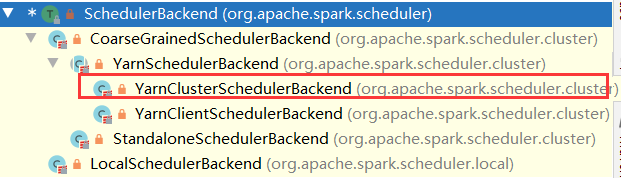
一、环境准备(Yarn集群)
1、Driver、Executor
二、组件通信
1、Driver => Executor
2、Executor => Driver
3、Executor => Executor
三、作业执行
1、RDD依赖
2、阶段的划分
3、任务的切分
4、任务的调度
5、任务的执行
四、Shuffle
1、Shuffle的原理和执行过程
2、Shuffle写磁盘
3、Shuffle读取磁盘
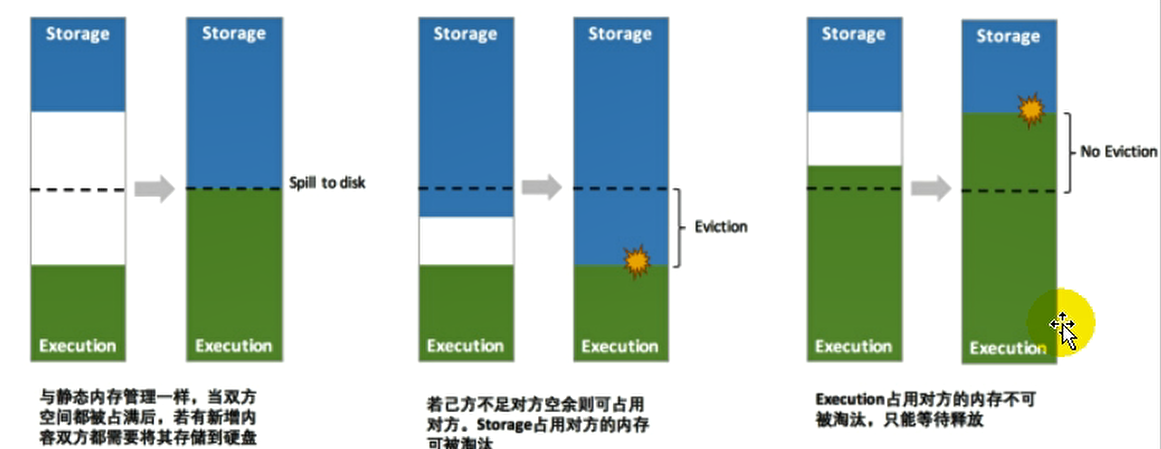
五、内存的管理
1、内存的分类
2、内存的配置
一、环境准备
1、起点:SparkSubmit
我们要向yarn集群提交任务,需要使用bin/spark-submit脚本来提交任务,
#!/usr/bin/env bashif [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; thensource "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-homefi# disable randomized hash for string in Python 3.3+export PYTHONHASHSEED=0# 执行spark-classexec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@"
执行spark-class脚本去执行org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit类。
而spark-classs
#!/usr/bin/env bash## Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at## http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0## Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and# limitations under the License.#if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; thensource "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-homefi. "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/load-spark-env.sh# Find the java binaryif [ -n "${JAVA_HOME}" ]; thenRUNNER="${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java"elseif [ "$(command -v java)" ]; thenRUNNER="java"elseecho "JAVA_HOME is not set" >&2exit 1fifi# Find Spark jars.if [ -d "${SPARK_HOME}/jars" ]; thenSPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/jars"elseSPARK_JARS_DIR="${SPARK_HOME}/assembly/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/jars"fiif [ ! -d "$SPARK_JARS_DIR" ] && [ -z "$SPARK_TESTING$SPARK_SQL_TESTING" ]; thenecho "Failed to find Spark jars directory ($SPARK_JARS_DIR)." 1>&2echo "You need to build Spark with the target \"package\" before running this program." 1>&2exit 1elseLAUNCH_CLASSPATH="$SPARK_JARS_DIR/*"fi# Add the launcher build dir to the classpath if requested.if [ -n "$SPARK_PREPEND_CLASSES" ]; thenLAUNCH_CLASSPATH="${SPARK_HOME}/launcher/target/scala-$SPARK_SCALA_VERSION/classes:$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH"fi# For testsif [[ -n "$SPARK_TESTING" ]]; thenunset YARN_CONF_DIRunset HADOOP_CONF_DIRfi# The launcher library will print arguments separated by a NULL character, to allow arguments with# characters that would be otherwise interpreted by the shell. Read that in a while loop, populating# an array that will be used to exec the final command.## The exit code of the launcher is appended to the output, so the parent shell removes it from the# command array and checks the value to see if the launcher succeeded.build_command() {"$RUNNER" -Xmx128m $SPARK_LAUNCHER_OPTS -cp "$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH" org.apache.spark.launcher.Main "$@"printf "%d\0" $?}# Turn off posix mode since it does not allow process substitutionset +o posixCMD=()DELIM=$'\n'CMD_START_FLAG="false"while IFS= read -d "$DELIM" -r ARG; doif [ "$CMD_START_FLAG" == "true" ]; thenCMD+=("$ARG")elseif [ "$ARG" == $'\0' ]; then# After NULL character is consumed, change the delimiter and consume command string.DELIM=''CMD_START_FLAG="true"elif [ "$ARG" != "" ]; thenecho "$ARG"fifidone < <(build_command "$@")COUNT=${#CMD[@]}LAST=$((COUNT - 1))LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE=${CMD[$LAST]}# Certain JVM failures result in errors being printed to stdout (instead of stderr), which causes# the code that parses the output of the launcher to get confused. In those cases, check if the# exit code is an integer, and if it's not, handle it as a special error case.if ! [[ $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]; thenecho "${CMD[@]}" | head -n-1 1>&2exit 1fiif [ $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODE != 0 ]; thenexit $LAUNCHER_EXIT_CODEfiCMD=("${CMD[@]:0:$LAST}")exec "${CMD[@]}"
最终执行就是
java -cp org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit -Xmx1g xxxxxxxx
要能够执行java,就需要执行这个类的main方法,所以一切的起点就在SparkSubmit中,Scala中的main方法肯定是在object伴生对象中的。
2、向Yarn提交程序
- super.doSubmit(args)
- 解析参数值 parseArguments(args: Array[String])
- new SparkSubmitArguments
- 解析参数 parse(args.asJava),通过正则表达式分割出来
- handle处理参数,获取到每个参数的值
- 校验合法参数 validateSubmitArguments,获取到action=SUBMIT
- SparkSubmitOptionParser中将每个参数解析得到
- 解析参数 parse(args.asJava),通过正则表达式分割出来
- new SparkSubmitArguments
- 提交任务 submit(appArgs, uninitLog)
- runMain执行main方法
- 准备环境 prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)
- 判断当前是哪种环境:kubernetes、yarn、standalone等,获取childMainClass信息
- 反射加载当前环境的Class
- 根据是否继承了SparkApplication创建不同对象
- start启动
- 准备环境 prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)
- runMain执行main方法
- 解析参数值 parseArguments(args: Array[String])
1、SparkSubmit的main方法开始提交任务
override def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {// 创建一个SparkSubmitval submit = new SparkSubmit() {self =>override protected def parseArguments(args: Array[String]): SparkSubmitArguments = {// 准备一个SparkSubmitArguments将命令行启动参数传入new SparkSubmitArguments(args) {override protected def logInfo(msg: => String): Unit = self.logInfo(msg)override protected def logWarning(msg: => String): Unit = self.logWarning(msg)override protected def logError(msg: => String): Unit = self.logError(msg)}}override protected def logInfo(msg: => String): Unit = printMessage(msg)override protected def logWarning(msg: => String): Unit = printMessage(s"Warning: $msg")override protected def logError(msg: => String): Unit = printMessage(s"Error: $msg")override def doSubmit(args: Array[String]): Unit = {try {// 父类提交super.doSubmit(args)} catch {case e: SparkUserAppException =>// 异常退出exitFn(e.exitCode)}}}// 执行提交submit.doSubmit(args)}
1.1、处理提交parseArguments。
def doSubmit(args: Array[String]): Unit = {// Initialize logging if it hasn't been done yet. Keep track of whether logging needs to// be reset before the application starts.val uninitLog = initializeLogIfNecessary(true, silent = true)// 解析参数val appArgs = parseArguments(args)if (appArgs.verbose) {logInfo(appArgs.toString)}// 匹配执行appArgs.action match {case SparkSubmitAction.SUBMIT => submit(appArgs, uninitLog)case SparkSubmitAction.KILL => kill(appArgs)case SparkSubmitAction.REQUEST_STATUS => requestStatus(appArgs)case SparkSubmitAction.PRINT_VERSION => printVersion()}}
1.1.1、解析命令行启动参数:new 了一个SparkSubmitArguments,准备了很多参数并且调用 parse(args.asJava)解析
private[deploy] class SparkSubmitArguments(args: Seq[String], env: Map[String, String] = sys.env)extends SparkSubmitArgumentsParser with Logging {var master: String = nullvar deployMode: String = nullvar executorMemory: String = nullvar executorCores: String = nullvar totalExecutorCores: String = nullvar propertiesFile: String = nullvar driverMemory: String = nullvar driverExtraClassPath: String = nullvar driverExtraLibraryPath: String = nullvar driverExtraJavaOptions: String = nullvar queue: String = nullvar numExecutors: String = nullvar files: String = nullvar archives: String = nullvar mainClass: String = null.........................// 解析参数parse(args.asJava)// Populate `sparkProperties` map from properties filemergeDefaultSparkProperties()// Remove keys that don't start with "spark." from `sparkProperties`.ignoreNonSparkProperties()// Use `sparkProperties` map along with env vars to fill in any missing parametersloadEnvironmentArguments()useRest = sparkProperties.getOrElse("spark.master.rest.enabled", "false").toBoolean....................// Action should be SUBMIT unless otherwise specified// action被赋予默认值SUBMITaction = Option(action).getOrElse(SUBMIT)// 在这里校验参数validateArguments()private def validateArguments(): Unit = {action match {// 校验合法参数case SUBMIT => validateSubmitArguments()case KILL => validateKillArguments()case REQUEST_STATUS => validateStatusRequestArguments()case PRINT_VERSION =>}}}
1.1.2、解析参数,通过正则表达式解析得到参数名和值,并调用handle处理
protected final void parse(List<String> args) {// 通过正则表达式解析Pattern eqSeparatedOpt = Pattern.compile("(--[^=]+)=(.+)");int idx = 0;for (idx = 0; idx < args.size(); idx++) {String arg = args.get(idx);String value = null;Matcher m = eqSeparatedOpt.matcher(arg);if (m.matches()) {// 解析到命令行参数和值arg = m.group(1);value = m.group(2);}// Look for options with a value.String name = findCliOption(arg, opts);if (name != null) {if (value == null) {if (idx == args.size() - 1) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("Missing argument for option '%s'.", arg));}idx++;value = args.get(idx);}if (!handle(name, value)) {break;}continue;}// Look for a switch.name = findCliOption(arg, switches);if (name != null) {// 处理这些参数和值if (!handle(name, null)) {break;}continue;}if (!handleUnknown(arg)) {break;}}if (idx < args.size()) {idx++;}handleExtraArgs(args.subList(idx, args.size()));}
1.1.3、handle处理参数,得到所有值
override protected def handle(opt: String, value: String): Boolean = {opt match {case NAME =>name = valuecase MASTER =>master = valuecase CLASS =>mainClass = valuecase DEPLOY_MODE =>if (value != "client" && value != "cluster") {error("--deploy-mode must be either \"client\" or \"cluster\"")}deployMode = valuecase NUM_EXECUTORS =>numExecutors = valuecase TOTAL_EXECUTOR_CORES =>totalExecutorCores = valuecase EXECUTOR_CORES =>executorCores = valuecase EXECUTOR_MEMORY =>executorMemory = valuecase DRIVER_MEMORY =>driverMemory = valuecase DRIVER_CORES =>driverCores = valuecase DRIVER_CLASS_PATH =>driverExtraClassPath = valuecase DRIVER_JAVA_OPTIONS =>driverExtraJavaOptions = valuecase DRIVER_LIBRARY_PATH =>driverExtraLibraryPath = valuecase PROPERTIES_FILE =>propertiesFile = valuecase KILL_SUBMISSION =>submissionToKill = valueif (action != null) {error(s"Action cannot be both $action and $KILL.")}action = KILLcase STATUS =>submissionToRequestStatusFor = valueif (action != null) {error(s"Action cannot be both $action and $REQUEST_STATUS.")}action = REQUEST_STATUScase SUPERVISE =>supervise = truecase QUEUE =>queue = valuecase FILES =>files = Utils.resolveURIs(value)case PY_FILES =>pyFiles = Utils.resolveURIs(value)case ARCHIVES =>archives = Utils.resolveURIs(value)case JARS =>jars = Utils.resolveURIs(value)case PACKAGES =>packages = valuecase PACKAGES_EXCLUDE =>packagesExclusions = valuecase REPOSITORIES =>repositories = valuecase CONF =>val (confName, confValue) = SparkSubmitUtils.parseSparkConfProperty(value)sparkProperties(confName) = confValuecase PROXY_USER =>proxyUser = valuecase PRINCIPAL =>principal = valuecase KEYTAB =>keytab = valuecase HELP =>printUsageAndExit(0)case VERBOSE =>verbose = truecase VERSION =>action = SparkSubmitAction.PRINT_VERSIONcase USAGE_ERROR =>printUsageAndExit(1)case _ =>error(s"Unexpected argument '$opt'.")}action != SparkSubmitAction.PRINT_VERSION}
这些参数就是SparkSubmitOptionParser定义的,通过命令行传的值
protected final String CLASS = "--class";protected final String CONF = "--conf";protected final String DEPLOY_MODE = "--deploy-mode";protected final String DRIVER_CLASS_PATH = "--driver-class-path";protected final String DRIVER_CORES = "--driver-cores";protected final String DRIVER_JAVA_OPTIONS = "--driver-java-options";protected final String DRIVER_LIBRARY_PATH = "--driver-library-path";protected final String DRIVER_MEMORY = "--driver-memory";protected final String EXECUTOR_MEMORY = "--executor-memory";protected final String FILES = "--files";protected final String JARS = "--jars";protected final String KILL_SUBMISSION = "--kill";protected final String MASTER = "--master";protected final String NAME = "--name";protected final String PACKAGES = "--packages";protected final String PACKAGES_EXCLUDE = "--exclude-packages";protected final String PROPERTIES_FILE = "--properties-file";protected final String PROXY_USER = "--proxy-user";protected final String PY_FILES = "--py-files";protected final String REPOSITORIES = "--repositories";protected final String STATUS = "--status";protected final String TOTAL_EXECUTOR_CORES = "--total-executor-cores";..........................
