环境变量



#include <unistd.h>#include <stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>//告诉编译器 这个全局变量在其他地方定义了,extern char **environ;//显示当前进程所有的环境变量void showall_env(){ //变量当前环境变量 for (char **ptr = environ; **ptr =!NULL; ++ptr){ printf("%s \n",*ptr); }}int main(){ //setenv("TEST","1234567890",1); //显示环境变量 //showall_env();或者写成下面这样 char* spath = getenv("PATH"); printf("%s\n",spath); return 0;}
进程
什么是进程
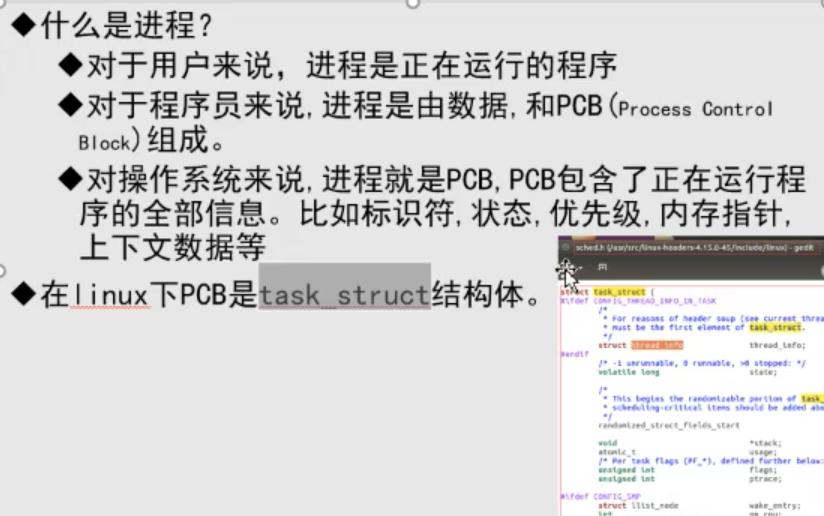
内存布局
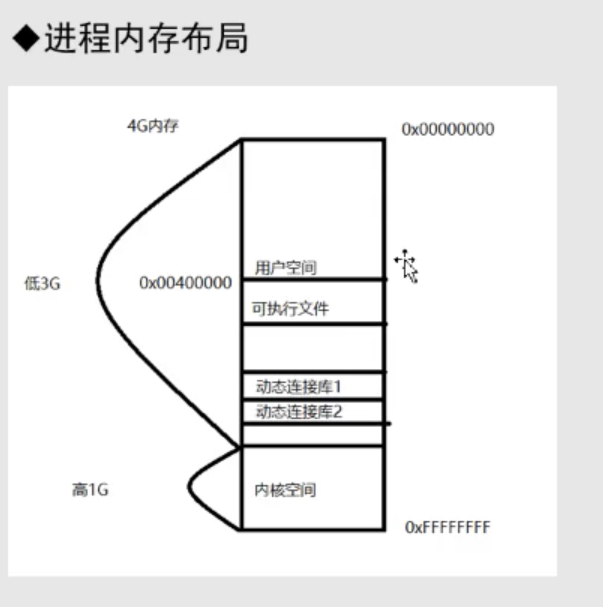
使用proc获取进程信息-进程先关命令


Linux proc文件系统介绍

常用proc目录

#include <unistd.h>#include <stdio.h>int main(){ //获取当前进程pid printf("curid = %d",getpid()); getchar();//暂停的功能 return 0;}
proc目录的使用

