Java集合概述
集合类结构与关系
Map结尾的实现了Map接口,其他的都实现了Collection接口.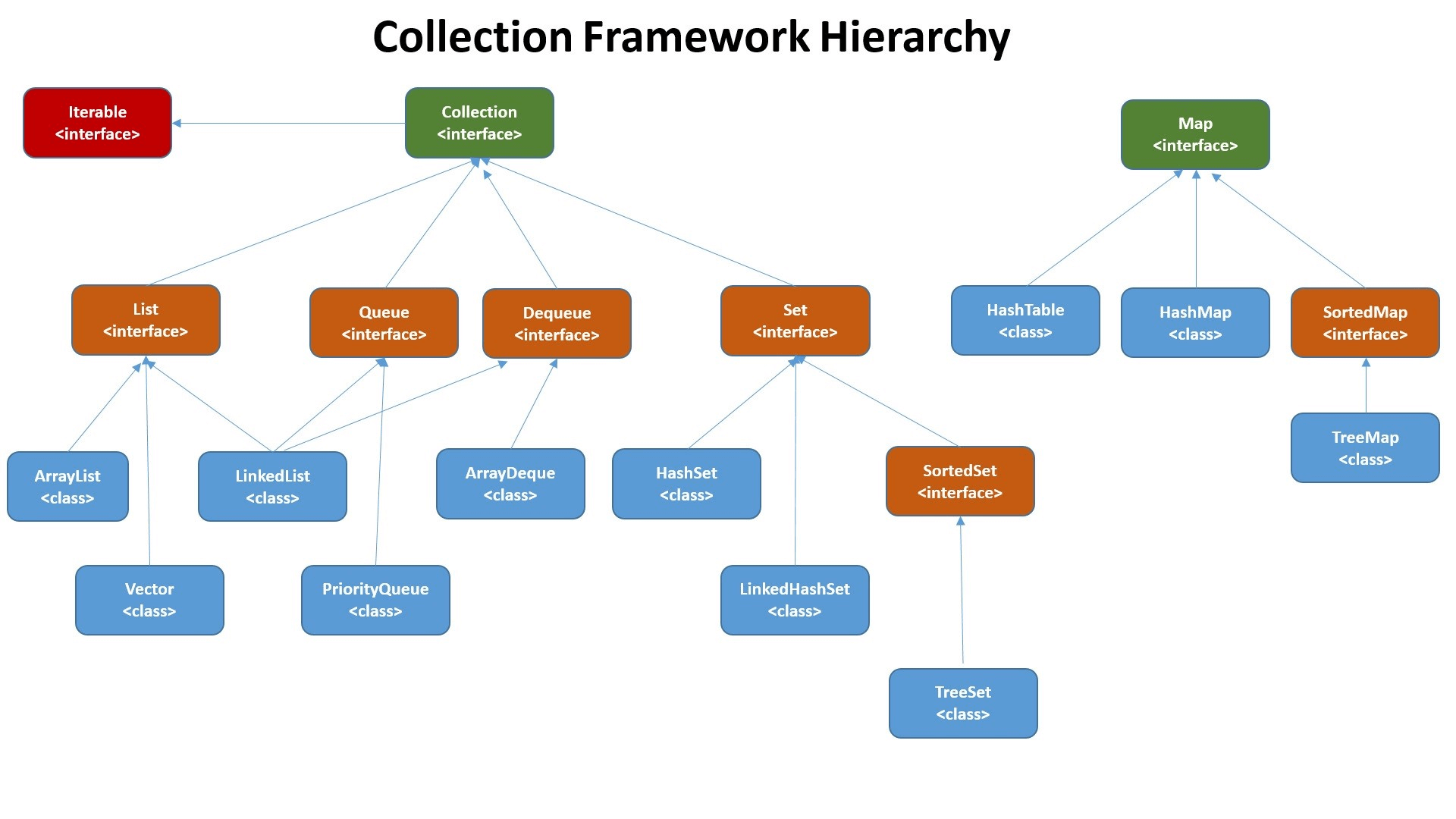
Map接口源码
JDK版本1.8.0_261,可以看到除了一些容器的增,删,查,迭代操作以外,还有一些JDK1.8以后提供的默认方法和静态方法,使用到了函数式编程参数传入的是一个Funcation对象。
package java.util;import java.util.function.BiConsumer;import java.util.function.BiFunction;import java.util.function.Function;import java.io.Serializable;** @param <K> the type of keys maintained by this map* @param <V> the type of mapped values** @author Josh Bloch* @see HashMap* @see TreeMap* @see Hashtable* @see SortedMap* @see Collection* @see Set* @since 1.2*/public interface Map<K,V> {int size();boolean isEmpty();boolean containsKey(Object key);boolean containsValue(Object value);V get(Object key);V put(K key, V value);V remove(Object key);void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);void clear();Set<K> keySet();Collection<V> values();Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();interface Entry<K,V> {K getKey();V getValue();V setValue(V value);boolean equals(Object o);int hashCode();/*** @since 1.8*/public static <K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByKey() {return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)(c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey());}/*** @since 1.8*/public static <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByValue() {return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)(c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue());}/*** @since 1.8*/public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByKey(Comparator<? super K> cmp) {Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getKey(), c2.getKey());}/*** @since 1.8*/public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByValue(Comparator<? super V> cmp) {Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getValue(), c2.getValue());}}boolean equals(Object o);int hashCode();// Defaultable methods/*** @since 1.8*/default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {V v;return (((v = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key))? v: defaultValue;}/*** @since 1.8*/default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {K k;V v;try {k = entry.getKey();v = entry.getValue();} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);}action.accept(k, v);}}/*** @since 1.8*/default void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {Objects.requireNonNull(function);for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {K k;V v;try {k = entry.getKey();v = entry.getValue();} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);}// ise thrown from function is not a cme.v = function.apply(k, v);try {entry.setValue(v);} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);}}}/*** If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped* to {@code null}) associates it with the given value and returns* {@code null}, else returns the current value.** @since 1.8*/default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {V v = get(key);if (v == null) {v = put(key, value);}return v;}/*** Removes the entry for the specified key only if it is currently* mapped to the specified value.* @since 1.8*/default boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {Object curValue = get(key);if (!Objects.equals(curValue, value) ||(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {return false;}remove(key);return true;}/*** Replaces the entry for the specified key only if currently* mapped to the specified value.** @since 1.8*/default boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {Object curValue = get(key);if (!Objects.equals(curValue, oldValue) ||(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {return false;}put(key, newValue);return true;}/*** Replaces the entry for the specified key only if it is* currently mapped to some value.** @since 1.8*/default V replace(K key, V value) {V curValue;if (((curValue = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key)) {curValue = put(key, value);}return curValue;}/*** If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped* to {@code null}), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping* function and enters it into this map unless {@code null}.* @since 1.8*/default V computeIfAbsent(K key,Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction);V v;if ((v = get(key)) == null) {V newValue;if ((newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key)) != null) {put(key, newValue);return newValue;}}return v;}/*** If the value for the specified key is present and non-null, attempts to* compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value.** <p>If the function returns {@code null}, the mapping is removed. If the* function itself throws an (unchecked) exception, the exception is* rethrown, and the current mapping is left unchanged.* @since 1.8*/default V computeIfPresent(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);V oldValue;if ((oldValue = get(key)) != null) {V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);if (newValue != null) {put(key, newValue);return newValue;} else {remove(key);return null;}} else {return null;}}/*** Attempts to compute a mapping for the specified key and its current* mapped value (or {@code null} if there is no current mapping). For* example, to either create or append a {@code String} msg to a value* mapping:** @since 1.8*/default V compute(K key,BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);V oldValue = get(key);V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);if (newValue == null) {// delete mappingif (oldValue != null || containsKey(key)) {// something to removeremove(key);return null;} else {// nothing to do. Leave things as they were.return null;}} else {// add or replace old mappingput(key, newValue);return newValue;}}/*** If the specified key is not already associated with a value or is* associated with null, associates it with the given non-null value.* Otherwise, replaces the associated value with the results of the given* remapping function, or removes if the result is {@code null}. This* method may be of use when combining multiple mapped values for a key.* For example, to either create or append a {@code String msg} to a* value mapping:* @since 1.8*/default V merge(K key, V value,BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);Objects.requireNonNull(value);V oldValue = get(key);V newValue = (oldValue == null) ? value :remappingFunction.apply(oldValue, value);if(newValue == null) {remove(key);} else {put(key, newValue);}return newValue;}}
Iterable源码
主要的方法只有一个iterator,但是为了支持Java8的函数式编程Stream也提供了一个默认方法for Each