action有了值,之后,就回到doSubmit中,可以提交了。
1.2、提交任务,runMain
private def submit(args: SparkSubmitArguments, uninitLog: Boolean): Unit = {// 3、def doRunMain(): Unit = {if (args.proxyUser != null) {val proxyUser = UserGroupInformation.createProxyUser(args.proxyUser,UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser())try {// 有没有代理服务器,proxyUser.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction[Unit]() {override def run(): Unit = {runMain(args, uninitLog)}})} catch {case e: Exception =>// Hadoop's AuthorizationException suppresses the exception's stack trace, which// makes the message printed to the output by the JVM not very helpful. Instead,// detect exceptions with empty stack traces here, and treat them differently.if (e.getStackTrace().length == 0) {error(s"ERROR: ${e.getClass().getName()}: ${e.getMessage()}")} else {throw e}}} else {// runMainrunMain(args, uninitLog)}}// In standalone cluster mode, there are two submission gateways:// (1) The traditional RPC gateway using o.a.s.deploy.Client as a wrapper// (2) The new REST-based gateway introduced in Spark 1.3// The latter is the default behavior as of Spark 1.3, but Spark submit will fail over// to use the legacy gateway if the master endpoint turns out to be not a REST server.// 1、判断是不是spark集群,是rest风格,我们是yarn集群,所以走下面if (args.isStandaloneCluster && args.useRest) {try {logInfo("Running Spark using the REST application submission protocol.")doRunMain()} catch {// Fail over to use the legacy submission gatewaycase e: SubmitRestConnectionException =>logWarning(s"Master endpoint ${args.master} was not a REST server. " +"Falling back to legacy submission gateway instead.")args.useRest = falsesubmit(args, false)}// In all other modes, just run the main class as prepared} else {// 2、走这里doRunMain()}}
1.2.1、判断当前是哪种环境,得到childMainClass。当前yarn环境获取到
private[deploy] val YARN_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASS = “org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplication”
if (isYarnCluster) {childMainClass = YARN_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASSif (args.isPython) {childArgs += ("--primary-py-file", args.primaryResource)childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.PythonRunner")} else if (args.isR) {val mainFile = new Path(args.primaryResource).getNamechildArgs += ("--primary-r-file", mainFile)childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.RRunner")} else {if (args.primaryResource != SparkLauncher.NO_RESOURCE) {childArgs += ("--jar", args.primaryResource)}childArgs += ("--class", args.mainClass)}if (args.childArgs != null) {args.childArgs.foreach { arg => childArgs += ("--arg", arg) }}}if (isMesosCluster) {assert(args.useRest, "Mesos cluster mode is only supported through the REST submission API")childMainClass = REST_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASSif (args.isPython) {// Second argument is main classchildArgs += (args.primaryResource, "")if (args.pyFiles != null) {sparkConf.set(SUBMIT_PYTHON_FILES, args.pyFiles.split(",").toSeq)}} else if (args.isR) {// Second argument is main classchildArgs += (args.primaryResource, "")} else {childArgs += (args.primaryResource, args.mainClass)}if (args.childArgs != null) {childArgs ++= args.childArgs}}if (isKubernetesCluster) {childMainClass = KUBERNETES_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASSif (args.primaryResource != SparkLauncher.NO_RESOURCE) {if (args.isPython) {childArgs ++= Array("--primary-py-file", args.primaryResource)childArgs ++= Array("--main-class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.PythonRunner")} else if (args.isR) {childArgs ++= Array("--primary-r-file", args.primaryResource)childArgs ++= Array("--main-class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.RRunner")}else {childArgs ++= Array("--primary-java-resource", args.primaryResource)childArgs ++= Array("--main-class", args.mainClass)}} else {childArgs ++= Array("--main-class", args.mainClass)}if (args.childArgs != null) {args.childArgs.foreach { arg =>childArgs += ("--arg", arg)}}}
1.2.2、反射加载当前环境的类
1.2.3、判断是否继承SparkApplication,创建SparkApplication或者JavaMainApplication
1.2.4、启动
private def runMain(args: SparkSubmitArguments, uninitLog: Boolean): Unit = {// 1、判断环境val (childArgs, childClasspath, sparkConf, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)// Let the main class re-initialize the logging system once it starts.if (uninitLog) {Logging.uninitialize()}if (args.verbose) {logInfo(s"Main class:\n$childMainClass")logInfo(s"Arguments:\n${childArgs.mkString("\n")}")// sysProps may contain sensitive information, so redact before printinglogInfo(s"Spark config:\n${Utils.redact(sparkConf.getAll.toMap).mkString("\n")}")logInfo(s"Classpath elements:\n${childClasspath.mkString("\n")}")logInfo("\n")}val loader = getSubmitClassLoader(sparkConf)for (jar <- childClasspath) {addJarToClasspath(jar, loader)}var mainClass: Class[_] = nulltry {// 2、利用反射加载childMainClassmainClass = Utils.classForName(childMainClass)} catch {case e: ClassNotFoundException =>logError(s"Failed to load class $childMainClass.")if (childMainClass.contains("thriftserver")) {logInfo(s"Failed to load main class $childMainClass.")logInfo("You need to build Spark with -Phive and -Phive-thriftserver.")}throw new SparkUserAppException(CLASS_NOT_FOUND_EXIT_STATUS)case e: NoClassDefFoundError =>logError(s"Failed to load $childMainClass: ${e.getMessage()}")if (e.getMessage.contains("org/apache/hadoop/hive")) {logInfo(s"Failed to load hive class.")logInfo("You need to build Spark with -Phive and -Phive-thriftserver.")}throw new SparkUserAppException(CLASS_NOT_FOUND_EXIT_STATUS)}// 3、判断当前类是否是继承了SparkApplication,如果继承,创建一个SparkApplication实例,// 没有就创建一个JavaMainApplicationval app: SparkApplication = if (classOf[SparkApplication].isAssignableFrom(mainClass)) {mainClass.getConstructor().newInstance().asInstanceOf[SparkApplication]} else {new JavaMainApplication(mainClass)}@tailrecdef findCause(t: Throwable): Throwable = t match {case e: UndeclaredThrowableException =>if (e.getCause() != null) findCause(e.getCause()) else ecase e: InvocationTargetException =>if (e.getCause() != null) findCause(e.getCause()) else ecase e: Throwable =>e}// 4、最终启动应用程序try {app.start(childArgs.toArray, sparkConf)} catch {case t: Throwable =>throw findCause(t)}}
3、启动应用程序
可以看到没有我们的Yarn环境,是因为我们没有引入yarn的依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId><artifactId>spark-yarn_2.12</artifactId><version>3.0.0</version></dependency>
启动程序
- 1、创建Client对象
- new YarnClientImpl
- 创建一个rmClient:ResourceManager
- new YarnClientImpl
2、Client.run()
- 提交任务
- 从rm创建一个YarnClientApplication
- 获取响应
- 准备容器环境 createContainerLaunchContext
- 如果是集群,创建org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster;否则创建org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ExecutorLauncher
- 封装applicationMaster的指令,发送给ResourceManager,让rm选择一个NodeManager启动am
- 提交任务 ```scala private[spark] class YarnClusterApplication extends SparkApplication {
override def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf): Unit = { // SparkSubmit would use yarn cache to distribute files & jars in yarn mode, // so remove them from sparkConf here for yarn mode. conf.remove(JARS) conf.remove(FILES)
// 创建Client对象并启动
new Client(new ClientArguments(args), conf, null).run() }
- 提交任务
}
创建Client```scalaprivate[spark] class Client(val args: ClientArguments,val sparkConf: SparkConf,val rpcEnv: RpcEnv)extends Logging {import Client._import YarnSparkHadoopUtil._// 一上来就创建YarnClientprivate val yarnClient = YarnClient.createYarnClientprivate val hadoopConf = new YarnConfiguration(SparkHadoopUtil.newConfiguration(sparkConf))private val isClusterMode = sparkConf.get(SUBMIT_DEPLOY_MODE) == "cluster"private val isClientUnmanagedAMEnabled = sparkConf.get(YARN_UNMANAGED_AM) && !isClusterModeprivate var appMaster: ApplicationMaster = _private var stagingDirPath: Path = _
public abstract class YarnClient extends AbstractService {@Publicpublic static YarnClient createYarnClient() {YarnClient client = new YarnClientImpl();return client;}
创建一个实现类对象,并创建ResourceManager
public YarnClientImpl() {super(YarnClientImpl.class.getName());}// 创建了一个rmClient:就是Yarn的ResourceManager@Overrideprotected void serviceStart() throws Exception {try {rmClient = ClientRMProxy.createRMProxy(getConfig(),ApplicationClientProtocol.class);// 如果配置了历史服务器和时间服务器,将这两个再启动if (historyServiceEnabled) {historyClient.start();}if (timelineServiceEnabled) {timelineClient.start();}} catch (IOException e) {throw new YarnRuntimeException(e);}super.serviceStart();}
Client.run()一上来就提交任务
def run(): Unit = {// 获取到yarn的全局任务idthis.appId = submitApplication()if (!launcherBackend.isConnected() && fireAndForget) {val report = getApplicationReport(appId)val state = report.getYarnApplicationStatelogInfo(s"Application report for $appId (state: $state)")logInfo(formatReportDetails(report))if (state == YarnApplicationState.FAILED || state == YarnApplicationState.KILLED) {throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId finished with status: $state")}} else {val YarnAppReport(appState, finalState, diags) = monitorApplication(appId)if (appState == YarnApplicationState.FAILED || finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED) {diags.foreach { err =>logError(s"Application diagnostics message: $err")}throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId finished with failed status")}if (appState == YarnApplicationState.KILLED || finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.KILLED) {throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId is killed")}if (finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.UNDEFINED) {throw new SparkException(s"The final status of application $appId is undefined")}}}
提交任务的时候,让YarnClient连接yarn集群,并创建一个Application
def submitApplication(): ApplicationId = {ResourceRequestHelper.validateResources(sparkConf)var appId: ApplicationId = nulltry {// 连接,初始化,启动clientlauncherBackend.connect()yarnClient.init(hadoopConf)yarnClient.start()logInfo("Requesting a new application from cluster with %d NodeManagers".format(yarnClient.getYarnClusterMetrics.getNumNodeManagers))// Get a new application from our RM// 创建一个applicationval newApp = yarnClient.createApplication()val newAppResponse = newApp.getNewApplicationResponse()appId = newAppResponse.getApplicationId()// The app staging dir based on the STAGING_DIR configuration if configured// otherwise based on the users home directory.val appStagingBaseDir = sparkConf.get(STAGING_DIR).map { new Path(_, UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser.getShortUserName) }.getOrElse(FileSystem.get(hadoopConf).getHomeDirectory())stagingDirPath = new Path(appStagingBaseDir, getAppStagingDir(appId))new CallerContext("CLIENT", sparkConf.get(APP_CALLER_CONTEXT),Option(appId.toString)).setCurrentContext()// Verify whether the cluster has enough resources for our AMverifyClusterResources(newAppResponse)// Set up the appropriate contexts to launch our AMval containerContext = createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse)val appContext = createApplicationSubmissionContext(newApp, containerContext)// Finally, submit and monitor the applicationlogInfo(s"Submitting application $appId to ResourceManager")yarnClient.submitApplication(appContext)launcherBackend.setAppId(appId.toString)reportLauncherState(SparkAppHandle.State.SUBMITTED)appId} catch {case e: Throwable =>if (stagingDirPath != null) {cleanupStagingDir()}throw e}}
YarnClient创建应用,创建一个YarnClientApplication
@Overridepublic YarnClientApplication createApplication()throws YarnException, IOException {ApplicationSubmissionContext context = Records.newRecord(ApplicationSubmissionContext.class);GetNewApplicationResponse newApp = getNewApplication();ApplicationId appId = newApp.getApplicationId();context.setApplicationId(appId);return new YarnClientApplication(newApp, context);}
准备容器环境createContainerLaunchContext
开始是一些jvm参数配置,后面准备am(ApplicationMaster的配置),运行java进程
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。val javaOpts = ListBuffer[String]()// Set the environment variable through a command prefix// to append to the existing value of the variablevar prefixEnv: Option[String] = None// Add Xmx for AM memoryjavaOpts += "-Xmx" + amMemory + "m"val tmpDir = new Path(Environment.PWD.$$(), YarnConfiguration.DEFAULT_CONTAINER_TEMP_DIR)javaOpts += "-Djava.io.tmpdir=" + tmpDir// TODO: Remove once cpuset version is pushed out.// The context is, default gc for server class machines ends up using all cores to do gc -// hence if there are multiple containers in same node, Spark GC affects all other containers'// performance (which can be that of other Spark containers)// Instead of using this, rely on cpusets by YARN to enforce "proper" Spark behavior in// multi-tenant environments. Not sure how default Java GC behaves if it is limited to subset// of cores on a node.val useConcurrentAndIncrementalGC = launchEnv.get("SPARK_USE_CONC_INCR_GC").exists(_.toBoolean)if (useConcurrentAndIncrementalGC) {// In our expts, using (default) throughput collector has severe perf ramifications in// multi-tenant machinesjavaOpts += "-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC"javaOpts += "-XX:MaxTenuringThreshold=31"javaOpts += "-XX:SurvivorRatio=8"javaOpts += "-XX:+CMSIncrementalMode"javaOpts += "-XX:+CMSIncrementalPacing"javaOpts += "-XX:CMSIncrementalDutyCycleMin=0"javaOpts += "-XX:CMSIncrementalDutyCycle=10"}。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。val amClass =// 集群环境用org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster// 否则用org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ExecutorLauncherif (isClusterMode) {Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster").getName} else {Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ExecutorLauncher").getName}val amArgs =Seq(amClass) ++ userClass ++ userJar ++ primaryPyFile ++ primaryRFile ++ userArgs ++Seq("--properties-file",buildPath(Environment.PWD.$$(), LOCALIZED_CONF_DIR, SPARK_CONF_FILE)) ++Seq("--dist-cache-conf",buildPath(Environment.PWD.$$(), LOCALIZED_CONF_DIR, DIST_CACHE_CONF_FILE))// Command for the ApplicationMasterval commands = prefixEnv ++// 使用java命令运行一个java进程Seq(Environment.JAVA_HOME.$$() + "/bin/java", "-server") ++javaOpts ++ amArgs ++Seq("1>", ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR + "/stdout","2>", ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR + "/stderr")。。。。。。。。。。。。// send the acl settings into YARN to control who has access via YARN interfacesval securityManager = new SecurityManager(sparkConf)amContainer.setApplicationACLs(YarnSparkHadoopUtil.getApplicationAclsForYarn(securityManager).asJava)setupSecurityToken(amContainer)amContainer
