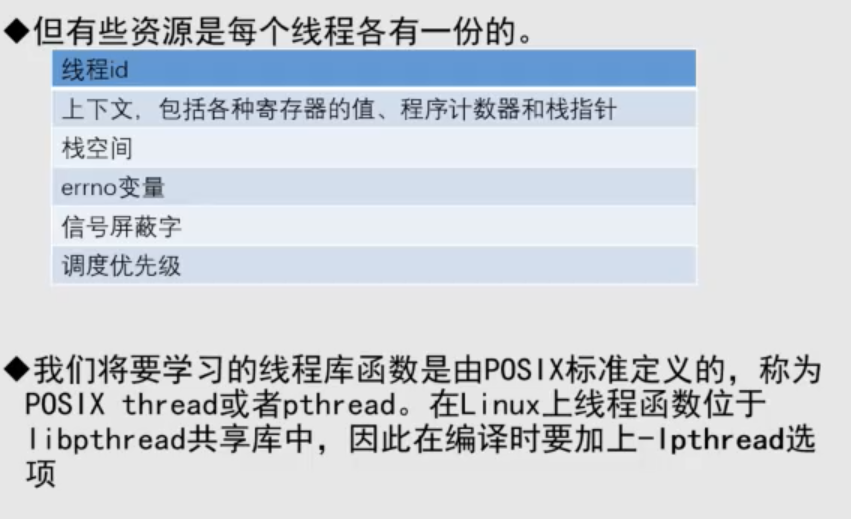
线程
概述
创建线程
#makefilefile: file.cgcc -g $^ -lpthread -o $@ -wclean:rm -rf file*
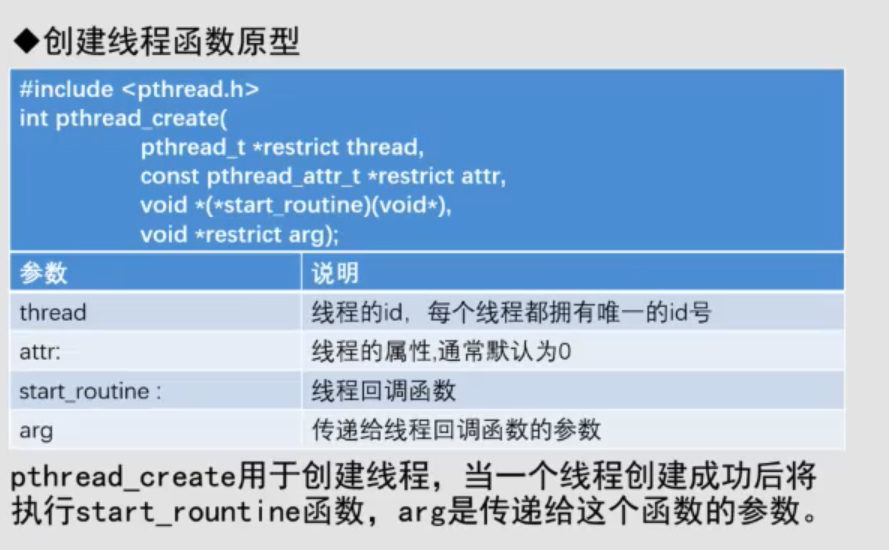
#main.c#include <unistd.h>#include <stdio.h>#include<pthread.h>//gcc xxx.c -lpthread -o main//线程回调函数void* workthread(void* param){//子进程循环10000次for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){printf("循环第[%d]次 ,child进程id :%x\n",i,pthread_self());sleep(1);}//销毁资源pthread_detach(pthread_self);//这里也可以不写,因为下面写了pthread_join,或者这里写了下面不写return NULL;}int main(){pthread_t tid;pthread_create(&tid, //线程idNULL, //线程属性workthread, //线程回调函数NULL //传递给线程的参数);//父进程循环10000次for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){printf("循环第[%d]次 ,parent父进程id :%x\n",i,pthread_self());sleep(1);}//等待线程结束pthread_join(tid,NULL);return 0;}
线程同步
共享冲突(线程不阻塞)
file: file.cgcc -g $^ -lpthread -o $@clean:rm -rf file*
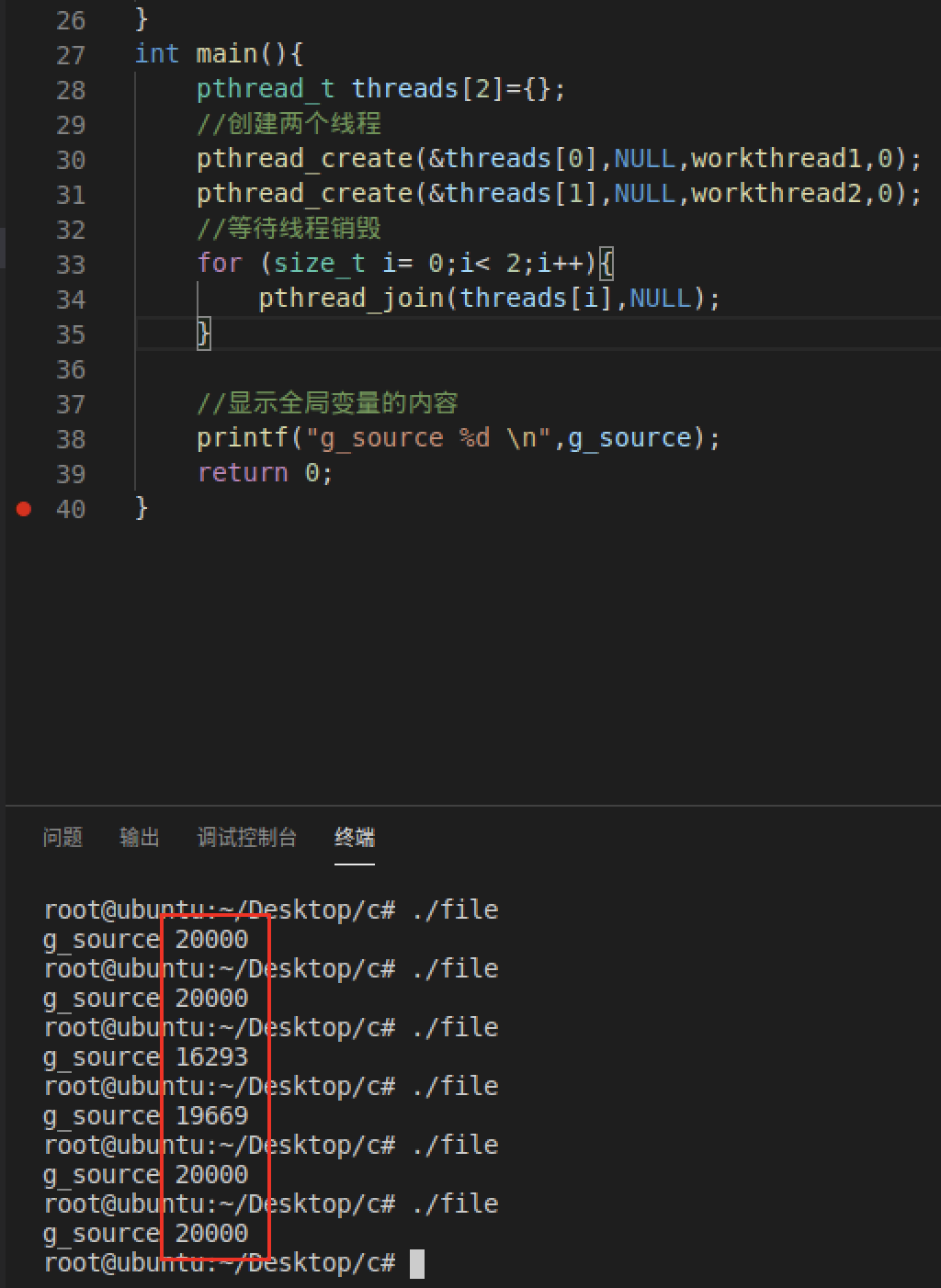
#include <stdio.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>//全局变量(共享资源)int g_source = 0;//线程1void* workthread1(void * param){//循环增加10000次for(size_t i= 0;i< 10000; i++){g_source += 1;// 0x00000000004007ac <+22>: mov 0x2008b2(%rip),%eax # 