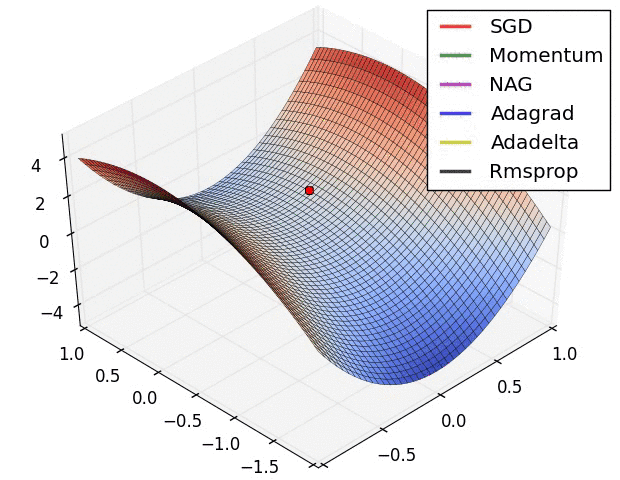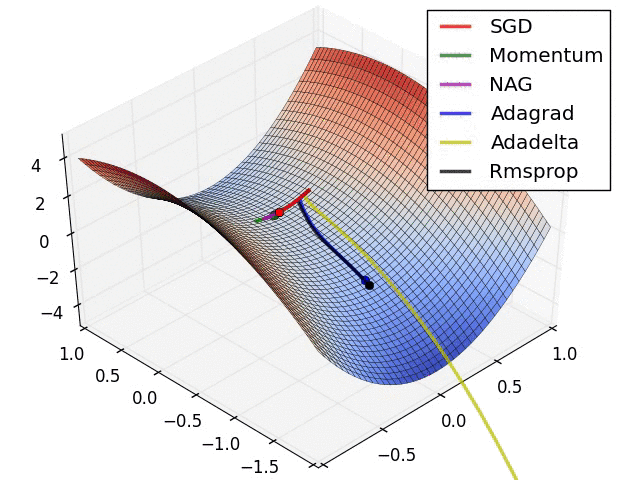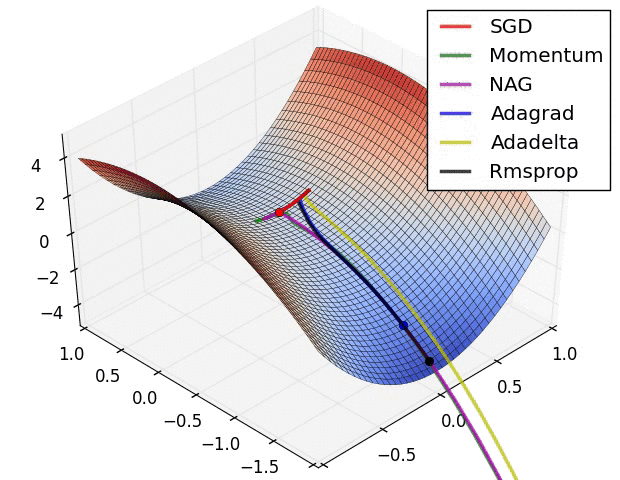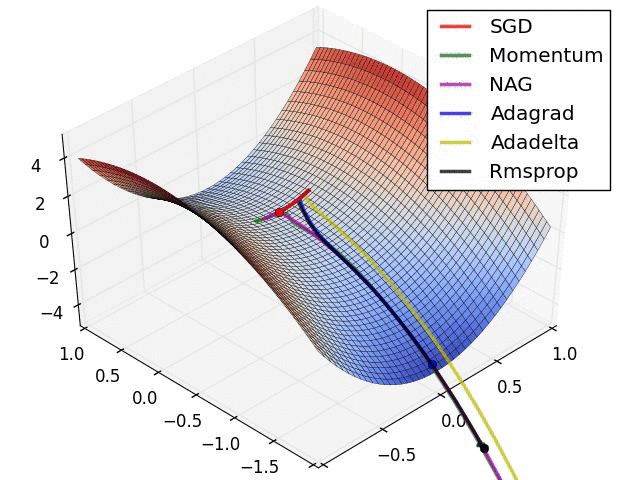
机器学习算法 = 模型表征+模型评估+优化算法
例子: 支持向量机=线性分类模型+最大间隔 逻辑回归对应=线性分类模型+交叉熵。
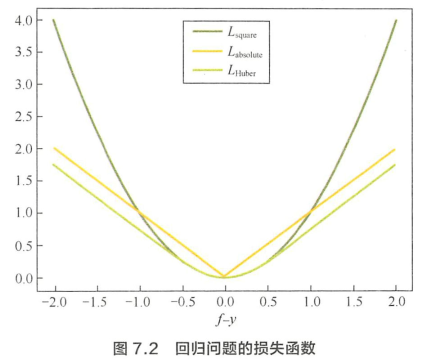
监督学习涉及的损失函数有哪些?
