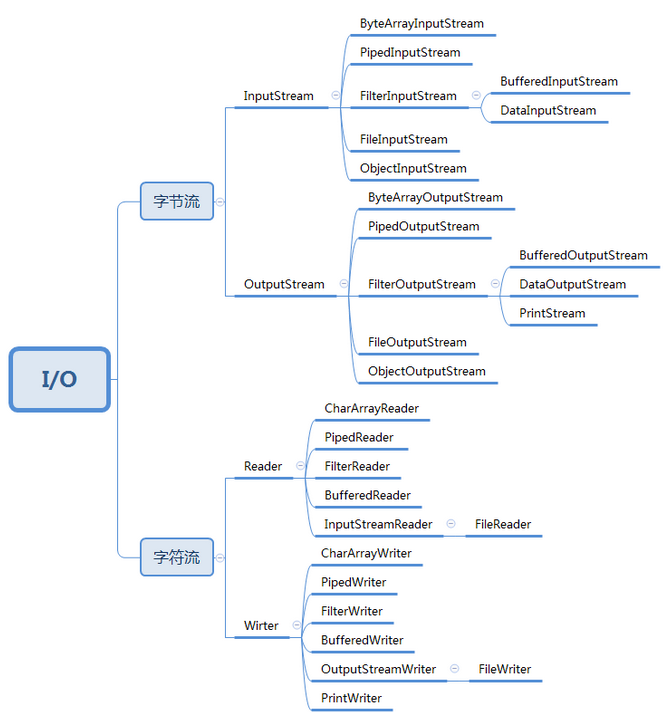
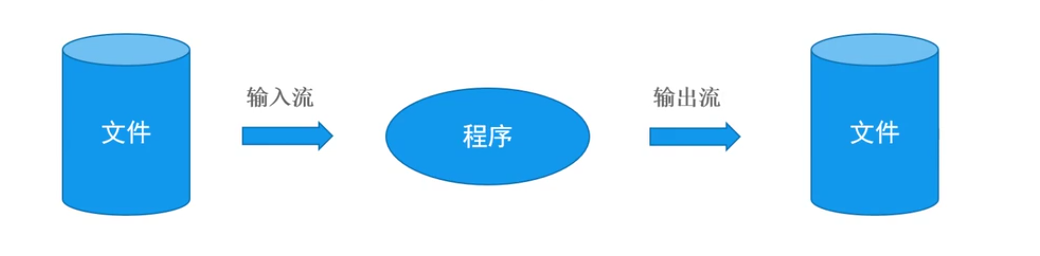
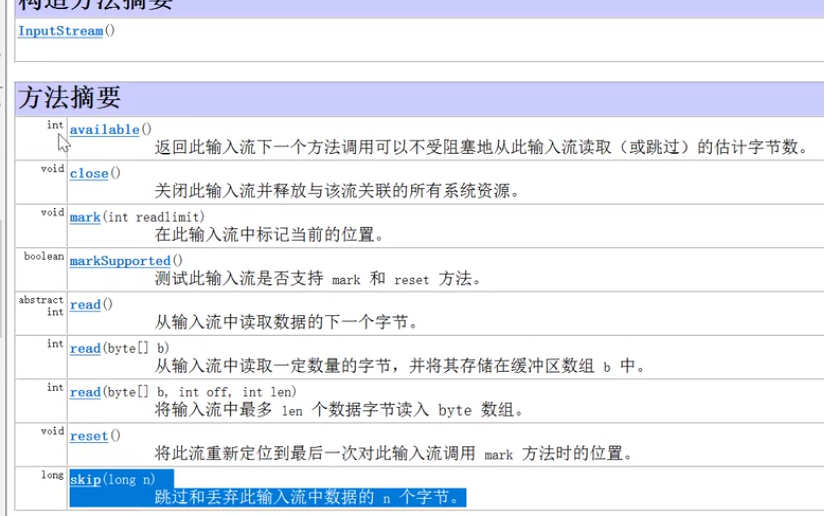
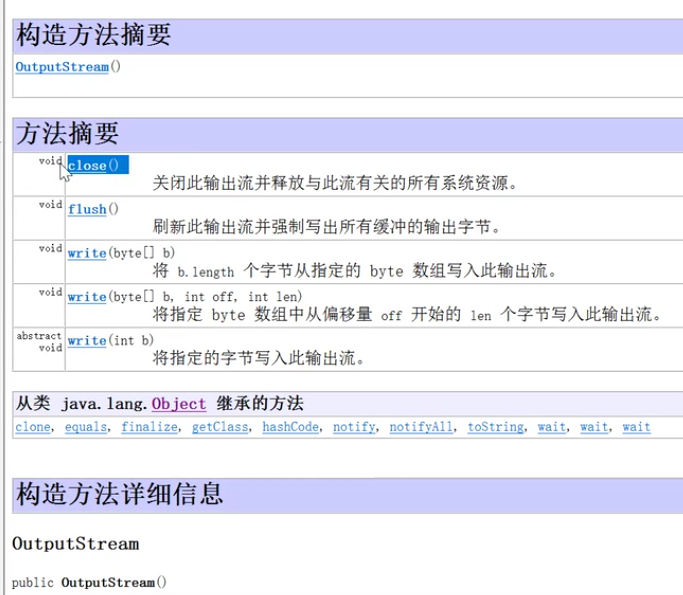
1.流的概念
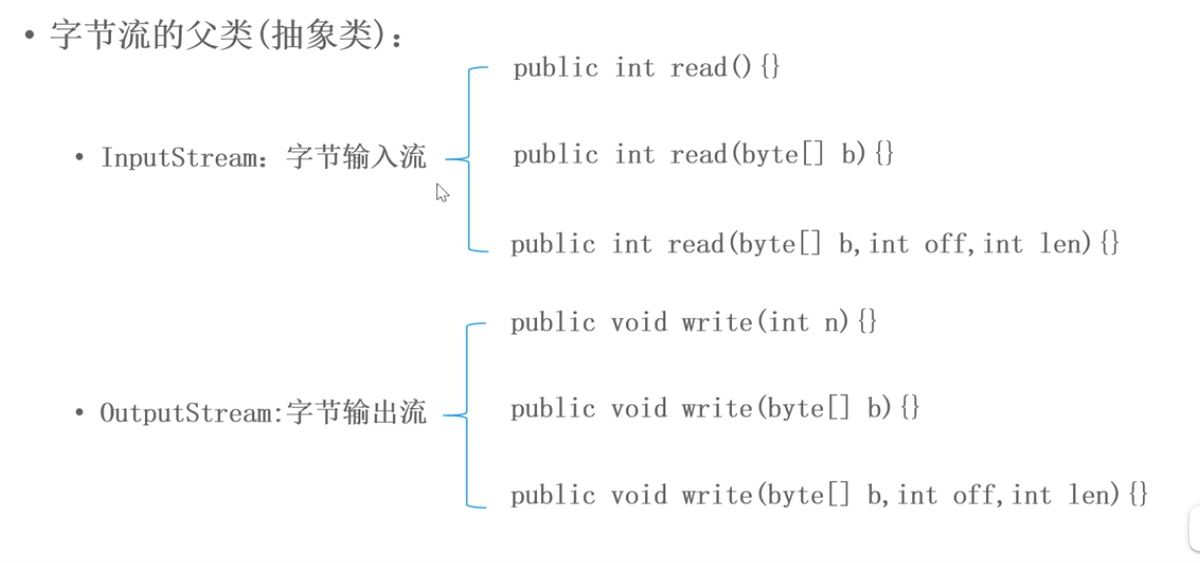
4.文件字节流
FileInputStream
- public int read(byte[] b)// 从流中读取多个字节,将读到的内容存放在b数组内,返回实际读到的数字,如果达到文件的地步,则返回-1
```java
/*
- @Descripttion: FileInputStream相关学习
- @version:
- @Author: Addicated
- @Date: 2020-11-07 20:18:06
- @LastEditors: Addicated
- @LastEditTime: 2020-11-07 20:47:53 */ package review.IO;
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 1,创建FileInputStream,并制定文件路径 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(“src\main\java\review\IO\memo.txt”); // // 2,读取文件 // fis.read(); // 一个字节一个字节的进行读取的方式 // int data =0; // while((data=fis.read())!=-1){ // System.out.println(data); // }
// 一次读多个字节 字节长度决定读多少个字节// byte[] buf = new byte[3];// // 返回值 为读取了的字节的个数// int count = fis.read(buf); // 读到的字节返回到buf这个字节类型的数组中// System.out.println(new String(buf));// System.out.println("读取了多少字节:" + count);// 优化,一次性读完所有数据byte[] buf = new byte[1024];int count = 0;// * @param b the buffer into which the data is read.// * @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or// * <code>-1</code> if there is no more data because the end of// * the file has been reached.// 观察原码得知,如果没有数据了,就返回-1,即,不返回-1,表示仍有数据,继续进行遍历while ((count = fis.read(buf)) != -1) {System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, count));}// 3,关闭fis.close();System.out.println("执行完毕");}
}
<a name="pdO9q"></a>## FileOutputStream- public ovid write(byte[] e) 一次性多写几个字节,将B数组中所有音节,写入输入流```java/** @Descripttion: 演示文件输出流* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-07 21:02:38* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-07 21:22:47*/package review.IO;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1.创建文件字节输出流对象// 当前调用的构造方法每次都会覆盖写入FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("memo1.txt");// 追加写入 添加一个参数为true即可// FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("memo1.txt",true);// 写入文件 以字符写入// fos.write(97);// fos.write('c');// fos.write('b');String string = "helloAddicated";// string.getBytes 将字符串自动转码成字节类型数组并返回fos.write(string.getBytes());fos.close();System.out.println("执行结束");}}
案例 文件字节流复制文件
/** @Descripttion:* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-07 21:29:33* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-07 21:37:40*/package review.IO;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1.创建流// 字节输入流读取FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\学生成绩证明.pdf");// 创建字节输出流输出FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\学生成绩证明copy.pdf");// 一边读,一边写入byte[] buf =new byte[1024*1024*1024];int count =0;while((fis.read(buf))!=-1){fos.write(buf,0,count);}fis.close();fos.close();System.out.println("文件复制完毕了~~~");}}
