在上一讲中,我们讲述了如何使用XML配置和@Bean注解两种方式来指定Bean初始化和销毁的方法。
除此之外,Spring中是否还提供了InitializingBean接口和DisposableBean进行Bean初始化和销毁呢
InitializingBean接口
InitializingBean接口为Bean提供了属性赋值后的初始化方法,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法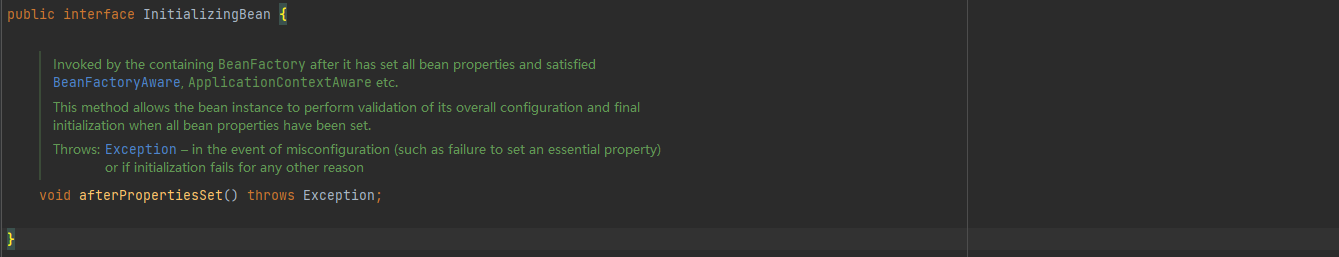
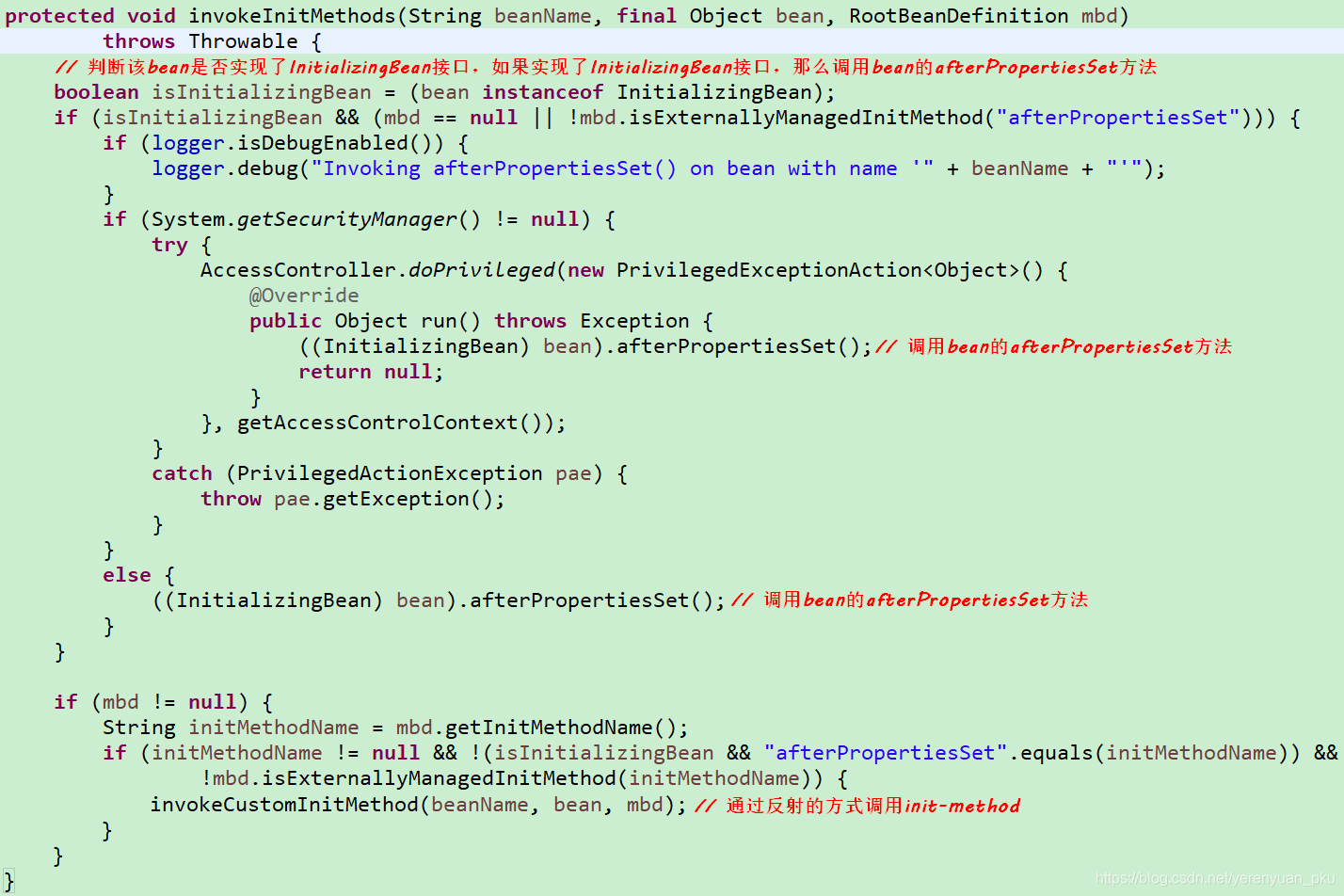
我们定位到Spring中的org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory这个类里面的invokeInitMethods()方法中
分析下述代码后,我们可以初步得出如下信息:Spring为bean提供了两种初始化的方式,实现InitializingBean接口或者指定init-method,两种方式可以同时使用。但是同时使用的时候会先调用afterPropertiesSet方法,后执行init-method指定的方法。
- 实现InitializingBean接口是直接调用afterPropertiesSet()方法,效率相对来说要高点。如果调用afterPropertiesSet方法时出错就不会继续调用init-method指定的方法了。
- @Bean注解通过init-method方式来指定,但是反射效率低
DisposableBean接口
这里的DisposableBean接口中的方法是由Spring容器来调用的,此外由于多实例Bean的生命周期不归Spring容器来管理,所以如果一个多实例Bean实现了DisposableBean接口是没有啥意义的,销毁方法不会生效。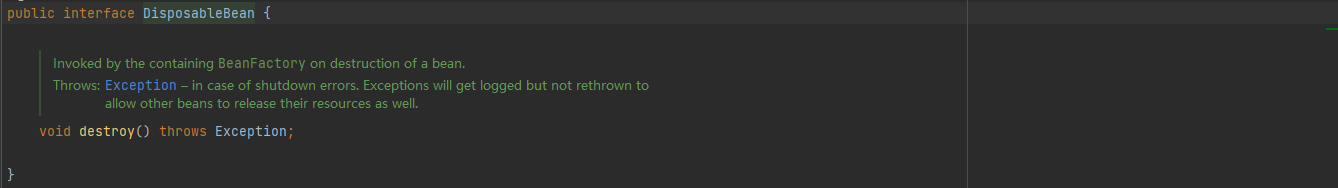
在Bean生命周期结束前调用DisposableBean#destroy()方法做一些收尾工作,亦可以使用destroy-method
- 前者与Spring耦合高,使用类型强转.方法名(),效率高;
- 后者耦合低,使用反射,效率相对来说较低。
单实例Bean的初始化与销毁
首先,创建一个Cat的类来实现InitializingBean和DisposableBean这俩接口,代码如下所示,注意该Cat类上标注了一个@Component注解。 ```java package com.meimeixia.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component public class Cat implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public Cat() {System.out.println("cat constructor...");}/*** 会在容器关闭的时候进行调用*/@Overridepublic void destroy() throws Exception {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("cat destroy...");}/*** 会在bean创建完成,并且属性都赋好值以后进行调用*/@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("cat afterPropertiesSet...");}
}
然后,在MainConfigOfLifeCycle配置类中通过包扫描的方式将以上类注入到Spring容器中。```javapackage com.meimeixia.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;import com.meimeixia.bean.Car;@ComponentScan("com.meimeixia.bean")@Configurationpublic class MainConfigOfLifeCycle {@Scope("prototype")@Bean(initMethod="init", destroyMethod="destroy")public Car car() {return new Car();}}