package java.lang;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.Objects;import java.util.Spliterator;import java.util.Spliterators;import java.util.function.Consumer;/*** Implementing this interface allows an object to be the target of* the "for-each loop" statement.** @since 1.5* @jls 14.14.2 The enhanced for statement*/public interface Iterable<T> {/*** Returns an iterator over elements of type {@code T}.** @return an Iterator.*/Iterator<T> iterator();/*** Performs the given action for each element of the {@code Iterable}* until all elements have been processed or the action throws an* exception. Unless otherwise specified by the implementing class,* actions are performed in the order of iteration (if an iteration order* is specified). Exceptions thrown by the action are relayed to the* caller* @since 1.8*/default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);for (T t : this) {action.accept(t);}}/*** Creates a {@link Spliterator} over the elements described by this* {@code Iterable}.* @since 1.8*/default Spliterator<T> spliterator() {return Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(iterator(), 0);}}
Collection源码
同样,为了支持Stream操作,增加了一些默认方法
package java.util;import java.util.function.Predicate;import java.util.stream.Stream;import java.util.stream.StreamSupport;/*** The root interface in the <i>collection hierarchy</i>. A collection* represents a group of objects, known as its <i>elements</i>. Some* collections allow duplicate elements and others do not. Some are ordered* and others unordered. The JDK does not provide any <i>direct</i>* implementations of this interface: it provides implementations of more* specific subinterfaces like <tt>Set</tt> and <tt>List</tt>. This interface* is typically used to pass collections around and manipulate them where* maximum generality is desired.** @author Josh Bloch* @author Neal Gafter* @see Set* @see List* @see Map* @see SortedSet* @see SortedMap* @see HashSet* @see TreeSet* @see ArrayList* @see LinkedList* @see Vector* @see Collections* @see Arrays* @see AbstractCollection* @since 1.2*/public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {int size();boolean isEmpty();boolean contains(Object o);Iterator<E> iterator();Object[] toArray();<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);boolean add(E e);boolean remove(Object o);boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);/*** Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given* predicate. Errors or runtime exceptions thrown during iteration or by* the predicate are relayed to the caller.* @since 1.8*/default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {Objects.requireNonNull(filter);boolean removed = false;final Iterator<E> each = iterator();while (each.hasNext()) {if (filter.test(each.next())) {each.remove();removed = true;}}return removed;}boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);void clear();boolean equals(Object o);int hashCode();/*** Creates a {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this collection.* @since 1.8*/@Overridedefault Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return Spliterators.spliterator(this, 0);}/*** Returns a sequential {@code Stream} with this collection as its source.* @since 1.8*/default Stream<E> stream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);}/*** Returns a possibly parallel {@code Stream} with this collection as its* source. It is allowable for this method to return a sequential stream.* @since 1.8*/default Stream<E> parallelStream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);}}
HashMap源码解析
简介
HashMap采用key/value存储结构,每个key对应唯一的value,查询和修改的速度都很快,能达到O(1)的平均时间复杂度。它是非线程安全的,且不保证元素存储的顺序;
继承体系
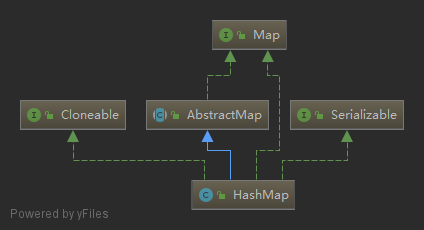
HashMap实现了Cloneable,可以被克隆。
HashMap实现了Serializable,可以被序列化。
HashMap继承自AbstractMap,实现了Map接口,具有Map的所有功能。
存储结构
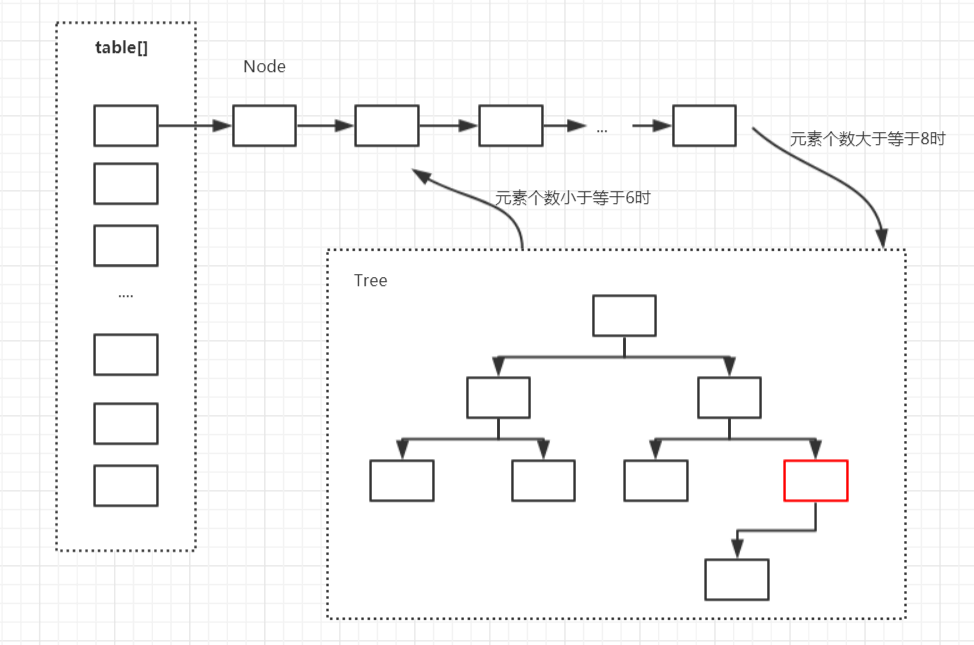
在Java中,HashMap的实现采用了(数组 + 链表 + 红黑树)的复杂结构,数组的一个元素又称作桶。
在添加元素时,会根据hash值算出元素在数组中的位置,如果该位置没有元素,则直接把元素放置在此处,如果该位置有元素了,则把元素以链表的形式放置在链表的尾部。
当一个链表的元素个数达到一定的数量(且数组的长度达到一定的长度)后,则把链表转化为红黑树,从而提高效率。
数组的查询效率为O(1),链表的查询效率是O(k),红黑树的查询效率是O(log k),k为桶中的元素个数,所以当元素数量非常多的时候,转化为红黑树能极大地提高效率。
源码解析
属性
/*** 默认的初始容量为16*/static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;/*** 最大的容量为2的30次方*/static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;/*** 默认的装载因子*/static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;/*** 当一个桶中的元素个数大于等于8时进行树化*/static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;/*** 当一个桶中的元素个数小于等于6时把树转化为链表*/static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;/*** 当桶的个数达到64的时候才进行树化*/static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64;/*** 数组,又叫作桶(bucket)*/transient Node<K,V>[] table;/*** 作为entrySet()的缓存*/transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;/*** 元素的数量*/transient int size;/*** 修改次数,用于在迭代的时候执行快速失败策略*/transient int modCount;/*** 当桶的使用数量达到多少时进行扩容,threshold = capacity * loadFactor*/int threshold;/*** 装载因子*/final float loadFactor;复制代码
(1)容量
容量为数组的长度,亦即桶的个数,默认为16,最大为2的30次方,当容量达到64时才可以树化。
(2)装载因子
装载因子用来计算容量达到多少时才进行扩容,默认装载因子为0.75。
(3)树化
树化,当容量达到64且链表的长度达到8时进行树化,当链表的长度小于6时反树化。
Node内部类-链表基类
Node是一个典型的单链表节点,其中,hash用来存储key计算得来的hash值。
/*** Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)*/static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {final int hash; //Key计算出来的Hash值final K key;V value;Node<K,V> next;Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {this.hash = hash;this.key = key;this.value = value;this.next = next;}public final K getKey() { return key; }public final V getValue() { return value; }public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }public final int hashCode() {return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);}public final V setValue(V newValue) {V oldValue = value;value = newValue;return oldValue;}public final boolean equals(Object o) {if (o == this)return true;if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))return true;}return false;}}复制代码
TreeNode内部类-红黑树基类
这是一个神奇的类,它继承自LinkedHashMap中的Entry类,关于LInkedHashMap.Entry这个类我们后面再讲。
TreeNode是一个典型的树型节点,它实现了一颗红黑树,其中,prev是链表中的节点,用于在删除元素的时候可以快速找到它的前置节点。
