您可以在JSON模式中定义额外的信息。
一个常见的用例是添加一个将在文档中显示的example。
有几种方法可以声明额外的 JSON 模式信息。
Pydantic schema_extra
您可以使用 Config 和 schema_extra 为Pydantic模型声明一个示例,如Pydantic 文档:定制 Schema 中所述:
from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Nonemodel_config = { "json_schema_extra": { "examples": [ { "name": "Foo", "description": "A very nice Item", "price": 35.4, "tax": 3.2, } ]}}@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results`
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Nonemodel_config = { "json_schema_extra": { "examples": [ { "name": "Foo", "description": "A very nice Item", "price": 35.4, "tax": 3.2, } ]}}@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results`
这些额外的信息将按原样添加到输出的JSON模式中。
Field 的附加参数
在 Field, Path, Query, Body 和其他你之后将会看到的工厂函数,你可以为JSON 模式声明额外信息,你也可以通过给工厂函数传递其他的任意参数来给JSON 模式声明额外信息,比如增加 example:
from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: str = Field(examples=["Foo"]) description: str | None = Field(default=None, examples=["A very nice Item"]) price: float = Field(examples=[35.4]) tax: float | None = Field(default=None, examples=[3.2])@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results`
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: str = Field(examples=["Foo"]) description: Union[str, None] = Field(default=None, examples=["A very nice Item"]) price: float = Field(examples=[35.4]) tax: Union[float, None] = Field(default=None, examples=[3.2])@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results`
Warning
请记住,传递的那些额外参数不会添加任何验证,只会添加注释,用于文档的目的。
Body 额外参数
你可以通过传递额外信息给 Field 同样的方式操作Path, Query, Body等。
比如,你可以将请求体的一个 example 传递给 Body:
Python 3.10+Python 3.9+Python 3.8+Python 3.10+ non-AnnotatedPython 3.8+ non-Annotated
from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int,item: Annotated[Item,Body(examples=[ { "name": "Foo", "description": "A very nice Item", "price": 35.4, "tax": 3.2, }],),],):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results`
from typing import Annotated, Unionfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int,item: Annotated[Item,Body(examples=[ { "name": "Foo", "description": "A very nice Item", "price": 35.4, "tax": 3.2, }],),],):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results`
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelfrom typing_extensions import Annotatedapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int,item: Annotated[Item,Body(examples=[ { "name": "Foo", "description": "A very nice Item", "price": 35.4, "tax": 3.2, }],),],):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results`
Tip
尽可能选择使用 Annotated 的版本。
from fastapi import Body, FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int,item: Item = Body(examples=[ { "name": "Foo", "description": "A very nice Item", "price": 35.4, "tax": 3.2, }],),):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results`
Tip
尽可能选择使用 Annotated 的版本。
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int,item: Item = Body(examples=[ { "name": "Foo", "description": "A very nice Item", "price": 35.4, "tax": 3.2, }],),):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results`
文档 UI 中的例子
使用上面的任何方法,它在 /docs 中看起来都是这样的:
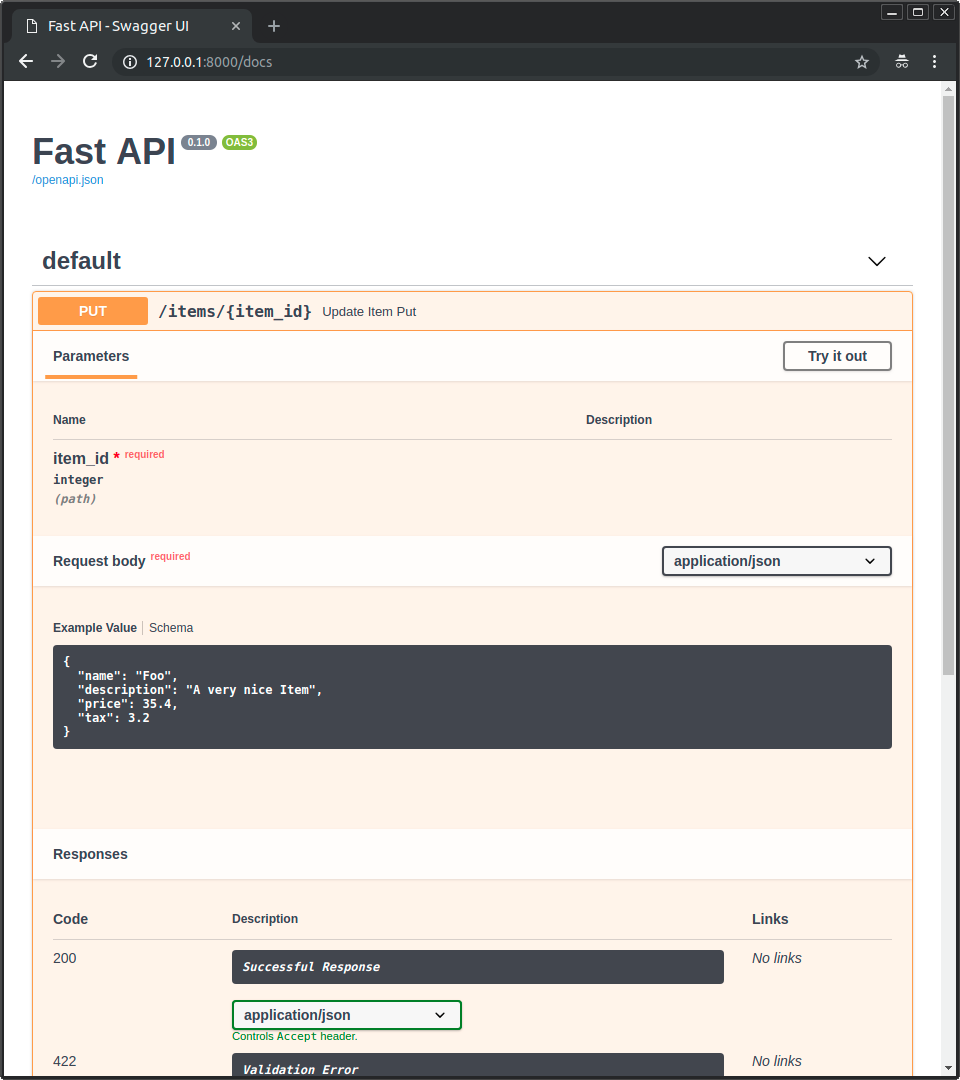
技术细节
关于 example 和 examples…
JSON Schema在最新的一个版本中定义了一个字段 examples ,但是 OpenAPI 基于之前的一个旧版JSON Schema,并没有 examples.
所以 OpenAPI为了相似的目的定义了自己的 example (使用 example, 而不是 examples), 这也是文档 UI 所使用的 (使用 Swagger UI).
所以,虽然 example 不是JSON Schema的一部分,但它是OpenAPI的一部分,这将被文档UI使用。
其他信息
同样的方法,你可以添加你自己的额外信息,这些信息将被添加到每个模型的JSON模式中,例如定制前端用户界面,等等。

