你可以在任意的路径操作中使用 response_model 参数来声明用于响应的模型:
@app.get()@app.post()@app.put()@app.delete()- 等等。
Python 3.10+ Python 3.9+ Python 3.8+
from typing import Anyfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Nonetags: list[str] = []@app.post("/items/", response_model=Item) async def create_item(item: Item) -> Any:return item@app.get("/items/", response_model=list[Item]) async def read_items() -> Any:return [ {"name": "Portal Gun", "price": 42.0}, {"name": "Plumbus", "price": 32.0}, ]
from typing import Any, Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Nonetags: list[str] = []@app.post("/items/", response_model=Item) async def create_item(item: Item) -> Any:return item@app.get("/items/", response_model=list[Item]) async def read_items() -> Any:return [ {"name": "Portal Gun", "price": 42.0}, {"name": "Plumbus", "price": 32.0}, ]
from typing import Any, List, Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Nonetags: List[str] = []@app.post("/items/", response_model=Item) async def create_item(item: Item) -> Any:return item@app.get("/items/", response_model=List[Item]) async def read_items() -> Any:return [ {"name": "Portal Gun", "price": 42.0}, {"name": "Plumbus", "price": 32.0}, ]
注意,
response_model是「装饰器」方法(get,post等)的一个参数。不像之前的所有参数和请求体,它不属于路径操作函数。
它接收的类型与你将为 Pydantic 模型属性所声明的类型相同,因此它可以是一个 Pydantic 模型,但也可以是一个由 Pydantic 模型组成的 list,例如 List[Item]。
FastAPI 将使用此 response_model 来:
- 将输出数据转换为其声明的类型。
- 校验数据。
- 在 OpenAPI 的路径操作中为响应添加一个 JSON Schema。
- 并在自动生成文档系统中使用。
但最重要的是:
- 会将输出数据限制在该模型定义内。下面我们会看到这一点有多重要。
技术细节
响应模型在参数中被声明,而不是作为函数返回类型的注解,这是因为路径函数可能不会真正返回该响应模型,而是返回一个 dict、数据库对象或其他模型,然后再使用 response_model 来执行字段约束和序列化。
返回与输入相同的数据
现在我们声明一个 UserIn 模型,它将包含一个明文密码属性。
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrapp = FastAPI()class UserIn(BaseModel):username: strpassword: str email: EmailStrfull_name: Union[str, None] = None# Don't do this in production!@app.post("/user/")async def create_user(user: UserIn) -> UserIn:return user