/*** Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn* extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or* linked node.*/static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {TreeNode<K,V> parent; //red-black tree linksTreeNode<K,V> left;TreeNode<K,V> right;TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletionboolean red;TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {super(hash, key, val, next);}/*** Returns root of tree containing this node.*/final TreeNode<K,V> root() {for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {if ((p = r.parent) == null)return r;r = p;}}/*** Ensures that the given root is the first node of its bin.*/static <K,V> void moveRootToFront(Node<K,V>[] tab, TreeNode<K,V> root) {int n;if (root != null && tab != null && (n = tab.length) > 0) {int index = (n - 1) & root.hash;TreeNode<K,V> first = (TreeNode<K,V>)tab[index];if (root != first) {Node<K,V> rn;tab[index] = root;TreeNode<K,V> rp = root.prev;if ((rn = root.next) != null)((TreeNode<K,V>)rn).prev = rp;if (rp != null)rp.next = rn;if (first != null)first.prev = root;root.next = first;root.prev = null;}assert checkInvariants(root);}}/*** Finds the node starting at root p with the given hash and key.* The kc argument caches comparableClassFor(key) upon first use* comparing keys.*/final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {TreeNode<K,V> p = this;do {int ph, dir; K pk;TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q;if ((ph = p.hash) > h)p = pl;else if (ph < h)p = pr;else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))return p;else if (pl == null)p = pr;else if (pr == null)p = pl;else if ((kc != null ||(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null)return q;elsep = pl;} while (p != null);return null;}/*** Calls find for root node.*/final TreeNode<K,V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) {return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null);}/*** Tie-breaking utility for ordering insertions when equal* hashCodes and non-comparable. We don't require a total* order, just a consistent insertion rule to maintain* equivalence across rebalancings. Tie-breaking further than* necessary simplifies testing a bit.*/static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) {int d;if (a == null || b == null ||(d = a.getClass().getName().compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0)d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ?-1 : 1);return d;}/*** Forms tree of the nodes linked from this node.*/final void treeify(Node<K,V>[] tab) {TreeNode<K,V> root = null;for (TreeNode<K,V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next;x.left = x.right = null;if (root == null) {x.parent = null;x.red = false;root = x;}else {K k = x.key;int h = x.hash;Class<?> kc = null;for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {int dir, ph;K pk = p.key;if ((ph = p.hash) > h)dir = -1;else if (ph < h)dir = 1;else if ((kc == null &&(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {x.parent = xp;if (dir <= 0)xp.left = x;elsexp.right = x;root = balanceInsertion(root, x);break;}}}}moveRootToFront(tab, root);}/*** Returns a list of non-TreeNodes replacing those linked from* this node.*/final Node<K,V> untreeify(HashMap<K,V> map) {Node<K,V> hd = null, tl = null;for (Node<K,V> q = this; q != null; q = q.next) {Node<K,V> p = map.replacementNode(q, null);if (tl == null)hd = p;elsetl.next = p;tl = p;}return hd;}/*** Tree version of putVal.*/final TreeNode<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,int h, K k, V v) {Class<?> kc = null;boolean searched = false;TreeNode<K,V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this;for (TreeNode<K,V> p = root;;) {int dir, ph; K pk;if ((ph = p.hash) > h)dir = -1;else if (ph < h)dir = 1;else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))return p;else if ((kc == null &&(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {if (!searched) {TreeNode<K,V> q, ch;searched = true;if (((ch = p.left) != null &&(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) ||((ch = p.right) != null &&(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null))return q;}dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);}TreeNode<K,V> xp = p;if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {Node<K,V> xpn = xp.next;TreeNode<K,V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);if (dir <= 0)xp.left = x;elsexp.right = x;xp.next = x;x.parent = x.prev = xp;if (xpn != null)((TreeNode<K,V>)xpn).prev = x;moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x));return null;}}}/*** Removes the given node, that must be present before this call.* This is messier than typical red-black deletion code because we* cannot swap the contents of an interior node with a leaf* successor that is pinned by "next" pointers that are accessible* independently during traversal. So instead we swap the tree* linkages. If the current tree appears to have too few nodes,* the bin is converted back to a plain bin. (The test triggers* somewhere between 2 and 6 nodes, depending on tree structure).*/final void removeTreeNode(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab,boolean movable) {int n;if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)return;int index = (n - 1) & hash;TreeNode<K,V> first = (TreeNode<K,V>)tab[index], root = first, rl;TreeNode<K,V> succ = (TreeNode<K,V>)next, pred = prev;if (pred == null)tab[index] = first = succ;elsepred.next = succ;if (succ != null)succ.prev = pred;if (first == null)return;if (root.parent != null)root = root.root();if (root == null|| (movable&& (root.right == null|| (rl = root.left) == null|| rl.left == null))) {tab[index] = first.untreeify(map); // too smallreturn;}TreeNode<K,V> p = this, pl = left, pr = right, replacement;if (pl != null && pr != null) {TreeNode<K,V> s = pr, sl;while ((sl = s.left) != null) // find successors = sl;boolean c = s.red; s.red = p.red; p.red = c; // swap colorsTreeNode<K,V> sr = s.right;TreeNode<K,V> pp = p.parent;if (s == pr) { // p was s's direct parentp.parent = s;s.right = p;}else {TreeNode<K,V> sp = s.parent;if ((p.parent = sp) != null) {if (s == sp.left)sp.left = p;elsesp.right = p;}if ((s.right = pr) != null)pr.parent = s;}p.left = null;if ((p.right = sr) != null)sr.parent = p;if ((s.left = pl) != null)pl.parent = s;if ((s.parent = pp) == null)root = s;else if (p == pp.left)pp.left = s;elsepp.right = s;if (sr != null)replacement = sr;elsereplacement = p;}else if (pl != null)replacement = pl;else if (pr != null)replacement = pr;elsereplacement = p;if (replacement != p) {TreeNode<K,V> pp = replacement.parent = p.parent;if (pp == null)root = replacement;else if (p == pp.left)pp.left = replacement;elsepp.right = replacement;p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;}TreeNode<K,V> r = p.red ? root : balanceDeletion(root, replacement);if (replacement == p) { // detachTreeNode<K,V> pp = p.parent;p.parent = null;if (pp != null) {if (p == pp.left)pp.left = null;else if (p == pp.right)pp.right = null;}}if (movable)moveRootToFront(tab, r);}/*** Splits nodes in a tree bin into lower and upper tree bins,* or untreeifies if now too small. Called only from resize;* see above discussion about split bits and indices.