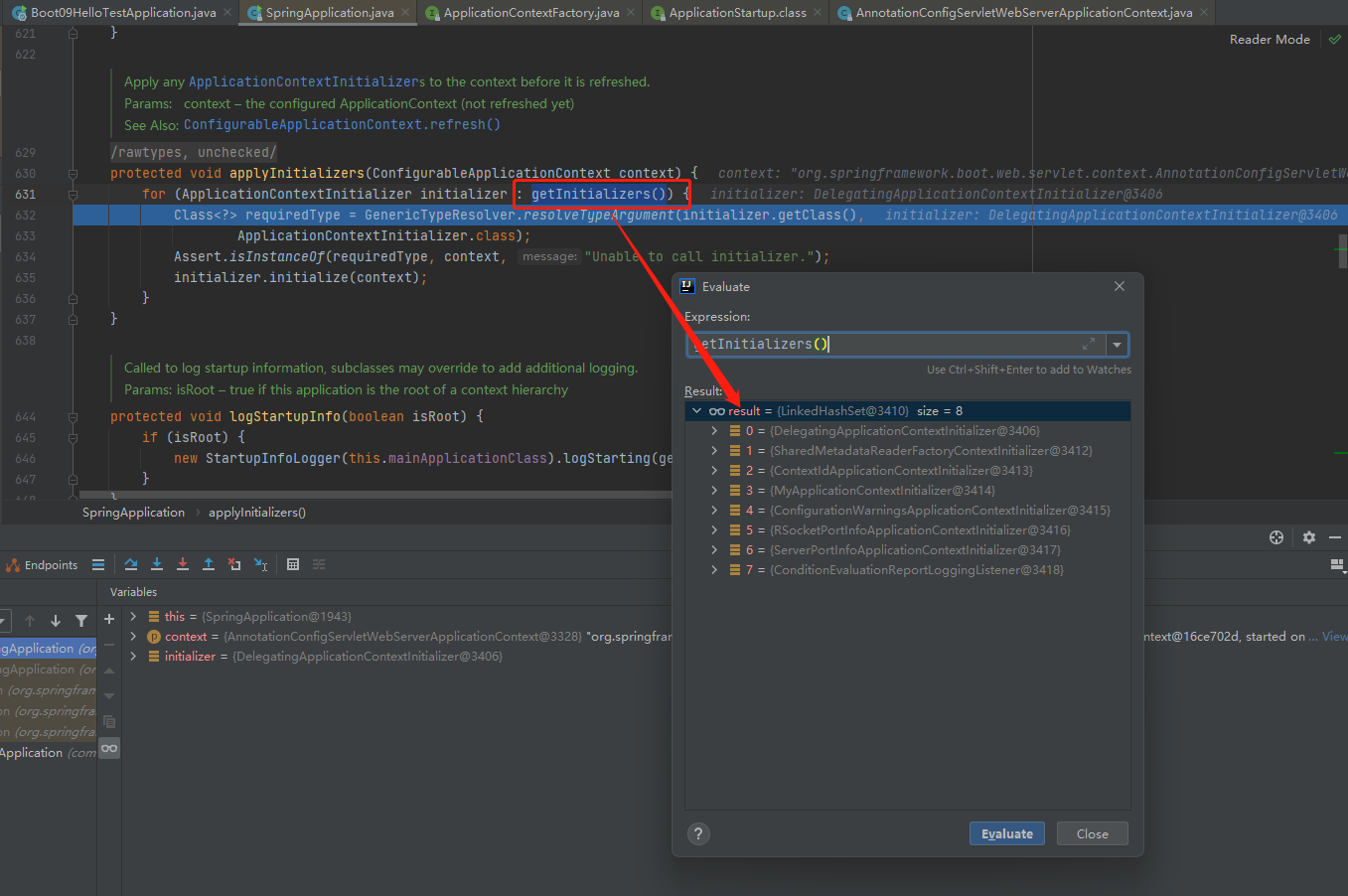
接下来看方法initializer.initialize(context);,stepinto进去,8个Initializers当中第一个Initializer是DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,他implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered,DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer重写的initialize方法如下: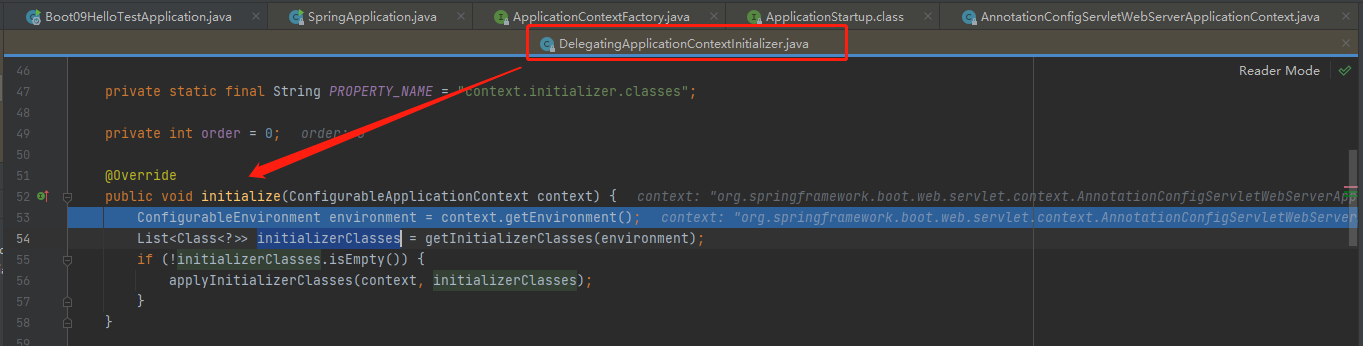