#include <unistd.h>#include <stdio.h>#include<dirent.h>#include<string.h>#include<errno.h>void proc_show_module(int pid){ char path[266]; sprintf(path,"/proc/%d/maps",pid); FILE *fd = fopen(path,"r"); if(fd == NULL){ printf("无法打开文件 :%s\n",path); return; } //%llx %llx %4s %x %5s %d %s unsigned long long base = 0,end = 0; char pageatt[5]; char offset; char time[6]; unsigned int inode; while (7 == fscanf(fd,"%llx-%llx %4s %x %5s %d %s", &base, &end, pageatt, &offset, time, &inode, path)) { if (offset == 0){ printf("\t%llx-%llx %4s %x %5s %d %s\n", base, end, pageatt, offset, time, inode, path); } } //关闭文件 fclose(fd);//注意fclosed后面不要d,fclosed报一大推错还找不到}void proc_show_name(int pid){ //打开文件 char path[266] ; sprintf(path,"/proc/%d/status",pid); FILE *fd = fopen(path, "r"); if (fd == NULL ){ printf("无法打开文件:%s\n", path); return ; } fscanf(fd, "Name: %s\n", path); printf("%s",path); //关闭文件 fclose(fd);} int main(){ //1.遍历/proc目录 struct DIR *pdir = opendir("/proc"); if (pdir == NULL){ printf("无法打开/proc目录\n"); return 0; }; // 2.遍历目录下所有数字的目录 int pid; char path[266] = {0}; char proc_name[100]; struct dirent *ent = NULL; while(ent = readdir(pdir)){ //得到进程id,如果无法将字符串转换成数字,说明目录名不是进程id if (1 != sscanf(ent->d_name,"%d",&pid)) continue; //进程信息(包括进程名)保存在status文件中中 proc_show_name(pid); //进程pid printf("%6d \n",pid); proc_show_module(pid); } //关闭目录流 closedir(pdir); return 0;}
进程的创建
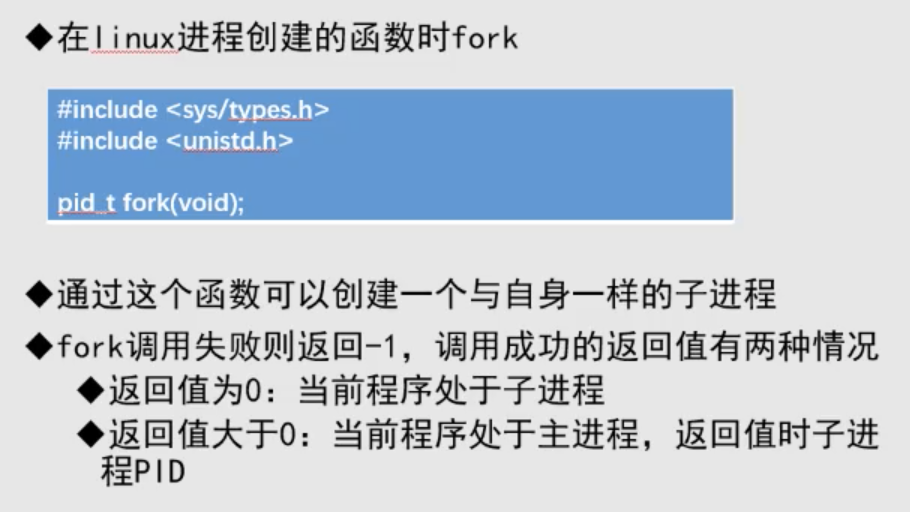