** @param map the map* @param tab the table for recording bin heads* @param index the index of the table being split* @param bit the bit of hash to split on*/final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) {TreeNode<K,V> b = this;// Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving orderTreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;int lc = 0, hc = 0;for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) {next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next;e.next = null;if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) {if ((e.prev = loTail) == null)loHead = e;elseloTail.next = e;loTail = e;++lc;}else {if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null)hiHead = e;elsehiTail.next = e;hiTail = e;++hc;}}if (loHead != null) {if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map);else {tab[index] = loHead;if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified)loHead.treeify(tab);}}if (hiHead != null) {if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map);else {tab[index + bit] = hiHead;if (loHead != null)hiHead.treeify(tab);}}}/* ------------------------------------------------------------ */// Red-black tree methods, all adapted from CLRstatic <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateLeft(TreeNode<K,V> root,TreeNode<K,V> p) {TreeNode<K,V> r, pp, rl;if (p != null && (r = p.right) != null) {if ((rl = p.right = r.left) != null)rl.parent = p;if ((pp = r.parent = p.parent) == null)(root = r).red = false;else if (pp.left == p)pp.left = r;elsepp.right = r;r.left = p;p.parent = r;}return root;}static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> rotateRight(TreeNode<K,V> root,TreeNode<K,V> p) {TreeNode<K,V> l, pp, lr;if (p != null && (l = p.left) != null) {if ((lr = p.left = l.right) != null)lr.parent = p;if ((pp = l.parent = p.parent) == null)(root = l).red = false;else if (pp.right == p)pp.right = l;elsepp.left = l;l.right = p;p.parent = l;}return root;}static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceInsertion(TreeNode<K,V> root,TreeNode<K,V> x) {x.red = true;for (TreeNode<K,V> xp, xpp, xppl, xppr;;) {if ((xp = x.parent) == null) {x.red = false;return x;}else if (!xp.red || (xpp = xp.parent) == null)return root;if (xp == (xppl = xpp.left)) {if ((xppr = xpp.right) != null && xppr.red) {xppr.red = false;xp.red = false;xpp.red = true;x = xpp;}else {if (x == xp.right) {root = rotateLeft(root, x = xp);xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;}if (xp != null) {xp.red = false;if (xpp != null) {xpp.red = true;root = rotateRight(root, xpp);}}}}else {if (xppl != null && xppl.red) {xppl.red = false;xp.red = false;xpp.red = true;x = xpp;}else {if (x == xp.left) {root = rotateRight(root, x = xp);xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;}if (xp != null) {xp.red = false;if (xpp != null) {xpp.red = true;root = rotateLeft(root, xpp);}}}}}}static <K,V> TreeNode<K,V> balanceDeletion(TreeNode<K,V> root,TreeNode<K,V> x) {for (TreeNode<K,V> xp, xpl, xpr;;) {if (x == null || x == root)return root;else if ((xp = x.parent) == null) {x.red = false;return x;}else if (x.red) {x.red = false;return root;}else if ((xpl = xp.left) == x) {if ((xpr = xp.right) != null && xpr.red) {xpr.red = false;xp.red = true;root = rotateLeft(root, xp);xpr = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.right;}if (xpr == null)x = xp;else {TreeNode<K,V> sl = xpr.left, sr = xpr.right;if ((sr == null || !sr.red) &&(sl == null || !sl.red)) {xpr.red = true;x = xp;}else {if (sr == null || !sr.red) {if (sl != null)sl.red = false;xpr.red = true;root = rotateRight(root, xpr);xpr = (xp = x.parent) == null ?null : xp.right;}if (xpr != null) {xpr.red = (xp == null) ? false : xp.red;if ((sr = xpr.right) != null)sr.red = false;}if (xp != null) {xp.red = false;root = rotateLeft(root, xp);}x = root;}}}else { // symmetricif (xpl != null && xpl.red) {xpl.red = false;xp.red = true;root = rotateRight(root, xp);xpl = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.left;}if (xpl == null)x = xp;else {TreeNode<K,V> sl = xpl.left, sr = xpl.right;if ((sl == null || !sl.red) &&(sr == null || !sr.red)) {xpl.red = true;x = xp;}else {if (sl == null || !sl.red) {if (sr != null)sr.red = false;xpl.red = true;root = rotateLeft(root, xpl);xpl = (xp = x.parent) == null ?null : xp.left;}if (xpl != null) {xpl.red = (xp == null) ? false : xp.red;if ((sl = xpl.left) != null)sl.red = false;}if (xp != null) {xp.red = false;root = rotateRight(root, xp);}x = root;}}}}}/*** Recursive invariant check*/static <K,V> boolean checkInvariants(TreeNode<K,V> t) {TreeNode<K,V> tp = t.parent, tl = t.left, tr = t.right,tb = t.prev, tn = (TreeNode<K,V>)t.next;if (tb != null && tb.next != t)return false;if (tn != null && tn.prev != t)return false;if (tp != null && t != tp.left && t != tp.right)return false;if (tl != null && (tl.parent != t || tl.hash > t.hash))return false;if (tr != null && (tr.parent != t || tr.hash < t.hash))return false;if (t.red && tl != null && tl.red && tr != null && tr.red)return false;if (tl != null && !checkInvariants(tl))return false;if (tr != null && !checkInvariants(tr))return false;return true;}}
为什么要用红黑树来替代双向连表?
当然是为了效率,其实树本身就是链表的二维展开,而在HashMap的实现里,链表就是为了解决Hash冲突而诞生的,当HashMap中插入大量元素,Hash冲突的概率提高,每个桶(数组的节点)上的链表就会很大,链表查询的时间复杂度是O()(n)的.插入和删除的时间复杂度是n(1)
所以使用红黑树来替代双向链表,这样就能将查询的时间复杂度降为O(logn)的级别
红黑树是什么树?
这就延伸出另外一个问题:为什么红黑树的查询复杂度是O(logN)?
因为红黑树本身上是一颗近似平衡二叉搜索树。
二叉搜搜索树的性质定义:
1.任意一个节点,它的左子树的所有结点都要小于这个根结点
2.它的右子树的所有结点都要大于根结点
3.且对于它的任何子树都要满足这样的特性
1.基于这样的特性,二叉搜索树查询.插入,删除的操作都是O(log2N)级别的时间复杂度,N是树的节点树.也就是说,二叉搜索树的时间复杂度只和树的高度有关(树的层级)
2.二叉搜索树的中序遍历就是升序排序
2.但是会有一种极端的情况,就是所有的子结点都在左(右)边,这样的话,二叉搜索树就退化成了一个双向链表,时间复杂度也变0(N),为了维持查询的高效率,我们需要把这个二叉搜索树折叠一下,变成V字型。这个过程我们把它叫做旋,左旋,右旋,左右旋,右左旋.
通过1,2两个理论我们可以推导出,要满足二叉搜索树查询的高效率.树的左右子树需要保持平衡,这里就延伸出了平衡二叉树的概念.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-balancing_binary_search_tree
平衡二叉树有很多种
- 2–3 tree
- AA tree
- AVL tree
- B-tree
- Red–black tree
- Scapegoat tree
- Splay tree
- Tango tree
- Treap
- Weight-balanced tree
常见的就是AVL,红黑树,B+树
AVL树
AVL树是最早被发明的自平衡二叉查找树。在AVL树中,任一节点对应的两棵子树的最大高度差为1,因此它也被称为高度平衡树。查找、插入和删除在平均和最坏情况下的时间复杂度都是O(log {n})增加和删除元素的操作则可能需要借由一次或多次树旋转,以实现树的重新平衡。
即Balance Factor(平衡因子)是它左子树减去右子树的高度在{-1,0,1}之间
通过旋转操作来自平衡,由于要保证高度平衡所以需要更多的旋转操作
红黑树的定义
(1)节点是红色或黑色。
(2)根节点是黑色。
(3)每个叶节点(NIL节点,空节点)是黑色的。
(4)每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色。(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
(5)从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点。
根据定义可以保证这颗树的大概平衡,不会很偏移,需要的操作就比较少,同时保证了时间复杂度不会从O(logN)向O(N)退化.