循环到第二个Initializer是,SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,同样implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered,SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer重写的initialize方法如下: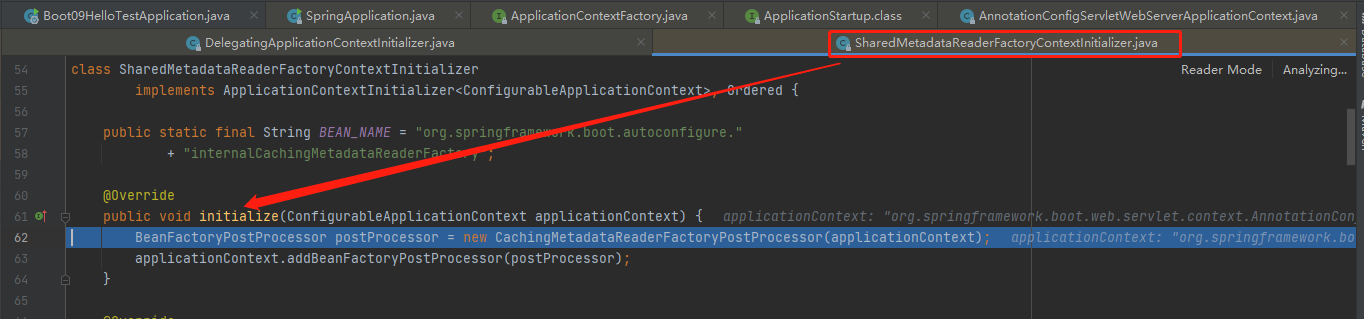
以此类推,遍历完所有8个Initializer
…
放行
listeners.contextPrepared
stepinto进去listeners.contextPrepared(context);