5.字节缓冲流
缓冲流:BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream
- 提高IO效率,减少访问磁盘的次数
- 数据存储在缓冲区,flush是将缓冲区的内容写入文件中,也可以直接close。
BufferedInputStream
```java /*- @Descripttion: 使用字节缓冲流来读取文件
- @version:
- @Author: Addicated
- @Date: 2020-11-07 22:59:59
- @LastEditors: Addicated
- @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 08:52:00 */ package review.IO;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 1.创建字节缓冲流 需要一个输入流对象象来作为参数传入 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(“src\main\java\review\IO\memo.txt”); BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); // 读取 // fis 是从硬盘读,bis是从缓存区读取 /**
* The maximum size of array to allocate. Some VMs reserve some header words in* an array. Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in OutOfMemoryError:* Requested array size exceeds VM limit*/// private static int MAX_BUFFER_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;// 查看原码得知buffered读的大小默认为8k// int data = 0;// while ((data = bis.read()) != -1) {// System.out.print((char) data);// }// 自己定义缓冲区的大小进行读取byte[] buf = new byte[1024];int count=0;while((count=bis.read(buf))!=-1){System.out.println(new String(buf,0,count));}// 关闭bis.close();}
}
<a name="JKlle"></a>### BufferedOutputStream- 该类实现缓冲的输出流,通过设置这种输出流,应用程序就可以将各个字节写入底层输出流中,而不必针对每次字节写入调用底层系统。从jdk1.0开始```java/** @Descripttion: 使用字节缓冲流写入文件* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-08 08:53:59* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 09:34:44*/package review.IO;import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;public class Demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 1,创建字节输出缓冲流FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("memo2.text");BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);// 2,写入文件for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {bos.write("hello addicated\r\n".getBytes()); // 先写入到8k的缓冲区bos.flush(); // 刷新到硬盘中}// 关闭(内部会自动调用flush方法,)即bos.close();}}
6.对象流
对象流 : ObjectOutputStream / ObjectInputStream
- 增强了缓冲区功能
- 增强了读写8中基本数据类型和字符串功能
- 增强了读写对象的功能
- readObject() 从流中读一个对象
- writeObject(Object obj) 向流中写入一个对象
-
注意点
在运用的时候必须要让实体类实现serializable接口
- 序列化类中的对象属性也要求实现serializable接口
- 序列化版本号ID,保证序列化的类和反序列化的类是同一个类
- 使用transient修饰属性,这个属性就不能序列化了,transient意为瞬间的
- 静态属性也是不能序列化的
- 序列化多个对象,可以借助集合的形式吧对杨压入集合中然后通过对集合进行序列化反序列化操作实现多对象序列化
// 对象流操作的pojo类public class Student implements Serializable{// 用来保证序列化和反序列化操作的是同一个类private static final long serialVersionUID=100L;private String name;// transient 修饰的属性不会被序列化,private transient int age;public String getName() {return name;}
ObjectOutputSteam
