- JDBC中的事务是自动提交的,什么是自动提交?
- 只要执行任何一条DML语句,则自动提交一次。这是JDBC默认的事务行为。
- 但是在实际的业务当中,通常都是N条DML语句共同联合才能完成
- 必须保证这些DML语句在同一个事务中同时成功或者同时失败
以下程序演示JDBC事务的自动提交(简单的银行转账业务)
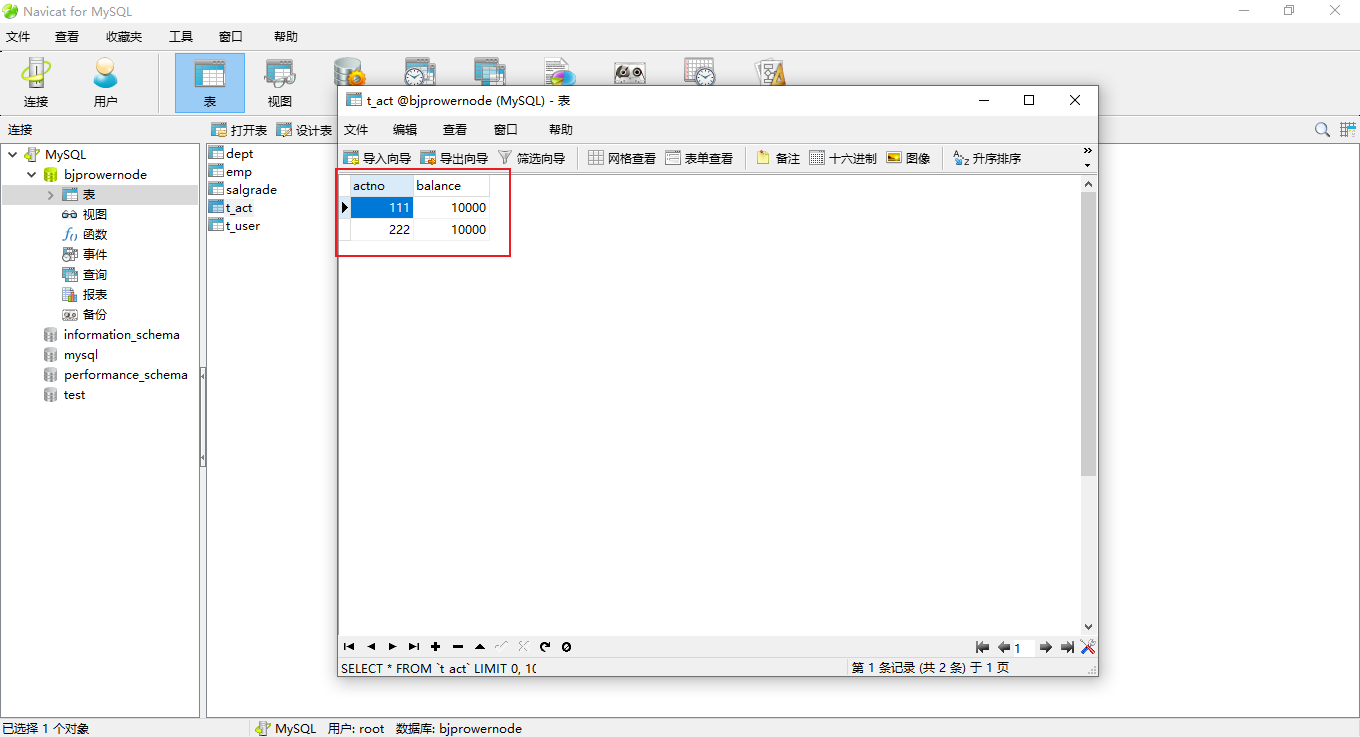
建表:t_act
drop table if exists t_act;create table t_act(actno int,balance double(7,2) -- 注意,7表示有效数字个数,2表示小数位个数);insert into t_act(actno,balance) values(111,20000);insert into t_act(actno,balance) values(222,0);commit;select * from t_act;
编写业务 ```java package com.glutnn.test;
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBCTest04 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bjprowernode","root","2000");
String sql = "update t_act set balance = ? where actno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setDouble(1,10000);
ps.setInt(2,111);
