一:表
1.1顺序表
实现-动态分配

#include<stdlib.h>#define InitSize 10typedef struct(){int *data;int MaxSize;int length;}SeqListint main(){SeqList(L);InitList(L);IncreaseList(L,5);return 0;}void InitList(SeqList &L){L.data = (int *)malloc(InitSize*sizeof(int))L.length=0;L.maxSize=InitSIze;}void IncreaseSize(SeqList &L,int len){int *p = L.data;L.data=(int *)malloc((L.MaxSize+len)*sizeof(int));for(i=0; i<L.lenght; i++){L.data[i]=p[i];}L.MaxSize=L.MaxSize+len;free(p)}
增加
#include<stlibs>#define MaxSize 10typedef sturct{int data[MaxSize];int length;}SqeList;int mian()}{SqeList L;InitList(L);InsertList(L, 3, 3);return 0;}bool InsertList(SqeList &L, int n, int e){if(i<1||i>L.length+1)return false;if(L.length>=MaxSize)return false;for(int j=L.length;j>=i;j--)L.data[j]=L.data[j-1];L.data[i-1]=e;L.length++;return ture;}
删除
int mian(){SeqList L;InitList(L);int e =-1;if(DeleteList(L,3,e))print("success=%d\n",e)elseprint("fail\n")return 0;}bool DeleteList(SqeList &L,int i,int &e){if(i<1||i>L.length)retrun false;e=L.data[i-1];for(int j=i;j<L.length;j++){L.data[j-1]=L.data[j];}L.length--;return true;}
按位查找
//静态分配#define MaxSize 10typedef struct{int data[MaxSize];int length;}//动态分配#define InitSize 10typedef struct{ElemType *data;int MaxSize;int lenght;}ElemType GETElem(SeqList &L, int i){return L.date[i-1];}
按值查找
typedef struct{int}
1.2单链表
定义
typedef struct LNode{ElemType data;struct LNode *next;}LNode, *LinkList;#没有头节点的单链表typedef struct LNode{Elemtype data;struct LNode *next;}LNode, *LinkList;bool InitList(LinkList &L){L = NULL;return true;}void test(){LinkList L;InitList(L);}bool Empty(LinkList L){if(L==NULL)return true;elsereturn false;}bool Empty(LinkList L){return (L==NULL)}#有头节点的单链表#1.1typedef struct LNode{ElemType data;struct LNode *next}LNode, *LinkList;#1.2bool InitList(LinkList &L){L = (LNode *) malloc(sizeof(LNode));if (L==null)return false;L->next = NULL;return ture;}#0#void test(){LinkList L;InitList(L);}#2 判断空表bool Empty(LinkList L){return (L->next==NULL)}