/** @Descripttion: 对象流系列--序列化(写入操作* 要求,必须让实体类实现seriable 接口* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-08 09:45:59* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 11:05:52*/package review.ObjIO;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;public class demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1.创建对象流FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("stu.bin"); // bin表示为一个二进制文件// 对象流的输出同时需要给与一个底层的流对象作为参数ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);// 2 序列化写入操作// 创建pojo对象,Student stu = new Student("adi", 13);oos.writeObject(stu);// 3 关闭oos.close();// Exception in thread "main" java.io.NotSerializableException:// review.ObjIO.Student// 对象不可写入的异常。对象如果想要序列化,需要实现一个Serializable接口// serializable 接口仅是一个表示,该接口中没有任何需要实现的接口方法声明}}
ObjectInputStream
/** @Descripttion: 使用objectinputstream实现反序列化(读取重构成对象* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-08 12:01:00* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 12:31:50*/package review.ObjIO;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;public class demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {// 1,创建独享流FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("stu.bin");ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);// 2.读取文件 反序列化文件 不可多次读取同一个对象文件,会抛出eof异常Student s = (Student)ois.readObject();// 3 关闭ois.close();System.out.println("执行完毕");System.out.println(s.toString());}}
7.编码方式
字符编码
- ISO-8859-1 收录除ASCII外,还包括西欧,希腊语,泰语,阿拉伯语,希伯来语对应的文字符号
- UTF-8 针对Unicode码表的可变长度字符编码
- GB2312 简体中文
- GBK 健体中文,扩充
- BIG 台湾,繁体中文
-
8.字符流
字符流的父类(抽象类):
Reader 字符输入流
public int read(char[] c) // 从流中读取多个字符,将读到的内容存入c数组,返回实际读到的字符数,如果达到文件的尾部。返回-1 ```java /*
- @Descripttion:
- @version:
- @Author: Addicated
- @Date: 2020-11-08 13:34:09
- @LastEditors: Addicated
- @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 15:15:28 */ package review.ObjIO;
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException;
public class demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 1.创建FileReader 文件字符输入流 FileReader fr = new FileReader(“stu.bin”); // 2.读取
// 2.1 单个字符读取// int data =0;// while((data=fr.read())!=-1){// System.out.print((char)data);// }char[] buf = new char[1024];int count = 0;while ((count = fr.read(buf)) != -1) {System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, count));}// 3.关闭fr.close();}
} /*
- @Descripttion:
- @version:
- @Author: Addicated
- @Date: 2020-11-08 13:34:09
- @LastEditors: Addicated
- @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 15:15:28 */ package review.ObjIO;
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException;
public class demo3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 1.创建FileReader 文件字符输入流 FileReader fr = new FileReader(“stu.bin”); // 2.读取