遍历所有的 listener 调用 contextPrepared。通知所有的监听器contextPrepared,目前这个List只有EventPublishRunListener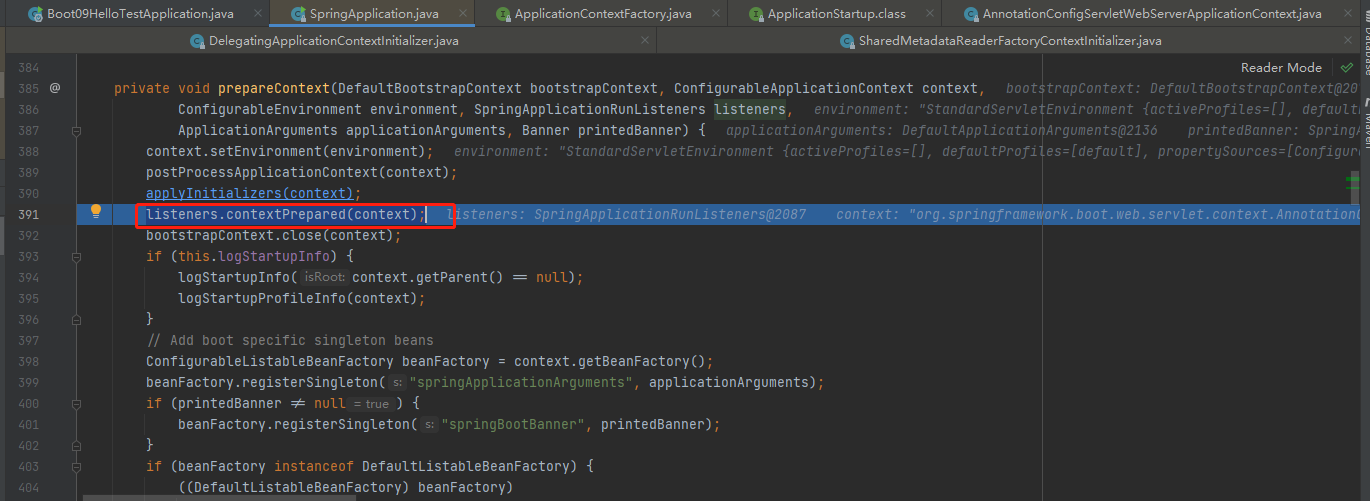
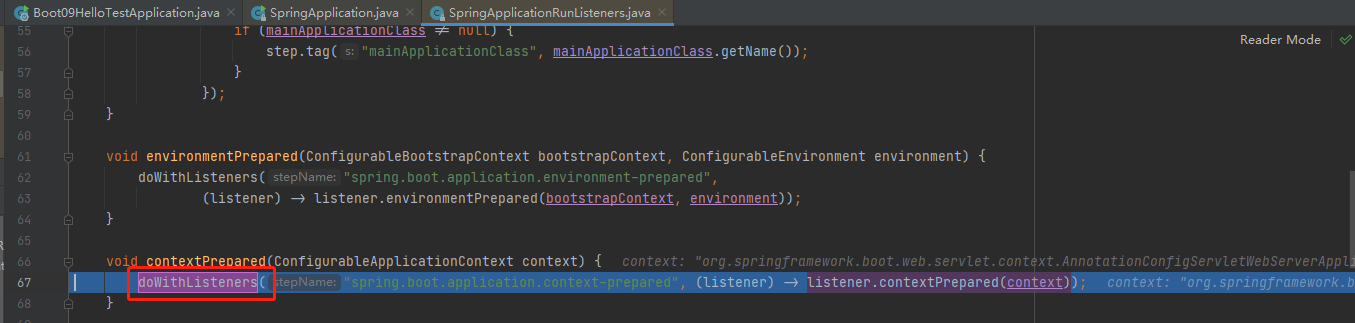
接着stepinto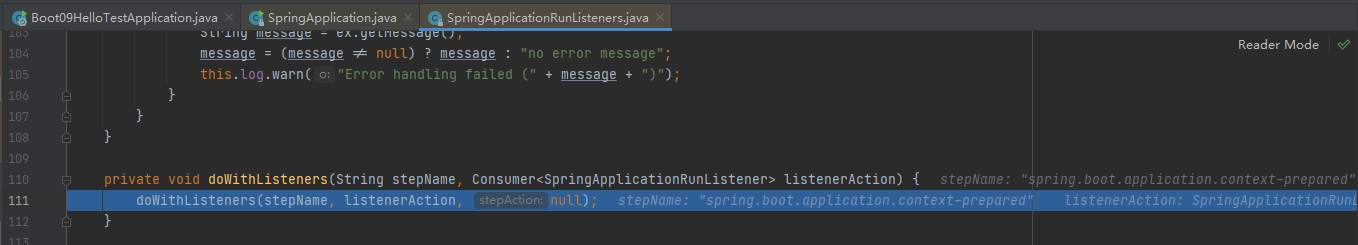
接着stepinto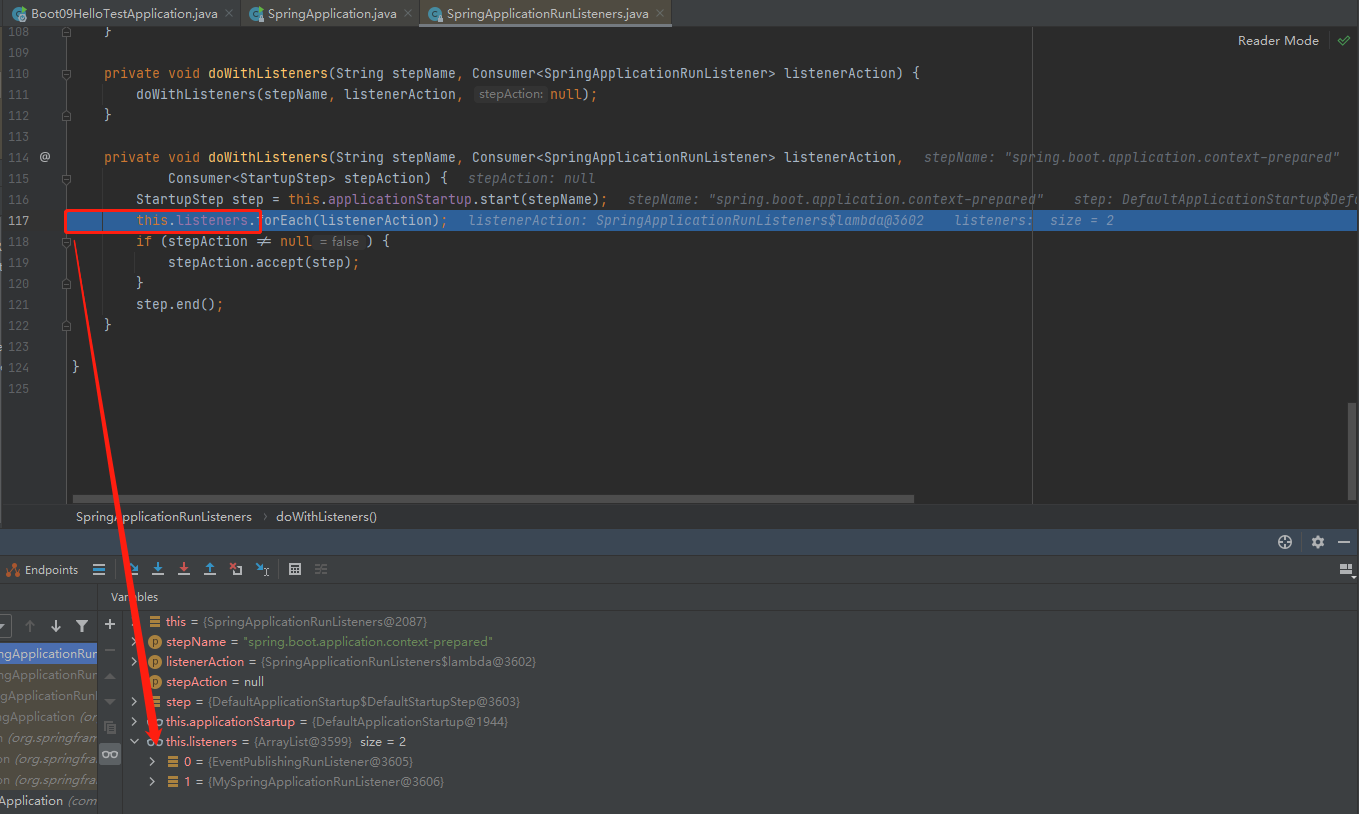
getBeanFactory
beanFactory.registerSingleton(“springApplicationArguments”, applicationArguments);
arg参数竟然在spring当中也是个组件,组件名叫做springApplicationArguments,注册到bean工厂当中