4、ApplicationMaster-启动Driver线程
我们已经看到ApplicationMaster被加载进来,所以接下来从ApplicationMaster入手。
- 1、创建ApplicationMaster
- 创建YarnRMClient
- 创建createAMRMClient,并启动
- 创建YarnRMClient
2、启动am进程: master.run()
- 通过
--class参数判断集群模式,分别创建Driver或Executor - 创建Driver:runDriver
- startUserApplication启动用户线程
- 获取main方法准备一个线程
- 调用main方法 invoke(mainMethod)
- Driver线程启动
- 等待SparkContext上下文环境准备完成 :hreadUtils.awaitResult(sparkContextPromise.future,
- startUserApplication启动用户线程
Duration(totalWaitTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
- 通过
main方法进入,创建ApplicationMaster
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {SignalUtils.registerLogger(log)val amArgs = new ApplicationMasterArguments(args)val sparkConf = new SparkConf()if (amArgs.propertiesFile != null) {Utils.getPropertiesFromFile(amArgs.propertiesFile).foreach { case (k, v) =>sparkConf.set(k, v)}}// Set system properties for each config entry. This covers two use cases:// - The default configuration stored by the SparkHadoopUtil class// - The user application creating a new SparkConf in cluster mode//// Both cases create a new SparkConf object which reads these configs from system properties.sparkConf.getAll.foreach { case (k, v) =>sys.props(k) = v}val yarnConf = new YarnConfiguration(SparkHadoopUtil.newConfiguration(sparkConf))// new一个ApplicationMastermaster = new ApplicationMaster(amArgs, sparkConf, yarnConf)val ugi = sparkConf.get(PRINCIPAL) match {// We only need to log in with the keytab in cluster mode. In client mode, the driver// handles the user keytab.case Some(principal) if master.isClusterMode =>val originalCreds = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getCredentials()SparkHadoopUtil.get.loginUserFromKeytab(principal, sparkConf.get(KEYTAB).orNull)val newUGI = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser()if (master.appAttemptId == null || master.appAttemptId.getAttemptId > 1) {// Re-obtain delegation tokens if this is not a first attempt, as they might be outdated// as of now. Add the fresh tokens on top of the original user's credentials (overwrite).// Set the context class loader so that the token manager has access to jars// distributed by the user.Utils.withContextClassLoader(master.userClassLoader) {val credentialManager = new HadoopDelegationTokenManager(sparkConf, yarnConf, null)credentialManager.obtainDelegationTokens(originalCreds)}}// Transfer the original user's tokens to the new user, since it may contain needed tokens// (such as those user to connect to YARN).newUGI.addCredentials(originalCreds)newUGIcase _ =>SparkHadoopUtil.get.createSparkUser()}ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction[Unit]() {override def run(): Unit = System.exit(master.run())})}
new 一个YarnRMClient,ResourceManager的Client客户端。
private[spark] class ApplicationMaster(args: ApplicationMasterArguments,sparkConf: SparkConf,yarnConf: YarnConfiguration) extends Logging {// TODO: Currently, task to container is computed once (TaskSetManager) - which need not be// optimal as more containers are available. Might need to handle this better.private val appAttemptId =if (System.getenv(ApplicationConstants.Environment.CONTAINER_ID.name()) != null) {YarnSparkHadoopUtil.getContainerId.getApplicationAttemptId()} else {null}private val isClusterMode = args.userClass != nullprivate val securityMgr = new SecurityManager(sparkConf)private var metricsSystem: Option[MetricsSystem] = Noneprivate val userClassLoader = {val classpath = Client.getUserClasspath(sparkConf)val urls = classpath.map { entry =>new URL("file:" + new File(entry.getPath()).getAbsolutePath())}if (isClusterMode) {if (Client.isUserClassPathFirst(sparkConf, isDriver = true)) {new ChildFirstURLClassLoader(urls, Utils.getContextOrSparkClassLoader)} else {new MutableURLClassLoader(urls, Utils.getContextOrSparkClassLoader)}} else {new MutableURLClassLoader(urls, Utils.getContextOrSparkClassLoader)}}private val client = new YarnRMClient()
在YarnRMClient中,创建
private[spark] class YarnRMClient extends Logging {private var amClient: AMRMClient[ContainerRequest] = _private var uiHistoryAddress: String = _private var registered: Boolean = falsedef register(driverHost: String,driverPort: Int,conf: YarnConfiguration,sparkConf: SparkConf,uiAddress: Option[String],uiHistoryAddress: String): Unit = {// 创建AM、RM通信的客户端并启动amClient = AMRMClient.createAMRMClient()amClient.init(conf)amClient.start()this.uiHistoryAddress = uiHistoryAddressval trackingUrl = uiAddress.getOrElse {if (sparkConf.get(ALLOW_HISTORY_SERVER_TRACKING_URL)) uiHistoryAddress else ""}logInfo("Registering the ApplicationMaster")synchronized {amClient.registerApplicationMaster(driverHost, driverPort, trackingUrl)registered = true}}
准备好之后,启动ApplicationMaster进程
ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction[Unit]() {override def run(): Unit = System.exit(master.run())})
通过判断—class参数判断是否是集群模式,并且创建Driver还是Executor
try {val attemptID = if (isClusterMode) {// Set the web ui port to be ephemeral for yarn so we don't conflict with// other spark processes running on the same boxSystem.setProperty(UI_PORT.key, "0")// Set the master and deploy mode property to match the requested mode.System.setProperty("spark.master", "yarn")System.setProperty(SUBMIT_DEPLOY_MODE.key, "cluster")// Set this internal configuration if it is running on cluster mode, this// configuration will be checked in SparkContext to avoid misuse of yarn cluster mode.System.setProperty("spark.yarn.app.id", appAttemptId.getApplicationId().toString())Option(appAttemptId.getAttemptId.toString)} else {None}new CallerContext("APPMASTER", sparkConf.get(APP_CALLER_CONTEXT),Option(appAttemptId.getApplicationId.toString), attemptID).setCurrentContext()logInfo("ApplicationAttemptId: " + appAttemptId)// This shutdown hook should run *after* the SparkContext is shut down.val priority = ShutdownHookManager.SPARK_CONTEXT_SHUTDOWN_PRIORITY - 1ShutdownHookManager.addShutdownHook(priority) { () =>val maxAppAttempts = client.getMaxRegAttempts(sparkConf, yarnConf)val isLastAttempt = appAttemptId.getAttemptId() >= maxAppAttemptsif (!finished) {// The default state of ApplicationMaster is failed if it is invoked by shut down hook.// This behavior is different compared to 1.x version.// If user application is exited ahead of time by calling System.exit(N), here mark// this application as failed with EXIT_EARLY. For a good shutdown, user shouldn't call// System.exit(0) to terminate the application.finish(finalStatus,ApplicationMaster.EXIT_EARLY,"Shutdown hook called before final status was reported.")}if (!unregistered) {// we only want to unregister if we don't want the RM to retryif (finalStatus == FinalApplicationStatus.SUCCEEDED || isLastAttempt) {unregister(finalStatus, finalMsg)cleanupStagingDir(new Path(System.getenv("SPARK_YARN_STAGING_DIR")))}}}// 判断是否是集群模式,通过--class参数是否设置判断// private val isClusterMode = args.userClass != nullif (isClusterMode) {runDriver()} else {runExecutorLauncher()}} catch {case e: Exception =>// catch everything else if not specifically handledlogError("Uncaught exception: ", e)finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED,ApplicationMaster.EXIT_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION,"Uncaught exception: " + StringUtils.stringifyException(e))} finally {try {metricsSystem.foreach { ms =>ms.report()ms.stop()}} catch {case e: Exception =>logWarning("Exception during stopping of the metric system: ", e)}}exitCode}
启动Driver线程
private def runDriver(): Unit = {addAmIpFilter(None, System.getenv(ApplicationConstants.APPLICATION_WEB_PROXY_BASE_ENV))// 1、startUserApplication先启动用户应用程序,将--class的类加载并启动userClassThread = startUserApplication()// This a bit hacky, but we need to wait until the spark.driver.port property has// been set by the Thread executing the user class.logInfo("Waiting for spark context initialization...")val totalWaitTime = sparkConf.get(AM_MAX_WAIT_TIME)try {// 2、当前线程阻塞等待context执行val sc = ThreadUtils.awaitResult(sparkContextPromise.future,Duration(totalWaitTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))if (sc != null) {val rpcEnv = sc.env.rpcEnvval userConf = sc.getConfval host = userConf.get(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS)val port = userConf.get(DRIVER_PORT)registerAM(host, port, userConf, sc.ui.map(_.webUrl), appAttemptId)val driverRef = rpcEnv.setupEndpointRef(RpcAddress(host, port),YarnSchedulerBackend.ENDPOINT_NAME)createAllocator(driverRef, userConf, rpcEnv, appAttemptId, distCacheConf)} else {// Sanity check; should never happen in normal operation, since sc should only be null// if the user app did not create a SparkContext.throw new IllegalStateException("User did not initialize spark context!")}resumeDriver()userClassThread.join()} catch {case e: SparkException if e.getCause().isInstanceOf[TimeoutException] =>logError(s"SparkContext did not initialize after waiting for $totalWaitTime ms. " +"Please check earlier log output for errors. Failing the application.")finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED,ApplicationMaster.EXIT_SC_NOT_INITED,"Timed out waiting for SparkContext.")} finally {resumeDriver()}}
启动用户线程startUserApplication
private def startUserApplication(): Thread = {logInfo("Starting the user application in a separate Thread")var userArgs = args.userArgsif (args.primaryPyFile != null && args.primaryPyFile.endsWith(".py")) {// When running pyspark, the app is run using PythonRunner. The second argument is the list// of files to add to PYTHONPATH, which Client.scala already handles, so it's empty.userArgs = Seq(args.primaryPyFile, "") ++ userArgs}if (args.primaryRFile != null &&(args.primaryRFile.endsWith(".R") || args.primaryRFile.endsWith(".r"))) {// TODO(davies): add R dependencies here}// 加载--class的类,获取main方法val mainMethod = userClassLoader.loadClass(args.userClass).getMethod("main", classOf[Array[String]])val userThread = new Thread {override def run(): Unit = {try {if (!Modifier.isStatic(mainMethod.getModifiers)) {logError(s"Could not find static main method in object ${args.userClass}")finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED, ApplicationMaster.EXIT_EXCEPTION_USER_CLASS)} else {// 调用main方法mainMethod.invoke(null, userArgs.toArray)finish(FinalApplicationStatus.SUCCEEDED, ApplicationMaster.EXIT_SUCCESS)logDebug("Done running user class")}} catch {case e: InvocationTargetException =>e.getCause match {case _: InterruptedException =>// Reporter thread can interrupt to stop user classcase SparkUserAppException(exitCode) =>val msg = s"User application exited with status $exitCode"logError(msg)finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED, exitCode, msg)case cause: Throwable =>logError("User class threw exception: " + cause, cause)finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED,ApplicationMaster.EXIT_EXCEPTION_USER_CLASS,"User class threw exception: " + StringUtils.stringifyException(cause))}sparkContextPromise.tryFailure(e.getCause())} finally {// Notify the thread waiting for the SparkContext, in case the application did not// instantiate one. This will do nothing when the user code instantiates a SparkContext// (with the correct master), or when the user code throws an exception (due to the// tryFailure above).sparkContextPromise.trySuccess(null)}}}// 设置该线程为Driver线程并启动userThread.setContextClassLoader(userClassLoader)userThread.setName("Driver")userThread.start()userThread}
5、ApplicationMaster-启动Executor线程
从am.run开始说起
创建Driver:runDriver
- startUserApplication启动用户线程
- 获取main方法准备一个线程
- 调用main方法 invoke(mainMethod)
- Driver线程启动
- 等待SparkContext上下文环境准备完成 :hreadUtils.awaitResult(sparkContextPromise.future,
- 准备rpc环境,向ResourceManager注册ApplicationMaster
- rmClient.register(host, port, yarnConf, _sparkConf, uiAddress, historyAddress)
创建分配器,分配资源 createAllocator(driverRef, userConf, rpcEnv, appAttemptId, distCacheConf)
- rpc建立am到rm的端点
- 分配资源 allocator.allocateResources()
- am分配资源 amClient.allocate(progressIndicator)
- 获取所有已经分配的容器
- 处理分配 handleAllocatedContainers(allocatedContainers.asScala)
- 运行所有容器 runAllocatedContainers
- 启动executor线程 run()
- startContainers
- prepareEnvironment
- prepareCommands 创建了一个YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend
- nmClient发送启动容器命令 ```scala private def runDriver(): Unit = { addAmIpFilter(None, System.getenv(ApplicationConstants.APPLICATION_WEB_PROXY_BASE_ENV)) // 1、startUserApplication先启动用户应用程序,将—class的类加载并启动 userClassThread = startUserApplication()
- 运行所有容器 runAllocatedContainers
// This a bit hacky, but we need to wait until the spark.driver.port property has // been set by the Thread executing the user class. logInfo(“Waiting for spark context initialization…”) val totalWaitTime = sparkConf.get(AM_MAX_WAIT_TIME) try { // 2、当前线程阻塞等待context执行 val sc = ThreadUtils.awaitResult(sparkContextPromise.future, Duration(totalWaitTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) if (sc != null) { // 3、初始化rpc远程调用信息 val rpcEnv = sc.env.rpcEnv
val userConf = sc.getConf val host = userConf.get(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS) val port = userConf.get(DRIVER_PORT)
// 向ResourceManager注册AM,建立通信 registerAM(host, port, userConf, sc.ui.map(_.webUrl), appAttemptId)
val driverRef = rpcEnv.setupEndpointRef(
RpcAddress(host, port),YarnSchedulerBackend.ENDPOINT_NAME)
createAllocator(driverRef, userConf, rpcEnv, appAttemptId, distCacheConf) } else { // Sanity check; should never happen in normal operation, since sc should only be null // if the user app did not create a SparkContext. throw new IllegalStateException(“User did not initialize spark context!”) } resumeDriver() userClassThread.join() } catch { case e: SparkException if e.getCause().isInstanceOf[TimeoutException] => logError(
s"SparkContext did not initialize after waiting for $totalWaitTime ms. " +"Please check earlier log output for errors. Failing the application.")
finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED,
ApplicationMaster.EXIT_SC_NOT_INITED,"Timed out waiting for SparkContext.")