// 2.1 单个字符读取// int data =0;// while((data=fr.read())!=-1){// System.out.print((char)data);// }char[] buf = new char[1024];int count = 0;while ((count = fr.read(buf)) != -1) {System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, count));}// 3.关闭fr.close();}
}
<a name="GjJcg"></a>## FileWriter- public void write(String str)// 一次写多个字符,将b数组中所有字符,写入输入流```java/** @Descripttion: 使用fileWriteer来写入文件,* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-08 15:18:12* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 16:16:33*/package review.ObjIO;import java.io.FileWriter;import java.io.IOException;public class demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1.创建一个filewriter对象FileWriter fw =new FileWriter("fwOutPut.text");// 2.写入for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {fw.write("hello this is addicated\r\n");fw.write("java no 1 ");fw.flush();}// 3关闭fw.close();}}
运用实例,,使用文件字符流来copy文件
- 注意点。使用fileReader 和 FileWriter 复制文本文件,不能复制图片或者二进制文件,因为二进制文件没有字符编码,无法被识别
```java
/*
- @Descripttion:
- @version:
- @Author: Addicated
- @Date: 2020-11-08 16:19:00
- @LastEditors: Addicated
- @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 16:33:17 */ package review.ObjIO;
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter;
public class demo5_homework { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.字符读取流这样的操作无法读除了文本意外的文件,应当使用字节流进行读取FileReader fReader = new FileReader("memo2.text");FileWriter fWriter = new FileWriter("homework.txt");// 进行读写int data =0;while((data=fReader.read())!=-1){fWriter.write(data);}// 关闭流fReader.close();fWriter.close();}
}
<a name="dzsoE"></a># 9.字符缓冲流<a name="eC2S3"></a>## 缓冲流,BufferedReader / BufferedWriter- 高效读写- 支持输入换行符- 可以一次写一行,读一行<a name="6X7Oy"></a>## BufferedReader```java/** @Descripttion:* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-08 16:49:01* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 16:59:43*/package review.ObjIO;import java.io.BufferedReader;import java.io.FileReader;public class demo6 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 字符缓冲流的学习 通过字符缓冲流读取文件FileReader fReader = new FileReader("memo1.txt");// 缓冲流需要一个输入流对象作为参数BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fReader);// 2 读取// 第一种方式读取// char[] buf = new char[1024]; // 设定读取到缓冲区的数据大小// int count =0; //// while((count=bufferedReader.read(buf))!=-1){// System.out.println(count); // count为实际读取的字符个数// System.out.println(new String(buf,0,count));// }// 第二种方式进行读取 一行一行的堵String line = null;while((line = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){// 如果line不为空,则代表仍有数据,可以继续向下进行遍历System.out.println(line);}// 关闭bufferedReader.close();}}
BufferedWriter