contextLoaded
stepinto进去listeners.contextLoaded(context);
所有的监听器 调用 contextLoaded。通知所有的监听器 contextLoaded;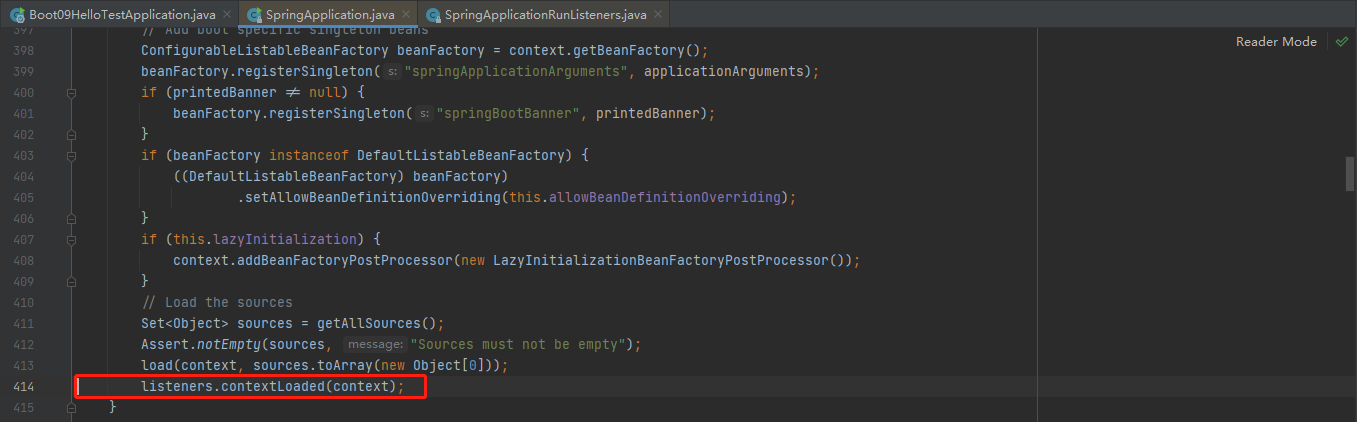
长得很像哈哈,我们已经多次遇到Listener监听器的监听处理了,Listener监听器真是无时无刻不存在。
这对我们是个启发,我们未来自定义实现MyListener监听器implements SpringApplicationRunListener,定制化的实现也能够被Spring管理
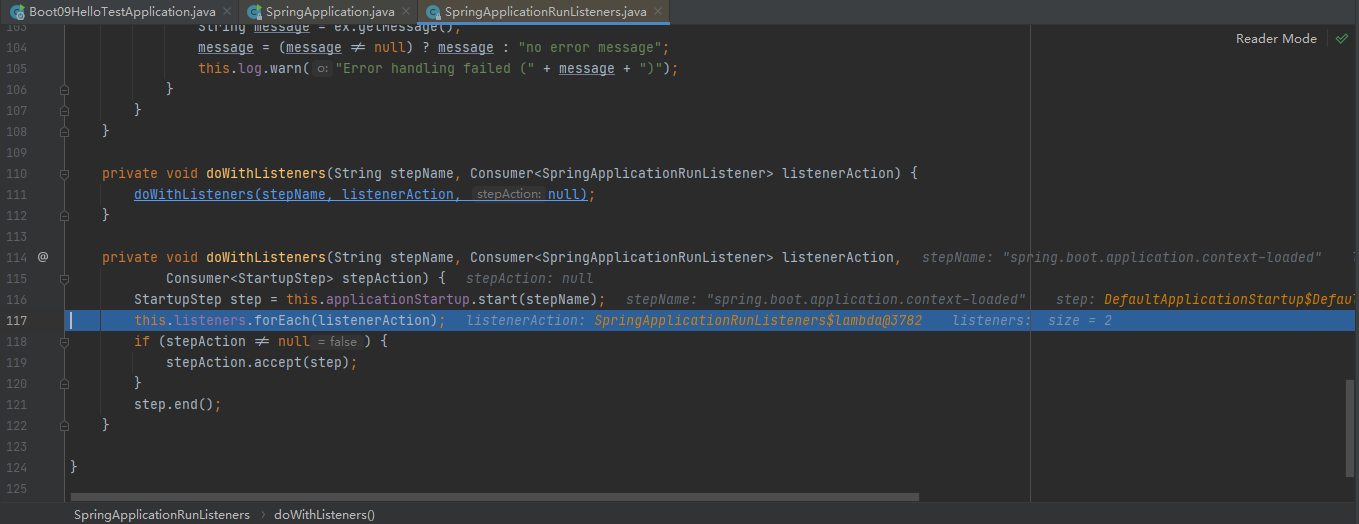
refreshContext【核心源码】