} finally { resumeDriver() } }
分配资源```scaladef allocateResources(): Unit = synchronized {// 1、更新资源请求updateResourceRequests()val progressIndicator = 0.1f// Poll the ResourceManager. This doubles as a heartbeat if there are no pending container// requests.// 1、amClient分配资源val allocateResponse = amClient.allocate(progressIndicator)// 2、获取所有已分配的容器val allocatedContainers = allocateResponse.getAllocatedContainers()allocatorBlacklistTracker.setNumClusterNodes(allocateResponse.getNumClusterNodes)if (allocatedContainers.size > 0) {logDebug(("Allocated containers: %d. Current executor count: %d. " +"Launching executor count: %d. Cluster resources: %s.").format(allocatedContainers.size,runningExecutors.size,numExecutorsStarting.get,allocateResponse.getAvailableResources))handleAllocatedContainers(allocatedContainers.asScala)}val completedContainers = allocateResponse.getCompletedContainersStatuses()if (completedContainers.size > 0) {logDebug("Completed %d containers".format(completedContainers.size))processCompletedContainers(completedContainers.asScala)logDebug("Finished processing %d completed containers. Current running executor count: %d.".format(completedContainers.size, runningExecutors.size))}}
- startUserApplication启动用户线程
运行所有容器:如果当前容器数量小于需要的数量,从线程池中再拿线程启动
private def runAllocatedContainers(containersToUse: ArrayBuffer[Container]): Unit = {for (container <- containersToUse) {executorIdCounter += 1val executorHostname = container.getNodeId.getHostval containerId = container.getIdval executorId = executorIdCounter.toStringassert(container.getResource.getMemory >= resource.getMemory)logInfo(s"Launching container $containerId on host $executorHostname " +s"for executor with ID $executorId")def updateInternalState(): Unit = synchronized {runningExecutors.add(executorId)numExecutorsStarting.decrementAndGet()executorIdToContainer(executorId) = containercontainerIdToExecutorId(container.getId) = executorIdval containerSet = allocatedHostToContainersMap.getOrElseUpdate(executorHostname,new HashSet[ContainerId])containerSet += containerIdallocatedContainerToHostMap.put(containerId, executorHostname)}// 如果正在运行的executor的数量小于目标所需要的数量,从launcherPool一个线程池中再次执行线程if (runningExecutors.size() < targetNumExecutors) {numExecutorsStarting.incrementAndGet()if (launchContainers) {launcherPool.execute(() => {try {new ExecutorRunnable(Some(container),conf,sparkConf,driverUrl,executorId,executorHostname,executorMemory,executorCores,appAttemptId.getApplicationId.toString,securityMgr,localResources,ResourceProfile.DEFAULT_RESOURCE_PROFILE_ID // use until fully supported// 每个executor线程要运行的run方法).run()updateInternalState()} catch {case e: Throwable =>numExecutorsStarting.decrementAndGet()if (NonFatal(e)) {logError(s"Failed to launch executor $executorId on container $containerId", e)// Assigned container should be released immediately// to avoid unnecessary resource occupation.amClient.releaseAssignedContainer(containerId)} else {throw e}}})} else {// For test onlyupdateInternalState()}} else {logInfo(("Skip launching executorRunnable as running executors count: %d " +"reached target executors count: %d.").format(runningExecutors.size, targetNumExecutors))}}}
启动executor
def run(): Unit = {logDebug("Starting Executor Container")// 创建NodeManager客户端nmClient = NMClient.createNMClient()nmClient.init(conf)nmClient.start()// 告诉NodeManager启动容器startContainer()}
startContainer()
def startContainer(): java.util.Map[String, ByteBuffer] = {val ctx = Records.newRecord(classOf[ContainerLaunchContext]).asInstanceOf[ContainerLaunchContext]// 准备环境val env = prepareEnvironment().asJavactx.setLocalResources(localResources.asJava)ctx.setEnvironment(env)val credentials = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getCredentials()val dob = new DataOutputBuffer()credentials.writeTokenStorageToStream(dob)ctx.setTokens(ByteBuffer.wrap(dob.getData()))// 准备启动命令val commands = prepareCommand()ctx.setCommands(commands.asJava)ctx.setApplicationACLs(YarnSparkHadoopUtil.getApplicationAclsForYarn(securityMgr).asJava)// If external shuffle service is enabled, register with the Yarn shuffle service already// started on the NodeManager and, if authentication is enabled, provide it with our secret// key for fetching shuffle files laterif (sparkConf.get(SHUFFLE_SERVICE_ENABLED)) {val secretString = securityMgr.getSecretKey()val secretBytes =if (secretString != null) {// This conversion must match how the YarnShuffleService decodes our secretJavaUtils.stringToBytes(secretString)} else {// Authentication is not enabled, so just provide dummy metadataByteBuffer.allocate(0)}ctx.setServiceData(Collections.singletonMap("spark_shuffle", secretBytes))}// Send the start request to the ContainerManagertry {// 向nodeManger 发送启动命令nmClient.startContainer(container.get, ctx)} catch {case ex: Exception =>throw new SparkException(s"Exception while starting container ${container.get.getId}" +s" on host $hostname", ex)}}
在prepareCommands中,创建启动命令,启动的是org.apache.spark.executor.YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend
val commands = prefixEnv ++Seq(Environment.JAVA_HOME.$$() + "/bin/java", "-server") ++javaOpts ++Seq("org.apache.spark.executor.YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend","--driver-url", masterAddress,"--executor-id", executorId,"--hostname", hostname,"--cores", executorCores.toString,"--app-id", appId,"--resourceProfileId", resourceProfileId.toString) ++userClassPath ++Seq(s"1>${ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR}/stdout",s"2>${ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR}/stderr")// TODO: it would be nicer to just make sure there are no null commands herecommands.map(s => if (s == null) "null" else s).toList
6、ApplicationMaster-建立通信环境以及Executor计算节点
从org.apache.spark.executor.YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend入手,
- 1、创建YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend执行环境,解析参数并run起来
- 1、根据rpcEnv创建远程调用信息 RpcEnv.create
- 2、创建远程端点的引用: driver: RpcEndpointRef = fetcher.setupEndpointRefByURI(arguments.driverUrl)
- 3、创建环境 SparkEnv.createExecutorEnv
- new NettyRpcEnvFactory().create(config)
- nettyEnv.startServer(config.bindAddress, actualPort)
- 1、创建netty的server : server = transportContext.createServer(bindAddress, port, bootstraps)
- 2、注册远程通信端点:dispatcher.registerRpcEndpoint(RpcEndpointVerifier.NAME, new RpcEndpointVerifier(this, dispatcher))}
- 3、注册端点,获取DedicatedMessageLoop不停收发消息
- 1、注册inbox信箱,维护线程池来接收信息
- 1、创建信箱的时候,会发送启动消息
- 2、Inbox有process方法,处理各种消息,现在处理OnStart
- 3、CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend处理,得到driver
- 4、driver.ask()/ / driver向我们的连接的Driver发送RegisterExecutor的请求
- 5、SparkContext中有一个属性private var _schedulerBackend: ,用来和我们后台通信
- 6、CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend的receiveAndReoly(),处理RegisterExecutor的请求
- 1、totalCoreCount.addAndGet(cores)、totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(1)自己增加核数
- 2、返回driver消息true: context.reply(true)
- 7、信箱收到之后,如果success,自己发送一条消息:case Success(_) =>self.send(RegisteredExecutor)表示注册成功
- 8、Inbox自己receive之后,开始new一个Executor,发送LaunchedExecutor消息
- 9、接收LaunchedExecutor消息,makeOffers()执行任务
- 1、注册inbox信箱,维护线程池来接收信息
- nettyEnv.startServer(config.bindAddress, actualPort)
- new NettyRpcEnvFactory().create(config)
- 4、和executor端建立端点
- 2、ApplicationMaster的resumeDriver()、userClassThread.join()让应用程序继续执行。
【现在开始是两条线开始走,一条计算资源、一条执行任务】
- 3、SparkContext的后置处理_taskScheduler.postStartHook(),抽象方法,来到YarnClusterScheduler中,ApplicationMaster.sparkContextInitialized(sc)初始化上下文环境
- 4、resumeDriver()中通知上下文sparkContextPromise.notify(),让Driver程序继续往下,执行用户的应用程序
// 和Executor建立端点env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("Executor",backendCreateFn(env.rpcEnv, arguments, env, cfg.resourceProfile))arguments.workerUrl.foreach { url =>env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("WorkerWatcher", new WorkerWatcher(env.rpcEnv, url))}
main方法入站:
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {// 创建一个YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend,执行Executorval createFn: (RpcEnv, CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.Arguments, SparkEnv, ResourceProfile) =>CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend = { case (rpcEnv, arguments, env, resourceProfile) =>new YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend(rpcEnv, arguments.driverUrl, arguments.executorId,arguments.bindAddress, arguments.hostname, arguments.cores, arguments.userClassPath, env,arguments.resourcesFileOpt, resourceProfile)}// 解析参数val backendArgs = CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.parseArguments(args,this.getClass.getCanonicalName.stripSuffix("$"))// run起来,带着环境CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.run(backendArgs, createFn)System.exit(0)}
run
def run(arguments: Arguments,backendCreateFn: (RpcEnv, Arguments, SparkEnv, ResourceProfile) =>CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend): Unit = {Utils.initDaemon(log)SparkHadoopUtil.get.runAsSparkUser { () =>// Debug codeUtils.checkHost(arguments.hostname)// Bootstrap to fetch the driver's Spark properties.val executorConf = new SparkConf// 根据rpcEnv创建远程调用信息,val fetcher = RpcEnv.create("driverPropsFetcher",arguments.bindAddress,arguments.hostname,-1,executorConf,new SecurityManager(executorConf),numUsableCores = 0,clientMode = true)// 创建远程端点引用var driver: RpcEndpointRef = nullval nTries = 3for (i <- 0 until nTries if driver == null) {try {// 根据url启动端点driver = fetcher.setupEndpointRefByURI(arguments.driverUrl)} catch {case e: Throwable => if (i == nTries - 1) {throw e}}}val cfg = driver.askSync[SparkAppConfig](RetrieveSparkAppConfig(arguments.resourceProfileId))val props = cfg.sparkProperties ++ Seq[(String, String)](("spark.app.id", arguments.appId))fetcher.shutdown()// Create SparkEnv using properties we fetched from the driver.val driverConf = new SparkConf()for ((key, value) <- props) {// this is required for SSL in standalone modeif (SparkConf.isExecutorStartupConf(key)) {driverConf.setIfMissing(key, value)} else {driverConf.set(key, value)}}cfg.hadoopDelegationCreds.foreach { tokens =>SparkHadoopUtil.get.addDelegationTokens(tokens, driverConf)}driverConf.set(EXECUTOR_ID, arguments.executorId)// 创建Executor的环境val env = SparkEnv.createExecutorEnv(driverConf, arguments.executorId, arguments.bindAddress,arguments.hostname, arguments.cores, cfg.ioEncryptionKey, isLocal = false)// 和Executor建立端点env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("Executor",backendCreateFn(env.rpcEnv, arguments, env, cfg.resourceProfile))arguments.workerUrl.foreach { url =>env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("WorkerWatcher", new WorkerWatcher(env.rpcEnv, url))}env.rpcEnv.awaitTermination()}}
创建Executor环境createExecutorEnv
private[spark] def createExecutorEnv(conf: SparkConf,executorId: String,bindAddress: String,hostname: String,numCores: Int,ioEncryptionKey: Option[Array[Byte]],isLocal: Boolean): SparkEnv = {// 创建环境val env = create(conf,executorId,bindAddress,hostname,None,isLocal,numCores,ioEncryptionKey)SparkEnv.set(env)env}
create方法
private def create(conf: SparkConf,executorId: String,bindAddress: String,advertiseAddress: String,port: Option[Int],isLocal: Boolean,numUsableCores: Int,ioEncryptionKey: Option[Array[Byte]],listenerBus: LiveListenerBus = null,mockOutputCommitCoordinator: Option[OutputCommitCoordinator] = None): SparkEnv = {val isDriver = executorId == SparkContext.DRIVER_IDENTIFIER// Listener bus is only used on the driverif (isDriver) {assert(listenerBus != null, "Attempted to create driver SparkEnv with null listener bus!")}val authSecretFileConf = if (isDriver) AUTH_SECRET_FILE_DRIVER else AUTH_SECRET_FILE_EXECUTORval securityManager = new SecurityManager(conf, ioEncryptionKey, authSecretFileConf)if (isDriver) {securityManager.initializeAuth()}ioEncryptionKey.foreach { _ =>if (!securityManager.isEncryptionEnabled()) {logWarning("I/O encryption enabled without RPC encryption: keys will be visible on the " +"wire.")}}val systemName = if (isDriver) driverSystemName else executorSystemName// 1、通过netty创建远程调用环境,非常重要val rpcEnv = RpcEnv.create(systemName, bindAddress, advertiseAddress, port.getOrElse(-1), conf,securityManager, numUsableCores, !isDriver)// Figure out which port RpcEnv actually bound to in case the original port is 0 or occupied.if (isDriver) {conf.set(DRIVER_PORT, rpcEnv.address.port)}
通过NettyRpcEnvFactory创建netty环境
def create(name: String,bindAddress: String,advertiseAddress: String,port: Int,conf: SparkConf,securityManager: SecurityManager,numUsableCores: Int,clientMode: Boolean): RpcEnv = {val config = RpcEnvConfig(conf, name, bindAddress, advertiseAddress, port, securityManager,numUsableCores, clientMode)// 创建环境new NettyRpcEnvFactory().create(config)}
Netty的创建
def create(config: RpcEnvConfig): RpcEnv = {val sparkConf = config.conf// Use JavaSerializerInstance in multiple threads is safe. However, if we plan to support// KryoSerializer in future, we have to use ThreadLocal to store SerializerInstanceval javaSerializerInstance =new JavaSerializer(sparkConf).newInstance().asInstanceOf[JavaSerializerInstance]val nettyEnv =new NettyRpcEnv(sparkConf, javaSerializerInstance, config.advertiseAddress,config.securityManager, config.numUsableCores)if (!config.clientMode) {val startNettyRpcEnv: Int => (NettyRpcEnv, Int) = { actualPort =>// 启动netty服务器nettyEnv.startServer(config.bindAddress, actualPort)(nettyEnv, nettyEnv.address.port)}try {Utils.startServiceOnPort(config.port, startNettyRpcEnv, sparkConf, config.name)._1} catch {case NonFatal(e) =>nettyEnv.shutdown()throw e}}nettyEnv}
注册通信端点,获取消息循环器DedicatedMessageLoop
def registerRpcEndpoint(name: String, endpoint: RpcEndpoint): NettyRpcEndpointRef = {// 1、获取通讯端点地址val addr = RpcEndpointAddress(nettyEnv.address, name)// 2、获取端点引用val endpointRef = new NettyRpcEndpointRef(nettyEnv.conf, addr, nettyEnv)synchronized {if (stopped) {throw new IllegalStateException("RpcEnv has been stopped")}if (endpoints.containsKey(name)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"There is already an RpcEndpoint called $name")}// This must be done before assigning RpcEndpoint to MessageLoop, as MessageLoop sets Inbox be// active when registering, and endpointRef must be put into endpointRefs before onStart is// called.endpointRefs.put(endpoint, endpointRef)// 3、获取消息循环器,不停收发消息var messageLoop: MessageLoop = nulltry {messageLoop = endpoint match {case e: IsolatedRpcEndpoint =>// 创建DedicatedMessageLoopnew DedicatedMessageLoop(name, e, this)case _ =>sharedLoop.register(name, endpoint)sharedLoop}endpoints.put(name, messageLoop)} catch {case NonFatal(e) =>endpointRefs.remove(endpoint)throw e}}endpointRef}