/** @Descripttion:* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-08 17:01:22* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 20:09:28*/package review.ObjIO;import java.io.BufferedWriter;import java.io.FileWriter;public class demo7 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// bufferedWriter 的学习和使用// 1,创建bufferedWriterFileWriter fw = new FileWriter("BUFOUT.txt");BufferedWriter bw =new BufferedWriter(fw);// 2.写入数据for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {bw.write("addicated studying bufferedWriter");bw.newLine(); // 写入一个换行符 根据操作系统决定的换行符bw.flush();}// 3,关闭流bw.close();}}
10.打印流
PrintWriter
- 封装了print() / println() 方法,支持写入后换行
- 支持数据原样打印
```java
/*
- @Descripttion: 学习printWriter
- @version:
- @Author: Addicated
- @Date: 2020-11-08 22:33:03
- @LastEditors: Addicated
- @LastEditTime: 2020-11-08 22:57:58 */ package review.ObjIO;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class demo8 { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { // 1 创建打印流 PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(“print.txt”);
// 2 打印pw.println("this is a printWriter test~");pw.println(3.14);pw.println(true);// 3 流关闭pw.close();}
}
<a name="VH60X"></a># 11.转换流<a name="MHMjG"></a>## 桥转换流:InputStreamReader / OutputStreamWriter可以将字节流转换为字符流。<br />可以设置字符的编码方式。<br />实际上是 内存中的字符,和硬盘中的字节之间的转换<a name="PR2xH"></a>### InputStreamReader```java/** @Descripttion: InputStreamReader 读取文件* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-09 14:27:10* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-09 15:04:46*/package review.StreamIO;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.InputStreamReader;public class demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 1 创建 inputStreamReader 对象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("memo1.txt");// 参数为一个文件输入流对象,还有字符编码// InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fis, "utf-8");// 如果字符编码与目标文件不一致,会输出乱码,所以在读写的时候必须保持编码一致InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fis, "gbk");// 2 读取文件int data = 0;while ((data = inputStreamReader.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char) data);}// 3.关闭流inputStreamReader.close();}}
OutputStreamWriter
/** @Descripttion: 使用outPutStreamWriter 写入文件,使用指定的编码* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-09 15:05:04* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-09 15:18:25*/package review.StreamIO;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;public class demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 创建 outPutStreamWriterFileOutputStream fOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("outputStream.txt");// 作为参数需要字节输出流OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fOutputStream, "utf-8");// 2进行写入for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {osw.write("我爱徐卓轶\r\n");osw.flush();}// 3 关闭流osw.close();}}
12.File类
- 概念:代表物理盼复中的一个文件或者盼复中的一个文件或者文件夹
文件操作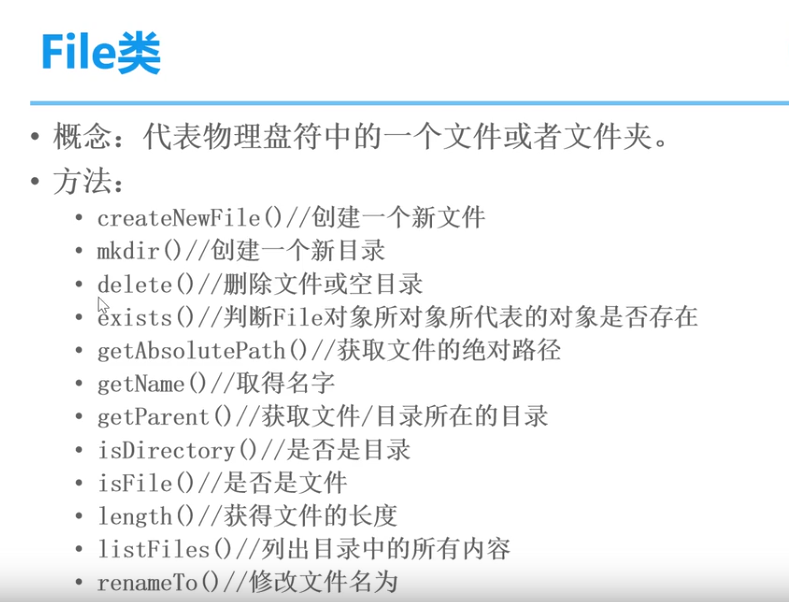