0x601064 <g_source>// 0x00000000004007b2 <+28>: add $0x1,%eax// 假设这是eax是1000,这是切换了线程,再切换回来,eax仍然是1000,刚刚的线程白加了// 0x00000000004007b5 <+31>: mov %eax,0x2008a9(%rip) # 0x601064 <g_source>}//销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}//线程2void* workthread2(void * param){//循环增加10000次for (size_t i= 0;i< 10000;i++){g_source += 1;}//销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}int main(){pthread_t threads[2]={};//创建两个线程pthread_create(&threads[0],NULL,workthread1,0);pthread_create(&threads[1],NULL,workthread2,0);//等待线程销毁for (size_t i= 0;i< 2;i++){pthread_join(threads[i],NULL);}//显示全局变量的内容printf("g_source %d \n",g_source);return 0;}
互斥锁
线程阻塞
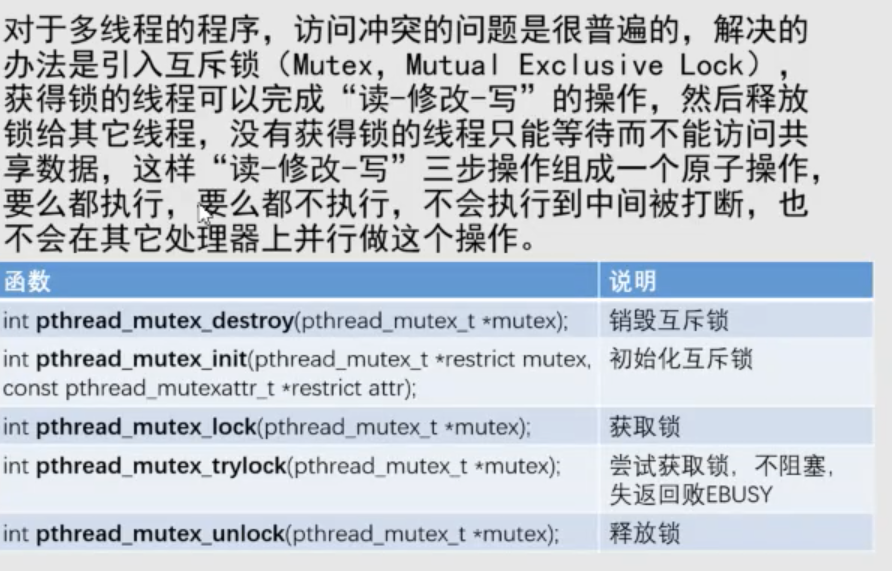
//定义互斥锁复量pthread_mutex_t g_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
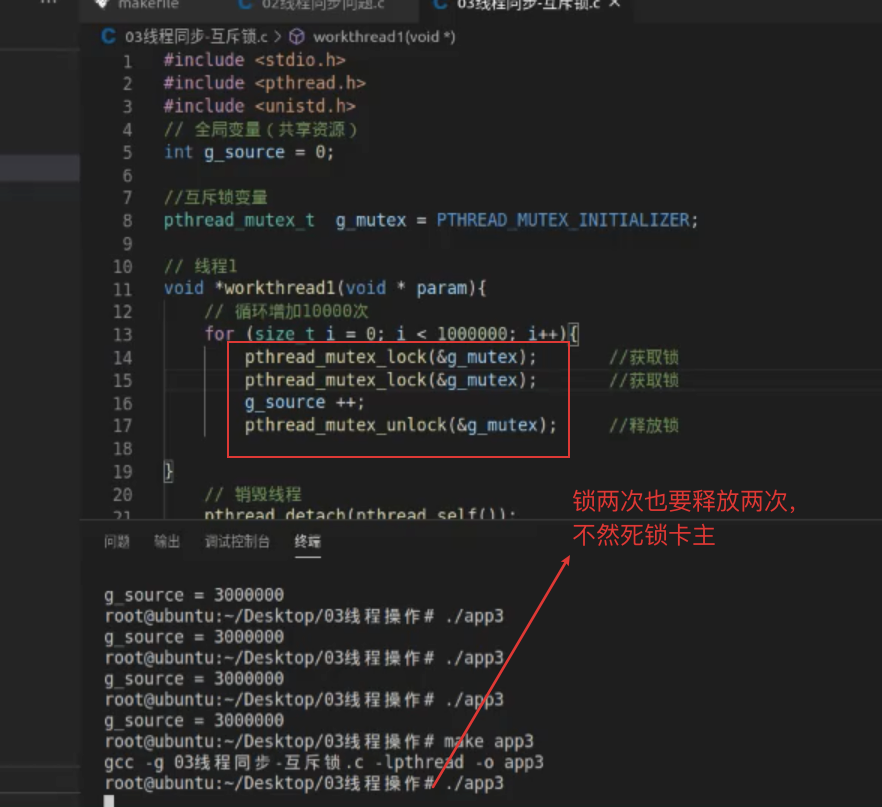
//加锁pthread_mutex_lock(&g_mutex);g_source += 1;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_mutex);
线程不阻塞
#include <stdio.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>//全局变量(共享资源)int g_source = 0;//互斥锁复量pthread_mutex_t g_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;//线程1void* workthread1(void * param){//循环增加10000次for(size_t i= 0;i< 10000; i++){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_mutex);g_source += 1;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_mutex);// 0x00000000004007ac <+22>: mov 0x2008b2(%rip),%eax # 0x601064 <g_source>// 0x00000000004007b2 <+28>: add $0x1,%eax// 假设这是eax是1000,这是切换了线程,再切换回来,eax仍然是1000,刚刚的线程白加了// 0x00000000004007b5 <+31>: mov %eax,0x2008a9(%rip) # 0x601064 <g_source>}//销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}//线程2void* workthread2(void * param){//循环增加10000次for (size_t i= 0;i< 10000;i++){pthread_mutex_lock(&g_mutex);g_source += 1;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_mutex);}//销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}//线程3 不阻塞的线程void* workthread3(void * param){//循环增加10000次for (size_t i= 0;i< 10000;i++){if(0!= pthread_mutex_trylock(&g_mutex)){i--;continue;}g_source += 1;pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_mutex);}//销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}int main(){pthread_t threads[3]={};//创建两个线程pthread_create(&threads[0],NULL,workthread1,0);pthread_create(&threads[1],NULL,workthread2,0);pthread_create(&threads[2],NULL,workthread3,0);//等待线程销毁for (size_t i= 0;i< 2;i++){pthread_join(threads[i],NULL);}//显示全局变量的内容printf("g_source %d \n",g_source);return 0;}
死锁
信号量
互斥锁用于互斥,信号量用于同步
#include <stdio.h>#include <pthread.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <semaphore.h>//全局变量(共享资源)int g_source = 0;//信号量sem_t g_semaphore;//线程1void* workthread1(void * param){//循环增加10000次for(size_t i= 0;i< 10000; i++){sem_wait(&g_semaphore);//等待信号 ,当等到信号后 ,会将数-1g_source += 1;sem_post(&g_semaphore);//释放信号,将信号值+1}//销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}//线程2void* workthread2(void * param){//循环增加10000次for(size_t i= 0;i< 10000; i++){sem_wait(&g_semaphore);//等待信号 ,当等到信号后 ,会将数-1g_source += 1;sem_post(&g_semaphore);//释放信号,将信号值+1}//销毁线程pthread_detach(pthread_self());return NULL;}int main(){//初始化信号量sem_init(&g_semaphore, //信号量0, //0表示同一个进程下的线程同步1 //信号量的最大值,1的时候可以互斥);pthread_t threads[2]={};//创建两个线程pthread_create(&threads[0],NULL,workthread1,0);pthread_create(&threads[1],NULL,workthread2,0);//等待线程销毁for (size_t i= 0;i< 2;i++){pthread_join(threads[i],NULL);}//显示全局变量的内容printf("g_source %d \n",g_source);//释放信号量sem_destroy(&g_semaphore);return 0;}
信号量常用与生成者与消费者模式