感知机 Perceptron
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport torch%matplotlib inline%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'svg'
加载数据集
数据集如下所示:
-0.63 -1.53 0-1.08 -1.23 00.39 -1.99 0-1.69 0.80 0-1.52 -1.14 03.88 0.65 10.73 2.97 10.83 3.94 11.59 1.25 13.92 3.48 1
第一二列为 x,y 坐标,最后一列为正负标签,正负样本各有50个。
数据预处理
将数据打散,并取70%作为训练集,30%作为测试集。
并将数据进行归一化处理。
data = np.genfromtxt('../data/perceptron_toydata.txt', delimiter='\t')# data.shape = (100, 3)X, y = data[:, :2], data[:, 2]# X.shape = (100, 2)y = y.astype(np.int)print('Class label counts:', np.bincount(y))# Class label counts: [50 50]# Shuffling & train/test splitshuffle_idx = np.arange(y.shape[0])shuffle_rng = np.random.RandomState(123)shuffle_rng.shuffle(shuffle_idx)X, y = X[shuffle_idx], y[shuffle_idx]X_train, X_test = X[shuffle_idx[:70]], X[shuffle_idx[70:]]y_train, y_test = y[shuffle_idx[:70]], y[shuffle_idx[70:]]# Normalize (mean zero, unit variance)mu, sigma = X_train.mean(axis=0), X_train.std(axis=0)X_train = (X_train - mu) / sigmaX_test = (X_test - mu) / sigma
接下来是把训练集的数据点可视化:
注意:直接用
plt.savefig()会导出空白图片
plt.scatter(X_train[y_train==0, 0], X_train[y_train==0, 1], label='class 0', marker='o')plt.scatter(X_train[y_train==1, 0], X_train[y_train==1, 1], label='class 1', marker='s')plt.xlabel('feature 1')plt.ylabel('feature 2')plt.legend()fig=plt.gcf()plt.show()fig.savefig("01.svg")
感知机模型
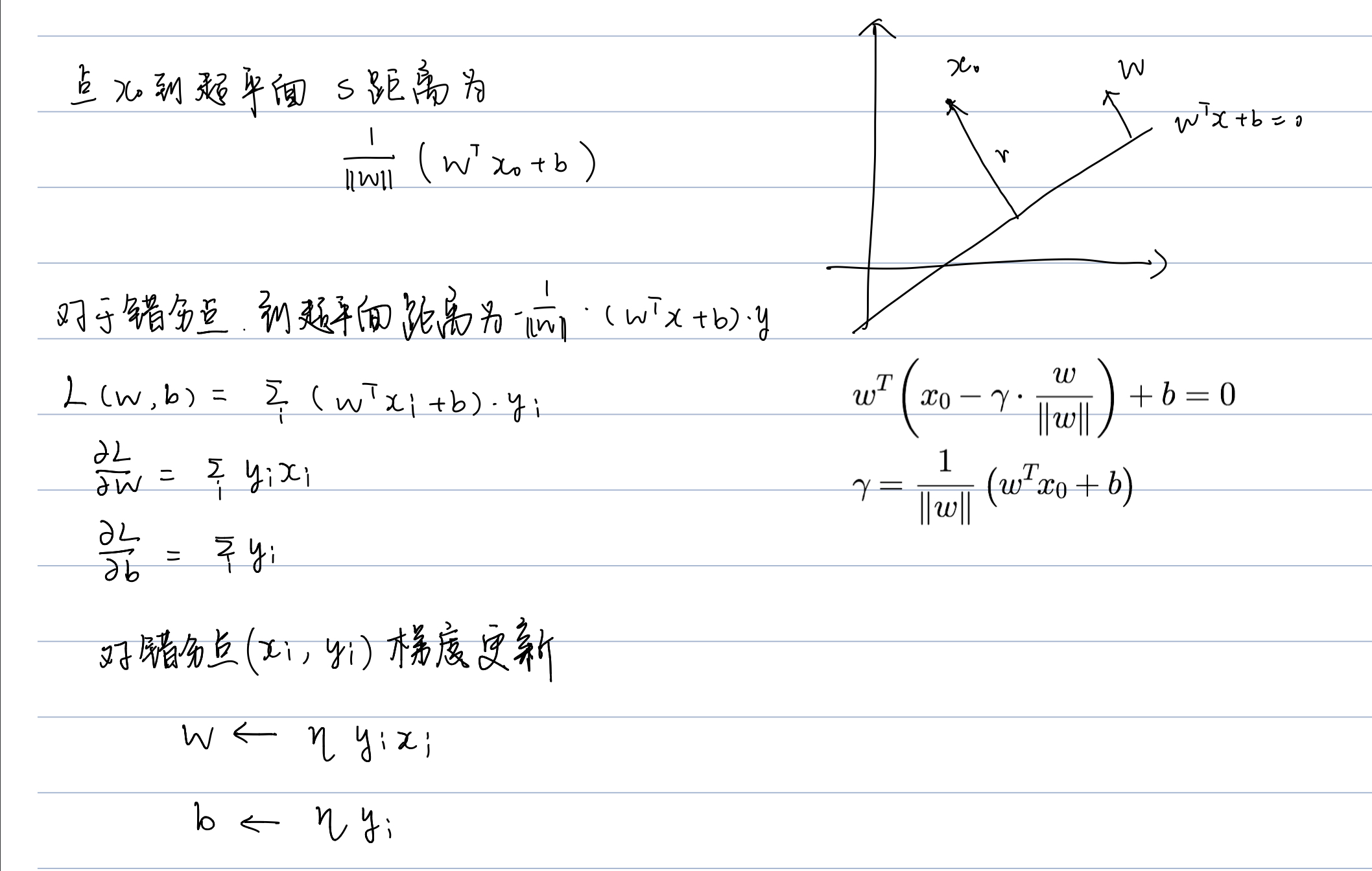

我们根据感知机的算法,能很轻松地写出模型代码:
epoch=5N=epoch*X.shape[0]w=torch.randn(2)b=torch.randn(1)inx=torch.randint(low=0, high=X.shape[0],size=(N,))for k in range(N):i=inx[k]if y[i]*(w@X[i]+b) <0:w=w+y[i]*X[i]b=b+y[i]
迭代5个epoch后,在训练集和测试集上的结果如下:
可视化
x_min = -2y_min = ( (-(w[0] * x_min) - b[0]) / w[1] )x_max = 2y_max = ( (-(w[0] * x_max) - b[0]) / w[1] )fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharex=True, figsize=(7, 3))ax[0].plot([x_min, x_max], [y_min, y_max])ax[1].plot([x_min, x_max], [y_min, y_max])ax[0].scatter(X_train[y_train==0, 0], X_train[y_train==0, 1], label='class 0', marker='o')ax[0].scatter(X_train[y_train==1, 0], X_train[y_train==1, 1], label='class 1', marker='s')ax[1].scatter(X_test[y_test==0, 0], X_test[y_test==0, 1], label='class 0', marker='o')ax[1].scatter(X_test[y_test==1, 0], X_test[y_test==1, 1], label='class 1', marker='s')ax[1].legend(loc='upper left')fig=plt.gcf()plt.show()fig.savefig("02.svg")
参考资料
https://machinelearningmastery.com/implement-perceptron-algorithm-scratch-python/