获取消息循环器之后,内部有inbox收件箱,持有线程池来监听事件
private class DedicatedMessageLoop(name: String,endpoint: IsolatedRpcEndpoint,dispatcher: Dispatcher)extends MessageLoop(dispatcher) {// 创建收件箱private val inbox = new Inbox(name, endpoint)// 维护线程池override protected val threadpool = if (endpoint.threadCount() > 1) {ThreadUtils.newDaemonCachedThreadPool(s"dispatcher-$name", endpoint.threadCount())} else {ThreadUtils.newDaemonSingleThreadExecutor(s"dispatcher-$name")}(1 to endpoint.threadCount()).foreach { _ =>// 循环处理接收到的信息threadpool.submit(receiveLoopRunnable)}// Mark active to handle the OnStart message.setActive(inbox)override def post(endpointName: String, message: InboxMessage): Unit = {require(endpointName == name)inbox.post(message)setActive(inbox)}override def unregister(endpointName: String): Unit = synchronized {require(endpointName == name)inbox.stop()// Mark active to handle the OnStop message.setActive(inbox)setActive(MessageLoop.PoisonPill)threadpool.shutdown()}}
Inbox信箱处理各种事件
private[netty] class Inbox(val endpointName: String, val endpoint: RpcEndpoint)extends Logging {inbox => // Give this an alias so we can use it more clearly in closures.@GuardedBy("this")protected val messages = new java.util.LinkedList[InboxMessage]()/** True if the inbox (and its associated endpoint) is stopped. */@GuardedBy("this")private var stopped = false/** Allow multiple threads to process messages at the same time. */@GuardedBy("this")private var enableConcurrent = false/** The number of threads processing messages for this inbox. */@GuardedBy("this")private var numActiveThreads = 0// OnStart should be the first message to process// 一创建就处理启动消息inbox.synchronized {messages.add(OnStart)}/*** Process stored messages.*/def process(dispatcher: Dispatcher): Unit = {var message: InboxMessage = nullinbox.synchronized {if (!enableConcurrent && numActiveThreads != 0) {return}message = messages.poll()if (message != null) {numActiveThreads += 1} else {return}}while (true) {safelyCall(endpoint) {message match {case RpcMessage(_sender, content, context) =>try {endpoint.receiveAndReply(context).applyOrElse[Any, Unit](content, { msg =>throw new SparkException(s"Unsupported message $message from ${_sender}")})} catch {case e: Throwable =>context.sendFailure(e)// Throw the exception -- this exception will be caught by the safelyCall function.// The endpoint's onError function will be called.throw e}case OneWayMessage(_sender, content) =>endpoint.receive.applyOrElse[Any, Unit](content, { msg =>throw new SparkException(s"Unsupported message $message from ${_sender}")})case OnStart =>endpoint.onStart()if (!endpoint.isInstanceOf[ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint]) {inbox.synchronized {if (!stopped) {enableConcurrent = true}}}case OnStop =>val activeThreads = inbox.synchronized { inbox.numActiveThreads }assert(activeThreads == 1,s"There should be only a single active thread but found $activeThreads threads.")dispatcher.removeRpcEndpointRef(endpoint)endpoint.onStop()assert(isEmpty, "OnStop should be the last message")case RemoteProcessConnected(remoteAddress) =>endpoint.onConnected(remoteAddress)case RemoteProcessDisconnected(remoteAddress) =>endpoint.onDisconnected(remoteAddress)case RemoteProcessConnectionError(cause, remoteAddress) =>endpoint.onNetworkError(cause, remoteAddress)}}inbox.synchronized {// "enableConcurrent" will be set to false after `onStop` is called, so we should check it// every time.if (!enableConcurrent && numActiveThreads != 1) {// If we are not the only one worker, exitnumActiveThreads -= 1return}message = messages.poll()if (message == null) {numActiveThreads -= 1return}}}}
处理启动事件,去启动端点
case OnStart =>// 启动端点endpoint.onStart()if (!endpoint.isInstanceOf[ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint]) {inbox.synchronized {if (!stopped) {enableConcurrent = true}}}
来到CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend的onStart方法,得到driver
override def onStart(): Unit = {logInfo("Connecting to driver: " + driverUrl)try {_resources = parseOrFindResources(resourcesFileOpt)} catch {case NonFatal(e) =>exitExecutor(1, "Unable to create executor due to " + e.getMessage, e)}rpcEnv.asyncSetupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl).flatMap { ref =>// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"// 得到driverdriver = Some(ref)// driver向我们的连接的Driver发送请求ref.ask[Boolean](RegisterExecutor(executorId, self, hostname, cores, extractLogUrls,extractAttributes, _resources, resourceProfile.id))}(ThreadUtils.sameThread).onComplete {case Success(_) =>self.send(RegisteredExecutor)case Failure(e) =>exitExecutor(1, s"Cannot register with driver: $driverUrl", e, notifyDriver = false)}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)}
处理消息的后端
在CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend中,有方法receiveAndReply(),用来处理请求和应答,正好处理注册请求
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {case RegisterExecutor(executorId, executorRef, hostname, cores, logUrls,attributes, resources, resourceProfileId) =>if (executorDataMap.contains(executorId)) {context.sendFailure(new IllegalStateException(s"Duplicate executor ID: $executorId"))} else if (scheduler.nodeBlacklist.contains(hostname) ||isBlacklisted(executorId, hostname)) {// If the cluster manager gives us an executor on a blacklisted node (because it// already started allocating those resources before we informed it of our blacklist,// or if it ignored our blacklist), then we reject that executor immediately.logInfo(s"Rejecting $executorId as it has been blacklisted.")context.sendFailure(new IllegalStateException(s"Executor is blacklisted: $executorId"))} else {// If the executor's rpc env is not listening for incoming connections, `hostPort`// will be null, and the client connection should be used to contact the executor.val executorAddress = if (executorRef.address != null) {executorRef.address} else {context.senderAddress}logInfo(s"Registered executor $executorRef ($executorAddress) with ID $executorId")addressToExecutorId(executorAddress) = executorIdtotalCoreCount.addAndGet(cores)totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(1)val resourcesInfo = resources.map{ case (k, v) =>(v.name,new ExecutorResourceInfo(v.name, v.addresses,// tell the executor it can schedule resources up to numParts times,// as configured by the user, or set to 1 as that is the default (1 task/resource)taskResourceNumParts.getOrElse(v.name, 1)))}val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorAddress, hostname,0, cores, logUrlHandler.applyPattern(logUrls, attributes), attributes,resourcesInfo, resourceProfileId)// This must be synchronized because variables mutated// in this block are read when requesting executorsCoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {executorDataMap.put(executorId, data)if (currentExecutorIdCounter < executorId.toInt) {currentExecutorIdCounter = executorId.toInt}if (numPendingExecutors > 0) {numPendingExecutors -= 1logDebug(s"Decremented number of pending executors ($numPendingExecutors left)")}}listenerBus.post(SparkListenerExecutorAdded(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, data))// Note: some tests expect the reply to come after we put the executor in the mapcontext.reply(true)}case StopDriver =>context.reply(true)stop()case StopExecutors =>logInfo("Asking each executor to shut down")for ((_, executorData) <- executorDataMap) {executorData.executorEndpoint.send(StopExecutor)}context.reply(true)case RemoveWorker(workerId, host, message) =>removeWorker(workerId, host, message)context.reply(true)case RetrieveSparkAppConfig(resourceProfileId) =>// note this will be updated in later prs to get the ResourceProfile from a// ResourceProfileManager that matches the resource profile id// for now just use default profileval rp = ResourceProfile.getOrCreateDefaultProfile(conf)val reply = SparkAppConfig(sparkProperties,SparkEnv.get.securityManager.getIOEncryptionKey(),Option(delegationTokens.get()),rp)context.reply(reply)}
注册成功消息之后,创建Executor,发送LaunchedExecutor消息
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {case RegisteredExecutor =>logInfo("Successfully registered with driver")try {//executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false,resources = _resources)driver.get.send(LaunchedExecutor(executorId))} catch {case NonFatal(e) =>exitExecutor(1, "Unable to create executor due to " + e.getMessage, e)}
case LaunchedExecutor(executorId) =>executorDataMap.get(executorId).foreach { data =>// 增加核数data.freeCores = data.totalCores}// 执行任务makeOffers(executorId)
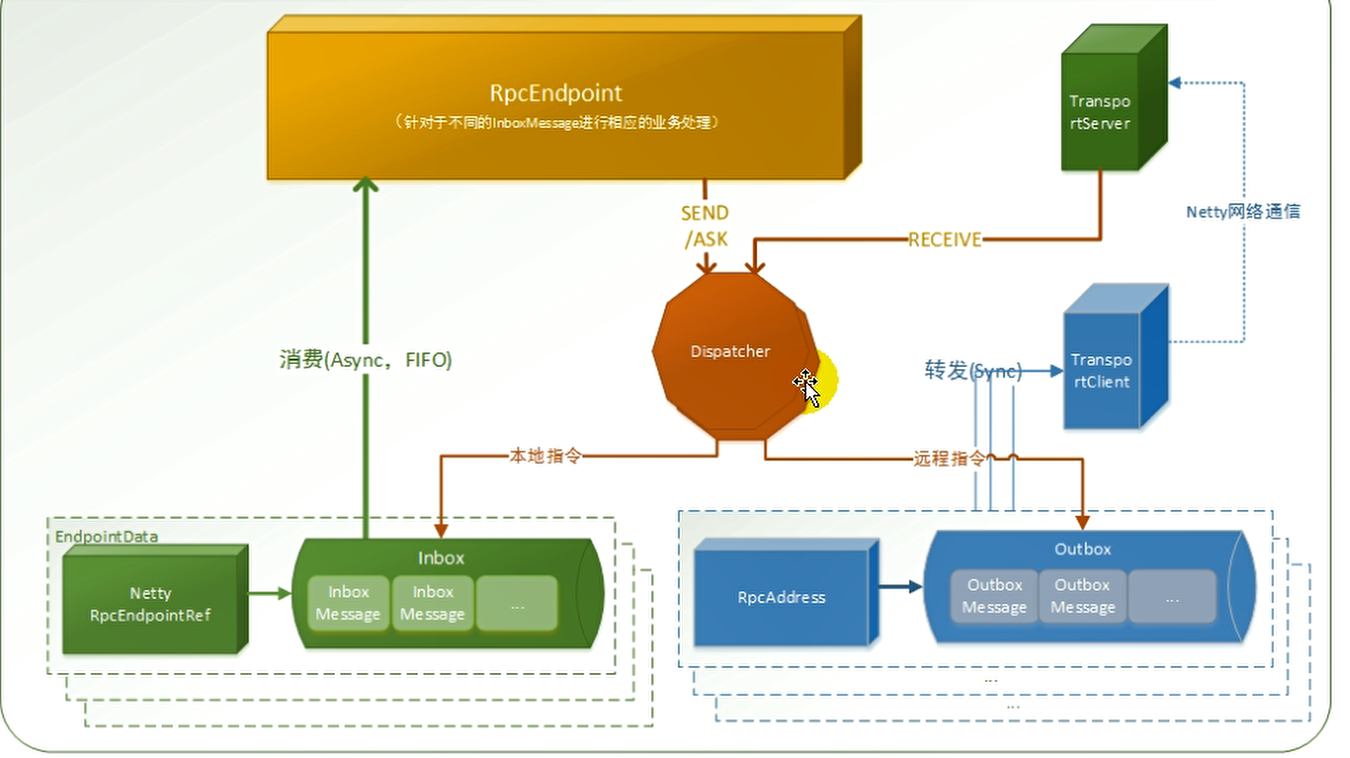
二、通信原理
Spark底层通信使用Netty作为通信框架,Netty支持NIO、AIO操作,但是Linux对AIO支持不够好,Windows支持AIO,但是Linux采用Epoll方式模仿AIO操作。
- 1、NettyRpcEnv.create()准备通信环境
- 1、启动服务器 nettyEnv.startServer(config.bindAddress, actualPort)
- 1、创建服务器 transportContext.createServer(bindAddress, port, bootstraps)
- 1、new TransportServer().init()
- 1、new ServerBootstrap()
- 2、initializePipeline初始化管道
- 1、new TransportServer().init()
- 2、注册通信端点 dispatcher.registerRpcEndpoint()
- 1、new NettyRpcEndpointRef注册通信端点的引用(有ask、send等方法,用来发送消息),内有outboxes发件箱,可以发送给多个人消息。
- 有多个client,TransportClient来往TransportServer发送消息
- 2、new DedicatedMessageLoop注册消息循环,内持有Inbox收信箱,有receive、reply等方法,用来接收消息
- 1、new NettyRpcEndpointRef注册通信端点的引用(有ask、send等方法,用来发送消息),内有outboxes发件箱,可以发送给多个人消息。
- 1、创建服务器 transportContext.createServer(bindAddress, port, bootstraps)
- 1、启动服务器 nettyEnv.startServer(config.bindAddress, actualPort)
1、通信组件
Driver、Executor之间如何通信?
我们都知道有一个RpcEnv作为远程环境。底层使用Netty进行通信,就找Netty的环境。
private[rpc] class NettyRpcEnvFactory extends RpcEnvFactory with Logging {def create(config: RpcEnvConfig): RpcEnv = {val sparkConf = config.conf// Use JavaSerializerInstance in multiple threads is safe. However, if we plan to support// KryoSerializer in future, we have to use ThreadLocal to store SerializerInstanceval javaSerializerInstance =new JavaSerializer(sparkConf).newInstance().asInstanceOf[JavaSerializerInstance]// 1、这里创建一个Netty的通信环境val nettyEnv =new NettyRpcEnv(sparkConf, javaSerializerInstance, config.advertiseAddress,config.securityManager, config.numUsableCores)if (!config.clientMode) {// 启动服务器val startNettyRpcEnv: Int => (NettyRpcEnv, Int) = { actualPort =>nettyEnv.startServer(config.bindAddress, actualPort)(nettyEnv, nettyEnv.address.port)}try {// 在指定端口启动服务器Utils.startServiceOnPort(config.port, startNettyRpcEnv, sparkConf, config.name)._1} catch {case NonFatal(e) =>nettyEnv.shutdown()throw e}}nettyEnv}}
启动服务器,得服务器,所以先创建服务器
def startServer(bindAddress: String, port: Int): Unit = {val bootstraps: java.util.List[TransportServerBootstrap] =if (securityManager.isAuthenticationEnabled()) {java.util.Arrays.asList(new AuthServerBootstrap(transportConf, securityManager))} else {java.util.Collections.emptyList()}// 创建服务器,server = transportContext.createServer(bindAddress, port, bootstraps)// 注册通信端点dispatcher.registerRpcEndpoint(RpcEndpointVerifier.NAME, new RpcEndpointVerifier(this, dispatcher))}
创建Transport Server
public TransportServer(TransportContext context,String hostToBind,int portToBind,RpcHandler appRpcHandler,List<TransportServerBootstrap> bootstraps) {this.context = context;this.conf = context.getConf();this.appRpcHandler = appRpcHandler;if (conf.sharedByteBufAllocators()) {this.pooledAllocator = NettyUtils.getSharedPooledByteBufAllocator(conf.preferDirectBufsForSharedByteBufAllocators(), true /* allowCache */);} else {this.pooledAllocator = NettyUtils.createPooledByteBufAllocator(conf.preferDirectBufs(), true /* allowCache */, conf.serverThreads());}this.bootstraps = Lists.newArrayList(Preconditions.checkNotNull(bootstraps));boolean shouldClose = true;try {// 执行init初始化方法init(hostToBind, portToBind);shouldClose = false;} finally {if (shouldClose) {JavaUtils.closeQuietly(this);}}}
三、应用程序的执行
应用程序的执行必然是都运行在准备好的环境之上。我们从环境入手
1、上下文对象-SparkContext
SparkContext里面的几个关键对象
- SparkConf
- 基础环境配置
- SparkEnv
- 通信环境
- SchedulerBackend
- 通信后端,与Executor进行通信
- TaskScheduler
- 任务调度器,主要用于任务的调度
- DAGScheduler
- 阶段调度器,主要用于阶段的划分和任务的切分
2、RDD依赖
// 2.2、将一行分割后转换val value: RDD[(String, Int)] = lines.flatMap(_.split(" ")).groupBy(word => word).map {case (word, list) => {(word, list.size)}}
最原始的RDD先经过flatMap,包装一个MapPartitionsRdd
def flatMap[U: ClassTag](f: T => TraversableOnce[U]): RDD[U] = withScope {val cleanF = sc.clean(f)// 当前对象转换new MapPartitionsRDD[U, T](this, (_, _, iter) => iter.flatMap(cleanF))}
private[spark] class MapPartitionsRDD[U: ClassTag, T: ClassTag](var prev: RDD[T],f: (TaskContext, Int, Iterator[T]) => Iterator[U], // (TaskContext, partition index, iterator)preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false,isFromBarrier: Boolean = false,isOrderSensitive: Boolean = false)// 继承自这个有参的RDD,extends RDD[U](prev) {
构建了一个OneToOneDependency并将之前的RDD传进去
/** Construct an RDD with just a one-to-one dependency on one parent */def this(@transient oneParent: RDD[_]) =this(oneParent.context, List(new OneToOneDependency(oneParent)))
OneToOneDependency继承了NarrowDependency,其中把RDD保存了。
class OneToOneDependency[T](rdd: RDD[T]) extends NarrowDependency[T](rdd) {override def getParents(partitionId: Int): List[Int] = List(partitionId)}abstract class NarrowDependency[T](_rdd: RDD[T]) extends Dependency[T] {/*** Get the parent partitions for a child partition.* @param partitionId a partition of the child RDD* @return the partitions of the parent RDD that the child partition depends upon*/def getParents(partitionId: Int): Seq[Int]override def rdd: RDD[T] = _rdd}
第二步,经过groupBy的时候,
def groupBy[K](f: T => K, p: Partitioner)(implicit kt: ClassTag[K], ord: Ordering[K] = null): RDD[(K, Iterable[T])] = withScope {val cleanF = sc.clean(f)// 走的时候groupByKeythis.map(t => (cleanF(t), t)).groupByKey(p)}
走combine
def groupByKey(partitioner: Partitioner): RDD[(K, Iterable[V])] = self.withScope {// groupByKey shouldn't use map side combine because map side combine does not// reduce the amount of data shuffled and requires all map side data be inserted// into a hash table, leading to more objects in the old gen.val createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v)val mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += vval mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2// 进这里val bufs = combineByKeyWithClassTag[CompactBuffer[V]](createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners, partitioner, mapSideCombine = false)bufs.asInstanceOf[RDD[(K, Iterable[V])]]}
