FastAPI 使用请求体从客户端(例如浏览器)向 API 发送数据。
请求体是客户端发送给 API 的数据。响应体是 API 发送给客户端的数据。
API 基本上肯定要发送响应体,但是客户端不一定发送请求体。
使用 Pydantic 模型声明请求体,能充分利用它的功能和优点。
说明
发送数据使用 POST(最常用)、PUT、DELETE、PATCH 等操作。
规范中没有定义使用 GET 发送请求体的操作,但不管怎样,FastAPI 也支持这种方式,只不过仅用于非常复杂或极端的用例。
我们不建议使用 GET,因此,在 Swagger UI 交互文档中不会显示有关 GET 的内容,而且代理协议也不一定支持 GET。
导入 Pydantic 的 BaseModel
从 pydantic 中导入 BaseModel:
from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")async def create_item(item: Item):return item`
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")async def create_item(item: Item):return item`
创建数据模型
把数据模型声明为继承 BaseModel 的类。
使用 Python 标准类型声明所有属性:
from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: str description: str | None = None price: float tax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")async def create_item(item: Item):return item`
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: str description: Union[str, None] = None price: float tax: Union[float, None] = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")async def create_item(item: Item):return item`
与声明查询参数一样,包含默认值的模型属性是可选的,否则就是必选的。默认值为 None 的模型属性也是可选的。
例如,上述模型声明如下 JSON 对象(即 Python 字典):
{
"name": "Foo",
"description": "An optional description",
"price": 45.2,
"tax": 3.5
}
……由于 description 和 tax 是可选的(默认值为 None),下面的 JSON 对象也有效:
{
"name": "Foo",
"price": 45.2
}
声明请求体参数
使用与声明路径和查询参数相同的方式声明请求体,把请求体添加至路径操作:
from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")async def create_item(item: Item):return item`
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")async def create_item(item: Item):return item`
……此处,请求体参数的类型为 Item 模型。
结论
仅使用 Python 类型声明,FastAPI 就可以:
- 以 JSON 形式读取请求体
- (在必要时)把请求体转换为对应的类型
- 校验数据:
- 数据无效时返回错误信息,并指出错误数据的确切位置和内容
- 把接收的数据赋值给参数
item- 把函数中请求体参数的类型声明为
Item,还能获得代码补全等编辑器支持
- 把函数中请求体参数的类型声明为
- 为模型生成 JSON Schema,在项目中所需的位置使用
- 这些概图是 OpenAPI 概图的部件,用于 API 文档 UI
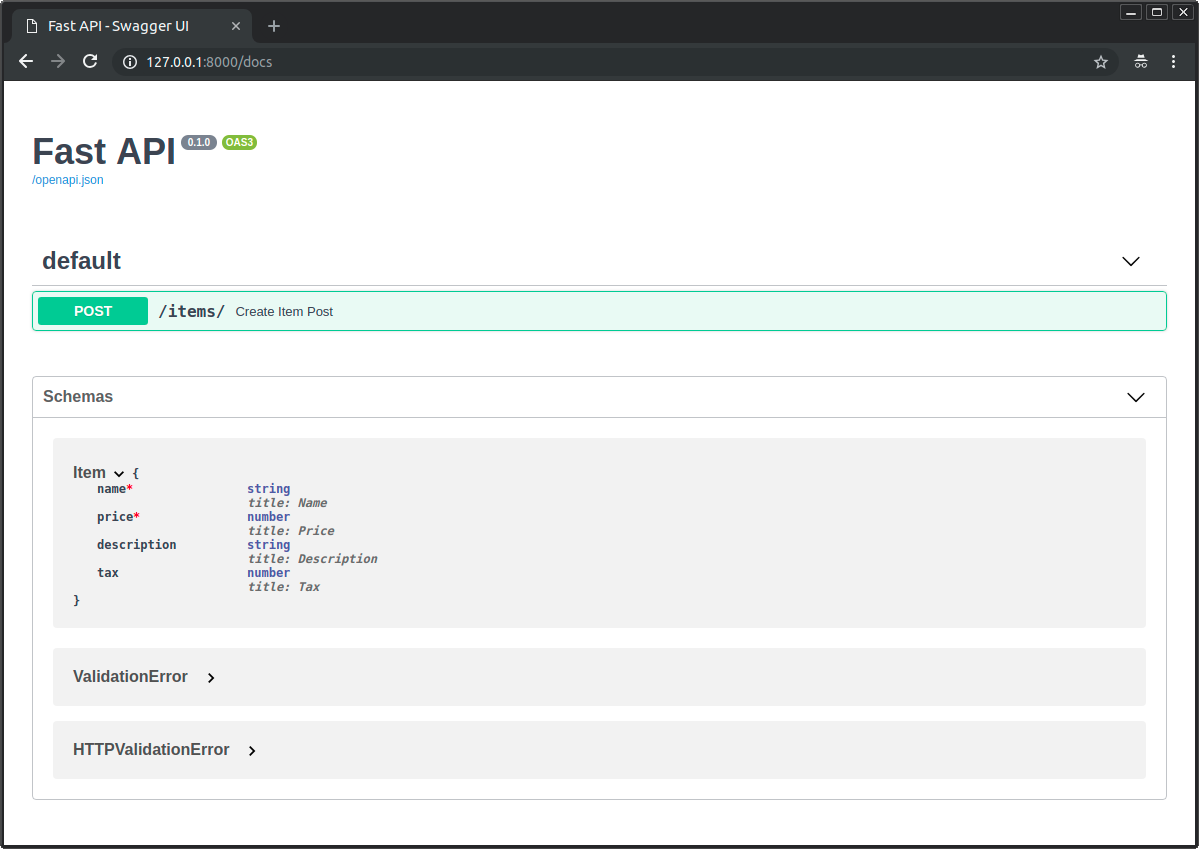
API 文档
Pydantic 模型的 JSON 概图是 OpenAPI 生成的概图部件,可在 API 文档中显示:
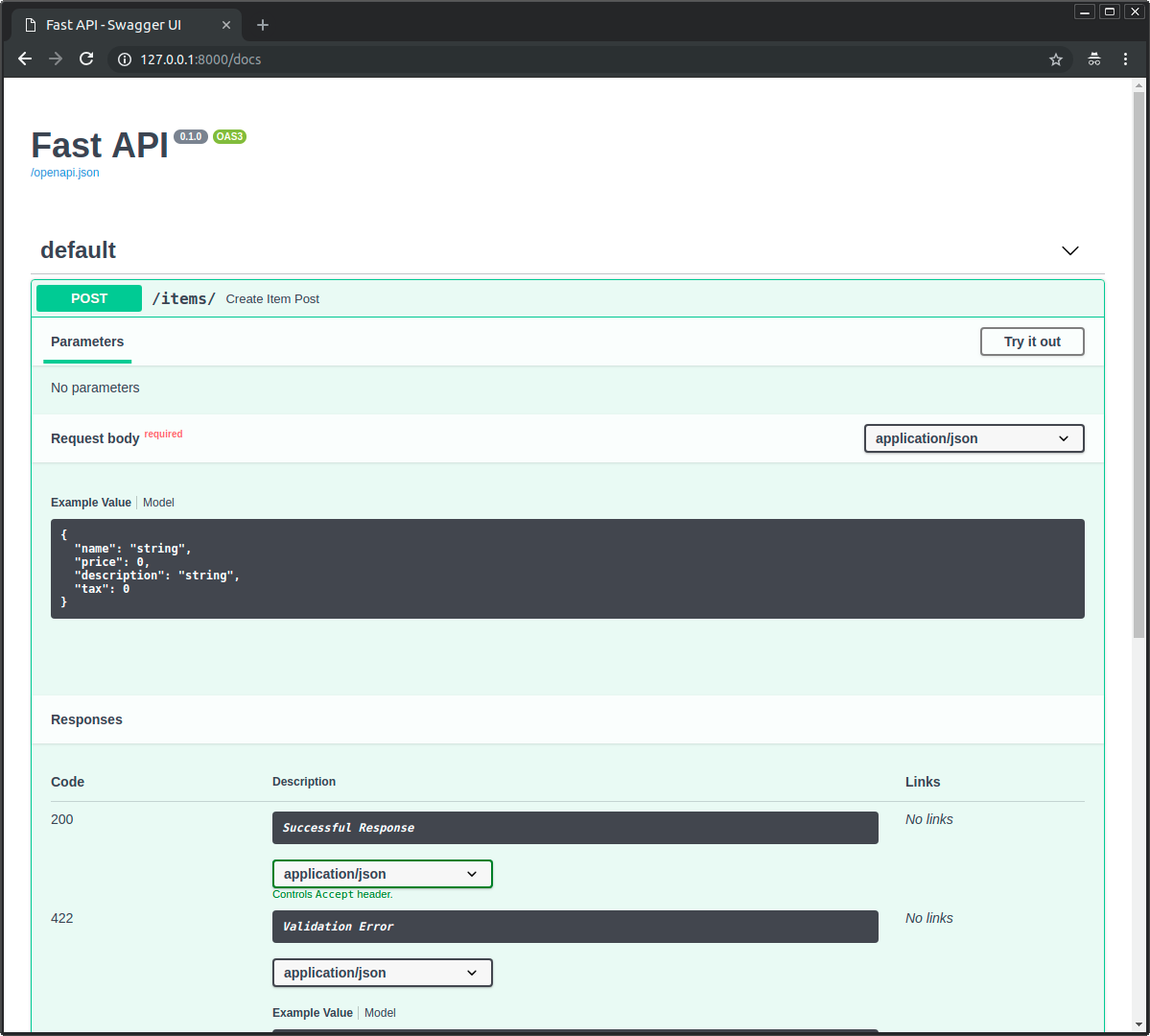
而且,还会用于 API 文档中使用了概图的路径操作:
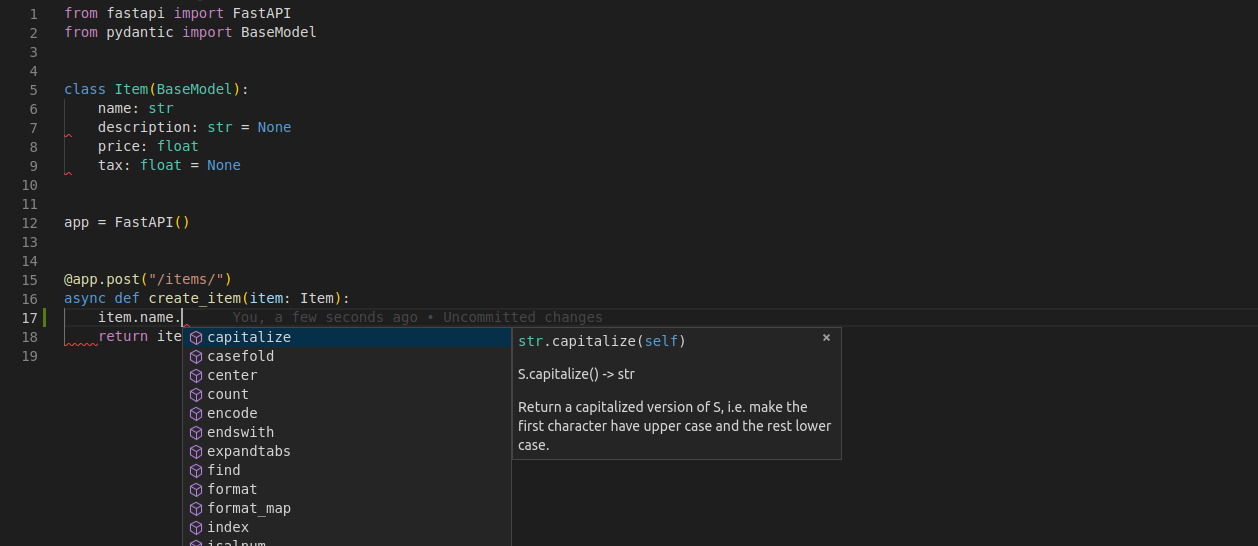
编辑器支持
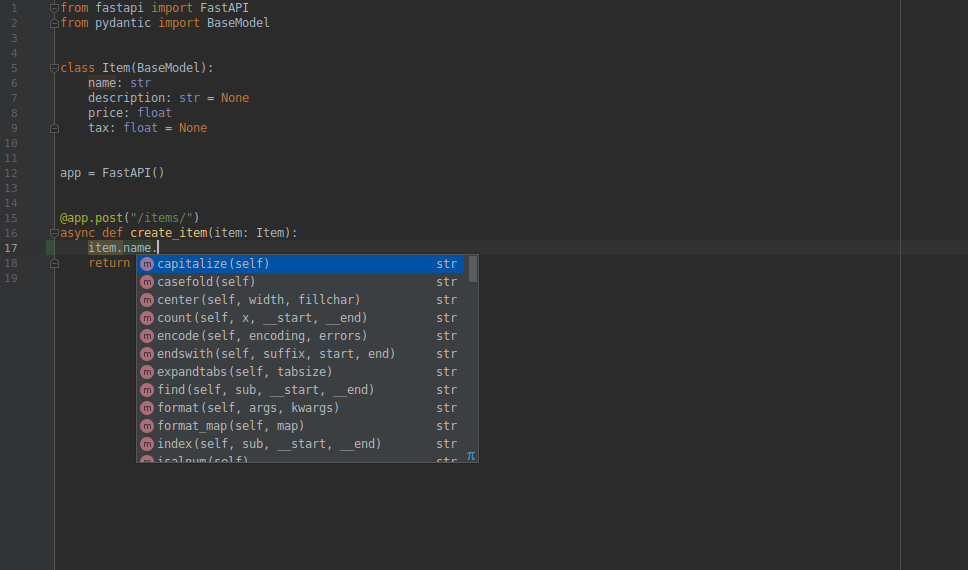
在编辑器中,函数内部均可使用类型提示、代码补全(如果接收的不是 Pydantic 模型,而是字典,就没有这样的支持):