我们正在使用此模型声明输入数据,并使用同一模型声明输出数据:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrapp = FastAPI()class UserIn(BaseModel):username: strpassword: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: Union[str, None] = None# Don't do this in production!@app.post("/user/") async def create_user(user: UserIn) -> UserIn:return user
现在,每当浏览器使用一个密码创建用户时,API 都会在响应中返回相同的密码。
在这个案例中,这可能不算是问题,因为用户自己正在发送密码。
但是,如果我们在其他的路径操作中使用相同的模型,则可能会将用户的密码发送给每个客户端。
永远不要存储用户的明文密码,也不要在响应中发送密码。
添加输出模型
相反,我们可以创建一个有明文密码的输入模型和一个没有明文密码的输出模型:
from typing import Anyfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrapp = FastAPI()class UserIn(BaseModel):username: strpassword: str email: EmailStrfull_name: str | None = Noneclass UserOut(BaseModel):username: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: str | None = None@app.post("/user/", response_model=UserOut)async def create_user(user: UserIn) -> Any:return user
from typing import Any, Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrapp = FastAPI()class UserIn(BaseModel):username: strpassword: str email: EmailStrfull_name: Union[str, None] = Noneclass UserOut(BaseModel):username: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: Union[str, None] = None@app.post("/user/", response_model=UserOut)async def create_user(user: UserIn) -> Any:return user
这样,即便我们的路径操作函数将会返回包含密码的相同输入用户:
from typing import Anyfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrapp = FastAPI()class UserIn(BaseModel):username: strpassword: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: str | None = Noneclass UserOut(BaseModel):username: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: str | None = None@app.post("/user/", response_model=UserOut)async def create_user(user: UserIn) -> Any:return user
