1. JDBC 工具类
为了方便后续有关JDBC相关的操作,我们最好将冗余的操作归纳为一个方法,从而创建有关JDBC的工具类。JDBC工具类主要包含两步操作:
- 编写配置文件:配置文件中设置driver、url、username和password
- 编写实现类:主要操作包含获取连接、关闭连接和SQL语句的执行
1.1 配置文件
driver = com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driverurl = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_name?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMTusername = rootpassword = xxxx
2.2 工具类
获取连接、关闭连接以及SQL语句的执行:
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class TransactionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
executeSQL();
}
public static void executeSQL() throws SQLException {
String sql = "update account set balance = balance - ? where id = ?";;
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try{
conn = getConnectionByProperties();
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
pstmt.setDouble(1,100);
pstmt.setInt(2,1);
int c = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(c);
conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e){
conn.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(null, pstmt, conn);
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet resultSet, PreparedStatement pst, Connection connection) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (pst != null) {
try {
pst.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static Connection getConnectionByProperties(){
try {
Class<Main> cls = Main.class;
Properties pro = new Properties();
InputStream is = cls.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("JDBC/jdbc.properties");
pro.load(is);
String driver = pro.getProperty("driver");
String url = pro.getProperty("url");
System.out.println(url);
String username = pro.getProperty("username");
String password = pro.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driver);
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@jdbc(driver = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver",
url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sql_test" +
"?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone = GMT",
username = "root", password = "xxxx")
public static Connection getConnection(){
try {
Class<Main> cls = Main.class;
jdbc annotation = cls.getAnnotation(jdbc.class);
String driver = annotation.driver();
String url = annotation.url();
System.out.println(url);
String username = annotation.username();
String password = annotation.password();
Class.forName(driver);
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
2. SQL注入问题
前面已经说了JDBC中的DriverManager、Connection、Statement和ResultSet四个重要的对象,只剩下PreparedStatement没有说,但提到一句PreparedStatement相比于Statement更加的强大。那么在学习PreparedStatement相关内容前,我们首先通过已经学习的知识编写一个登录(Login)的例子,即判断输入的用户名和密码在数据库表中是否存在。既然需要查询表,我们首先在数据库中新建表account,由于只是演示所用,它只有两个字段username和password。
CREATE TABLE account(
username varchar(20),
password varchar(20)
);
然后往表中插入几条记录
mysql> SELECT * FROM account;
+----------+----------+
| username | password |
+----------+----------+
| Forlogen | 100 |
| Kobe | 101 |
+----------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
最后我们需要编写一个实现登录判断的类,代码如下,由于逻辑很简单,这里就不多做解释了:
package JDBC;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LoginDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input your username...");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("please input your password...");
String password = sc.nextLine();
boolean b = safeLogin(username, password);
String message = b == true ? "welcome..." : "please input correct username and password!";
System.out.println(message);
}
public static boolean safeLogin(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
if (username == null || password == null){
return false;
}
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet res = null;
