1. 源码简介
官网简介:Run multiple promise-returning & async functions with limited concurrency
简单理解,控制有限的并发数量,运行多个promise-returning和async functions。就是常见的控制并发请求,刚好有一个实践的场景:大文件上传,看完这个库看看能不能派上用场。
2. 测试用例
测试用例有点难看懂,花费了不少时间。地址:https://github1s.com/sindresorhus/p-limit/blob/main/test.js
concurrency: 1,这个测试用例测试并发数量为1时的场景。
test('concurrency: 1', async t => {const input = [[10, 300],[20, 200],[30, 100],];const end = timeSpan();const limit = pLimit(1);const mapper = ([value, ms]) => limit(async () => {await delay(ms);return value;});// 判断输出的值是否等于[10,20,30]t.deepEqual(await Promise.all(input.map(x => mapper(x))), [10, 20, 30]);// 判断执行时间是否在预期内t.true(inRange(end(), {start: 590, end: 650}));});
concurrency: 4,测试多个并发时,running数是否小于等于并发数
- non-promise returning function,测试非promise返回值
- continues after sync throw,测试抛出异常的情况是否正常执行
- accepts additional arguments,没太看懂这个,字面意思是接受其他参数
- does not ignore errors,测试抛出错误的情况,能否正常接收到错误的值
- activeCount and pendingCount properties,测试activeCount和pendingCount属性
- clearQueue,清空队列
- throws on invalid concurrency argument,测试输入无效参数时的情况
3. 源码
简单写写注释,总结流程:
- 先校验
- 生成一个promise,入队操作是,queue.enqueue(run.bind(…)),意思是把请求放在队列里了
- 如果当前执行数 < 并发数,且队列中存在数据,出队运行请求;否则就在队列里等着吧。
当上一个运行完了(run函数的await result),会唤醒next()函数,出队运行请求。 ```javascript import Queue from ‘yocto-queue’; export default function pLimit(concurrency) { // 检验参数是Integer,且校验最大最小值 if (!((Number.isInteger(concurrency) || concurrency === Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY) && concurrency > 0)) {
throw new TypeError('Expected `concurrency` to be a number from 1 and up');
} // 并发队列 const queue = new Queue(); // 当前正在执行的请求数 let activeCount = 0; // 执行下一个请求 const next = () => {
activeCount--;if (queue.size > 0) {
// 出队操作并执行
queue.dequeue()();}
}; // 执行请求任务 const run = async (fn, resolve, args) => { // 当前执行请求数+1
activeCount++;const result = (async () => fn(...args))();
// resolve出去
resolve(result);try {
// await 保证执行顺序
await result;} catch {}next();
}; // 入队操作 const enqueue = (fn, resolve, args) => {
queue.enqueue(run.bind(undefined, fn, resolve, args));(async () => {await Promise.resolve();
// 如果当前执行数 < 并发数,且队列还有请求
if (activeCount < concurrency && queue.size > 0) {// 出队运行queue.dequeue()();}})();
}; // 生成一个promise,入队 const generator = (fn, …args) => new Promise(resolve => {
enqueue(fn, resolve, args);
});
Object.defineProperties(generator, {
activeCount: {get: () => activeCount,},pendingCount: {get: () => queue.size,},clearQueue: {value: () => {queue.clear();},},
}); return generator; }
4. 总结
这个库应用场景挺广泛的,明天就加到项目里去。可以多看,面试也经常会被问到。
实际使用场景,大文件切片上传并发控制(不控制并发,会有大量接口请求处于pending状态,会有超时的风险)。
代码: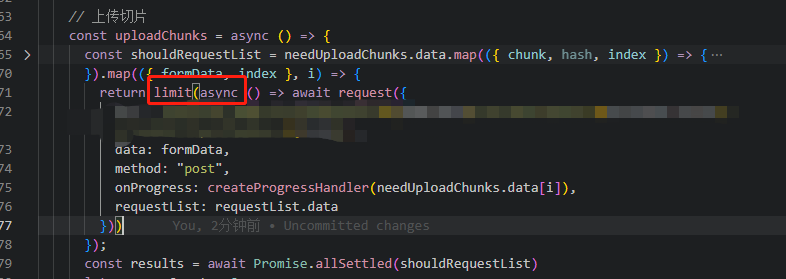
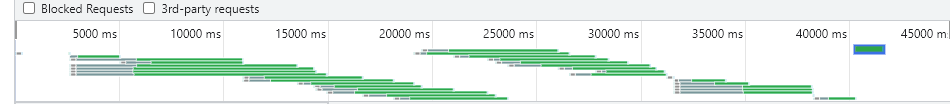
效果: