是啥子?
ThreadLocal ,即thread 本身需要携带内容的处理; 与多线程无关,不涉及资源竞争;
怎么玩?
通常设置 ThreadLocal 为private static ,当一个线程结束时,ThreadLocal 的所有副本信息均可被回收;
代码
/*** @desc threadLocal 使用* @author xxx* @date 2020/12/02 14:20*/public class ThreadPoolDemo {private static final ThreadLocal<String> THREAD_NAME_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();private static final ThreadLocal<TradeOrder> TRADE_THREAD_LOCAL = new ThreadLocal<>();public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {int tradeId = i;new Thread(() -> {THREAD_NAME_LOCAL.set("name" + tradeId);TradeOrder tradeOrder = new TradeOrder(tradeId, tradeId % 2 == 0 ? "已支付" : "未支付");TRADE_THREAD_LOCAL.set(tradeOrder);System.out.println("threadName: " + THREAD_NAME_LOCAL.get());System.out.println("tradeOrder info:" + TRADE_THREAD_LOCAL.get());}, "thread-" + i).start();}}static class TradeOrder {long id;String status;public TradeOrder(int id, String status) {this.id = id;this.status = status;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "id=" + id + ", status=" + status;}}}
运行结果
threadName: name0tradeOrder info:id=0, status=已支付threadName: name1tradeOrder info:id=1, status=未支付
为啥呢?
存储结构如下
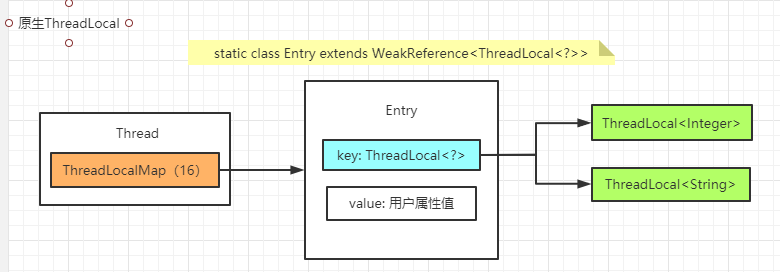
原理分析
ThredLocalMap 在原生Thread 中的体现
public class Thread implements Runnable {/** InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is* maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class.*/// 由此看出ThreadLocalMap 为 java 原生Thread 的一个属性ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;}
我们从ThreadLocal set 方法入手分析;
public void set(T value) {Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程(即调用线程)ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); // 获取当前线程绑定的ThreadLocalMapif (map != null)map.set(this, value);elsecreateMap(t, value);}void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { // 初始化ThreadLocalMapt.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);}ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY]; // 初始化大小为16的Entry 数组int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1); // 与运算获取位置table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);size = 1;setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);}
从以上源码中我们可以直观看到set 过程,那么ThreadLocal 是如何解决hash 冲突的呢?
public class ThreadLocal<T> {private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode(); // threadLocal hash定义private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger();private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;// 获取下一个hash,在上一个hash 基础上+魔术(HASH_INCREMENT)private static int nextHashCode() {return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);}}
因为有魔术的存在,可以保证结果均匀落在数组中;
常见问题
内存泄漏
内存泄漏:由于疏忽或错误造成程序未能释放已经不再使用的内存,从而造成了内存的浪费;
弱引用何时GC: 在内存不足的情况下,会被JVM 垃圾回收;
threadLocal内存泄漏,ThreadLocalMap 中的Entry ,弱引用ThreadLocal ; 即Map中的 Key 是弱引用;
static class ThreadLocalMap {static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */Object value;Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {super(k);value = v;}}}
使用弱引用目的在于在 没有强引用指向ThreadLocal 时,它可以被回收。避免ThreadLocal不能回收造成的内存泄露问题;
但可能出现ThreadLocal 被回收了,Value还存在(value 是强引用),由此造成的内存泄露;故需要在ThreadLocal 使用完毕后调用remove,移除Entry;
经典使用场景
- 接口中获取客户端类型(避免此参数传递太深)