String sql = "SELECT * FROM account WHERE username = ? AND password = ?";
try{
conn = getConnectionByProperties();
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, password);
res = pstmt.executeQuery();
return res.next();
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(res, pstmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
public static Connection getConnectionByProperties(){
try {
Class<Main> cls = Main.class;
Properties pro = new Properties();
InputStream is = cls.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("JDBC/jdbc.properties");
pro.load(is);
String driver = pro.getProperty("driver");
String url = pro.getProperty("url");
String username = pro.getProperty("username");
String password = pro.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driver);
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static void close(ResultSet resultSet, PreparedStatement pst, Connection connection) {
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (pst != null) {
try {
pst.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
我们看一下编写的类能否实现想要的功能。首先输入Forlogen和100,控制台显示:
然后再随便写个密码试一下: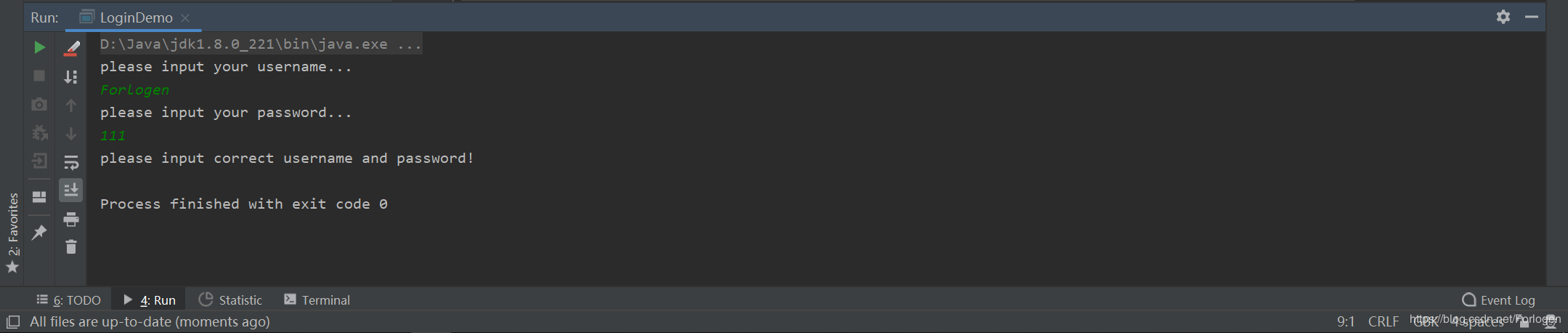
或是输入一个不存在的用户: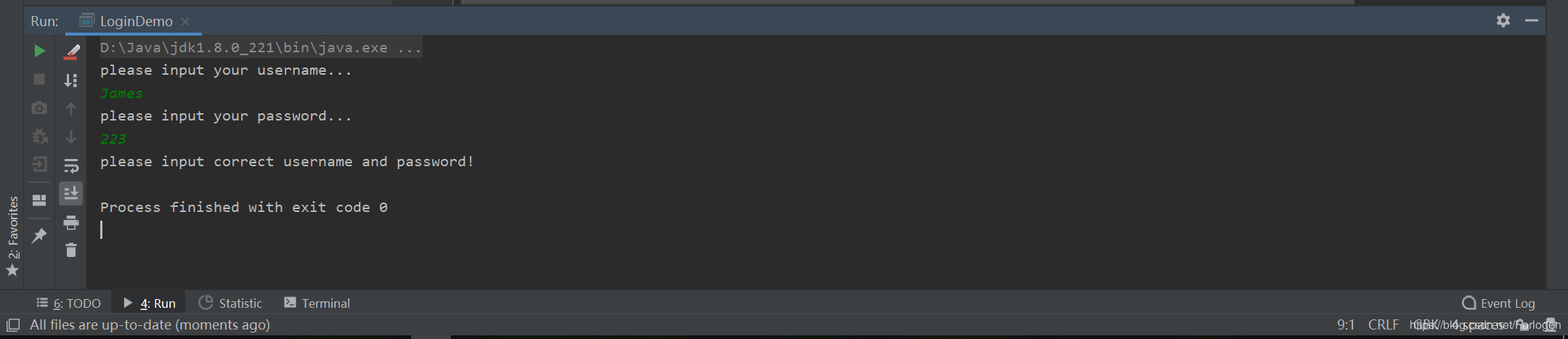
从上面的的试验结果中可以看到,我们编写的类确实可以识别输入的用户名和密码是否存在于表中,哇~可是别高兴太早,下面我们输入Forlogen和a' or 'a' = 'a,然后看一下输出:
发现它居然通过了验证!这么神奇吗?其实这个案例就显示了Statement的一个问题 - - SQL 注入问题,这也是为什么更推荐使用PreparedStatement的原因。
SQL注入问题是指在拼接SQL语句时,有一些SQL的特殊关键字参与了字符串的拼接,从而导致安全性问题的发生。例如上面拼接好的SQL语句为:
SELECT * FROM account WHERE username = 'Forlogen' and password = 'a' or 'a' = 'a'
虽然password输入时错误的,但是'a' = 'a'这个逻辑表达式的存在,使得WHERE语句的结果为true,从而被判断输入是合法的,但这显然是不合理的。
3. PreparedStatement
因此,PreparedStatement通过占位符?来标识数据的位置,然后再逐一的填入数据,最后执行SQL语句。而使用了占位符的SQL语句又被称为预编译SQL语句。使用占位符后,填充数据需使用各种重载的setxxx(),方法中第一个参数为填充的位置,第二个是准备填入的数据。
void setDouble(int parameterIndex, double x)void setFloat(int parameterIndex, float x)void setInt(int parameterIndex, int x)- …
然后同样需要获取PreparedStatement对象,最后使用executexxx()执行SQL语句,获取结果。
executeQuery():执行查询类语句使用,返回一个结果集executeUpdate():执行更新类语句(insert、update、delete等),返回一个表示受影响行数的int型整数
那么,下面我们更新一下上面的Login程序。
public static boolean safeLogin(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
if (username == null || password == null){
return false;
}
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet res = null;
String sql = "SELECT * FROM account WHERE username = ? AND password = ?";
try{
conn = getConnectionByProperties();
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, password);
res = pstmt.executeQuery();
return res.next();
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(res, pstmt, conn);
}
return false;
}
然后同样输入Forlogen和a' or 'a' = 'a,发现此时程序已经解决了之前的问题。
4. JDBC事务管理
4.1 事务
4.1.1 概念
事务指一系列要执行的操作,而这些操作要么完全执行,要么完全不执行。通过事务管理来维护数据库的完整性,保证成批的 SQL 语句要么全部执行,要么全部不执行。而且事务管理主要和DML语句相关,即insert、update和delete语句。
4.1.2 特征
事务主要拥有四大特征,即常说的ACID,它们分别对应:
- 原子性(Atomicity):一个事务(transaction)中的所有操作,要么全部完成,要么全部不完成,不会结束在中间某个环节。事务在执行过程中发生错误,会被回滚(Rollback)到事务开始前的状态,就像这个事务从来没有执行过一样。
- 一致性(Consistency):在事务开始之前和事务结束以后,数据库的完整性没有被破坏。这表示写入的资料必须完全符合所有的预设规则,这包含资料的精确度、串联性以及后续数据库可以自发性地完成预定的工作
- 隔离性(Isolation):数据库允许多个并发事务同时对其数据进行读写和修改的能力,隔离性可以防止多个事务并发执行时由于交叉执行而导致数据的不一致。事务隔离分为不同级别,包括读未提交(Read uncommitted)、读提交(read committed)、可重复读(repeatable read)和串行化(Serializable)
- 持久性(Duability):事务处理结束后,对数据的修改就是永久的,即便系统故障也不会丢失
4.1.3 MySQL中的事务操作
- 开启事务:
start transaction - 回退操作:
rollback - 事务提交:
commit
4.2 示例
下面通过一个账户转账的例子来理解一下事务管理,首先新建表account,它包含id、name和balance三个字段,并在表中插入两条记录。因为要进行事务操作,因此数据引擎应选择支持事务管理的innodb:
mysql> SELECT * FROM account;
+----+----------+---------+
| id | name | balance |
+----+----------+---------+
| 1 | Forlogen | 1000 |
| 2 | Kobe | 1000 |
+----+----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