《百面机器学习》P142
- 二分类问题
- 0-1损失
- 非凸、非光滑,难以优化
- Hinge损失
- 凸,在fy≥1时不做任何惩罚,在fy=1处不可导,不能用gradient descent优化,而是用subgradient descent
- logistc损失
- 凸,处处光滑,可以用gradient descent优化,但其对所有样本点都有所惩罚,因此对异常值相对敏感一些
- 0-1损失
- 分类问题
- 光滑

- 回归问题
- 平方损失
- 光滑,可用GD优化
- 当预测值距离真实值越远时,惩罚力度越大,因此对异常点比较敏感
- 绝对损失
- 对异常点相对更鲁棒一些
- 在f=y处无法求导
- Huber损失
- 较小时为平方损失,较大时为线性损失,对异常点鲁棒
- 处处可导
- 平方损失
机器学习中的优化问题,哪些是凸优化问题,哪些是非凸优化问题?举例子
《百面》P145
- 凸优化:
- 逻辑回归:损失函数的海塞矩阵半正定
- 支持向量机
- 线性回归
非凸优化:
直接法
- 需要满足两个条件
- 损失函数L为凸函数
- L有解析解
求解方法
求解充分必要条件:
例子:岭回归
- 需要满足两个条件
迭代法
- 一阶迭代:Gradiet Descent 《机数》P185 算法4.1
- 动机:L不是凸函数/没有解析解,不能直接求解
- 思想:根据泰勒展开,得出函数下降最快的方向为梯度反方向
- 二阶迭代:牛顿法《机数》P192 算法4.2
- 动机:GD只利用了一阶导数信息,收敛速度慢
- 思想:根据泰勒展开,在每个迭代点处将目标函数近似为二次函数,求解梯度为0的点。因为这是函数的近似,所以得到的不一定是驻点,而是迭代方向。
- 问题:
- 无法保证每次迭代时目标函数值下降
- 需要计算梯度和黑塞矩阵,计算成本更高
- 黑塞矩阵不一定可逆
- 优点:收敛速度更快
- 拟牛顿法:牛顿法的改进
- 思想:不精确计算目标函数的黑塞矩阵然后求逆,而是通过其他手段得到黑塞矩阵的逆。
《机器学习的数学》4.2, 4.3 CS7015 Lecture 5
- 思想:不精确计算目标函数的黑塞矩阵然后求逆,而是通过其他手段得到黑塞矩阵的逆。
- 一阶迭代:Gradiet Descent 《机数》P185 算法4.1
如何验证求目标函数梯度功能的正确性?
《百面》P152,不好理解
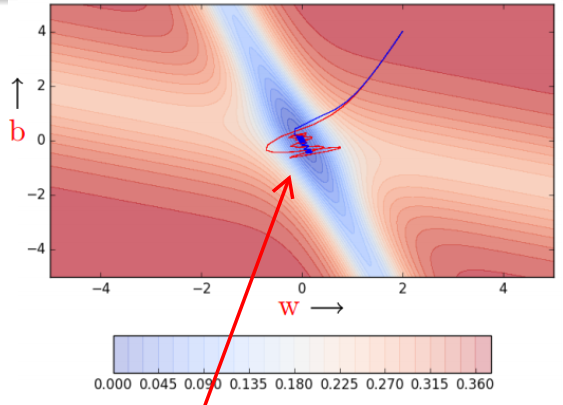
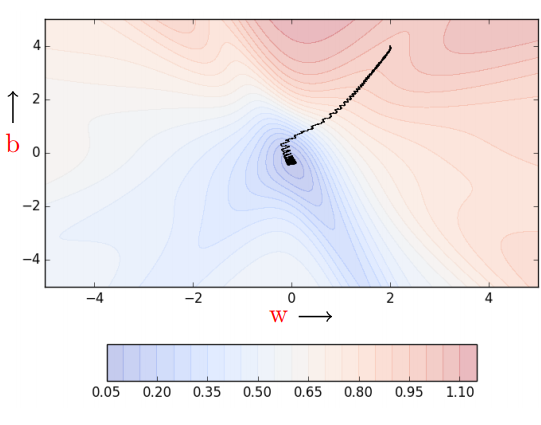
Gradient Descent的三个问题及改进
deep learning book CS7015 Lecture 5 《百面》P158 写得很好!!
