Preview
前文提到了 Caddy 的启动流程 和 Run 函数,现在我们顺着启动流程的第一步,读取 Caddyfile 的 源码阅读开始。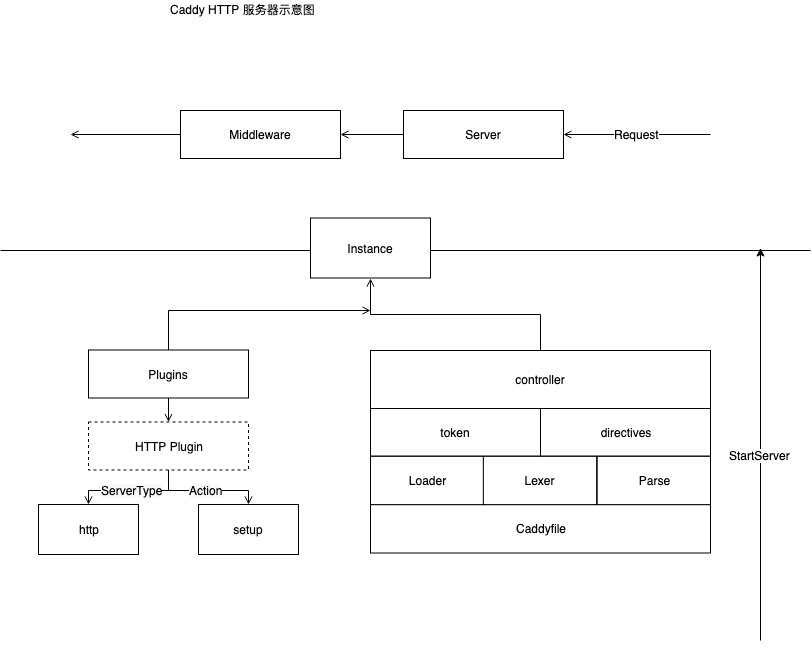
Loader
概念
可以理解为读取器。
在 caddy 中 由 Loader 执行 装载 配置文件的职能。看一下它的工作流程。
这个图来源于 plugin.go 文件
可以看到这里通过 Loader 解耦了 caddyfile 文件的读取,所以把它放在了 plugin.go 文件中,作为一个插件注册在 caddy app 中。
- 可以多定义 caddyfileloader 在图中由三个长方形的表示为数组
- 自定义的 caddyfileloader 会实现 右半部分的 Loader 接口
- caddyfileloader 会有对应读取的 ServerType 的 name
- 最后生产出的是 Input
保存
在 plugin.go 中有一个全局变量保存
// caddyfileLoaders is the list of all Caddyfile loaders// in registration order.caddyfileLoaders []caddyfileLoader
设计
我们看这个接口
type Loader interface {Load(serverType string) (Input, error)}
这是用来 load caddyfile 的 你可以为自己的所有独有的 server 自定义读取 caddyfile 的方式
Usage
我们自定义的时候,只需要实现一个 LoaderFunc 即可。因为它使用了 类似 http.HandlerFunc 的模式,帮你自动实现了上文所说的 Loader 接口
// LoaderFunc is a convenience type similar to http.HandlerFunc// that allows you to use a plain function as a Load() method.type LoaderFunc func(serverType string) (Input, error)// Load loads a Caddyfile.func (lf LoaderFunc) Load(serverType string) (Input, error) {return lf(serverType)}
扩展
两个方法,
- 可以注册新的 Loader
- 或者设置为默认的 Loader ```go // RegisterCaddyfileLoader registers loader named name. func RegisterCaddyfileLoader(name string, loader Loader) { caddyfileLoaders = append(caddyfileLoaders, caddyfileLoader{name: name, loader: loader}) }
// SetDefaultCaddyfileLoader registers loader by name // as the default Caddyfile loader if no others produce // a Caddyfile. If another Caddyfile loader has already // been set as the default, this replaces it. // // Do not call RegisterCaddyfileLoader on the same // loader; that would be redundant. func SetDefaultCaddyfileLoader(name string, loader Loader) { defaultCaddyfileLoader = caddyfileLoader{name: name, loader: loader} }
<a name="VMa94"></a>### Logic```go// loadCaddyfileInput iterates the registered Caddyfile loaders// and, if needed, calls the default loader, to load a Caddyfile.// It is an error if any of the loaders return an error or if// more than one loader returns a Caddyfile.func loadCaddyfileInput(serverType string) (Input, error) {var loadedBy stringvar caddyfileToUse Inputfor _, l := range caddyfileLoaders {cdyfile, err := l.loader.Load(serverType)if err != nil {return nil, fmt.Errorf("loading Caddyfile via %s: %v", l.name, err)}if cdyfile != nil {if caddyfileToUse != nil {return nil, fmt.Errorf("Caddyfile loaded multiple times; first by %s, then by %s", loadedBy, l.name)}loaderUsed = lcaddyfileToUse = cdyfileloadedBy = l.name}}if caddyfileToUse == nil && defaultCaddyfileLoader.loader != nil {cdyfile, err := defaultCaddyfileLoader.loader.Load(serverType)if err != nil {return nil, err}if cdyfile != nil {loaderUsed = defaultCaddyfileLoadercaddyfileToUse = cdyfile}}return caddyfileToUse, nil}
很轻松的看到,装载 caddyfile 的逻辑 是尝试调用 所有的 Loader 并且重复装载会报错。
如果尝试过之后装载失败,则使用 默认的 defaultCaddyfileLoader
这里可以看到最终流程是 caddyfile -> caddy.Input 那么这个 Input 是什么呢?