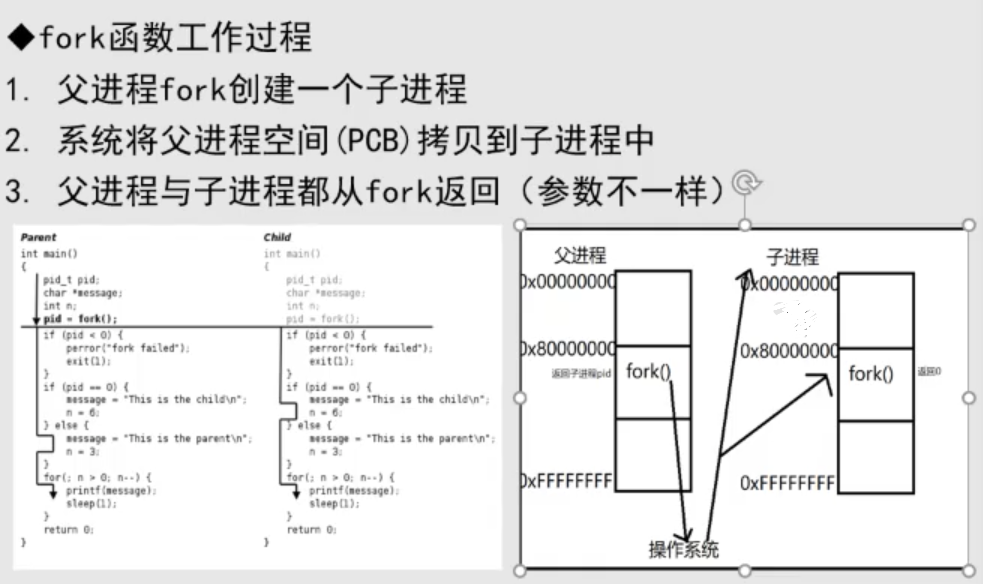
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <stdio.h> int main() { pid_t pid; //创建一个进程 pid = fork(); char* message; int n; //如果返回值是-1那么,创建失败 if(pid<0) { message="fork falled\n"; return 0; } //如果返回值是,那么当前处于子进程 if(pid ==0) { message="this is the parent \n"; n = 3; } //如果返回值是>0,那么当前处于主进程 else { message="this is the child \n"; n = 6; } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("%s",message); } return 0; }
exec函数
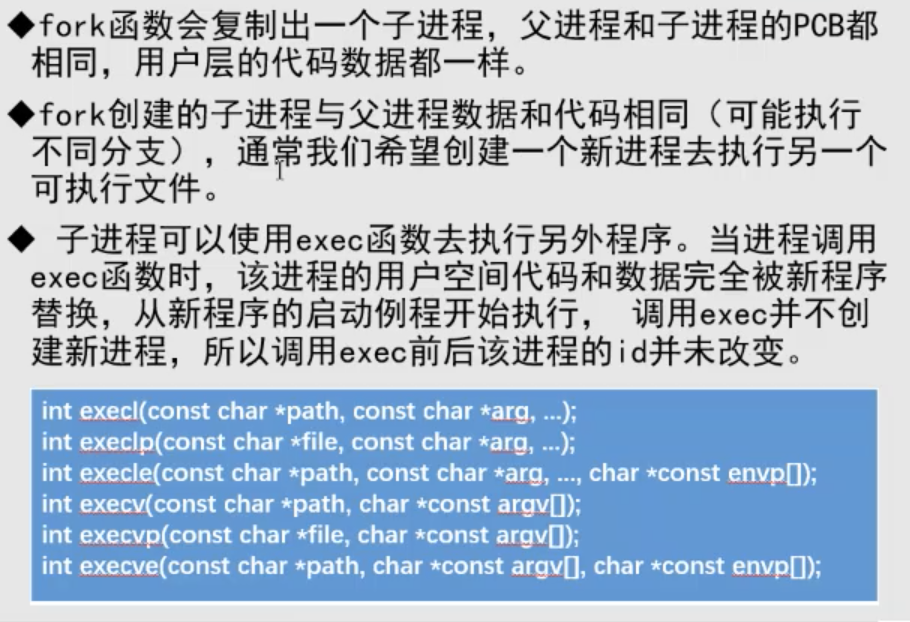
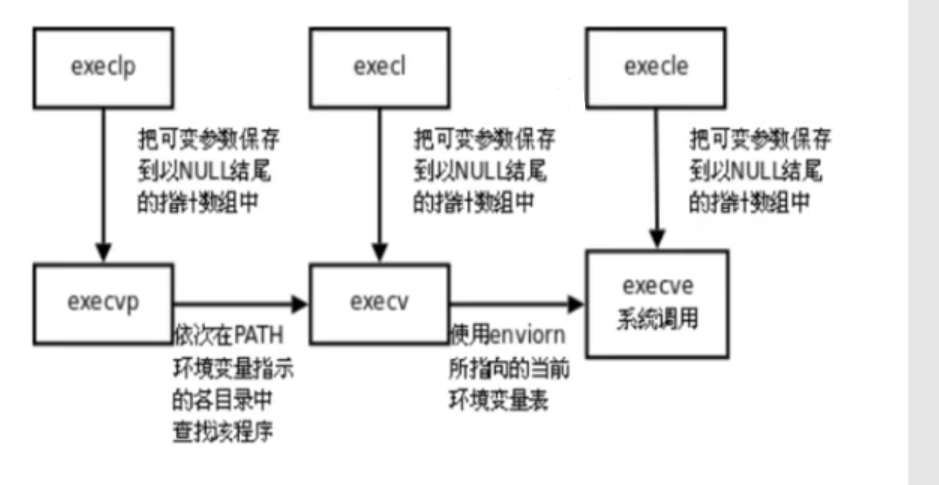
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <stdio.h> void CreateProcess(char* path) { pid_t pid; //创建一个进程 pid = fork(); //如果返回值是-1那么,创建失败 if(pid<0) { printf("create process falled\n"); return 0; } //如果返回值是,那么当前处于子进程 if(pid ==0) { execl(path,NULL); } return; }int main(){ CreateProcess("/usr/bin/firefox"); printf("this is the parent\n"); getchar(); return 0;}
僵尸进程

等待函数

#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main(){ pid_t pid; pid= fork(); if(pid<0){ perror("fork failed\n"); exit(0); } if(pid == 0){//子进程 for(int i=0; i<5;i++){ printf("this is child %d\n",getpid()); sleep(1);//微秒usleep } } else//父进程 { int stat_val; getchar(); pid_t child_pid = wait(&stat_val);//阻塞当前进程,直到子进程结束 //waitpid(&stat_val,0) printf("pid = %d exit",child_pid); if(WIFEXITED(stat_val)){//如果子进程正常值 printf("child exite with code %d\n",WEXITSTATUS(stat_val)); } } }






