prepareContext结束,终于来到了refreshContext(context);,stepinto进去。这里是我们springboot的核心源码,可以参照Spring源码容器创建全流程
刷新IOC容器。refreshContext,创建容器中的所有组件(Spring源码)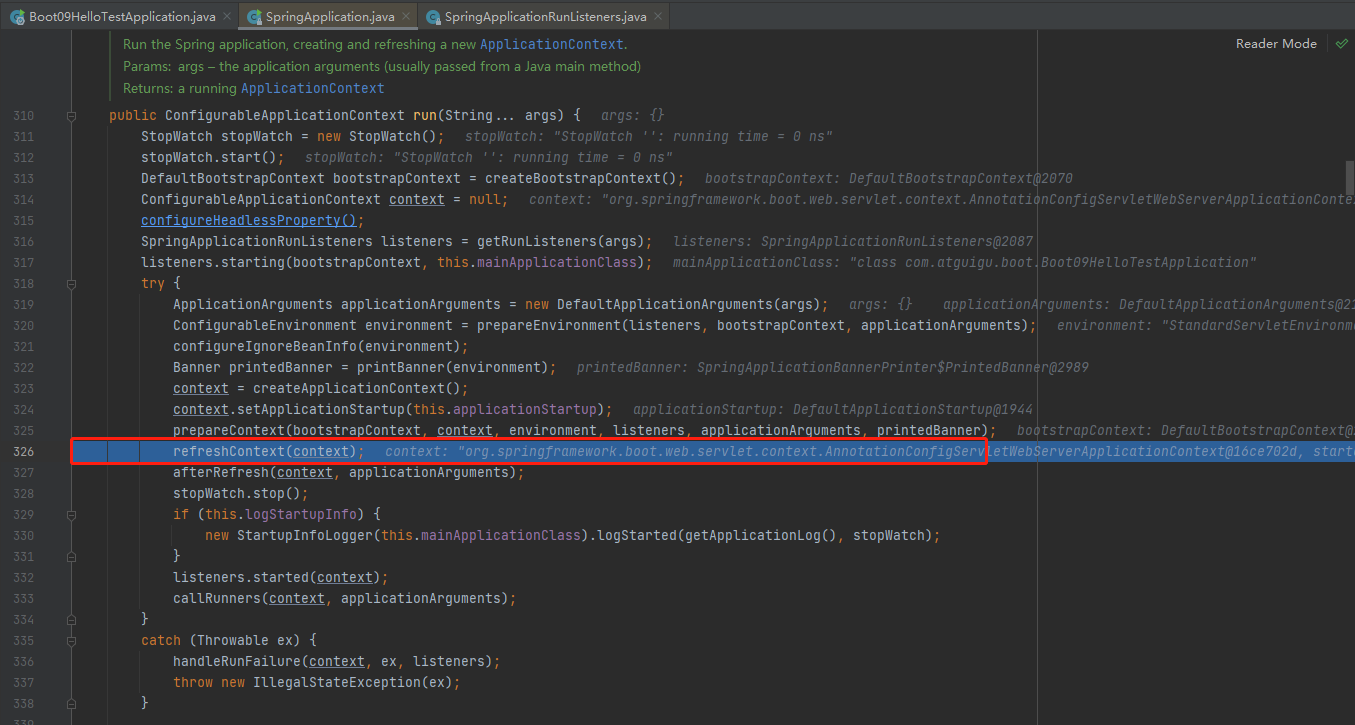
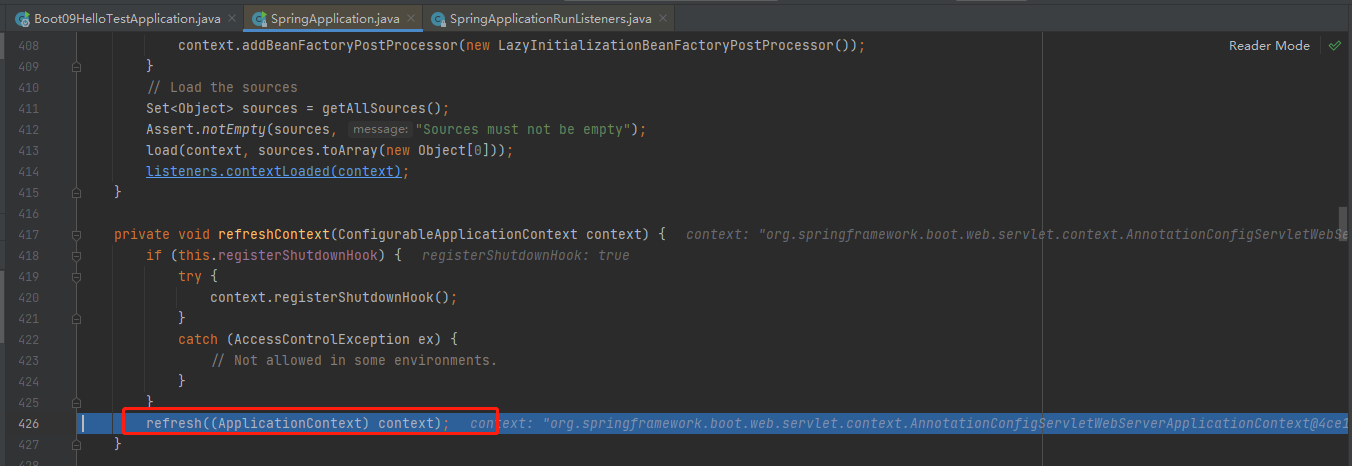
接着stepinto进去refresh((ApplicationContext) context);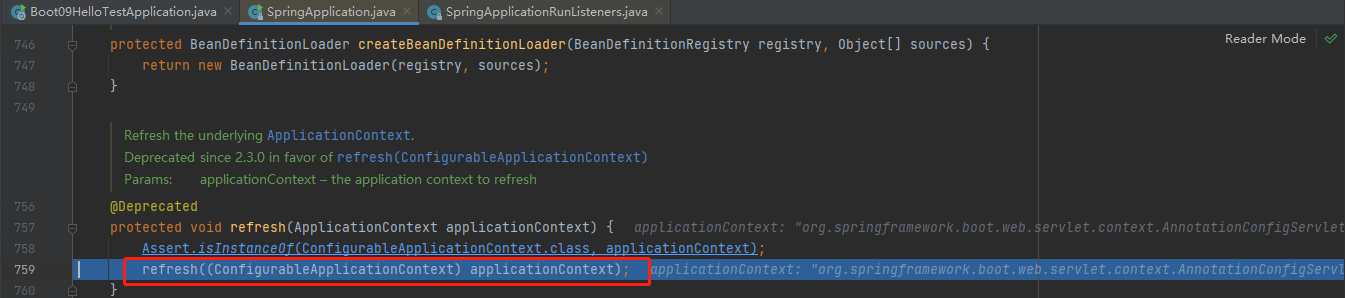
接着stepinto进去refresh((ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext);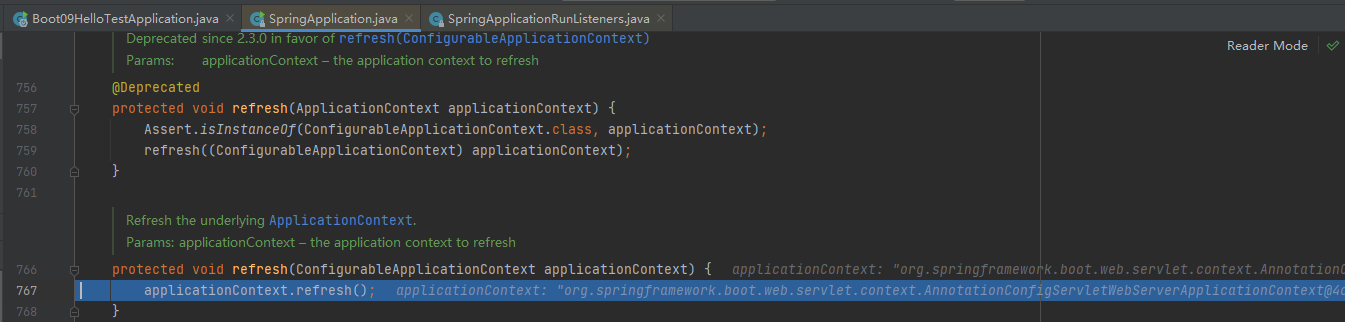
接着stepinto进去applicationContext.refresh();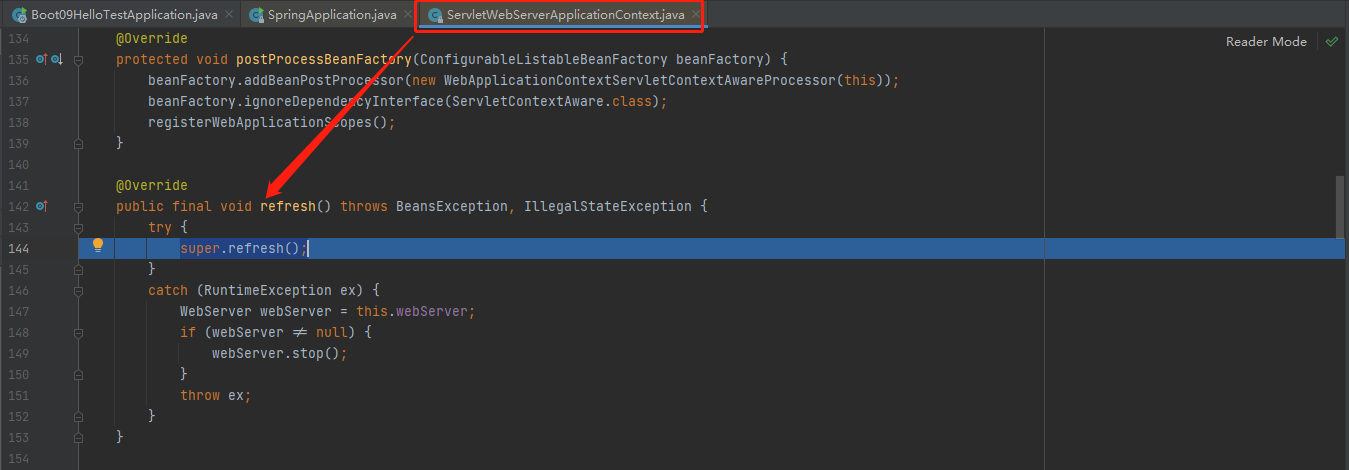
接着stepinto进去super.refresh();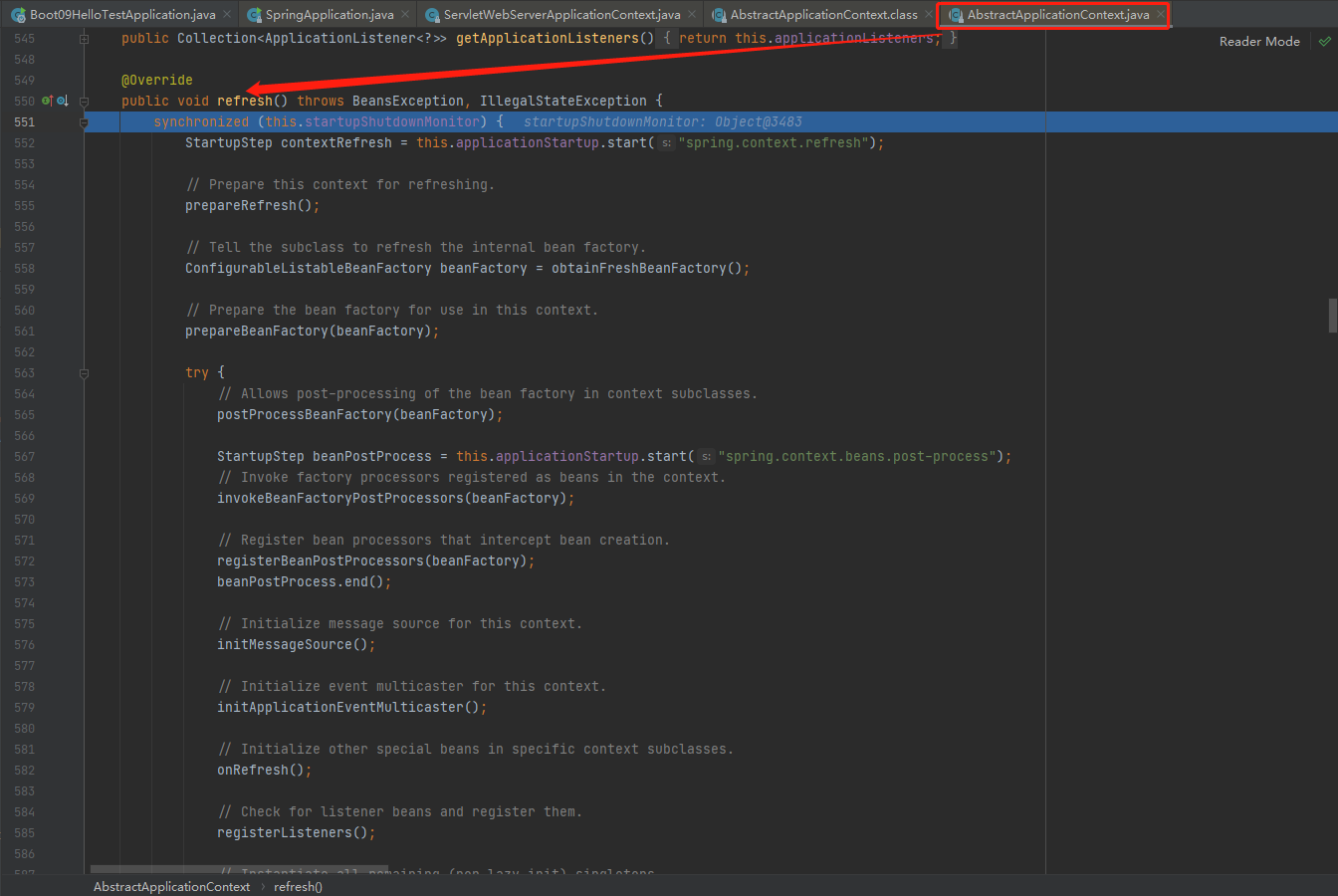
afterRefresh
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
容器刷新完成后工作
StopWatch.stop()
listeners.started
listeners.started(context);