接着,运行IOCTest_LifeCycle类中的test01()方法,输出的结果信息如下所示。
package com.meimeixia.test;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;import com.meimeixia.config.MainConfigOfLifeCycle;public class IOCTest_LifeCycle {@Testpublic void test01() {// 1. 创建IOC容器AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfLifeCycle.class);System.out.println("容器创建完成");// 关闭容器applicationContext.close();}}
从输出的结果信息中可以看出,单实例bean情况下,IOC容器创建完成后,会自动调用bean的初始化方法;而在容器销毁前,会自动调用bean的销毁方法。
cat constructor...cat afterPropertiesSet...容器创建完成cat destroy...
多实例Bean的初始化与销毁
多实例bean的案例代码基本与单实例bean的案例代码相同,只不过是在Cat类上添加了一个@Scope("prototype")注解,如下所示。
package com.meimeixia.bean;import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Scope("prototype")@Componentpublic class Cat implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {public Cat() {System.out.println("cat constructor...");}/*** 会在容器关闭的时候进行调用*/@Overridepublic void destroy() throws Exception {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("cat destroy...");}/*** 会在bean创建完成,并且属性都赋好值以后进行调用*/@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {// TODO Auto-generated method stubSystem.out.println("cat afterPropertiesSet...");}}
然后,我们在IOCTest_LifeCycle类中新增一个test02()方法来进行测试,如下所示。
@Testpublic void test02() {// 1. 创建IOC容器AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfLifeCycle.class);System.out.println("容器创建完成");System.out.println("--------");// 调用时创建对象Object bean = applicationContext.getBean("cat");System.out.println("--------");// 调用时创建对象Object bean1 = applicationContext.getBean("cat");System.out.println("--------");// 关闭容器applicationContext.close();}
接着,运行IOCTest_LifeCycle类中的test02()方法,从输出的结果信息中可以看出,在多实例bean情况下,Spring不会自动调用bean的销毁方法。
容器创建完成--------------cat constructor...cat afterPropertiesSet...--------------cat constructor...cat afterPropertiesSet...--------------