插入(按位插入)
bool
#现在要在位序为i的地方插入数据e(带头节点)#找到位置i-1,在后面插入数据bool ListInsert(LinkList &L, int i, ElemType e){if(i<1)return false;LNode *p;********************************#循环找到第i-1个节点int j=0;p = L;while(!p=NULL && j<i-1){p = p->next;j++;}********************************if(p==NULL)return false;LNode *s=(LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));s->data = e;s->next=p->next;p->next=s;return true;}#不带头节点#插入第一个节点的操作与其他节点不同bool ListInsert(LinkList &L, int i, ElemType e){if(i<1)retrun false;if(i == 1){LNode *s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));}#j=1代表是int j=1;}#指定结点的后插操作bool InsertNextNode(LNode *p, ElemType e){if (p == NULL)return false;LNode *s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));if (s==NULL)return false;s->date = e;s->next = p->next;p->next = s;return true;}bool InsertPriorNode(LNode *p,ElemType e){if(p==NULL)return false;LNode *s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));if(s==NULL)return false;s->next = p->next;p->next = s;s->data=p->data;p->date = e;return true;}bool InserPriorNode(LNode *p, LNode *s){if(p==NULL || s == NULL)return false;s->next = p->next;p->next = s;ElemType temp = s->data;s->data = p->data;p->data = temp;return true;}
bool ListDelte(LinkList &L, int i, ElemType &e){int j = 0;LNode * p;p =L;if(p!=NULL && j<i-1){p =p->next;j++;}if (p==NULL)return false;if(p->next == NULL)return false;LNode * q = p->next;p->next =q->next;e = q->data;free(q);return true;}
新建
#尾插法#头插法
二:栈LIFO(只在一端进出)
联想记忆:坑
2.1基本操作
初始化(两种实现1.top=-1 2.top=0)
- top=0,栈满为top==MaxSize
- top=-1,栈满为top==MaxSize-1(下面代码top=-1)
```cpp
define MaxSize 10
typedef struct{ Elemtype data[Maxsize]; int top; }SeStack; void InitStack(SqStack &S){ S.top=-1; } void testStack(){ SqStack S; InitStack(S); }
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S){ if S.top==-1 return true; else return false; }