Q1
Stochastic GD
- Problem: 基础的GD算法每次更新梯度时,考虑所有的训练点,当数据集非常大时,计算量非常大
- Solution: Stochastic GD
- updates the parameters for every single data point
- Stochastic because we are estimating the total gradient based on a single data point. Almost like tossing a coin only once and estimating P.
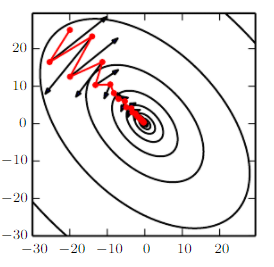
- New Problem: many oscillations
- Cause:
Stochastic does not guarantee that each local greedy move reduces the global error
Mini-Batch GD
- Reason: more data, more accurate stochastic estimates of the gradient
- Solution:
Q2
Momentum based GD
- Problem: It takes a lot of time to navigate regions having a gentle slope
- Cause: because the gradient in these regions is very small
- Reason:
类比到物理的物体运动,w是位置,update是速度,运动时间t=1,w的梯度是加速度,系数*w的梯度就是速度的变化量。每次运动的时候加入历史的速度,即加入惯性。
- Solution: Momentum based GD
- Benifit:
- 在梯度变化小的地方,更新得更快
- 在stochastic GD到山谷时,可以减少oscillation
Nestrov Accelerated GD
- New Problem: Momentum oscillates in and out of the minima valley as the momentum carries it out of the valley, takes a lot of u-turns before finally converging.

- Reason: Look ahead before leap, correcting its course quicker than momentum based gradient descent.
- Solution: Nestrov Accelerated GD
- Benifit:
- the oscillations are smaller, the chances of escaping the minima valley also smaller
Q3
Adaptive Learning(Adagrad)(环境感知)
- Problem: If some feature happens to be sparse as well as important we would want to take the updates to its parameter more seriously
 example: 一开始特征稀疏的参数w更新很少
example: 一开始特征稀疏的参数w更新很少
- Solution: Adagrad
Decay the learning rate for parameters in proportion to their update history
- Benifit: despite sparsity, w gets a higher learning rate and hence larger updates
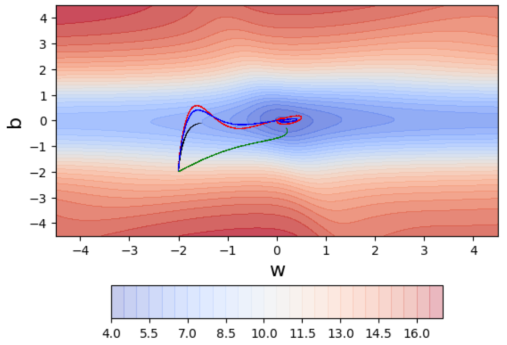
- New Problem: Adagrad decays the learning rate very aggressively. after a while the frequent parameters will start receiving very small updates because of the decayed learning rate
RMSProp
- Solution: decay the denominator and prevent its rapid growth
Adam
- Reason:
- Solution: Do everything that RMSProp does to solve the decay problem of Adagrad. Plus use a cumulative history of the gradients
In pratice,


鞍点问题
其他问题
训练数据量特别大时经典梯度法存在的问题,如何改进?
《百面》 P155 mini-batch
随机梯度下降法失效的原因。
《百面》P158
如何验证求目标函数梯度功能的正确性?
《百面》P152