重点-HashMap(int initialCapacity)构造方法
判断传入的初始容量和装载因子是否合法,并计算扩容门槛,扩容门槛为传入的初始容量往上取最近的2的n次方。
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {// 检查传入的初始容量是否合法if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +initialCapacity);if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;// 检查装载因子是否合法if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +loadFactor);this.loadFactor = loadFactor;// 计算扩容门槛this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);}static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {// 扩容门槛为传入的初始容量往上取最近的2的n次方int n = cap - 1;n |= n >>> 1;n |= n >>> 2;n |= n >>> 4;n |= n >>> 8;n |= n >>> 16;return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;}复制代码
重点-put(K key, V value)方法
添加元素的入口。
public V put(K key, V value) {// 调用hash(key)计算出key的hash值return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);}static final int hash(Object key) {int h;// 如果key为null,则hash值为0,否则调用key的hashCode()方法// 并让高16位与整个hash异或,这样做是为了使计算出的hash更分散return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);}final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {Node<K, V>[] tab;Node<K, V> p;int n, i;// 如果桶的数量为0,则初始化if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)// 调用resize()初始化n = (tab = resize()).length;// (n - 1) & hash 计算元素在哪个桶中// 如果这个桶中还没有元素,则把这个元素放在桶中的第一个位置if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)// 新建一个节点放在桶中tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);else {// 如果桶中已经有元素存在了Node<K, V> e;K k;// 如果桶中第一个元素的key与待插入元素的key相同,保存到e中用于后续修改value值if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))e = p;else if (p instanceof TreeNode)// 如果第一个元素是树节点,则调用树节点的putTreeVal插入元素e = ((TreeNode<K, V>) p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);else {// 遍历这个桶对应的链表,binCount用于存储链表中元素的个数for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {// 如果链表遍历完了都没有找到相同key的元素,说明该key对应的元素不存在,则在链表最后插入一个新节点if ((e = p.next) == null) {p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);// 如果插入新节点后链表长度大于8,则判断是否需要树化,因为第一个元素没有加到binCount中,所以这里-1if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1sttreeifyBin(tab, hash);break;}// 如果待插入的key在链表中找到了,则退出循环if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))break;p = e;}}// 如果找到了对应key的元素if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key// 记录下旧值V oldValue = e.value;// 判断是否需要替换旧值if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)// 替换旧值为新值e.value = value;// 在节点被访问后做点什么事,在LinkedHashMap中用到afterNodeAccess(e);// 返回旧值return oldValue;}}// 到这里了说明没有找到元素// 修改次数加1++modCount;// 元素数量加1,判断是否需要扩容if (++size > threshold)// 扩容resize();// 在节点插入后做点什么事,在LinkedHashMap中用到afterNodeInsertion(evict);// 没找到元素返回nullreturn null;}复制代码
(1)计算key的hash值;
(2)如果桶(数组)数量为0,则初始化桶;
(3)如果key所在的桶没有元素,则直接插入;
(4)如果key所在的桶中的第一个元素的key与待插入的key相同,说明找到了元素,转后续流程(9)处理;
(5)如果
第一个元素是树节点,则调用树节点的putTreeVal()寻找元素或插入树节点;
(6)如果不是以上三种情况,则遍历桶对应的链表查找key是否存在于链表中;
(7)如果找到了对应key的元素,则转后续流程(9)处理;
(8)如果没找到对应key的元素,则在链表最后插入一个新节点并判断是否需要树化;
(9)如果找到了对应key的元素,则判断是否需要替换旧值,并直接返回旧值;
(10)如果插入了元素,则数量加1并判断是否需要扩容;
重点-resize()方法
扩容方法。
final Node<K, V>[] resize() {// 旧数组Node<K, V>[] oldTab = table;// 旧容量int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;// 旧扩容门槛int oldThr = threshold;int newCap, newThr = 0;if (oldCap > 0) {if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {// 如果旧容量达到了最大容量,则不再进行扩容threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;return oldTab;} else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)// 如果旧容量的两倍小于最大容量并且旧容量大于默认初始容量(16),则容量扩大为两部,扩容门槛也扩大为两倍newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold} else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold// 使用非默认构造方法创建的map,第一次插入元素会走到这里// 如果旧容量为0且旧扩容门槛大于0,则把新容量赋值为旧门槛newCap = oldThr;else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults// 调用默认构造方法创建的map,第一次插入元素会走到这里// 如果旧容量旧扩容门槛都是0,说明还未初始化过,则初始化容量为默认容量,扩容门槛为默认容量*默认装载因子newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;newThr = (int) (DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);}if (newThr == 0) {// 如果新扩容门槛为0,则计算为容量*装载因子,但不能超过最大容量float ft = (float) newCap * loadFactor;newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float) MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?(int) ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);}// 赋值扩容门槛为新门槛threshold = newThr;// 新建一个新容量的数组@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})Node<K, V>[] newTab = (Node<K, V>[]) new Node[newCap];// 把桶赋值为新数组table = newTab;// 如果旧数组不为空,则搬移元素if (oldTab != null) {// 遍历旧数组for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {Node<K, V> e;// 如果桶中第一个元素不为空,赋值给eif ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {// 清空旧桶,便于GC回收oldTab[j] = null;// 如果这个桶中只有一个元素,则计算它在新桶中的位置并把它搬移到新桶中// 因为每次都扩容两倍,所以这里的第一个元素搬移到新桶的时候新桶肯定还没有元素if (e.next == null)newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;else if (e instanceof TreeNode)// 如果第一个元素是树节点,则把这颗树打散成两颗树插入到新桶中去((TreeNode<K, V>) e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);else { // preserve order// 如果这个链表不止一个元素且不是一颗树// 则分化成两个链表插入到新的桶中去// 比如,假如原来容量为4,3、7、11、15这四个元素都在三号桶中// 现在扩容到8,则3和11还是在三号桶,7和15要搬移到七号桶中去// 也就是分化成了两个链表Node<K, V> loHead = null, loTail = null;Node<K, V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;Node<K, V> next;do {next = e.next;// (e.hash & oldCap) == 0的元素放在低位链表中// 比如,3 & 4 == 0if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {if (loTail == null)loHead = e;elseloTail.next = e;loTail = e;} else {// (e.hash & oldCap) != 0的元素放在高位链表中// 比如,7 & 4 != 0if (hiTail == null)hiHead = e;elsehiTail.next = e;hiTail = e;}} while ((e = next) != null);// 遍历完成分化成两个链表了// 低位链表在新桶中的位置与旧桶一样(即3和11还在三号桶中)if (loTail != null) {loTail.next = null;newTab[j] = loHead;}// 高位链表在新桶中的位置正好是原来的位置加上旧容量(即7和15搬移到七号桶了)if (hiTail != null) {hiTail.next = null;newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;}}}}}return newTab;}复制代码
(1)如果使用是默认构造方法,则第一次插入元素时初始化为默认值,容量为16,扩容门槛为12;
(2)如果使用的是非默认构造方法,则第一次插入元素时初始化容量等于扩容门槛,扩容门槛在构造方法里等于传入容量向上最近的2的n次方;
(3)如果旧容量大于0,则新容量等于旧容量的2倍,但不超过最大容量2的30次方,新扩容门槛为旧扩容门槛的2倍;
(4)创建一个新容量的桶;
(5)搬移元素,原链表分化成两个链表,低位链表存储在原来桶的位置,高位链表搬移到原来桶的位置加旧容量的位置;
TreeNode.putTreeVal(…)方法
插入元素到红黑树中的方法。
final TreeNode<K, V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K, V> map, Node<K, V>[] tab,int h, K k, V v) {Class<?> kc = null;// 标记是否找到这个key的节点boolean searched = false;// 找到树的根节点TreeNode<K, V> root = (parent != null) ? root() : this;// 从树的根节点开始遍历for (TreeNode<K, V> p = root; ; ) {// dir=direction,标记是在左边还是右边// ph=p.hash,当前节点的hash值int dir, ph;// pk=p.key,当前节点的key值K pk;if ((ph = p.hash) > h) {// 当前hash比目标hash大,说明在左边dir = -1;}else if (ph < h)// 当前hash比目标hash小,说明在右边dir = 1;else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))// 两者hash相同且key相等,说明找到了节点,直接返回该节点// 回到putVal()中判断是否需要修改其value值return p;else if ((kc == null &&// 如果k是Comparable的子类则返回其真实的类,否则返回null(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||// 如果k和pk不是同样的类型则返回0,否则返回两者比较的结果(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) {// 这个条件表示两者hash相同但是其中一个不是Comparable类型或者两者类型不同// 比如key是Object类型,这时可以传String也可以传Integer,两者hash值可能相同// 在红黑树中把同样hash值的元素存储在同一颗子树,这里相当于找到了这颗子树的顶点// 从这个顶点分别遍历其左右子树去寻找有没有跟待插入的key相同的元素if (!searched) {TreeNode<K, V> q, ch;searched = true;// 遍历左右子树找到了直接返回if (((ch = p.left) != null &&(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null) ||((ch = p.right) != null &&(q = ch.find(h, k, kc)) != null))return q;}// 如果两者类型相同,再根据它们的内存地址计算hash值进行比较dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);}TreeNode<K, V> xp = p;if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {// 如果最后确实没找到对应key的元素,则新建一个节点Node<K, V> xpn = xp.next;TreeNode<K, V> x = map.newTreeNode(h, k, v, xpn);if (dir <= 0)xp.left = x;elsexp.right = x;xp.next = x;x.parent = x.prev = xp;if (xpn != null)((TreeNode<K, V>) xpn).prev = x;// 插入树节点后平衡// 把root节点移动到链表的第一个节点moveRootToFront(tab, balanceInsertion(root, x));return null;}}}复制代码
(1)寻找根节点;
(2)从根节点开始查找;
(3)比较hash值及key值,如果都相同,直接返回,在putVal()方法中决定是否要替换value值;
(4)根据hash值及key值确定在树的左子树还是右子树查找,找到了直接返回;
(5)如果最后没有找到则在树的相应位置插入元素,并做平衡;
treeifyBin()方法
如果插入元素后链表的长度大于等于8则判断是否需要树化。
final void treeifyBin(Node<K, V>[] tab, int hash) {int n, index;Node<K, V> e;if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)// 如果桶数量小于64,直接扩容而不用树化// 因为扩容之后,链表会分化成两个链表,达到减少元素的作用// 当然也不一定,比如容量为4,里面存的全是除以4余数等于3的元素// 这样即使扩容也无法减少链表的长度resize();else if ((e = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {TreeNode<K, V> hd = null, tl = null;// 把所有节点换成树节点do {TreeNode<K, V> p = replacementTreeNode(e, null);if (tl == null)hd = p;else {p.prev = tl;tl.next = p;}tl = p;} while ((e = e.next) != null);// 如果进入过上面的循环,则从头节点开始树化if ((tab[index] = hd) != null)hd.treeify(tab);}}复制代码
TreeNode.treeify()方法
真正树化的方法。
final void treeify(Node<K, V>[] tab) {TreeNode<K, V> root = null;for (TreeNode<K, V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {next = (TreeNode<K, V>) x.next;x.left = x.right = null;// 第一个元素作为根节点且为黑节点,其它元素依次插入到树中再做平衡if (root == null) {x.parent = null;x.red = false;root = x;} else {K k = x.key;int h = x.hash;Class<?> kc = null;// 从根节点查找元素插入的位置for (TreeNode<K, V> p = root; ; ) {int dir, ph;K pk = p.key;if ((ph = p.hash) > h)dir = -1;else if (ph < h)dir = 1;else if ((kc == null &&(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);// 如果最后没找到元素,则插入TreeNode<K, V> xp = p;if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {x.parent = xp;if (dir <= 0)xp.left = x;elsexp.right = x;// 插入后平衡,默认插入的是红节点,在balanceInsertion()方法里root = balanceInsertion(root, x);break;}}}}// 把根节点移动到链表的头节点,因为经过平衡之后原来的第一个元素不一定是根节点了moveRootToFront(tab, root);}复制代码
(1)从链表的第一个元素开始遍历;
(2)将第一个元素作为根节点;
(3)其它元素依次插入到红黑树中,再做平衡;
(4)将根节点移到链表第一元素的位置(因为平衡的时候根节点会改变);
重点-get(Object key)方法
public V get(Object key) {Node<K, V> e;return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;}final Node<K, V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {Node<K, V>[] tab;Node<K, V> first, e;int n;K k;// 如果桶的数量大于0并且待查找的key所在的桶的第一个元素不为空if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {// 检查第一个元素是不是要查的元素,如果是直接返回if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))return first;if ((e = first.next) != null) {// 如果第一个元素是树节点,则按树的方式查找if (first instanceof TreeNode)return ((TreeNode<K, V>) first).getTreeNode(hash, key);// 否则就遍历整个链表查找该元素do {if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))return e;} while ((e = e.next) != null);}}return null;}复制代码
(1)计算key的hash值;
(2)找到key所在的桶及其第一个元素;
(3)如果第一个元素的key等于待查找的key,直接返回;
(4)如果第一个元素是树节点就按树的方式来查找,否则按链表方式查找;
TreeNode.getTreeNode(int h, Object k)方法
final TreeNode<K, V> getTreeNode(int h, Object k) {// 从树的根节点开始查找return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(h, k, null);}final TreeNode<K, V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {TreeNode<K, V> p = this;do {int ph, dir;K pk;TreeNode<K, V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q;if ((ph = p.hash) > h)// 左子树p = pl;else if (ph < h)// 右子树p = pr;else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))// 找到了直接返回return p;else if (pl == null)// hash相同但key不同,左子树为空查右子树p = pr;else if (pr == null)// 右子树为空查左子树p = pl;else if ((kc != null ||(kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&(dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)// 通过compare方法比较key值的大小决定使用左子树还是右子树p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null)// 如果以上条件都不通过,则尝试在右子树查找return q;else// 都没找到就在左子树查找p = pl;} while (p != null);return null;}复制代码
经典二叉查找树的查找过程,先根据hash值比较,再根据key值比较决定是查左子树还是右子树。
重点-remove(Object key)方法
public V remove(Object key) {Node<K, V> e;return (e = removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true)) == null ?null : e.value;}final Node<K, V> removeNode(int hash, Object key, Object value,boolean matchValue, boolean movable) {Node<K, V>[] tab;Node<K, V> p;int n, index;// 如果桶的数量大于0且待删除的元素所在的桶的第一个元素不为空if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(p = tab[index = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) {Node<K, V> node = null, e;K k;V v;if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))// 如果第一个元素正好就是要找的元素,赋值给node变量后续删除使用node = p;else if ((e = p.next) != null) {if (p instanceof TreeNode)// 如果第一个元素是树节点,则以树的方式查找节点node = ((TreeNode<K, V>) p).getTreeNode(hash, key);else {// 否则遍历整个链表查找元素do {if (e.hash == hash &&((k = e.key) == key ||(key != null && key.equals(k)))) {node = e;break;}p = e;} while ((e = e.next) != null);}}// 如果找到了元素,则看参数是否需要匹配value值,如果不需要匹配直接删除,如果需要匹配则看value值是否与传入的value相等if (node != null && (!matchValue || (v = node.value) == value ||(value != null && value.equals(v)))) {if (node instanceof TreeNode)// 如果是树节点,调用树的删除方法(以node调用的,是删除自己)((TreeNode<K, V>) node).removeTreeNode(this, tab, movable);else if (node == p)// 如果待删除的元素是第一个元素,则把第二个元素移到第一的位置tab[index] = node.next;else// 否则删除node节点p.next = node.next;++modCount;--size;// 删除节点后置处理afterNodeRemoval(node);return node;}}return null;}复制代码
(1)先查找元素所在的节点;
(2)如果找到的节点是树节点,则按树的移除节点处理;
(3)如果找到的节点是桶中的第一个节点,则把第二个节点移到第一的位置;
(4)否则按链表删除节点处理;
(5)修改size,调用移除节点后置处理等;
TreeNode.removeTreeNode(…)方法
final void removeTreeNode(HashMap<K, V> map, Node<K, V>[] tab,boolean movable) {int n;// 如果桶的数量为0直接返回if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)return;// 节点在桶中的索引int index = (n - 1) & hash;// 第一个节点,根节点,根左子节点TreeNode<K, V> first = (TreeNode<K, V>) tab[index], root = first, rl;// 后继节点,前置节点TreeNode<K, V> succ = (TreeNode<K, V>) next, pred = prev;if (pred == null)// 如果前置节点为空,说明当前节点是根节点,则把后继节点赋值到第一个节点的位置,相当于删除了当前节点tab[index] = first = succ;else// 否则把前置节点的下个节点设置为当前节点的后继节点,相当于删除了当前节点pred.next = succ;// 如果后继节点不为空,则让后继节点的前置节点指向当前节点的前置节点,相当于删除了当前节点if (succ != null)succ.prev = pred;// 如果第一个节点为空,说明没有后继节点了,直接返回if (first == null)return;// 如果根节点的父节点不为空,则重新查找父节点if (root.parent != null)root = root.root();// 如果根节点为空,则需要反树化(将树转化为链表)// 如果需要移动节点且树的高度比较小,则需要反树化if (root == null|| (movable&& (root.right == null|| (rl = root.left) == null|| rl.left == null))) {tab[index] = first.untreeify(map); // too smallreturn;}// 分割线,以上都是删除链表中的节点,下面才是直接删除红黑树的节点(因为TreeNode本身即是链表节点又是树节点)// 删除红黑树节点的大致过程是寻找右子树中最小的节点放到删除节点的位置,然后做平衡,此处不过多注释TreeNode<K, V> p = this, pl = left, pr = right, replacement;if (pl != null && pr != null) {TreeNode<K, V> s = pr, sl;while ((sl = s.left) != null) // find successors = sl;boolean c = s.red;s.red = p.red;p.red = c; // swap colorsTreeNode<K, V> sr = s.right;TreeNode<K, V> pp = p.parent;if (s == pr) { // p was s's direct parentp.parent = s;s.right = p;} else {TreeNode<K, V> sp = s.parent;if ((p.parent = sp) != null) {if (s == sp.left)sp.left = p;elsesp.right = p;}if ((s.right = pr) != null)pr.parent = s;}p.left = null;if ((p.right = sr) != null)sr.parent = p;if ((s.left = pl) != null)pl.parent = s;if ((s.parent = pp) == null)root = s;else if (p == pp.left)pp.left = s;elsepp.right = s;if (sr != null)replacement = sr;elsereplacement = p;} else if (pl != null)replacement = pl;else if (pr != null)replacement = pr;elsereplacement = p;if (replacement != p) {TreeNode<K, V> pp = replacement.parent = p.parent;if (pp == null)root = replacement;else if (p == pp.left)pp.left = replacement;elsepp.right = replacement;p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;}TreeNode<K, V> r = p.red ? root : balanceDeletion(root, replacement);if (replacement == p) { // detachTreeNode<K, V> pp = p.parent;p.parent = null;if (pp != null) {if (p == pp.left)pp.left = null;else if (p == pp.right)pp.right = null;}}if (movable)moveRootToFront(tab, r);}复制代码
(1)TreeNode本身既是链表节点也是红黑树节点;
(2)先删除链表节点;
(3)再删除红黑树节点并做平衡;
总结
(1)HashMap是一种散列表,采用(数组 + 链表 + 红黑树)的存储结构;
(2)HashMap的默认初始容量为16(1<<4),默认装载因子为0.75f,容量总是2的n次方;
(3)HashMap扩容时每次容量变为原来的两倍;
(4)当桶的数量小于64时不会进行树化,只会扩容;
(5)当桶的数量大于64且单个桶中元素的数量大于8时,进行树化;
(6)当单个桶中元素数量小于6时,进行反树化;
(7)HashMap是非线程安全的容器;
(8)HashMap查找添加元素的时间复杂度都为O(1);
ArrayList源码
简介
ArrayList是一种以数组实现的List,与数组相比,它具有动态扩展的能力,因此也可称之为动态数组。
继承体系
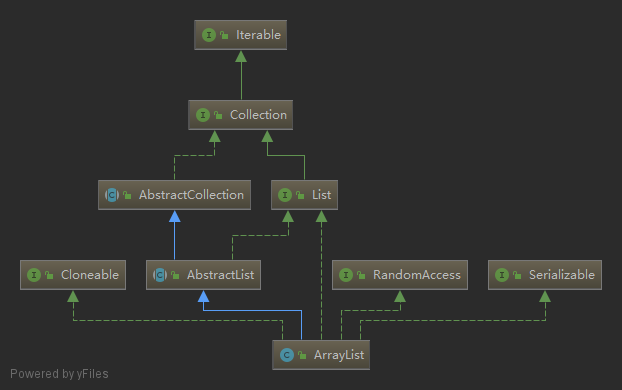
ArrayList实现了List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable等接口。
ArrayList实现了List,提供了基础的添加、删除、遍历等操作。
ArrayList实现了RandomAccess,提供了随机访问的能力。
ArrayList实现了Cloneable,可以被克隆。
ArrayList实现了Serializable,可以被序列化。
源码解析
属性
/*** 默认容量*/private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;/*** 空数组,如果传入的容量为0时使用*/private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};/*** 空数组,传传入容量时使用,添加第一个元素的时候会重新初始为默认容量大小*/private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};/*** 存储元素的数组,本文由公从号“彤哥读源码”原创*/transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access/*** 集合中元素的个数*/private int size;复制代码
(1)DEFAULT_CAPACITY
默认容量为10,也就是通过new ArrayList()创建时的默认容量。
(2)EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
空的数组,这种是通过new ArrayList(0)创建时用的是这个空数组。
(3)DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
也是空数组,这种是通过new ArrayList()创建时用的是这个空数组,与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA的区别是在添加第一个元素时使用这个空数组的会初始化为DEFAULT_CAPACITY(10)个元素。
(4)elementData
真正存放元素的地方,使用transient是为了不序列化这个字段。
至于没有使用private修饰,后面注释是写的“为了简化嵌套类的访问”,但是楼主实测加了private嵌套类一样可以访问。
private表示是类私有的属性,只要是在这个类内部都可以访问,嵌套类或者内部类也是在类的内部,所以也可以访问类的私有成员。
(5)size
真正存储元素的个数,而不是elementData数组的长度。
ArrayList(int initialCapacity)构造方法
传入初始容量,如果大于0就初始化elementData为对应大小,如果等于0就使用EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA空数组,如果小于0抛出异常。
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {if (initialCapacity > 0) {// 如果传入的初始容量大于0,就新建一个数组存储元素this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {// 如果传入的初始容量等于0,使用空数组EMPTY_ELEMENTDATAthis.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;} else {// 如果传入的初始容量小于0,抛出异常throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: " + initialCapacity);}}复制代码
ArrayList()构造方法
不传初始容量,初始化为DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA空数组,会在添加第一个元素的时候扩容为默认的大小,即10。
public ArrayList() {// 如果没有传入初始容量,则使用空数组DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA// 使用这个数组是在添加第一个元素的时候会扩容到默认大小10this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}复制代码
ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)构造方法
传入集合并初始化elementData,这里会使用拷贝把传入集合的元素拷贝到elementData数组中,如果元素个数为0,则初始化为EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA空数组。
/*** 把传入集合的元素初始化到ArrayList中*/public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {// 集合转数组elementData = c.toArray();if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {// 检查c.toArray()返回的是不是Object[]类型,如果不是,重新拷贝成Object[].class类型if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);} else {// 如果c的空集合,则初始化为空数组EMPTY_ELEMENTDATAthis.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}}复制代码
为什么c.toArray();返回的有可能不是Object[]类型呢?请看下面的代码:
public class ArrayTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Father[] fathers = new Son[]{};// 打印结果为class [Lcom.coolcoding.code.Son;System.out.println(fathers.getClass());List<String> strList = new MyList();// 打印结果为class [Ljava.lang.String;//,本文由公从号“彤哥读源码”原创System.out.println(strList.toArray().getClass());}}class Father {}class Son extends Father {}class MyList extends ArrayList<String> {/*** 子类重写父类的方法,返回值可以不一样* 但这里只能用数组类型,换成Object就不行* 应该算是java本身的bug*/@Overridepublic String[] toArray() {// 为了方便举例直接写死return new String[]{"1", "2", "3"};}}复制代码
add(E e)方法
添加元素到末尾,平均时间复杂度为O(1)。
public boolean add(E e) {// 检查是否需要扩容ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);// 把元素插入到最后一位elementData[size++] = e;return true;}private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));}private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {// 如果是空数组DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,就初始化为默认大小10if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}return minCapacity;}private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {modCount++;if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)// 扩容grow(minCapacity);}private void grow(int minCapacity) {int oldCapacity = elementData.length;// 新容量为旧容量的1.5倍int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);// 如果新容量发现比需要的容量还小,则以需要的容量为准if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;// 如果新容量已经超过最大容量了,则使用最大容量if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// 以新容量拷贝出来一个新数组elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}复制代码
(1)检查是否需要扩容;