from typing import Any, Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrapp = FastAPI()class UserIn(BaseModel):username: strpassword: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: Union[str, None] = Noneclass UserOut(BaseModel):username: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: Union[str, None] = None@app.post("/user/", response_model=UserOut)async def create_user(user: UserIn) -> Any:return user
…我们已经将 response_model 声明为了不包含密码的 UserOut 模型:
from typing import Anyfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrapp = FastAPI()class UserIn(BaseModel):username: strpassword: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: str | None = Noneclass UserOut(BaseModel):username: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: str | None = None@app.post("/user/", response_model=UserOut) async def create_user(user: UserIn) -> Any:return user
from typing import Any, Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStrapp = FastAPI()class UserIn(BaseModel):username: strpassword: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: Union[str, None] = Noneclass UserOut(BaseModel):username: stremail: EmailStrfull_name: Union[str, None] = None@app.post("/user/", response_model=UserOut) async def create_user(user: UserIn) -> Any:return user
因此,FastAPI 将会负责过滤掉未在输出模型中声明的所有数据(使用 Pydantic)。
在文档中查看
当你查看自动化文档时,你可以检查输入模型和输出模型是否都具有自己的 JSON Schema:
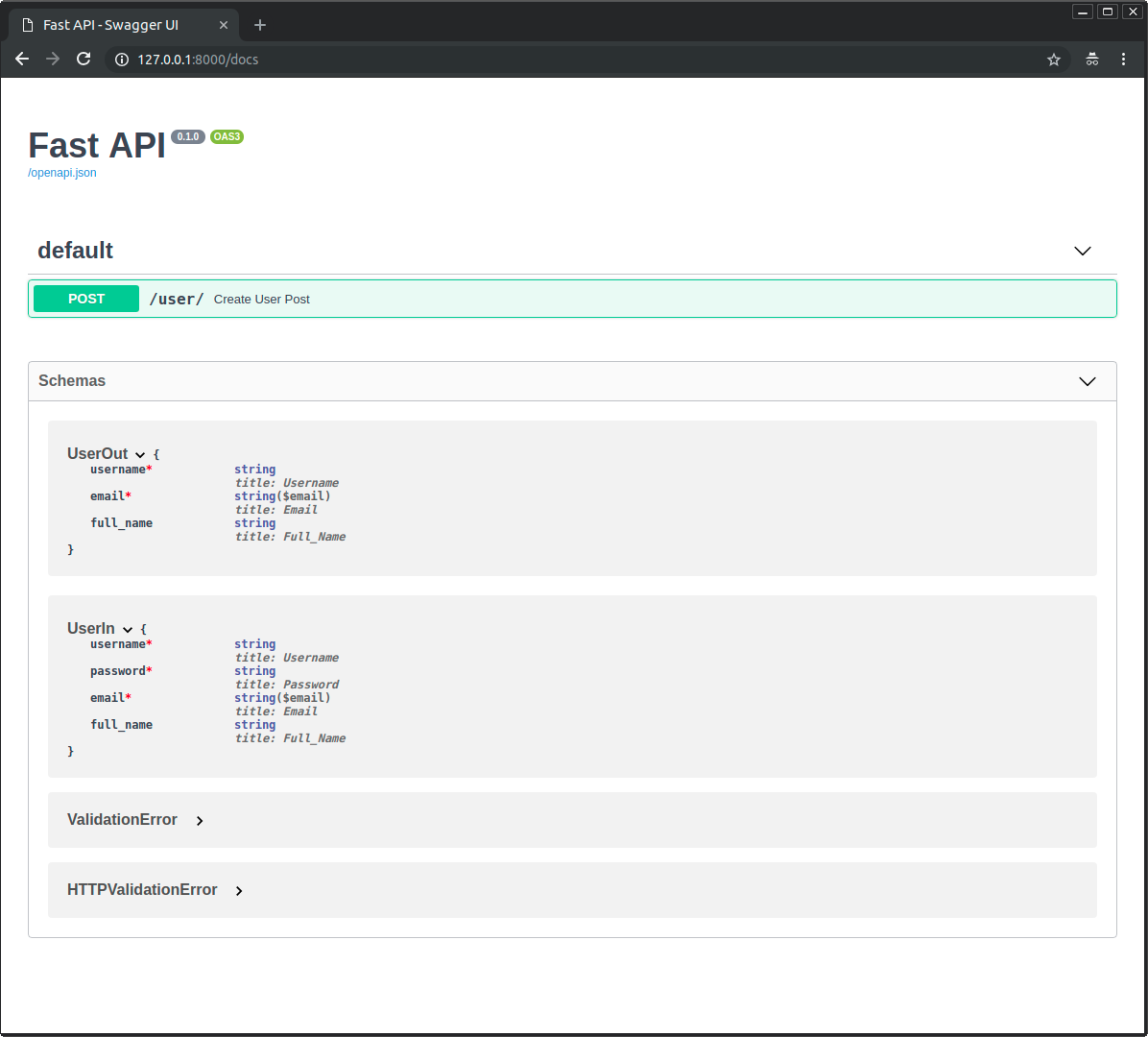
并且两种模型都将在交互式 API 文档中使用:
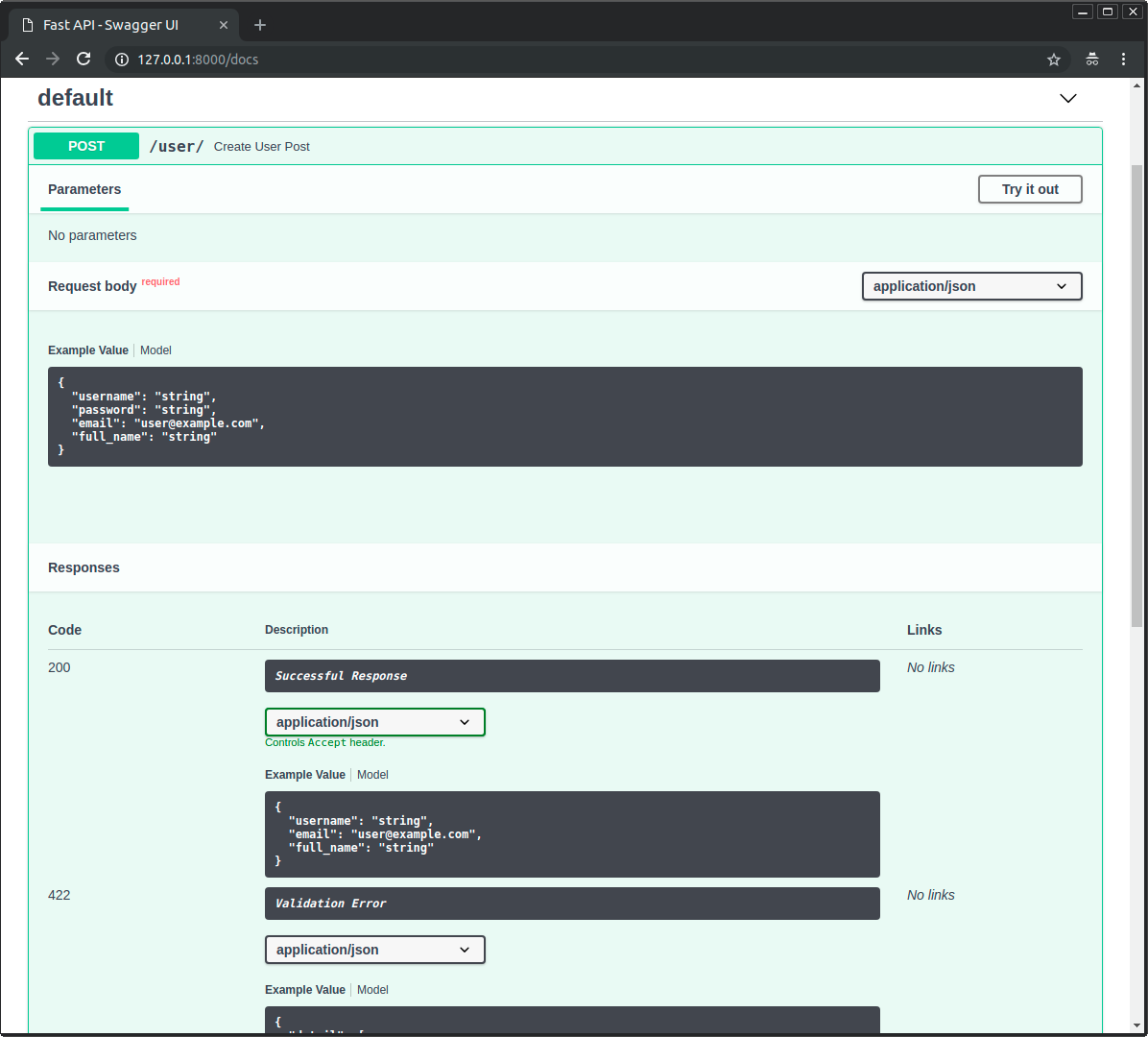
响应模型编码参数
你的响应模型可以具有默认值,例如:
from typing import List, Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = None price: floattax: float = 10.5 tags: List[str] = []items = {"foo": {"name": "Foo", "price": 50.2},"bar": {"name": "Bar", "description": "The bartenders", "price": 62, "tax": 20.2},"baz": {"name": "Baz", "description": None, "price": 50.2, "tax": 10.5, "tags": []},}@app.get("/items/{item_id}", response_model=Item, response_model_exclude_unset=True)async def read_item(item_id: str):return items[item_id]
description: Union[str, None] = None具有默认值None。tax: float = 10.5具有默认值10.5.tags: List[str] = []具有一个空列表作为默认值:[].
