循环依赖
两个类都用构造器注入对方
解决:打破循环,把其中一个类用非构造器注入
单例多例
线程安全
注入方式:
手动注入:需要手动指定哪个 bean 注入到当前对象中
- setter
- 构造方法
自动注入:根据类型或名字,自动将容器中的 bean 注入当前对象
- XML 中指定 autowire 属性
- byName:取 setter 方法的后缀名作为将要注入 bean 名称。优选走构造方法
- byType
- no:默认
- @AutoWired
- 属性
- 构造
- 方法
开启注解:
- xml 中
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 容器
@Scope、@Bean、@Autowired
Bean 作用域:
- singleton:单例,默认作用域。
- prototype:原型,每次创建一个新对象。
- request:请求,每次 Http 请求创建一个新对象,适用于 WebApplicationContext 环境下。
- session:会话,同一个会话共享一个实例,不同会话使用不用的实例。
- global-session:全局会话,所有会话共享一个实例。
注入注解区别:
@Autowired, @Resource and @Inject
1、包不同
- @Autowired 是 spring 自带的,spring-beans-xx.jar
- @Inject 是 JSR330 规范实现的,javax.inject01.jar
- @Resource 是 JSR250 规范实现的,rt.jar
2、@Autowired、@Inject 用法基本一样,不同的是@Autowired 有一个request属性
3、@Autowired、@Inject 是默认按照类型匹配的,@Resource 是按照名称匹配的
4、@Autowired 如果需要按照名称匹配需要和 @Qualifier 一起使用,@Inject 和 @Name 一起使用
注入过程:
AbstractApplicationContext.refresh() 方法
@Overridepublic void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {// Prepare this context for refreshing.prepareRefresh();// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);try {// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Initialize message source for this context.initMessageSource();// Initialize event multicaster for this context.initApplicationEventMulticaster();// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.onRefresh();// Check for listener beans and register them.registerListeners();// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// Last step: publish corresponding event.finishRefresh();}catch (BeansException ex) {if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);}// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.destroyBeans();// Reset 'active' flag.cancelRefresh(ex);// Propagate exception to caller.throw ex;}finally {// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...resetCommonCaches();}}}
从 refresh() 到开始类扫描 doScan():
对于 SpringBoot 来说,首先从 Application 类所在的包作为 basePackages,然后扫描同包以及子包下的全部类(.class 文件):
- 可以指定多个 basePackages
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.scanCandidateComponents() :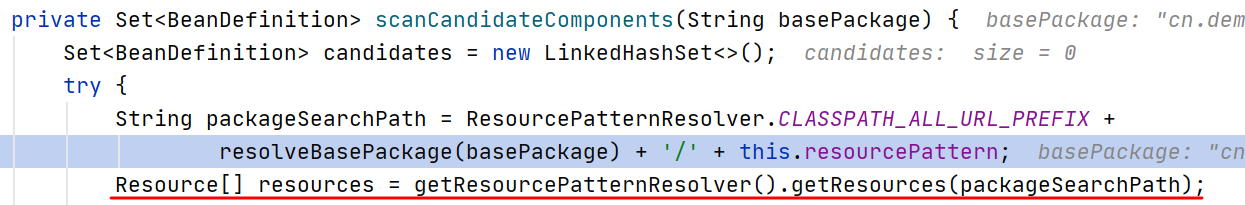
除了 Application 类所在的包,还可以通过注解传入:
- 程序中通过获取 basePackages 和 basePackageClasses 这两个 attribute 来指定额外的扫描类 ```java // Spirng context 中通过 ComponentScan 注解来传入这俩个属性 @ComponentScan(basePackages = {“com.demojie.*”}, basePackageClasses = {“”})
// SpringBoot 中的 SpringBootApplication 注解给 ComponentScan 的这两个属性设置了别名 // 这样就不需要额外再使用 ComponentScan 注解了 @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {“cn.demojie”}, scanBasePackageClasses = {“”})
将扫描的代码提取出来:
- 最终可以得到指定类所在包以及子包下的所有 .class 文件
- 用到的类都是 spring-core 库中的
```java
package cn.demojie.simplehttpserver;
import org.springframework.core.env.StandardEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String resourcePattern = "**/*.class";
// 获取指定类的包名
String basePackage = ClassUtils.getPackageName(Test.class);
// 转换成路径的形式
String resourcePathForClass = ClassUtils.convertClassNameToResourcePath(new StandardEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(basePackage));
// 拼接成搜索表达式
// classpath*:cn/demojie/simplehttpserver/**/*.class
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + resourcePathForClass + '/' + resourcePattern;
// 扫描,得到 FileSystemResource 数组,指向了每个 .class 文件
Resource[] resources = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
for (Resource resource : resources) {
System.out.println(resource);
}
}
}
Spring 使用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用注解。需要指定配置类
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
// 使用 xml
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spirng.xml");
// 获取 bean
HelloController helloController = applicationContext.getBean("helloController", HelloController.class);
helloController.hello();
}
@ComponentScan("com.demojie")
public class AppConfig {
}