然后编写实现转账功能的类,代码如下:
package JDBC;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class TransactionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
bank();
}
public static void bank() throws SQLException {
String sql1 = "update account set balance = balance - ? where id = ?";
String sql2 = "update account set balance = balance + ? where id = ?";
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt1 = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt2 = null;
try{
conn = getConnectionByProperties();
pstmt1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
pstmt2 = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
pstmt1.setDouble(1,100);
pstmt1.setInt(2,1);
pstmt2.setDouble(1,100);
pstmt2.setInt(2,2);
int c = pstmt1.executeUpdate();
pstmt2.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(c);
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(null, pstmt1, conn);
close(null, pstmt2, null);
}
}
}
我们执行一次代码,然后查看数据库中的表,表更新为:
mysql> SELECT * FROM account;
+----+----------+---------+
| id | name | balance |
+----+----------+---------+
| 1 | Forlogen | 900 |
| 2 | Kobe | 1100 |
+----+----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
发现执行成功!
但如果在执行完sql1后程序抛出了异常,那么表是如何变化的呢?下面我们在代码中插入一个简单的数学异常:
public static void bank() throws SQLException {
String sql1 = "update account set balance = balance - ? where id = ?";
String sql2 = "update account set balance = balance + ? where id = ?";
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt1 = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt2 = null;
try{
conn = getConnectionByProperties();
pstmt1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
pstmt2 = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
pstmt1.setDouble(1,100);
pstmt1.setInt(2,1);
pstmt2.setDouble(1,100);
pstmt2.setInt(2,2);
int c = pstmt1.executeUpdate();
int i = 3 / 0;
pstmt2.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(c);
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(null, pstmt1, conn);
close(null, pstmt2, null);
}
}
然后再去看一下表中的记录,发现Forlgoen的钱扣掉了,但是Kobe的余额并没有增加,这显然是不正常的。为了解决这种问题,就需要使用事务来进行操作。
mysql> select * from account;
+----+----------+---------+
| id | name | balance |
+----+----------+---------+
| 1 | Forlogen | 800 |
| 2 | Kobe | 1100 |
+----+----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4.3事务操作
JDBC中涉及到事务操作的主要有:
连接对象.setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit):当参数为true时表示自动提交,即不使用事务;如果为false,启用事务,SQL操作会在commit之后统一提交连接对象.commit():提交事务连接对象.rollback():事务回滚
我们在前面的例子中开启事务,执行转账操作来看一下是否有作用。
public static void bank() throws SQLException {
String sql1 = "update account set balance = balance - ? where id = ?";
String sql2 = "update account set balance = balance + ? where id = ?";
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt1 = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt2 = null;
try{
conn = getConnectionByProperties();
pstmt1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
pstmt2 = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
pstmt1.setDouble(1,100);
pstmt1.setInt(2,1);
pstmt2.setDouble(1,100);
pstmt2.setInt(2,2);
int c = pstmt1.executeUpdate();
pstmt2.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(c);
conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e){
conn.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
close(null, pstmt1, conn);
close(null, pstmt2, null);
}
}
执行代码后,表中记录为
mysql> select * from account;
+----+----------+---------+
| id | name | balance |
+----+----------+---------+
| 1 | Forlogen | 800 |
| 2 | Kobe | 1100 |
+----+----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
从结果中可以看出,由于开启了事务,当发生异常时,事务会自动回滚,这样就不会发生一方减钱了,另一方却没有收到钱的尴尬。
5. 更多阅读
这里只是对事务的基本内容以及JDBC中的事务操作做基本的介绍,有关MySQL中更多关于事务的内容可选择继续阅读以下文章