但如果它们并没有存储实际的值,你可能想从结果中忽略它们的默认值。
举个例子,当你在 NoSQL 数据库中保存了具有许多可选属性的模型,但你又不想发送充满默认值的很长的 JSON 响应。
使用 response_model_exclude_unset 参数
你可以设置路径操作装饰器的 response_model_exclude_unset=True 参数:
from typing import List, Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: float = 10.5tags: List[str] = []items = {"foo": {"name": "Foo", "price": 50.2},"bar": {"name": "Bar", "description": "The bartenders", "price": 62, "tax": 20.2},"baz": {"name": "Baz", "description": None, "price": 50.2, "tax": 10.5, "tags": []},}@app.get("/items/{item_id}", response_model=Item, response_model_exclude_unset=True) async def read_item(item_id: str):return items[item_id]
然后响应中将不会包含那些默认值,而是仅有实际设置的值。
因此,如果你向路径操作发送 ID 为 foo 的商品的请求,则响应(不包括默认值)将为:
{
"name": "Foo",
"price": 50.2
}
Info
FastAPI 通过 Pydantic 模型的 .dict() 配合 该方法的 exclude_unset 参数 来实现此功能。
Info
你还可以使用:
response_model_exclude_defaults=Trueresponse_model_exclude_none=True
参考 Pydantic 文档 中对 exclude_defaults 和 exclude_none 的描述。
默认值字段有实际值的数据
但是,如果你的数据在具有默认值的模型字段中有实际的值,例如 ID 为 bar 的项:
{
"name": "Bar",
"description": "The bartenders", "price": 62,
"tax": 20.2 }
这些值将包含在响应中。
具有与默认值相同值的数据
如果数据具有与默认值相同的值,例如 ID 为 baz 的项:
{
"name": "Baz",
"description": None, "price": 50.2,
"tax": 10.5, "tags": [] }
即使 description、tax 和 tags 具有与默认值相同的值,FastAPI 足够聪明 (实际上是 Pydantic 足够聪明) 去认识到这一点,它们的值被显式地所设定(而不是取自默认值)。
因此,它们将包含在 JSON 响应中。
Tip
请注意默认值可以是任何值,而不仅是None。
它们可以是一个列表([]),一个值为 10.5的 float,等等。
response_model_include 和 response_model_exclude
你还可以使用路径操作装饰器的 response_model_include 和 response_model_exclude 参数。
它们接收一个由属性名称 str 组成的 set 来包含(忽略其他的)或者排除(包含其他的)这些属性。
如果你只有一个 Pydantic 模型,并且想要从输出中移除一些数据,则可以使用这种快捷方法。
Tip
但是依然建议你使用上面提到的主意,使用多个类而不是这些参数。
这是因为即使使用 response_model_include 或 response_model_exclude 来省略某些属性,在应用程序的 OpenAPI 定义(和文档)中生成的 JSON Schema 仍将是完整的模型。
这也适用于作用类似的 response_model_by_alias。
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: float = 10.5items = {"foo": {"name": "Foo", "price": 50.2},"bar": {"name": "Bar", "description": "The Bar fighters", "price": 62, "tax": 20.2},"baz": {"name": "Baz","description": "There goes my baz","price": 50.2,"tax": 10.5,},}@app.get("/items/{item_id}/name",response_model=Item,response_model_include={"name", "description"}, )async def read_item_name(item_id: str):return items[item_id]@app.get("/items/{item_id}/public", response_model=Item, response_model_exclude={"tax"}) async def read_item_public_data(item_id: str):return items[item_id]
Tip
{"name", "description"} 语法创建一个具有这两个值的 set。
等同于 set(["name", "description"])。
使用 list 而不是 set
如果你忘记使用 set 而是使用 list 或 tuple,FastAPI 仍会将其转换为 set 并且正常工作:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIfrom pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: float = 10.5items = {"foo": {"name": "Foo", "price": 50.2},"bar": {"name": "Bar", "description": "The Bar fighters", "price": 62, "tax": 20.2},"baz": {"name": "Baz","description": "There goes my baz","price": 50.2,"tax": 10.5,},}@app.get("/items/{item_id}/name",response_model=Item,response_model_include=["name", "description"], )async def read_item_name(item_id: str):return items[item_id]@app.get("/items/{item_id}/public", response_model=Item, response_model_exclude=["tax"]) async def read_item_public_data(item_id: str):return items[item_id]
总结
使用路径操作装饰器的 response_model 参数来定义响应模型,特别是确保私有数据被过滤掉。
使用 response_model_exclude_unset 来仅返回显式设定的值。