入栈```cpp#把指针+1,再把e数据进栈#栈满要报错bool Push(SqStack &S, Elemtype e){#top0为第一个数if(S.top==MaxSize-1)return false;S.data[++S.top]=e;return true;}
出栈
#栈顶数据出栈(用e返回),再把指针-1;#栈空要报错bool POP(SqStack &s, Elemtype &e){if(S.top==-1)return false;e = S.data[S.top];top--;return true;}
读栈顶
bool ReadTop(SqStack &S, ElemType &e){if(S.top==-1)return false;e = S.data[S.top];return true;}
链栈(按照上面链的定义自己敲一遍基础操作的代码)
三:队列FIFO(一端进另一端出)
3.1顺序存储
联想记忆:排队
定义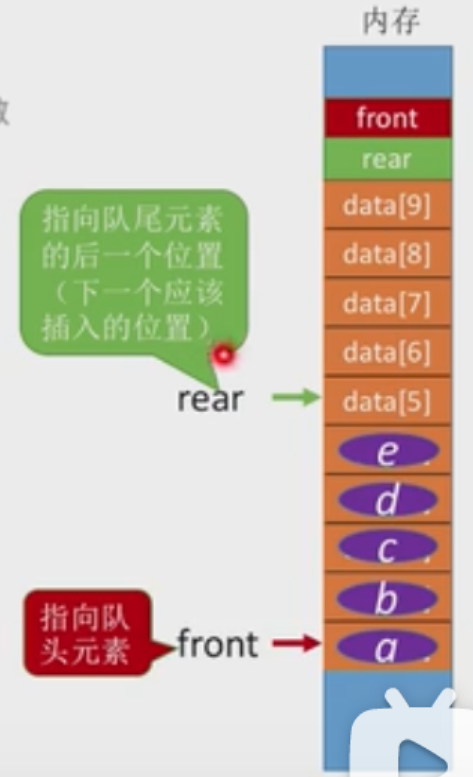
#因为rear指向下一个应该插入的位置,故初始化的时候rear=front=0#define MaxSize 10typedef struct {ElemType data[maxsize];int front, rear;}SqQueue;void InitQueue(SqQueue &Q){Q.rear=Q.front=0;}void testQueue(){SeQueue Q;InitQueue(Q);}bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue Q){if(Q.rear=Q.front)return true;elsereturn false;}
入队
#往队尾添加数据,并让rear+1,考虑到前面可能有空位置,故应让(rear+1)%MaxSize从而变为循环队列#队列已满则错误bool QueuePush(SqQueue &q, int i, Elemtype e){if((Q.rear+1)%MaxSize==Q.front)return false;Q.data[Q.rear]=e;Q.rear=(Q.rear+1)%MaxSize;return ture;}
判断队列满
1.一般
2.设置一个size记录队列长度
3.设置一个tag记录上一次的动作是删除还是添加
出队
#把队头的数据用x返回,并把front+1,考虑到循环性,让(front+1)%MaxSize#队列空则出错bool QueuePop(SqQueue &Q,Elemtype &e){if(Q.rear==Q.front)return false;e=Q.data[Q.front];Q.front=(Q.front+1)%MaxSize;return ture;}
3.2链式存储
初始化
#带头节点:申请一个头结点,并让front(头节点)和rear都指向它;接着让头节点next为NULLtypedef struct LinkNode{ElemType data;struct LinkNode *next;}LinkNode;typedef struct {LinkNode *front,*rear;}LinkQueue;void InitQueue(LinkQueue &Q){Q.front=Q.rear=(LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));Q.front->next=NULL;}void testLinkQueue(){LinkQueue Q;InitQueue(Q);}#判断为空:Q.front==Q.rear || front->next=NULLbool IsEmpty(LinkQueue &Q){if(Q.front==Q.rear)return true;elsereturn false;}#不带头节点:front和rear全部指向NULLvoid InitQueue(LinkQueue &Q){Q.front=NULL;Q.rear=NULL;}#判断为空:front=NULL || rear=NULLbool IsEmpty(LinkQueue &Q){if(Q.front==NULL)return true;elsereturn false;}