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
//给两次赋值之间设置一个空指针异常
String s = null;
s.toString();
ps.setDouble(1,10000);
ps.setInt(2,222);
count += ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count == 2 ? "转账成功" : "转账失败");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (ps == null) {
ps.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (conn == null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
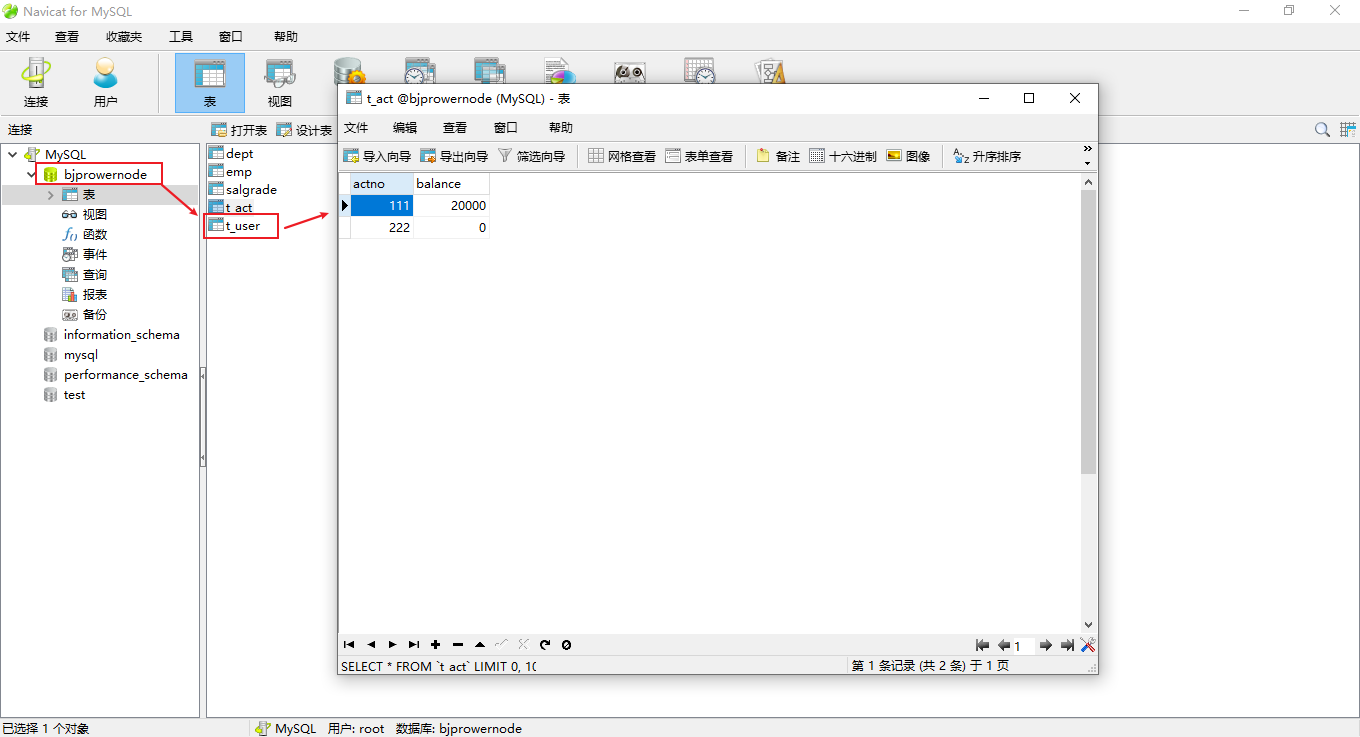
- 此时程序出现异常
- 发现转账不仅失败了,而且还丢失了数据,账户111丢失了10000元!! 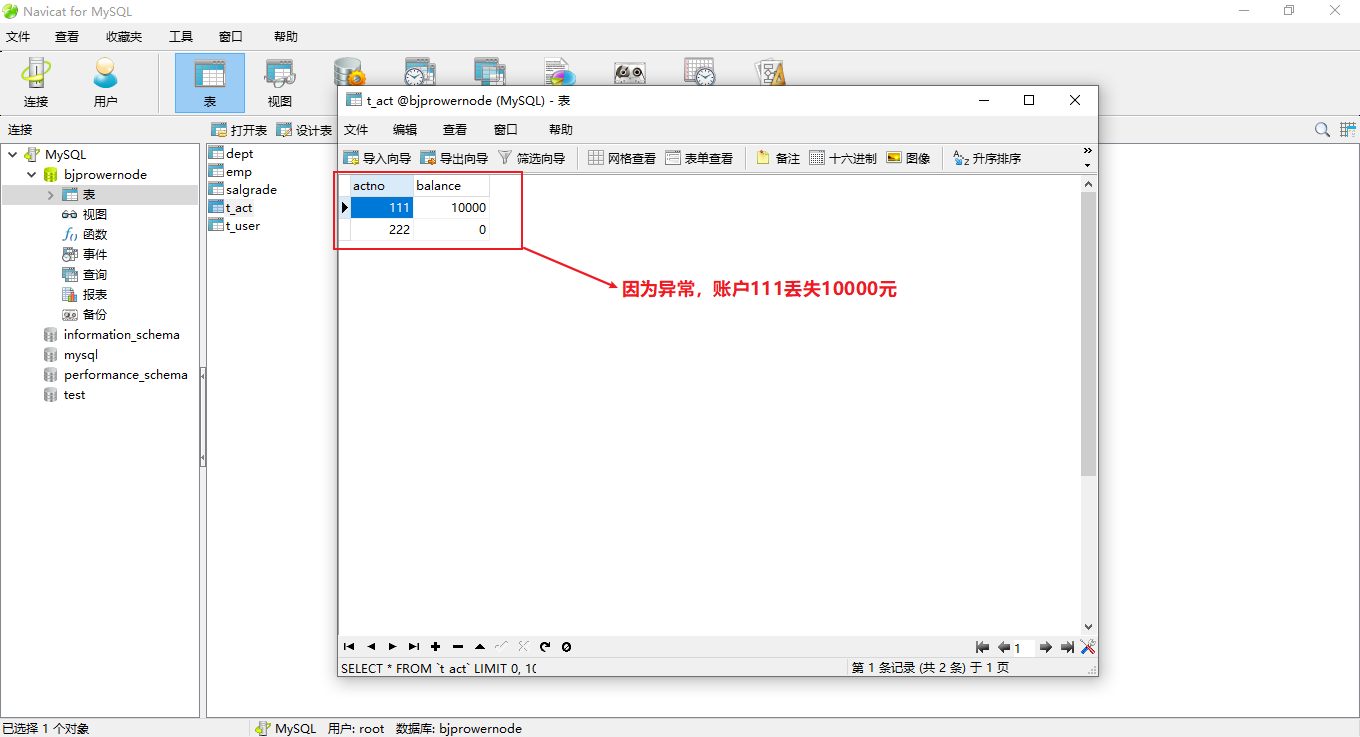
- 禁用JDBC的事务自动提交
```java
package com.glutnn.test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBCTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bjprowernode","root","2000");
//将自动提交设置为手动提交
conn.setAutoCommit(false);//开启事务
String sql = "update t_act set balance = ? where actno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setDouble(1,10000);
ps.setInt(2,111);
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
ps.setDouble(1,10000);
ps.setInt(2,222);
count += ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count == 2 ? "转账成功" : "转账失败");
//程序可以执行到这里,说明没有异常,事务结束,手动提交数据
conn.commit();//提交事务
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
//回滚事务
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.rollback();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (ps == null) {
ps.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (conn == null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 此时程序成功执行,即使存在异常,也不会丢失数据