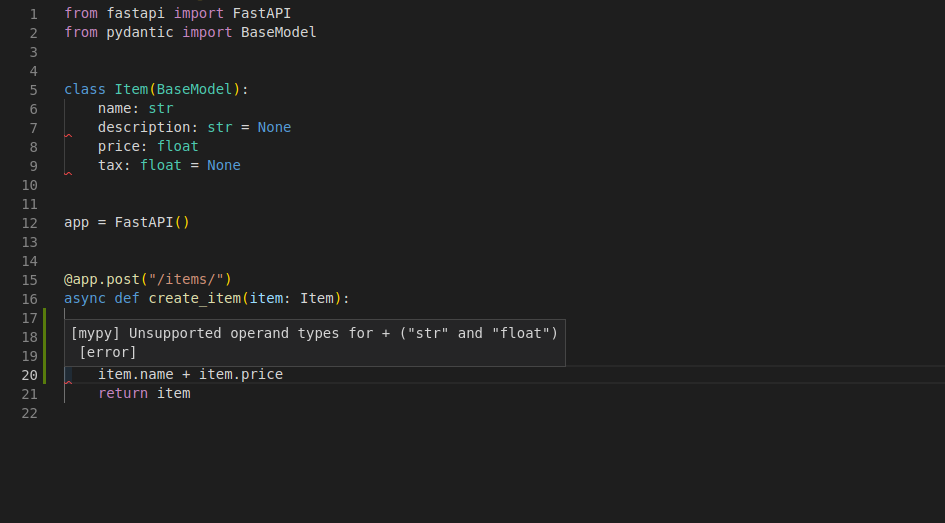
还支持检查错误的类型操作:
这并非偶然,整个 FastAPI 框架都是围绕这种思路精心设计的。
并且,在 FastAPI 的设计阶段,我们就已经进行了全面测试,以确保 FastAPI 可以获得所有编辑器的支持。
我们还改进了 Pydantic,让它也支持这些功能。
虽然上面的截图取自 Visual Studio Code。
但 PyCharm 和大多数 Python 编辑器也支持同样的功能:
提示
使用 PyCharm 编辑器时,推荐安装 Pydantic PyCharm 插件。
该插件用于完善 PyCharm 对 Pydantic 模型的支持,优化的功能如下:
- 自动补全
- 类型检查
- 代码重构
- 查找
- 代码审查
使用模型
在路径操作函数内部直接访问模型对象的属性:
from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")async def create_item(item: Item):item_dict = item.dict()if item.tax:price_with_tax = item.price + item.tax item_dict.update({"price_with_tax": price_with_tax})return item_dict`
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")async def create_item(item: Item):item_dict = item.dict()if item.tax:price_with_tax = item.price + item.tax item_dict.update({"price_with_tax": price_with_tax})return item_dict`
请求体 + 路径参数
FastAPI 支持同时声明路径参数和请求体。
FastAPI 能识别与路径参数匹配的函数参数,还能识别从请求体中获取的类型为 Pydantic 模型的函数参数。
from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.put("/items/{item_id}") async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):return {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}`
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.put("/items/{item_id}") async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):return {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}`
请求体 + 路径参数 + 查询参数
FastAPI 支持同时声明请求体、路径参数和查询参数。
FastAPI 能够正确识别这三种参数,并从正确的位置获取数据。
from fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item, q: str | None = None):result = {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}if q:result.update({"q": q})return result`
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.put("/items/{item_id}")async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item, q: Union[str, None] = None):result = {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}if q:result.update({"q": q})return result`
函数参数按如下规则进行识别:
- 路径中声明了相同参数的参数,是路径参数
- 类型是(
int、float、str、bool等)单类型的参数,是查询参数 - 类型是 Pydantic 模型的参数,是请求体
笔记
因为默认值是 None, FastAPI 会把 q 当作可选参数。
FastAPI 不使用 Optional[str] 中的 Optional, 但 Optional 可以让编辑器提供更好的支持,并检测错误。
不使用 Pydantic
即便不使用 Pydantic 模型也能使用 Body 参数。详见请求体 - 多参数:请求体中的单值。