里面有一个ShuffleRDD
new ShuffledRDD[K, V, C](self, partitioner)
点一个,看继承关系,传的是一个Nil?没关系,我们获取依赖关系的时候,通过getDependencies方法
class ShuffledRDD[K: ClassTag, V: ClassTag, C: ClassTag](@transient var prev: RDD[_ <: Product2[K, V]],part: Partitioner)extends RDD[(K, C)](prev.context, Nil) {
override def getDependencies: Seq[Dependency[_]] = {val serializer = userSpecifiedSerializer.getOrElse {val serializerManager = SparkEnv.get.serializerManagerif (mapSideCombine) {serializerManager.getSerializer(implicitly[ClassTag[K]], implicitly[ClassTag[C]])} else {serializerManager.getSerializer(implicitly[ClassTag[K]], implicitly[ClassTag[V]])}}// 创建一个ShuffleDependency,将先前的prev的RDD传入并指向List(new ShuffleDependency(prev, part, serializer, keyOrdering, aggregator, mapSideCombine))}
所以依赖关系就是将RDDDependency指向前一个依赖的RDD,形成有向无环图。
3、阶段的划分
collect算子的执行会触发作业的提交,就会进行阶段的划分
def collect(): Array[T] = withScope {val results = sc.runJob(this, (iter: Iterator[T]) => iter.toArray)Array.concat(results: _*)}
运行任务
dagScheduler.runJob(rdd, cleanedFunc, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, localProperties.get)// 提交任务val waiter = submitJob(rdd, func, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, properties)// 提交一个JobSubmitted事件eventProcessLoop.post(JobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func2, partitions.toArray, callSite, waiter,Utils.cloneProperties(properties)))
提交的时候将消息放在消息队列中
/*** Put the event into the event queue. The event thread will process it later.*/def post(event: E): Unit = {if (!stopped.get) {// 判断当前线程是不是还活着,往事件队列中放事件if (eventThread.isAlive) {eventQueue.put(event)} else {onError(new IllegalStateException(s"$name has already been stopped accidentally."))}}}
这个线程一启动的时候就会从事件队列中拿事件
// Exposed for testing.private[spark] val eventThread = new Thread(name) {setDaemon(true)override def run(): Unit = {try {while (!stopped.get) {// 拿事件val event = eventQueue.take()try {// 进行接收事件状态onReceive(event)} catch {case NonFatal(e) =>try {onError(e)} catch {case NonFatal(e) => logError("Unexpected error in " + name, e)}}}} catch {case ie: InterruptedException => // exit even if eventQueue is not emptycase NonFatal(e) => logError("Unexpected error in " + name, e)}}}
EventLoop中接收事件最终来到doOnReceive方法,这里面定义了各种事件如何进行处理
private def doOnReceive(event: DAGSchedulerEvent): Unit = event match {case JobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties) =>dagScheduler.handleJobSubmitted(jobId, rdd, func, partitions, callSite, listener, properties)case MapStageSubmitted(jobId, dependency, callSite, listener, properties) =>dagScheduler.handleMapStageSubmitted(jobId, dependency, callSite, listener, properties)case StageCancelled(stageId, reason) =>dagScheduler.handleStageCancellation(stageId, reason)case JobCancelled(jobId, reason) =>dagScheduler.handleJobCancellation(jobId, reason)case JobGroupCancelled(groupId) =>dagScheduler.handleJobGroupCancelled(groupId)
在handleJobSubmitted中,创建一个createResultStage最终的结果阶段
finalStage = createResultStage(finalRDD, func, partitions, jobId, callSite)
在创建结果阶段之前,还要判断是否有上级阶段,如果有就创建出来
private def createResultStage(rdd: RDD[_],func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _,partitions: Array[Int],jobId: Int,callSite: CallSite): ResultStage = {checkBarrierStageWithDynamicAllocation(rdd)checkBarrierStageWithNumSlots(rdd)checkBarrierStageWithRDDChainPattern(rdd, partitions.toSet.size)// 创建上级阶段val parents = getOrCreateParentStages(rdd, jobId)val id = nextStageId.getAndIncrement()// 创建结果阶段val stage = new ResultStage(id, rdd, func, partitions, parents, jobId, callSite)stageIdToStage(id) = stageupdateJobIdStageIdMaps(jobId, stage)stage}
创建上级阶段的依据是判断是不是Shuffle依赖,如果有就创建一个ShuffleMapStage,Shuffle写磁盘数据的过程
private def getOrCreateParentStages(rdd: RDD[_], firstJobId: Int): List[Stage] = {getShuffleDependencies(rdd).map { shuffleDep =>getOrCreateShuffleMapStage(shuffleDep, firstJobId)}.toList}
获取ShuffleDependencies的时候,从上一级rdd中拿出依赖,模式匹配遍历,如果是Shuffle依赖,加1
private[scheduler] def getShuffleDependencies(rdd: RDD[_]): HashSet[ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]] = {val parents = new HashSet[ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]]val visited = new HashSet[RDD[_]]val waitingForVisit = new ListBuffer[RDD[_]]waitingForVisit += rddwhile (waitingForVisit.nonEmpty) {val toVisit = waitingForVisit.remove(0)if (!visited(toVisit)) {visited += toVisittoVisit.dependencies.foreach {// 如果是Shuffle依赖,父阶段+1case shuffleDep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _] =>parents += shuffleDepcase dependency =>waitingForVisit.prepend(dependency.rdd)}}}parents}
创建ShuffleMapStage的时候createShuffleMapStage,获取到ShuffleDependency中的rdd,也就是上一个阶段的rdd,接着再去判断上一个rdd是否是shuffleRdd等等等。
val parents = getOrCreateParentStages(rdd, jobId)val stage = new ShuffleMapStage(id, rdd, numTasks, parents, jobId, rdd.creationSite, shuffleDep, mapOutputTracker)
总结:
阶段会先创建一个ResultStage,如果过程中有ShuffleRdd ,就会创建ShuffleMapStage,有多少次shuffle就加几个阶段。
4、任务的切分
在handleJobSubmitted方法中,会创建一个ActiveJob,并在最后提交阶段
submitStage(finalStage)
提交阶段的时候,先查看缺失的阶段
/** Submits stage, but first recursively submits any missing parents. */private def submitStage(stage: Stage): Unit = {val jobId = activeJobForStage(stage)if (jobId.isDefined) {logDebug(s"submitStage($stage (name=${stage.name};" +s"jobs=${stage.jobIds.toSeq.sorted.mkString(",")}))")if (!waitingStages(stage) && !runningStages(stage) && !failedStages(stage)) {// 先获取丢失的阶段,就是获取shuffle阶段,val missing = getMissingParentStages(stage).sortBy(_.id)logDebug("missing: " + missing)if (missing.isEmpty) {logInfo("Submitting " + stage + " (" + stage.rdd + "), which has no missing parents")// 提交缺失的任务submitMissingTasks(stage, jobId.get)} else {// 如果有哦缺失的阶段,将缺失的阶段先提交for (parent <- missing) {submitStage(parent)}waitingStages += stage}}} else {abortStage(stage, "No active job for stage " + stage.id, None)}}
提交丢失任务的时候,判断是不是ShuffleMapStage,将每个id遍历执行不过
val tasks: Seq[Task[_]] = try {val serializedTaskMetrics = closureSerializer.serialize(stage.latestInfo.taskMetrics).array()stage match {// 判断阶段case stage: ShuffleMapStage =>stage.pendingPartitions.clear()// 获取每个阶段id并且创建同数量任务去执行!partitionsToCompute.map { id =>val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)val part = partitions(id)stage.pendingPartitions += idnew ShuffleMapTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber,taskBinary, part, locs, properties, serializedTaskMetrics, Option(jobId),Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId, stage.rdd.isBarrier())}case stage: ResultStage =>partitionsToCompute.map { id =>val p: Int = stage.partitions(id)val part = partitions(p)val locs = taskIdToLocations(id)// 创建ResultTask一个new ResultTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber,taskBinary, part, locs, id, properties, serializedTaskMetrics,Option(jobId), Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId,stage.rdd.isBarrier())}}
到底有多少个阶段呢?就需要看partitionsToCompute了
// Figure out the indexes of partition ids to compute.val partitionsToCompute: Seq[Int] = stage.findMissingPartitions()// ShuffleMapStage/** Returns the sequence of partition ids that are missing (i.e. needs to be computed). */override def findMissingPartitions(): Seq[Int] = {mapOutputTrackerMaster.findMissingPartitions(shuffleDep.shuffleId)// 有多少分区就创建多少个ShuffleMapTask任务,而且是所有的Shuffle阶段,如果有两个shuffle阶段就是两倍.getOrElse(0 until numPartitions)}// ResultStageval job = activeJob.get(0 until job.numPartitions).filter(id => !job.finished(id))
总结:
任务的数量等于所有阶段中每个阶段的最后一个Rdd的分区数量之和
5、任务的调度
在submitMissingsTasks中,创建完阶段Task之后,下面就提交Task,将所有Task封装成一个任务集中
taskScheduler.submitTasks(new TaskSet(tasks.toArray, stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber, jobId, properties))
提交结果集。
override def submitTasks(taskSet: TaskSet): Unit = {// 获取结果集的任务val tasks = taskSet.taskslogInfo("Adding task set " + taskSet.id + " with " + tasks.length + " tasks")this.synchronized {// 创建TaskManager管理任务集val manager = createTaskSetManager(taskSet, maxTaskFailures)val stage = taskSet.stageIdval stageTaskSets =taskSetsByStageIdAndAttempt.getOrElseUpdate(stage, new HashMap[Int, TaskSetManager])stageTaskSets.foreach { case (_, ts) =>ts.isZombie = true}stageTaskSets(taskSet.stageAttemptId) = managerschedulableBuilder.addTaskSetManager(manager, manager.taskSet.properties)if (!isLocal && !hasReceivedTask) {starvationTimer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {override def run(): Unit = {if (!hasLaunchedTask) {logWarning("Initial job has not accepted any resources; " +"check your cluster UI to ensure that workers are registered " +"and have sufficient resources")} else {this.cancel()}}}, STARVATION_TIMEOUT_MS, STARVATION_TIMEOUT_MS)}hasReceivedTask = true}// 后端拉取任务backend.reviveOffers()}
CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend集群后端处理消息
case ReviveOffers =>makeOffers()// ...........................// Make fake resource offers on all executorsprivate def makeOffers(): Unit = {// Make sure no executor is killed while some task is launching on it// 获取任务的描述信息val taskDescs = withLock {// Filter out executors under killingval activeExecutors = executorDataMap.filterKeys(isExecutorActive)val workOffers = activeExecutors.map {case (id, executorData) =>new WorkerOffer(id, executorData.executorHost, executorData.freeCores,Some(executorData.executorAddress.hostPort),executorData.resourcesInfo.map { case (rName, rInfo) =>(rName, rInfo.availableAddrs.toBuffer)})}.toIndexedSeq// 刷新offersscheduler.resourceOffers(workOffers)}// 运行任务if (taskDescs.nonEmpty) {launchTasks(taskDescs)}}
在获取资源中:,从rootPool中获取排好序的任务集,遍历每个排好序的task,交给executor执行
,rootPool就是一个池子,包含多个任务集
val sortedTaskSets = rootPool.getSortedTaskSetQueue.filterNot(_.isZombie)for (taskSet <- sortedTaskSets) {logDebug("parentName: %s, name: %s, runningTasks: %s".format(taskSet.parent.name, taskSet.name, taskSet.runningTasks))if (newExecAvail) {// 让任务交给executor执行taskSet.executorAdded()}}
executor执行Task的时候,会进行本地化级别计算recomputeLocality
ef recomputeLocality(): Unit = {// A zombie TaskSetManager may reach here while executorLost happensif (isZombie) return// 计算本地化级别val previousLocalityLevel = myLocalityLevels(currentLocalityIndex)myLocalityLevels = computeValidLocalityLevels()localityWaits = myLocalityLevels.map(getLocalityWait)// 依次尝试,适配本地化级别currentLocalityIndex = getLocalityIndex(previousLocalityLevel)}
本地化级别:就是计算和任务运行的级别。
如果一个任务和数据在同一个进程中,那么就不用移动数据,有一句话:移动数据不如移动计算
数据和任务不一定是在 一起。**这种级别称为本地化级别:
有以下本地化级别:
- 进程本地化:数据和计算都在同一个进程
- 节点本地化:数据和计算在一台机器上但是不在同一个进程
- 机架本地化:数据和计算在一个机架
- 其他任意
所以在本地化计算的时候,会经过以下步骤:
private def computeValidLocalityLevels(): Array[TaskLocality.TaskLocality] = {import TaskLocality.{PROCESS_LOCAL, NODE_LOCAL, NO_PREF, RACK_LOCAL, ANY}val levels = new ArrayBuffer[TaskLocality.TaskLocality]// 进程本地化if (!pendingTasks.forExecutor.isEmpty &&pendingTasks.forExecutor.keySet.exists(sched.isExecutorAlive(_))) {levels += PROCESS_LOCAL}// 节点本地化if (!pendingTasks.forHost.isEmpty &&pendingTasks.forHost.keySet.exists(sched.hasExecutorsAliveOnHost(_))) {levels += NODE_LOCAL}if (!pendingTasks.noPrefs.isEmpty) {levels += NO_PREF}// 机架本地化if (!pendingTasks.forRack.isEmpty &&pendingTasks.forRack.keySet.exists(sched.hasHostAliveOnRack(_))) {levels += RACK_LOCAL}// 随意levels += ANYlogDebug("Valid locality levels for " + taskSet + ": " + levels.mkString(", "))levels.toArray}
进行本地化级别依次尝试,否则降低本地化级别
def getLocalityIndex(locality: TaskLocality.TaskLocality): Int = {var index = 0while (locality > myLocalityLevels(index)) {index += 1}index}
最后将这些任务返回return tasks,然后后端将任务序列化之后发给executor端执行。
// Launch tasks returned by a set of resource offersprivate def launchTasks(tasks: Seq[Seq[TaskDescription]]): Unit = {for (task <- tasks.flatten) {// 将任务编码val serializedTask = TaskDescription.encode(task)if (serializedTask.limit() >= maxRpcMessageSize) {Option(scheduler.taskIdToTaskSetManager.get(task.taskId)).foreach { taskSetMgr =>try {var msg = "Serialized task %s:%d was %d bytes, which exceeds max allowed: " +s"${RPC_MESSAGE_MAX_SIZE.key} (%d bytes). Consider increasing " +s"${RPC_MESSAGE_MAX_SIZE.key} or using broadcast variables for large values."msg = msg.format(task.taskId, task.index, serializedTask.limit(), maxRpcMessageSize)taskSetMgr.abort(msg)} catch {case e: Exception => logError("Exception in error callback", e)}}}else {val executorData = executorDataMap(task.executorId)// Do resources allocation here. The allocated resources will get released after the task// finishes.executorData.freeCores -= scheduler.CPUS_PER_TASKtask.resources.foreach { case (rName, rInfo) =>assert(executorData.resourcesInfo.contains(rName))executorData.resourcesInfo(rName).acquire(rInfo.addresses)}logDebug(s"Launching task ${task.taskId} on executor id: ${task.executorId} hostname: " +s"${executorData.executorHost}.")// 讲这些任务序列化之后发给executor端执行executorData.executorEndpoint.send(LaunchTask(new SerializableBuffer(serializedTask)))}}}
6、任务的执行
SchedulerBackend已经将任务发给了executorEnd,所以那边肯定有接收消息
executorData.executorEndpoint.send(LaunchTask(new SerializableBuffer(serializedTask)))
CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend的receive方法中接收运行任务的消息,判断有没有executor,如果没有就退出,有就将任务解码之后,executor运行。
case LaunchTask(data) =>
if (executor == null) {
exitExecutor(1, "Received LaunchTask command but executor was null")
} else {
val taskDesc = TaskDescription.decode(data.value)
logInfo("Got assigned task " + taskDesc.taskId)
taskResources(taskDesc.taskId) = taskDesc.resources
// 运行任务
executor.launchTask(this, taskDesc)
}
每个任务被封装成一个TaskRunner,运行任务是从线程池中拿出一个线程来执行这个TaskRunner的run方法。run方法中有一处调用task.run(),让任务真正执行。
def launchTask(context: ExecutorBackend, taskDescription: TaskDescription): Unit = {
// 创建一个TaskRunner来跑任务
val tr = new TaskRunner(context, taskDescription)
// 将任务放入正在运行的任务集合中
runningTasks.put(taskDescription.taskId, tr)
// 执行这个TaskRunner
threadPool.execute(tr)
}
// Maintains the list of running tasks.
private val runningTasks = new ConcurrentHashMap[Long, TaskRunner]
private val threadPool = {
val threadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setDaemon(true)
.setNameFormat("Executor task launch worker-%d")
.setThreadFactory((r: Runnable) => new UninterruptibleThread(r, "unused"))
.build()
class TaskRunner(
execBackend: ExecutorBackend,
private val taskDescription: TaskDescription)
extends Runnable {
..........