所有监听 器 调用 listeners.started(context); 通知所有的监听器 正式开始了started
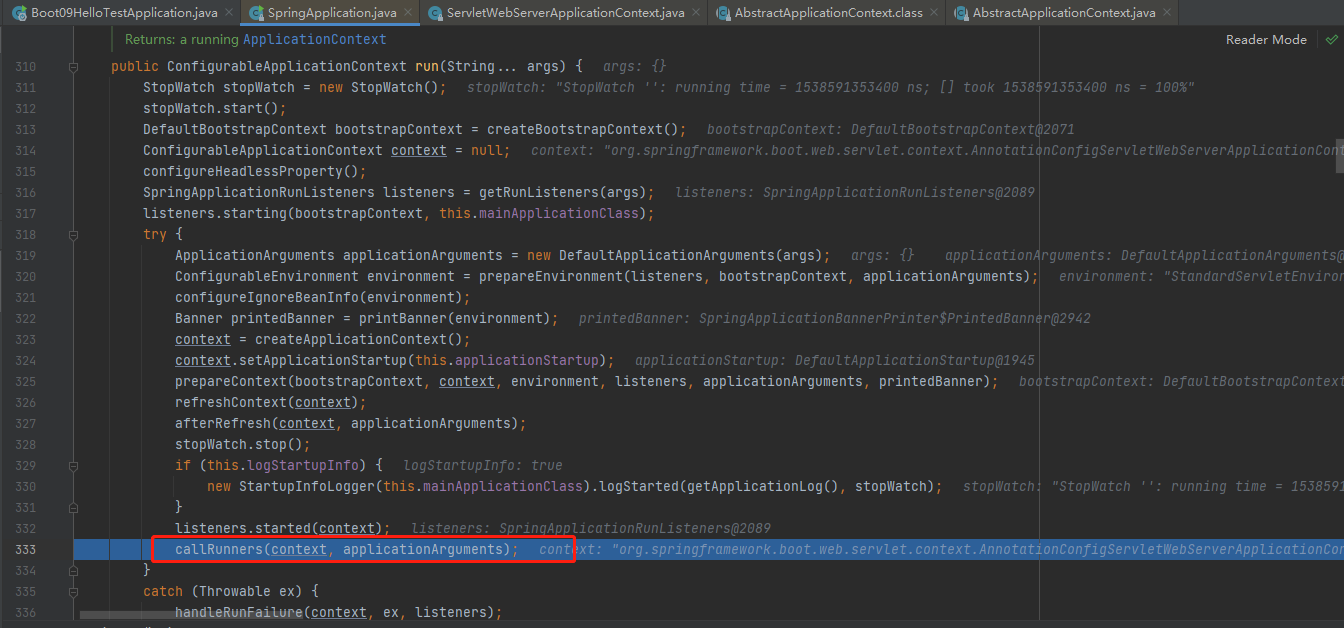
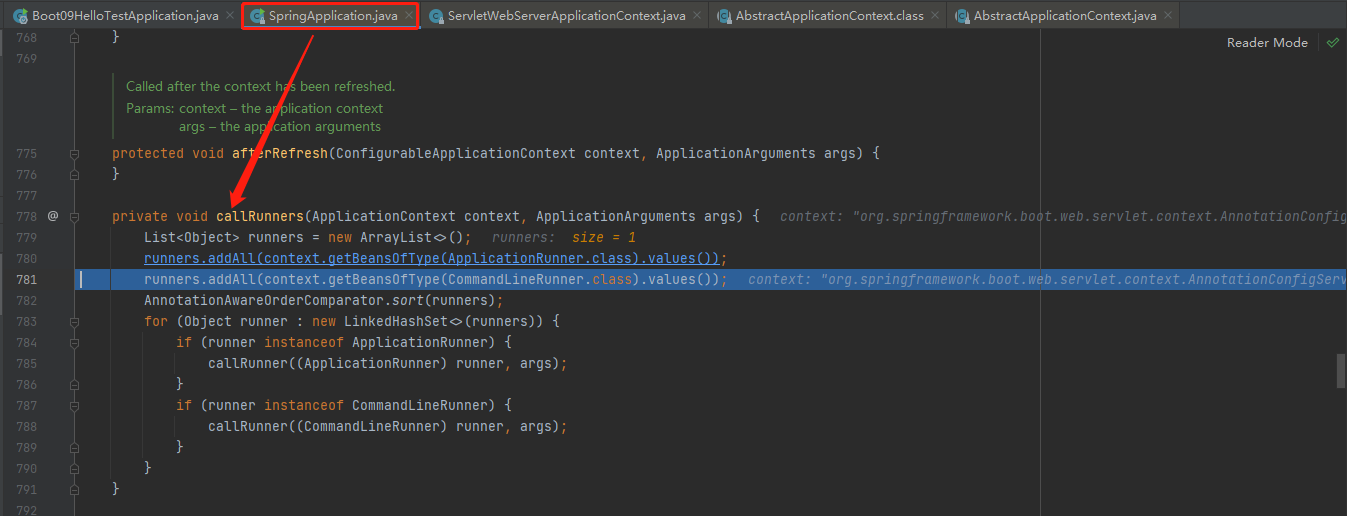
callRunners
stepinto进去callRunners(context, applicationArguments);调用所有runners;callRunners()
- 获取容器中的ApplicationRunner
- 获取容器中的 CommandLineRunner
- 合并所有runner并且按照@Order进行排序
- 遍历所有的runner。先ApplicationRunner 后CommandLineRunner调用 run 方法
handleRunFailure