入出
#申请一个节点,把节点赋值后让它next为空(因为一定是添加到队尾的);把队尾指针next给s,# 并移动队尾指针到s上bool LinkQueuePush(LinkQueue &Q,Elemtype e){LinkNode *s = (LinkNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));s.data = e;s->next=NULL;Q.rear->next=s;Q.rear=s;}bool LinkQueuePop
四:串
4.1基本操作实现
4.1.1求子串

#遍历pos到pos+len-1,依次赋值给Sub串,记得让Sun长度变为len#记得判断字串范围是否越界SubString(&Sub, S, pos, len)bool SubString(SString &Sub, SString S, int pos, int len){if(pos+len-1>S.length)return false;for(int i = pos; i<pos+len;i++)Sub.ch[i-pos+1]=S.ch[i];Sub.length = len;return true;}
4.1.2比较大小
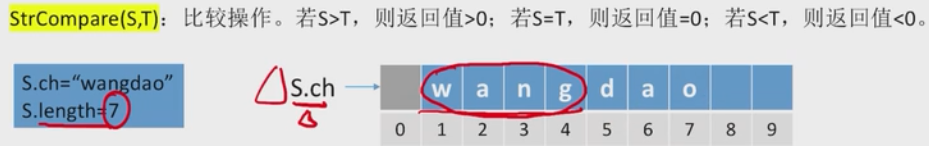
#同时遍历两个串,比较第一个不相同字符的大小。#若扫描过的所有字符都相同,则长度长的串更大StrCompare(S,T)int StrCompare(SString S, SString T){for(int i=1;i<=S.length&&i<=T.length;i++){if(S.ch[i]!=T.ch[i])return S.ch[i]-T.ch[i];}return S.length-T.length;}
4.1.3定位操作
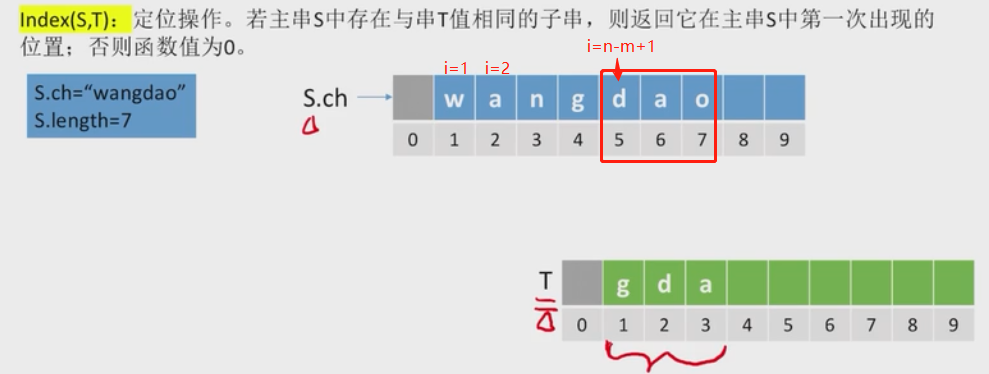
#对主串从头到尾依次取出长度为3的字串,再比较子串int Index(SString S, SString T){int i=1, n=StrLength(S), m= StrLength(T);SString Sub;while(i<=n-m+1){SubString(sub, S, i, m)if(StrCompare(Sub,T)!=0) ++i;else return i;}return 0;}
4.2朴素模式匹配算法:(不用基本操作完成字符匹配)
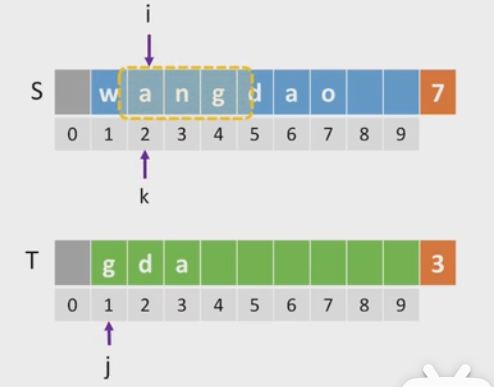
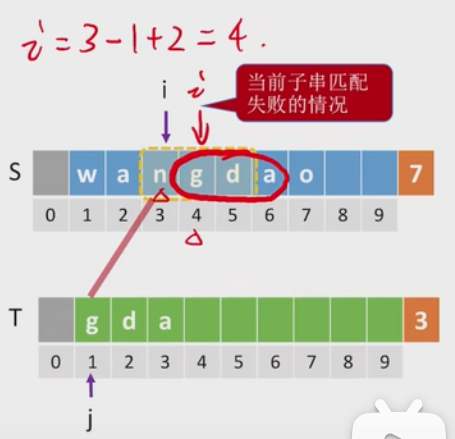

#用i,j逐个比较两串,并定义k作为主串匹配开始的标志符.ruo匹配失败,则继续下一个int Index(SString S, SString T){int k=1,i=1,j=1;while(i<=S.Length&&i<=T.Length){if(S.ch[i]==T.ch[j]){i++;j++;}else{k++;i=k;j=1;}}if(j>T.length)return k;elsereturn 0;}
#课本代码没有另外定义一个k,而是用i,j之间的逻辑关系来表示(指针后退重新开始匹配)
4.3KMP算法**


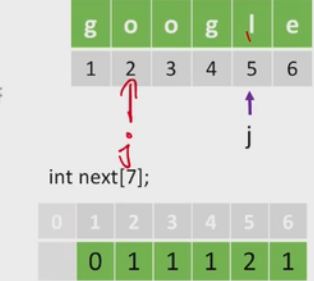
#和朴素匹配基本一样,只是不匹配时,不回溯i,只回溯jint KMP(SString S, String T){int i=1,j=1;int next[T.length+1]; #看上图get_next(T, next);while(i<=S.Length&&i<=T.Length){if(j==0||S.ch[i]==T.ch[i]){ #j=0是特殊情况i++;j++;}else{j=next[j];}}if(j>T.length)return i-T.length;elsereturn 0;}
4.3.1KMP算法的优化-nextval数组
g与l不匹配,next[4]=1,继续看g与l匹配,重复了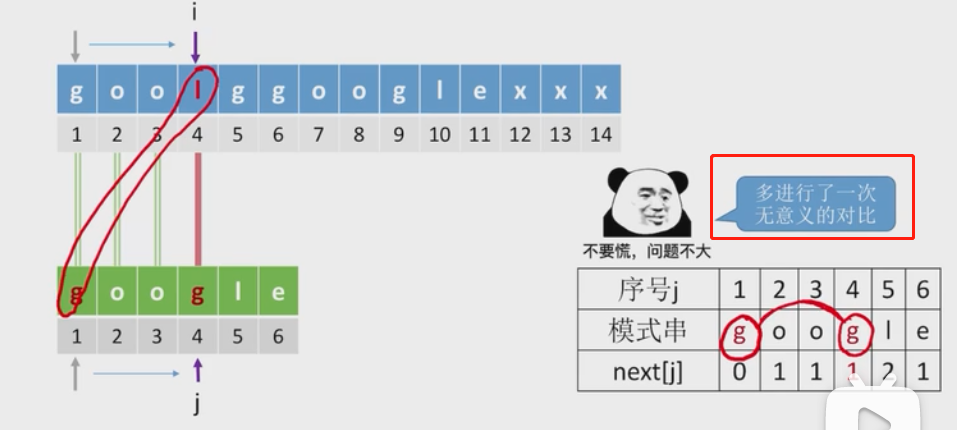
j=0时,i++;j++;所以l被跳过,匹配g与g