val value = Utils.tryWithSafeFinally {
val res = task.run(
taskAttemptId = taskId,
attemptNumber = taskDescription.attemptNumber,
metricsSystem = env.metricsSystem,
resources = taskDescription.resources)
threwException = false
res
}
task.run()中会调用runTask(context执行任务,这是一个抽象方法,具体执行判断该任务是什么类型,ShuffleMapTask还是ResultTask。都有具体的实现去完成自己的任务
def runTask(context: TaskContext): T
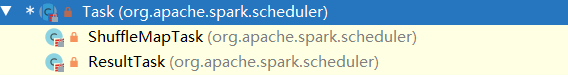
四、Shuffle
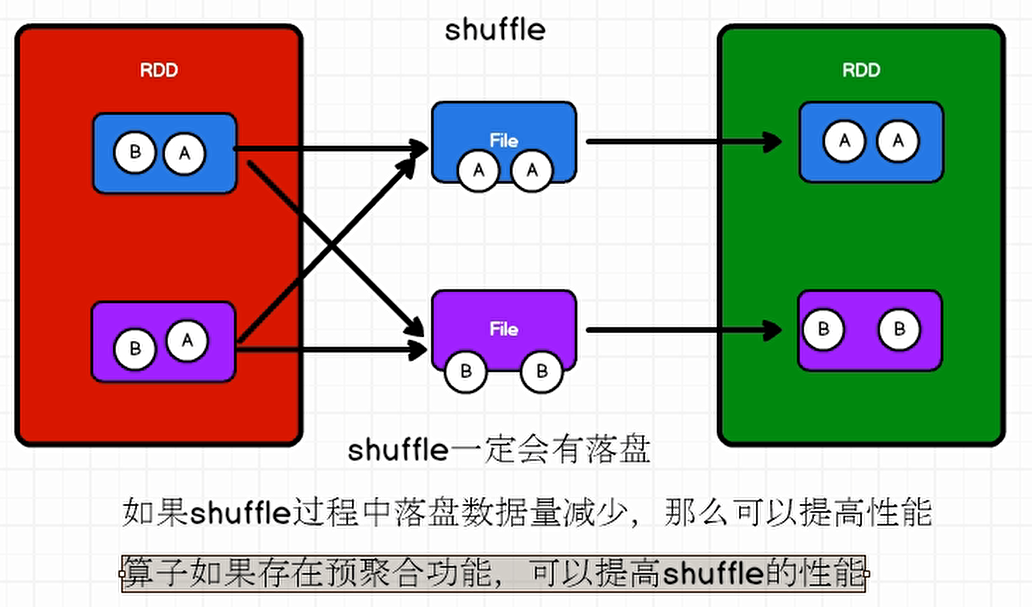
为了提高性能,Shuffle采取生成一个File数据文件和Index索引文件的方式,让其他下游的Task读取该文件找到自己的数据去处理。
1、流程梳理
- 1、DAGSchedule调度任务,判断是ShuffleMapStage还是ResultStage,分别创建ShuffleMapTask和ResultTask对象,最终TaskScheduler会submit任务。任务会被SchedulerBackend发给ExecutorBackend,将任务封装成TaskRunner给每个executor从线程池内拿取线程执行任务。每个任务会运行自己的runTask()逻辑。我们Shuffle发生在ShuffleMapTask任务中,所以从ShuffleMapTask入手
- 2、ShuffleMapTask的runTask()方法中会拿取一个shuffleWriterProcessor,调用write方法写出数据
- 1、先获取到ShuffleManager,从ShuffleManager中获取writer,写出数据,获取到的是SortShuffleWriter
- 2、对数据排个序,并准备好写出器 mapOutputWriter
- 3、sorter.insertAll(records)
- 4、按照分区写出数据 writePartitionedMapOutput
- 获取按照分区的迭代器,一个一个分区写出
- 5、提交所有分区 commitAllPartitions
- 实现类LocalDiskShuffleMapOutputWriter
- 写出索引文件并提交 blockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, resolvedTmp);
- 获取索引和数据文件
- writeLong()写出
- 3、ShuffleMapTask完成任务,接着往后执行,比如ResultTask的runTask()方法
- 遍历每一个rdd,func(context, rdd.iterator(partition, context))
- 判断是否设置过存储级别(缓存、文件等)
- 如果没有禁止缓存,getOrCompute(split, context)
- 还是走检查点
- 禁止缓存,读取检查点computeOrReadCheckpoint(split, context)
- compute()计算,是一个抽象方法,每个rdd都有自己的计算规则。但我们知道是ShuffledRdd,需要将落盘的文件读取进来。
- ShuffledRdd的read()方法,来到BlockStoreShuffleReader.read()
- readMetrics.incRecordsRead(1)
- 在TempShuffleReadMetrics中读取数据override def incRecordsRead(v: Long): Unit = _recordsRead += v
- 完成shuffle操作
- ShuffledRdd的read()方法,来到BlockStoreShuffleReader.read()
- compute()计算,是一个抽象方法,每个rdd都有自己的计算规则。但我们知道是ShuffledRdd,需要将落盘的文件读取进来。
- 遍历每一个rdd,func(context, rdd.iterator(partition, context))
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = {
// Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable.
val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean
val deserializeStartTimeNs = System.nanoTime()
val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime
} else 0L
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val rddAndDep = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
_executorDeserializeTimeNs = System.nanoTime() - deserializeStartTimeNs
_executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime
} else 0L
val rdd = rddAndDep._1
val dep = rddAndDep._2
// While we use the old shuffle fetch protocol, we use partitionId as mapId in the
// ShuffleBlockId construction.
val mapId = if (SparkEnv.get.conf.get(config.SHUFFLE_USE_OLD_FETCH_PROTOCOL)) {
partitionId
} else context.taskAttemptId()
// 写出数据
dep.shuffleWriterProcessor.write(rdd, dep, mapId, context, partition)
}
写出数据
/**
* The write process for particular partition, it controls the life circle of [[ShuffleWriter]]
* get from [[ShuffleManager]] and triggers rdd compute, finally return the [[MapStatus]] for
* this task.
*/
def write(
rdd: RDD[_],
dep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _],
mapId: Long,
context: TaskContext,
partition: Partition): MapStatus = {
var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null
try {
// 获取shuffleManager
val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager
// 从shuffleManager获取writer准备写出
writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](
dep.shuffleHandle,
mapId,
context,
createMetricsReporter(context))
// 写出数据
writer.write(
rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
writer.stop(success = true).get
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
try {
if (writer != null) {
writer.stop(success = false)
}
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
log.debug("Could not stop writer", e)
}
throw e
}
}
写数据是个抽象方法,现在可以告诉是SortShuffleWriter,因为ShuffleManager是特质,有实现类SortShuffleManager根据ShuffleHandle的类型来处理不同的Shuffle,给与不同的写出器。
handle match {
// 不安全的Shuffle
case unsafeShuffleHandle: SerializedShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] =>
new UnsafeShuffleWriter(
env.blockManager,
context.taskMemoryManager(),
unsafeShuffleHandle,
mapId,
context,
env.conf,
metrics,
shuffleExecutorComponents)
// bypas归并排序
case bypassMergeSortHandle: BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked] =>
new BypassMergeSortShuffleWriter(
env.blockManager,
bypassMergeSortHandle,
mapId,
env.conf,
metrics,
shuffleExecutorComponents)
// 基本Shuffle
case other: BaseShuffleHandle[K @unchecked, V @unchecked, _] =>
new SortShuffleWriter(
shuffleBlockResolver, other, mapId, context, shuffleExecutorComponents)
}
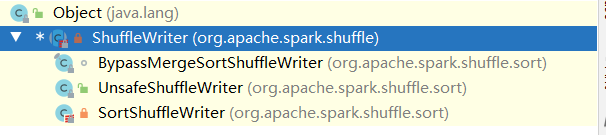
SortShuffleWriter写出数据,
override def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
sorter = if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
context, dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
} else {
// In this case we pass neither an aggregator nor an ordering to the sorter, because we don't
// care whether the keys get sorted in each partition; that will be done on the reduce side
// if the operation being run is sortByKey.
new ExternalSorter[K, V, V](
context, aggregator = None, Some(dep.partitioner), ordering = None, dep.serializer)
}
sorter.insertAll(records)
// Don't bother including the time to open the merged output file in the shuffle write time,
// because it just opens a single file, so is typically too fast to measure accurately
// (see SPARK-3570).
// 准备写出器
val mapOutputWriter = shuffleExecutorComponents.createMapOutputWriter(
dep.shuffleId, mapId, dep.partitioner.numPartitions)
// 按照分区写出
sorter.writePartitionedMapOutput(dep.shuffleId, mapId, mapOutputWriter)
// 提交所有分区
val partitionLengths = mapOutputWriter.commitAllPartitions()
mapStatus = MapStatus(blockManager.shuffleServerId, partitionLengths, mapId)
}
按照分区写出数据
def writePartitionedMapOutput(
shuffleId: Int,
mapId: Long,
mapOutputWriter: ShuffleMapOutputWriter): Unit = {
var nextPartitionId = 0
if (spills.isEmpty) {
// Case where we only have in-memory data
val collection = if (aggregator.isDefined) map else buffer
val it = collection.destructiveSortedWritablePartitionedIterator(comparator)
while (it.hasNext()) {
val partitionId = it.nextPartition()
var partitionWriter: ShufflePartitionWriter = null
var partitionPairsWriter: ShufflePartitionPairsWriter = null
TryUtils.tryWithSafeFinally {
partitionWriter = mapOutputWriter.getPartitionWriter(partitionId)
val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(shuffleId, mapId, partitionId)
partitionPairsWriter = new ShufflePartitionPairsWriter(
partitionWriter,
serializerManager,
serInstance,
blockId,
context.taskMetrics().shuffleWriteMetrics)
while (it.hasNext && it.nextPartition() == partitionId) {
it.writeNext(partitionPairsWriter)
}
} {
if (partitionPairsWriter != null) {
partitionPairsWriter.close()
}
}
nextPartitionId = partitionId + 1
}
} else {
// We must perform merge-sort; get an iterator by partition and write everything directly.
for ((id, elements) <- this.partitionedIterator) {
val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(shuffleId, mapId, id)
var partitionWriter: ShufflePartitionWriter = null
var partitionPairsWriter: ShufflePartitionPairsWriter = null
TryUtils.tryWithSafeFinally {
partitionWriter = mapOutputWriter.getPartitionWriter(id)
partitionPairsWriter = new ShufflePartitionPairsWriter(
partitionWriter,
serializerManager,
serInstance,
blockId,
context.taskMetrics().shuffleWriteMetrics)
if (elements.hasNext) {
for (elem <- elements) {
partitionPairsWriter.write(elem._1, elem._2)
}
}
} {
if (partitionPairsWriter != null) {
partitionPairsWriter.close()
}
}
nextPartitionId = id + 1
}
}
context.taskMetrics().incMemoryBytesSpilled(memoryBytesSpilled)
context.taskMetrics().incDiskBytesSpilled(diskBytesSpilled)
context.taskMetrics().incPeakExecutionMemory(peakMemoryUsedBytes)
}
写出索引文件并提交
def writeIndexFileAndCommit(
shuffleId: Int,
mapId: Long,
lengths: Array[Long],
dataTmp: File): Unit = {
// 获取索引文件
val indexFile = getIndexFile(shuffleId, mapId)
val indexTmp = Utils.tempFileWith(indexFile)
try {
// 获取数据文件
val dataFile = getDataFile(shuffleId, mapId)
// There is only one IndexShuffleBlockResolver per executor, this synchronization make sure
// the following check and rename are atomic.
synchronized {
// 检查索引和数据文件
val existingLengths = checkIndexAndDataFile(indexFile, dataFile, lengths.length)
if (existingLengths != null) {
// Another attempt for the same task has already written our map outputs successfully,
// so just use the existing partition lengths and delete our temporary map outputs.
System.arraycopy(existingLengths, 0, lengths, 0, lengths.length)
if (dataTmp != null && dataTmp.exists()) {
dataTmp.delete()
}
} else {
// This is the first successful attempt in writing the map outputs for this task,
// so override any existing index and data files with the ones we wrote.
val out = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(indexTmp)))
Utils.tryWithSafeFinally {
// We take in lengths of each block, need to convert it to offsets.
var offset = 0L
// 写出
out.writeLong(offset)
for (length <- lengths) {
offset += length
out.writeLong(offset)
}
} {
out.close()
}
if (indexFile.exists()) {
indexFile.delete()
}
if (dataFile.exists()) {
dataFile.delete()
}
if (!indexTmp.renameTo(indexFile)) {
throw new IOException("fail to rename file " + indexTmp + " to " + indexFile)
}
if (dataTmp != null && dataTmp.exists() && !dataTmp.renameTo(dataFile)) {
throw new IOException("fail to rename file " + dataTmp + " to " + dataFile)
}
}
}
} finally {
if (indexTmp.exists() && !indexTmp.delete()) {
logError(s"Failed to delete temporary index file at ${indexTmp.getAbsolutePath}")
}
}
}
ResultTask读取shuffle的数据
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): U = {
// Deserialize the RDD and the func using the broadcast variables.
val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean
val deserializeStartTimeNs = System.nanoTime()
val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime
} else 0L
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val (rdd, func) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[T], (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U)](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
_executorDeserializeTimeNs = System.nanoTime() - deserializeStartTimeNs
_executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime
} else 0L
// rdd.iterator迭代获取
func(context, rdd.iterator(partition, context))
}
迭代rdd,获取数据
final def iterator(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = {
if (storageLevel != StorageLevel.NONE) {
// 计算执行
getOrCompute(split, context)
} else {
// 读取检查点
computeOrReadCheckpoint(split, context)
}
}
private[spark] def getOrCompute(partition: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = {
val blockId = RDDBlockId(id, partition.index)
var readCachedBlock = true
// This method is called on executors, so we need call SparkEnv.get instead of sc.env.
SparkEnv.get.blockManager.getOrElseUpdate(blockId, storageLevel, elementClassTag, () => {
readCachedBlock = false
// 计算或读取检查点
computeOrReadCheckpoint(partition, context)
}) match {
case Left(blockResult) =>
if (readCachedBlock) {
val existingMetrics = context.taskMetrics().inputMetrics
existingMetrics.incBytesRead(blockResult.bytes)
new InterruptibleIterator[T](context, blockResult.data.asInstanceOf[Iterator[T]]) {
override def next(): T = {
existingMetrics.incRecordsRead(1)
delegate.next()
}
}
} else {
new InterruptibleIterator(context, blockResult.data.asInstanceOf[Iterator[T]])
}
case Right(iter) =>
new InterruptibleIterator(context, iter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[T]])
}
}
读取shuffle数据
override def read(): Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = {
val wrappedStreams = new ShuffleBlockFetcherIterator(
context,
blockManager.blockStoreClient,
blockManager,
blocksByAddress,
serializerManager.wrapStream,
// Note: we use getSizeAsMb when no suffix is provided for backwards compatibility
SparkEnv.get.conf.get(config.REDUCER_MAX_SIZE_IN_FLIGHT) * 1024 * 1024, // 48m
SparkEnv.get.conf.get(config.REDUCER_MAX_REQS_IN_FLIGHT),
SparkEnv.get.conf.get(config.REDUCER_MAX_BLOCKS_IN_FLIGHT_PER_ADDRESS),
SparkEnv.get.conf.get(config.MAX_REMOTE_BLOCK_SIZE_FETCH_TO_MEM),
SparkEnv.get.conf.get(config.SHUFFLE_DETECT_CORRUPT),
SparkEnv.get.conf.get(config.SHUFFLE_DETECT_CORRUPT_MEMORY),
readMetrics,
fetchContinuousBlocksInBatch).toCompletionIterator
val serializerInstance = dep.serializer.newInstance()
// Create a key/value iterator for each stream
val recordIter = wrappedStreams.flatMap { case (blockId, wrappedStream) =>
// Note: the asKeyValueIterator below wraps a key/value iterator inside of a
// NextIterator. The NextIterator makes sure that close() is called on the
// underlying InputStream when all records have been read.
serializerInstance.deserializeStream(wrappedStream).asKeyValueIterator
}
// Update the context task metrics for each record read.
val metricIter = CompletionIterator[(Any, Any), Iterator[(Any, Any)]](
recordIter.map { record =>
// 读取记录
readMetrics.incRecordsRead(1)
record
},
context.taskMetrics().mergeShuffleReadMetrics())
// An interruptible iterator must be used here in order to support task cancellation
val interruptibleIter = new InterruptibleIterator[(Any, Any)](context, metricIter)
val aggregatedIter: Iterator[Product2[K, C]] = if (dep.aggregator.isDefined) {
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
// We are reading values that are already combined
val combinedKeyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, C)]]
dep.aggregator.get.combineCombinersByKey(combinedKeyValuesIterator, context)
} else {
// We don't know the value type, but also don't care -- the dependency *should*
// have made sure its compatible w/ this aggregator, which will convert the value
// type to the combined type C
val keyValuesIterator = interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[(K, Nothing)]]
dep.aggregator.get.combineValuesByKey(keyValuesIterator, context)
}
} else {
interruptibleIter.asInstanceOf[Iterator[Product2[K, C]]]
}
2、写流程
获取到写出器,对数据排序之后按分区写出。
获取到什么样的写出器?