/** @Descripttion: 演示file类的使用* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-09 15:46:17* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-09 16:58:00*/package review.StreamIO;import java.io.File;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.Date;public class FileC {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 分隔符// 文件操作// 文件夹操作separator();fileOpe();dirOper();}// 分隔符public static void separator() {System.out.println("路径分隔符" + File.pathSeparator);System.out.println("名称分隔符" + File.separator);}// 文件操作public static void fileOpe() throws IOException {// 1.创建文件// 创建文件对象,然后使用对象的createNewFile方法File file = new File("newFile.txt");System.out.println(file.toString());// 判断文件是否存在 真 为存在,假 为不存在if (!(file.exists())) {boolean b = file.createNewFile();System.out.println("创建结果:" + b);}// 2 删除文件// 直接删除System.out.println("删除结果:" + file.delete());// 使用jvm退出时进行删除// file.deleteOnExit();// Thread.sleep(5000);// 3 获取文件信息System.out.println("获取文件的绝对路径:" + file.getAbsolutePath());System.out.println("获取路径:" + file.getPath());System.out.println("获取名称:" + file.getName());System.out.println("获取父目录:" + file.getParent());System.out.println("获得文件长度:" + file.length());System.out.println("获得文件的创建时间:" + new Date(file.lastModified()).toLocaleString());// 4 判断System.out.println("是否可写" + file.canWrite());System.out.println("是否可读" + file.canRead());System.out.println("是否可执行" + file.canExecute());System.out.println("是否是文件" + file.isFile());System.out.println("是否隐藏" + file.isHidden());}// 文件夹操作public static void dirOper() {// 1.创建文件夹File dir = new File("D:\\addicated\\test");if (!(dir.exists())) {System.out.println(dir.mkdirs());// 返回为布尔型// dir.mkdirs();// 创建多级目录// dir.mkdir(); // 创建单级目录}// 2 删除文件夹// 直接删除 ,,使用jvm删除dir.delete(); // 直接删除,只能删除空目录,且是最后一个目录// jvm进行删除dir.deleteOnExit();// 3 获取文件夹信息System.out.println("获取绝对路径:" + dir.getAbsolutePath());System.out.println("获取路径:" + dir.getPath());System.out.println("获取文件夹名称:" + dir.getName());System.out.println("获取父级目录:" + dir.getParent());System.out.println("获得文件的创建时间:" + new Date(dir.lastModified()).toLocaleString());// 4 判断System.out.println("是否是文件夹:" + dir.isDirectory());System.out.println("是否是隐藏的" + dir.isHidden());// 5 遍历文件夹File dir2 = new File("D:\\");String[] files = dir2.list();File[] f1 = dir2.listFiles(); // listFiles 返回的是file类型的数组for (String string : files) {System.out.println(string);}}}
13.FileFilter接口
- public interface FileFilter
- boolean accept(File pathname)
当调用File类中的listFiles()方法时,支持传入FileFilter接口接口实现类,对获取文件进行过滤,只有满足条件的文件的才可出现在listFiles()的返回值中
// 通过lamda表达式的方式重写accept方法 即 进行过滤的规则,然后达到规则System.out.println("---------演示 fileFileter接口的使用");File[] f2= dir2.listFiles(new FileFilter(){@Overridepublic boolean accept(File pathname) {if(pathname.getName().endsWith(".pdf")){return true;}return false;}});for (File file : f2) {System.out.println(file.getName());}}