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
如果以上有异常,调用Listener 的 failed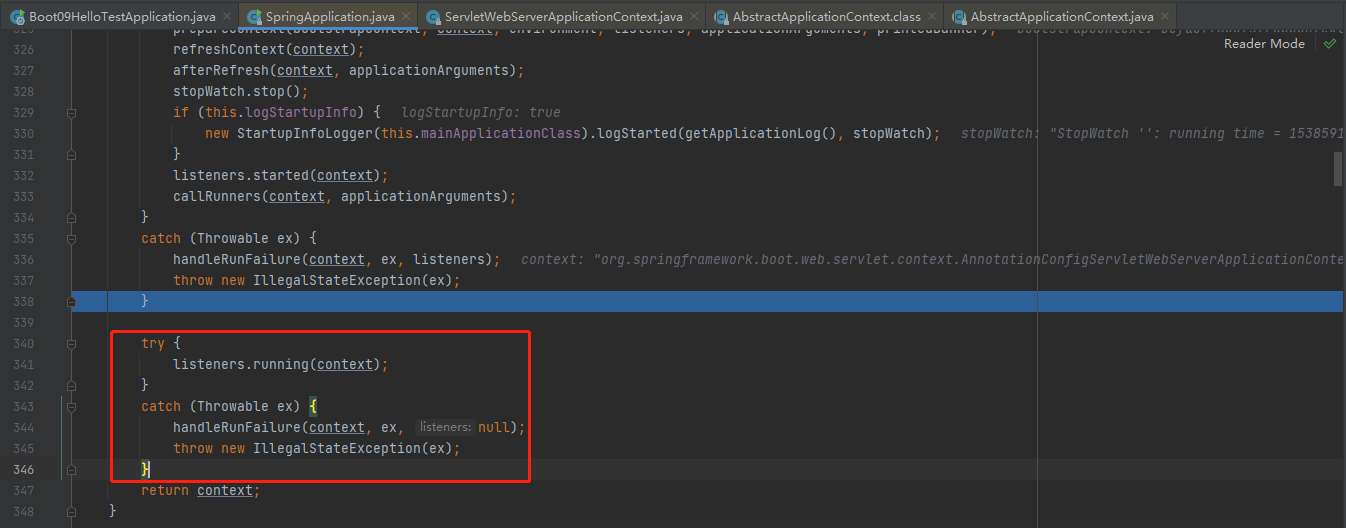
listeners.running
listeners.running(context);
调用所有监听器的 running 方法 listeners.running(context); 通知所有的监听器 running
running如果有问题。继续通知 failed 。调用所有 Listener 的 failed;通知所有的监听器 failed
return context;
返回IOC容器
...context = createApplicationContext();...return context;