在ShuffleWriterProcessor的write方法中,获取写出器时传入了一个shuffleHandle依赖,就是根据这个依赖条件判断是什么样的写出器,它向ShuffleManager注册一个Shuffle,
writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](
dep.shuffleHandle,
val shuffleHandle: ShuffleHandle = _rdd.context.env.shuffleManager.registerShuffle(
shuffleId, this)
所以来到SortShuffleManager中注册Shuffle
override def registerShuffle[K, V, C](
shuffleId: Int,
dependency: ShuffleDependency[K, V, C]): ShuffleHandle = {
// 如果应该忽略合并排序,就使用BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle
if (SortShuffleWriter.shouldBypassMergeSort(conf, dependency)) {
// If there are fewer than spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold partitions and we don't
// need map-side aggregation, then write numPartitions files directly and just concatenate
// them at the end. This avoids doing serialization and deserialization twice to merge
// together the spilled files, which would happen with the normal code path. The downside is
// having multiple files open at a time and thus more memory allocated to buffers.
new BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId, dependency.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, V]])
// 如果能序列化shuffle,使用SerializedShuffleHandle
} else if (SortShuffleManager.canUseSerializedShuffle(dependency)) {
// Otherwise, try to buffer map outputs in a serialized form, since this is more efficient:
new SerializedShuffleHandle[K, V](
shuffleId, dependency.asInstanceOf[ShuffleDependency[K, V, V]])
} else {
// 其他使用BaseShuffleHandle
// Otherwise, buffer map outputs in a deserialized form:
new BaseShuffleHandle(shuffleId, dependency)
}
}
- BypassMergeSortShuffleHandle
- 1、应该忽略归并排序 shouldBypassMergeSort
- 1、如果有预聚合功能,则不可以使用 if (dep.mapSideCombine) false
- 2、分区数量小于等于200. dep.partitioner.numPartitions <= bypassMergeThreshold
- SHUFFLE_SORT_BYPASS_MERGE_THRESHOLD取配置项
spark.shuffle.sort.bypassMergeThreshold - 默认200 createWithDefault(200)
- SHUFFLE_SORT_BYPASS_MERGE_THRESHOLD取配置项
- 1、应该忽略归并排序 shouldBypassMergeSort
- SerializedShuffleHandle
- 1、能支持序列化 canUseSerializedShuffle
- 1、是否支持序列化重分配位置
- Java序列化不支持,Kryo支持
- 2、如果有预聚合功能,不可以使用
- 3、分区数量必须小于等于16777216
- numPartitions > MAX_SHUFFLE_OUTPUT_PARTITIONS_FOR_SERIALIZED_MODE
- val MAX_SHUFFLE_OUTPUT_PARTITIONS_FOR_SERIALIZED_MODE =PackedRecordPointer.MAXIMUM_PARTITION_ID + 1
- static final int MAXIMUM_PARTITION_ID = (1 << 24) - 1; // 16777215
- 1、是否支持序列化重分配位置
- 1、能支持序列化 canUseSerializedShuffle
- BaseShuffleHandle
什么情况算应该忽略归并排序?
def shouldBypassMergeSort(conf: SparkConf, dep: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]): Boolean = {
// We cannot bypass sorting if we need to do map-side aggregation.
if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
false
} else {
val bypassMergeThreshold: Int = conf.get(config.SHUFFLE_SORT_BYPASS_MERGE_THRESHOLD)
dep.partitioner.numPartitions <= bypassMergeThreshold
}
}
什么情况能序列化?
def canUseSerializedShuffle(dependency: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]): Boolean = {
val shufId = dependency.shuffleId
val numPartitions = dependency.partitioner.numPartitions
// 是否支持重定位
if (!dependency.serializer.supportsRelocationOfSerializedObjects) {
log.debug(s"Can't use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId because the serializer, " +
s"${dependency.serializer.getClass.getName}, does not support object relocation")
false
} else if (dependency.mapSideCombine) {
log.debug(s"Can't use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId because we need to do " +
s"map-side aggregation")
false
} else if (numPartitions > MAX_SHUFFLE_OUTPUT_PARTITIONS_FOR_SERIALIZED_MODE) {
log.debug(s"Can't use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId because it has more than " +
s"$MAX_SHUFFLE_OUTPUT_PARTITIONS_FOR_SERIALIZED_MODE partitions")
false
} else {
log.debug(s"Can use serialized shuffle for shuffle $shufId")
true
}
}
3、归并排序和读
- 1、获取到SortShuffleWriter之后,write数据,会先进行排序,然后插入数据
- 2、sorter.insertAll(records)
- 1、如果有聚合器(预聚合功能),会创建一个map,来按照相同k进行预聚合 @volatile private var map = new PartitionedAppendOnlyMap[K, C]
- 2、没有预聚合,创建数组把@volatile private var buffer = new PartitionedPairBuffer[K, C]
- 3、写数据的时候,可能内存不够用,会产生溢写临时文件:maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = true)
- 先预估容量
- 是否应该溢写?maybeSpill
- 如果当前内存超过阈值5m,就应该溢写,或者大于Integer.MAX_VALUE
- 1、记录溢写日志
- 2、溢写:spill(collection)
- map类型溢写map
- 将内存写入磁盘:spillMemoryIteratorToDisk(inMemoryIterator)
- 1、创建临时块存储
- 2、获取磁盘写入器,有一个缓冲区大小为32k
- private val fileBufferSize = sparkConf.get(config.SHUFFLE_FILE_BUFFER_SIZE).toInt * 1024
- 将内存写入磁盘:spillMemoryIteratorToDisk(inMemoryIterator)
- buffer溢写buffer
- map类型溢写map
- 3、释放多余内存 releaseMemory()
- 堆内内存
- 堆外内存
- 如果是map,创建map
- 如果是buffer,创建buffer
- 3、按照分区写出数据 sorter.writePartitionedMapOutput(dep.shuffleId, mapId, mapOutputWriter)
- 1、判断是否有溢写操作if (spills.isEmpty) {
- 如果没有,直接写
- 如果存在溢写操作,遍历this.partitionedIterator,
- 分区迭代器中判断是否产生溢写,
- 如果溢写,合并溢写文件:merge(spills, destructiveIterator(collection.partitionedDestructiveSortedIterator(comparator)))
- 进行聚合、归并排序
- 分区迭代器中判断是否产生溢写,
- 1、判断是否有溢写操作if (spills.isEmpty) {
- 4、提交所有分区 mapOutputWriter.commitAllPartitions()
- 1、从临时文件中获取所以和数据
- 2、删除临时数据文件
- 3、将数据写出
- 4、删除索引和数据文件
override def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
sorter = if (dep.mapSideCombine) {// 如果预聚合,传入aggregator聚合器,并且按照相同key排序
new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
context, dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
} else {
// In this case we pass neither an aggregator nor an ordering to the sorter, because we don't
// care whether the keys get sorted in each partition; that will be done on the reduce side
// if the operation being run is sortByKey.
new ExternalSorter[K, V, V]( // 没有聚合则没有哦聚合器和排序
context, aggregator = None, Some(dep.partitioner), ordering = None, dep.serializer)
}
// 在这里插入数据
sorter.insertAll(records)
// Don't bother including the time to open the merged output file in the shuffle write time,
// because it just opens a single file, so is typically too fast to measure accurately
// (see SPARK-3570).
val mapOutputWriter = shuffleExecutorComponents.createMapOutputWriter(
dep.shuffleId, mapId, dep.partitioner.numPartitions)
sorter.writePartitionedMapOutput(dep.shuffleId, mapId, mapOutputWriter)
val partitionLengths = mapOutputWriter.commitAllPartitions()
mapStatus = MapStatus(blockManager.shuffleServerId, partitionLengths, mapId)
}
排序
def insertAll(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
// TODO: stop combining if we find that the reduction factor isn't high
val shouldCombine = aggregator.isDefined
if (shouldCombine) {
// Combine values in-memory first using our AppendOnlyMap
val mergeValue = aggregator.get.mergeValue
val createCombiner = aggregator.get.createCombiner
var kv: Product2[K, V] = null
val update = (hadValue: Boolean, oldValue: C) => {
if (hadValue) mergeValue(oldValue, kv._2) else createCombiner(kv._2)
}
while (records.hasNext) {
addElementsRead()
kv = records.next()
map.changeValue((getPartition(kv._1), kv._1), update)
maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = true)
}
} else {
// Stick values into our buffer
while (records.hasNext) {
addElementsRead()
val kv = records.next()
buffer.insert(getPartition(kv._1), kv._1, kv._2.asInstanceOf[C])
maybeSpillCollection(usingMap = false)
}
}
}
溢写
private def maybeSpillCollection(usingMap: Boolean): Unit = {
var estimatedSize = 0L
if (usingMap) {
estimatedSize = map.estimateSize()
if (maybeSpill(map, estimatedSize)) {
map = new PartitionedAppendOnlyMap[K, C]
}
} else {
estimatedSize = buffer.estimateSize()
if (maybeSpill(buffer, estimatedSize)) {
buffer = new PartitionedPairBuffer[K, C]
}
}
if (estimatedSize > _peakMemoryUsedBytes) {
_peakMemoryUsedBytes = estimatedSize
}
}
是否应该溢写,当内存中的数据是32的倍数并且当前内存超过阈值(5m)时,应该溢写
protected def maybeSpill(collection: C, currentMemory: Long): Boolean = {
var shouldSpill = false
if (elementsRead % 32 == 0 && currentMemory >= myMemoryThreshold) {
// Claim up to double our current memory from the shuffle memory pool
val amountToRequest = 2 * currentMemory - myMemoryThreshold
val granted = acquireMemory(amountToRequest)
myMemoryThreshold += granted
// If we were granted too little memory to grow further (either tryToAcquire returned 0,
// or we already had more memory than myMemoryThreshold), spill the current collection
shouldSpill = currentMemory >= myMemoryThreshold
}
shouldSpill = shouldSpill || _elementsRead > numElementsForceSpillThreshold
// Actually spill
if (shouldSpill) {
_spillCount += 1
logSpillage(currentMemory)
spill(collection)
_elementsRead = 0
_memoryBytesSpilled += currentMemory
releaseMemory()
}
shouldSpill
}
@volatile private[this] var myMemoryThreshold = initialMemoryThreshold
private[this] val initialMemoryThreshold: Long =
SparkEnv.get.conf.get(SHUFFLE_SPILL_INITIAL_MEM_THRESHOLD)
private[spark] val SHUFFLE_SPILL_INITIAL_MEM_THRESHOLD =
ConfigBuilder("spark.shuffle.spill.initialMemoryThreshold")
.internal()
.doc("Initial threshold for the size of a collection before we start tracking its " +
"memory usage.")
.version("1.1.1")
.bytesConf(ByteUnit.BYTE)
.createWithDefault(5 * 1024 * 1024)
spill溢写
override protected[this] def spill(collection: SizeTracker): Unit = {
val inMemoryIterator = currentMap.destructiveSortedIterator(keyComparator)
// 将内存数据写出磁盘
val diskMapIterator = spillMemoryIteratorToDisk(inMemoryIterator)
spilledMaps += diskMapIterator
}
溢写缓冲区32k
private[spark] val SHUFFLE_FILE_BUFFER_SIZE =
ConfigBuilder("spark.shuffle.file.buffer")
.doc("Size of the in-memory buffer for each shuffle file output stream, in KiB unless " +
"otherwise specified. These buffers reduce the number of disk seeks and system calls " +
"made in creating intermediate shuffle files.")
.version("1.4.0")
.bytesConf(ByteUnit.KiB)
.checkValue(v => v > 0 && v <= ByteArrayMethods.MAX_ROUNDED_ARRAY_LENGTH / 1024,
s"The file buffer size must be positive and less than or equal to" +
s" ${ByteArrayMethods.MAX_ROUNDED_ARRAY_LENGTH / 1024}.")
.createWithDefaultString("32k")
合并溢写文件
private def merge(spills: Seq[SpilledFile], inMemory: Iterator[((Int, K), C)])
: Iterator[(Int, Iterator[Product2[K, C]])] = {
val readers = spills.map(new SpillReader(_))
val inMemBuffered = inMemory.buffered
(0 until numPartitions).iterator.map { p =>
val inMemIterator = new IteratorForPartition(p, inMemBuffered)
val iterators = readers.map(_.readNextPartition()) ++ Seq(inMemIterator)
// 聚合
if (aggregator.isDefined) {
// Perform partial aggregation across partitions
(p, mergeWithAggregation(
iterators, aggregator.get.mergeCombiners, keyComparator, ordering.isDefined))
// 归并排序
} else if (ordering.isDefined) {
// No aggregator given, but we have an ordering (e.g. used by reduce tasks in sortByKey);
// sort the elements without trying to merge them
(p, mergeSort(iterators, ordering.get))
} else {
(p, iterators.iterator.flatten)
}
}
}
五、内存管理
1、内存的分类
- 存储内存(60%的50%=30%)
- 缓存数据
- 广播变量
- 执行内存(60%的50%=30%)
- Shuffle过程中的操作
- 其它内存(40%)
- 系统,rdd元数据的信息
- 预留内存
- 300m
有一个类MemoryManager,统一内存管理
private[spark] abstract class MemoryManager(
conf: SparkConf,
numCores: Int,
onHeapStorageMemory: Long,
onHeapExecutionMemory: Long) extends Logging {
require(onHeapExecutionMemory > 0, "onHeapExecutionMemory must be > 0")
// -- Methods related to memory allocation policies and bookkeeping ------------------------------
@GuardedBy("this")
protected val onHeapStorageMemoryPool = new StorageMemoryPool(this, MemoryMode.ON_HEAP)
@GuardedBy("this")
protected val offHeapStorageMemoryPool = new StorageMemoryPool(this, MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP)
@GuardedBy("this")
protected val onHeapExecutionMemoryPool = new ExecutionMemoryPool(this, MemoryMode.ON_HEAP)
@GuardedBy("this")
protected val offHeapExecutionMemoryPool = new ExecutionMemoryPool(this, MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP)
动态占用机制:
- 存储内存和执行内存可以互相占用
- 1、当存储内存和执行内存占满了内存,将存储内存的数据溢写文件。如果没有开启溢写功能,可能丢失
- 2、当存储内存借用执行内存的空间,如果占满了,会让存储内存释放,考虑是否溢写文件
- 3、当执行内存借用存储内存的空间,占满了则不归还内存,继续动刀存储内存!