14.递归遍历和递归删除
案例,递归遍历文件夹,包括子文件夹
```java /*- @Descripttion:
- @version:
- @Author: Addicated
- @Date: 2020-11-09 18:13:20
- @LastEditors: Addicated
- @LastEditTime: 2020-11-09 18:18:25 */ package review.StreamIO;
import java.io.File;
public class case1 { public static void main(String[] args) { listDir(new File(“D:\“));
// 递归遍历文件夹}public static void listDir(File dir) {File[] files = dir.listFiles(); // 返回为file类型的数组,System.out.println(dir.getAbsolutePath());if (files != null && files.length > 0) { // 对其意义判断,只要是目录,就进行for (File file : files) {if (file.isDirectory()) {listDir(file);// 这个地方用到了递归 ,} else {System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());}}}}// 递归删除文件夹public static void deleteDir(File dir) {File[] files = dir.listFiles();// 首先判断files对象不为空,长度大于0if (files != null && files.length > 0) {for (File file : files) {if(file.isDirectory()){deleteDir(file); // 如果是目录,就递归删除}else{// 删除文件System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()+"删除" + file.delete());}}}System.out.println(dir.getAbsolutePath()+"删除" + dir.delete());}
}
<a name="DScyN"></a># 15. 补充 Properties- properties 属性集合 继承hashtable 线程安全- 特点- 存储属性名和属性值- 属性名和属性值都是字符串类型- 没有泛型- 和流有关```java/** @Descripttion:* @version:* @Author: Addicated* @Date: 2020-11-09 18:34:46* @LastEditors: Addicated* @LastEditTime: 2020-11-09 18:45:28*/package review.StreamIO;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileNotFoundException;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IOException;import java.io.PrintWriter;import java.util.Properties;import java.util.Set;public class properties {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1 创建集合Properties properties = new Properties();// 2 添加数据properties.setProperty("username", "addicated");properties.setProperty("age", "26");System.out.println(properties.toString());// 3 遍历方式// keyset 取key的set集合// entrySet 取 键值对的集合// stringPropertyNames() 返回所有属性名集合Set<String> names = properties.stringPropertyNames();for (String string : names) {System.out.println(string);// 取值的话可以根据键来进行对应值的取System.out.println(properties.getProperty(string));}// 4 和流有关的方法// =======list方法// PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("print.txt");// properties.list(pw);// pw.close(); // 将properties集合中的属性写入到本地的文件中/// -------store 方法// FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("print.properties");// properties.store(fos, "first commit ");// fos.close();// --------load 方法Properties p1= new Properties();FileInputStream fis =new FileInputStream("print.properties");p1.load(fis);fis.close();System.out.println(p1.stringPropertyNames());}}
总结
流的概念
流的分类
序列化,反序列化
讲对象通过流写入文件,成为序列化
吧对象从流中读到内存,叫反序列化
File对象
代表物理盼复中的一个文件或者文件夹
IO框架图解