(2)如果elementData等于DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA则初始化容量大小为DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
(3)新容量是老容量的1.5倍(oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)),如果加了这么多容量发现比需要的容量还小,则以需要的容量为准;
(4)创建新容量的数组并把老数组拷贝到新数组;
add(int index, E element)方法
添加元素到指定位置,平均时间复杂度为O(n)。
public void add(int index, E element) {// 检查是否越界rangeCheckForAdd(index);// 检查是否需要扩容ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);// 将inex及其之后的元素往后挪一位,则index位置处就空出来了System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,size - index);// 将元素插入到index的位置elementData[index] = element;// 大小增1size++;}private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {if (index > size || index < 0)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}复制代码
(1)检查索引是否越界;
(2)检查是否需要扩容;
(3)把插入索引位置后的元素都往后挪一位;
(4)在插入索引位置放置插入的元素;
(5)大小加1;
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)方法
求两个集合的并集。
/*** 将集合c中所有元素添加到当前ArrayList中*/public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {// 将集合c转为数组Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;// 检查是否需要扩容ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew);// 将c中元素全部拷贝到数组的最后System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);// 大小增加c的大小size += numNew;// 如果c不为空就返回true,否则返回falsereturn numNew != 0;}复制代码
(1)拷贝c中的元素到数组a中;
(2)检查是否需要扩容;
(3)把数组a中的元素拷贝到elementData的尾部;
get(int index)方法
获取指定索引位置的元素,时间复杂度为O(1)。
public E get(int index) {// 检查是否越界rangeCheck(index);// 返回数组index位置的元素return elementData(index);}private void rangeCheck(int index) {if (index >= size)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}E elementData(int index) {return (E) elementData[index];}复制代码
(1)检查索引是否越界,这里只检查是否越上界,如果越上界抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常,如果越下界抛出的是ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException异常。
(2)返回索引位置处的元素;
remove(int index)方法
删除指定索引位置的元素,时间复杂度为O(n)。
public E remove(int index) {// 检查是否越界rangeCheck(index);modCount++;// 获取index位置的元素E oldValue = elementData(index);// 如果index不是最后一位,则将index之后的元素往前挪一位int numMoved = size - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);// 将最后一个元素删除,帮助GCelementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work// 返回旧值return oldValue;}复制代码
(1)检查索引是否越界;
(2)获取指定索引位置的元素;
(3)如果删除的不是最后一位,则其它元素往前移一位;
(4)将最后一位置为null,方便GC回收;
(5)返回删除的元素,本文由公从号“彤哥读源码”原创。
可以看到,ArrayList删除元素的时候并没有缩容。
remove(Object o)方法
删除指定元素值的元素,时间复杂度为O(n)。
public boolean remove(Object o) {if (o == null) {// 遍历整个数组,找到元素第一次出现的位置,并将其快速删除for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)// 如果要删除的元素为null,则以null进行比较,使用==if (elementData[index] == null) {fastRemove(index);return true;}} else {// 遍历整个数组,找到元素第一次出现的位置,并将其快速删除for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)// 如果要删除的元素不为null,则进行比较,使用equals()方法if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {fastRemove(index);return true;}}return false;}private void fastRemove(int index) {// 少了一个越界的检查modCount++;// 如果index不是最后一位,则将index之后的元素往前挪一位int numMoved = size - index - 1;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);// 将最后一个元素删除,帮助GCelementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work}复制代码
(1)找到第一个等于指定元素值的元素;
(2)快速删除;
fastRemove(int index)相对于remove(int index)少了检查索引越界的操作,可见jdk将性能优化到极致。
retainAll(Collection<?> c)方法
求两个集合的交集。
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {// 集合c不能为nullObjects.requireNonNull(c);// 调用批量删除方法,这时complement传入true,表示删除不包含在c中的元素return batchRemove(c, true);}/*** 批量删除元素* complement为true表示删除c中不包含的元素* complement为false表示删除c中包含的元素*/private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;// 使用读写两个指针同时遍历数组// 读指针每次自增1,写指针放入元素的时候才加1// 这样不需要额外的空间,只需要在原有的数组上操作就可以了int r = 0, w = 0;boolean modified = false;try {// 遍历整个数组,如果c中包含该元素,则把该元素放到写指针的位置(以complement为准)for (; r < size; r++)if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)elementData[w++] = elementData[r];} finally {// 正常来说r最后是等于size的,除非c.contains()抛出了异常if (r != size) {// 如果c.contains()抛出了异常,则把未读的元素都拷贝到写指针之后System.arraycopy(elementData, r,elementData, w,size - r);w += size - r;}if (w != size) {// 将写指针之后的元素置为空,帮助GCfor (int i = w; i < size; i++)elementData[i] = null;modCount += size - w;// 新大小等于写指针的位置(因为每写一次写指针就加1,所以新大小正好等于写指针的位置)size = w;modified = true;}}// 有修改返回truereturn modified;}复制代码
(1)遍历elementData数组;
(2)如果元素在c中,则把这个元素添加到elementData数组的w位置并将w位置往后移一位;
(3)遍历完之后,w之前的元素都是两者共有的,w之后(包含)的元素不是两者共有的;
(4)将w之后(包含)的元素置为null,方便GC回收;
removeAll(Collection<?> c)
求两个集合的单方向差集,只保留当前集合中不在c中的元素,不保留在c中不在当前集体中的元素。
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {// 集合c不能为空Objects.requireNonNull(c);// 同样调用批量删除方法,这时complement传入false,表示删除包含在c中的元素return batchRemove(c, false);}复制代码
与retainAll(Collection<?> c)方法类似,只是这里保留的是不在c中的元素。
总结
(1)ArrayList内部使用数组存储元素,当数组长度不够时进行扩容,每次加一半的空间,ArrayList不会进行缩容;
(2)ArrayList支持随机访问,通过索引访问元素极快,时间复杂度为O(1);
(3)ArrayList添加元素到尾部极快,平均时间复杂度为O(1);
(4)ArrayList添加元素到中间比较慢,因为要搬移元素,平均时间复杂度为O(n);
(5)ArrayList从尾部删除元素极快,时间复杂度为O(1);
(6)ArrayList从中间删除元素比较慢,因为要搬移元素,平均时间复杂度为O(n);
(7)ArrayList支持求并集,调用addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)方法即可;
(8)ArrayList支持求交集,调用retainAll(Collection<? extends E> c)方法即可;
(7)ArrayList支持求单向差集,调用removeAll(Collection<? extends E> c)方法即可;
彩蛋
elementData设置成了transient,那ArrayList是怎么把元素序列化的呢?
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)throws java.io.IOException{// 防止序列化期间有修改int expectedModCount = modCount;// 写出非transient非static属性(会写出size属性)s.defaultWriteObject();// 写出元素个数s.writeInt(size);// 依次写出元素for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {s.writeObject(elementData[i]);}// 如果有修改,抛出异常,本文由公从号“彤哥读源码”原创if (modCount != expectedModCount) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {// 声明为空数组elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;// 读入非transient非static属性(会读取size属性)s.defaultReadObject();// 读入元素个数,没什么用,只是因为写出的时候写了size属性,读的时候也要按顺序来读s.readInt();if (size > 0) {// 计算容量int capacity = calculateCapacity(elementData, size);SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity);// 检查是否需要扩容ensureCapacityInternal(size);Object[] a = elementData;// 依次读取元素到数组中for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {a[i] = s.readObject();}}}复制代码
查看writeObject()方法可知,先调用s.defaultWriteObject()方法,再把size写入到流中,再把元素一个一个的写入到流中。
一般地,只要实现了Serializable接口即可自动序列化,writeObject()和readObject()是为了自己控制序列化的方式,这两个方法必须声明为private,在java.io.ObjectStreamClass#getPrivateMethod()方法中通过反射获取到writeObject()这个方法。
在ArrayList的writeObject()方法中先调用了s.defaultWriteObject()方法,这个方法是写入非static非transient的属性,在ArrayList中也就是size属性。同样地,在readObject()方法中先调用了s.defaultReadObject()方法解析出了size属性。
elementData定义为transient的优势,自己根据size序列化真实的元素,而不是根据数组的长度序列化元素,减少了空间占用。
作者:彤哥读源码
链接:https://juejin.im/post/6866301216989642765
来源:掘金
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。