实际上 Input 就是 caddyfile 在代码中的映射。可以理解为,caddyfile 转化为了 Input 给 caddy 读取。
Parser
文件结构
我们想看到各个流程中的 Token 是如何被分析出来的,需要知道,这里的 Token 代表着 caddyfile 中的每行选项配置
lexer.go
一个实用工具,它可以从 Reader获取一个token接一个token的值。通过 next()函数token 是一个单词,token由空格分隔。如果一个单词包含空格,可以用引号括起来。
即 lexer 用来做 caddyfile 的语法分析 被其他程序调用
词法分析
next()函数就是 lexer 用来提供功能的函数
// next loads the next token into the lexer.// A token is delimited by whitespace, unless// the token starts with a quotes character (")// in which case the token goes until the closing// quotes (the enclosing quotes are not included).// Inside quoted strings, quotes may be escaped// with a preceding \ character. No other chars// may be escaped. The rest of the line is skipped// if a "#" character is read in. Returns true if// a token was loaded; false otherwise.func (l *lexer) next() bool {var val []runevar comment, quoted, escaped boolmakeToken := func() bool {l.token.Text = string(val)return true}for {ch, _, err := l.reader.ReadRune()if err != nil {if len(val) > 0 {return makeToken()}if err == io.EOF {return false}panic(err)}if quoted {if !escaped {if ch == '\\' {escaped = truecontinue} else if ch == '"' {quoted = falsereturn makeToken()}}if ch == '\n' {l.line++}if escaped {// only escape quotesif ch != '"' {val = append(val, '\\')}}val = append(val, ch)escaped = falsecontinue}if unicode.IsSpace(ch) {if ch == '\r' {continue}if ch == '\n' {l.line++comment = false}if len(val) > 0 {return makeToken()}continue}if ch == '#' {comment = true}if comment {continue}if len(val) == 0 {l.token = Token{Line: l.line}if ch == '"' {quoted = truecontinue}}val = append(val, ch)}}
他会根据 caddyfile 定义的写法,进行多种判断来实现分词
理解了 next 函数,就很容易知道如何分析一块选项的 token 了,不过都是 next() 的包装函数罢了。
这就是 lexer.go 中的解读,接下来我们看 parse.go
Parser.go
serverBlock
实际上, ServerBlock 存储的是 一组 token 信息,
//ServerBlock associates any number of keys//(usually addresses of some sort) with tokens//(grouped by directive name).type ServerBlock struct {Keys []stringTokens map[string][]Token}
它包含的 Token 正是 Parser 在 Caddyfile 中得来的。
context 还负责生成 caddy 管理的 Server,用来提供供 caddy Start 的信息
注意:这里的 Server 是 TCPServer 和 UDPServer,用来 Listen 等操作的。
parse
在 parser.go 中,由 Parse 函数进行生成 ServerBlock 的操作。
// Parse parses the input just enough to group tokens, in// order, by server block. No further parsing is performed.// Server blocks are returned in the order in which they appear.// Directives that do not appear in validDirectives will cause// an error. If you do not want to check for valid directives,// pass in nil instead.func Parse(filename string, input io.Reader, validDirectives []string) ([]ServerBlock, error) {p := parser{Dispenser: NewDispenser(filename, input), validDirectives: validDirectives}return p.parseAll()}
这里使用的 Dispenser ,是令牌分发器,我们下面马上讨论
allTokens
在 praser.go 中使用 allTokens 进行 lexer 分词生成 token
// allTokens lexes the entire input, but does not parse it.// It returns all the tokens from the input, unstructured// and in order.func allTokens(input io.Reader) ([]Token, error) {l := new(lexer)err := l.load(input)if err != nil {return nil, err}var tokens []Tokenfor l.next() {tokens = append(tokens, l.token)}return tokens, nil}
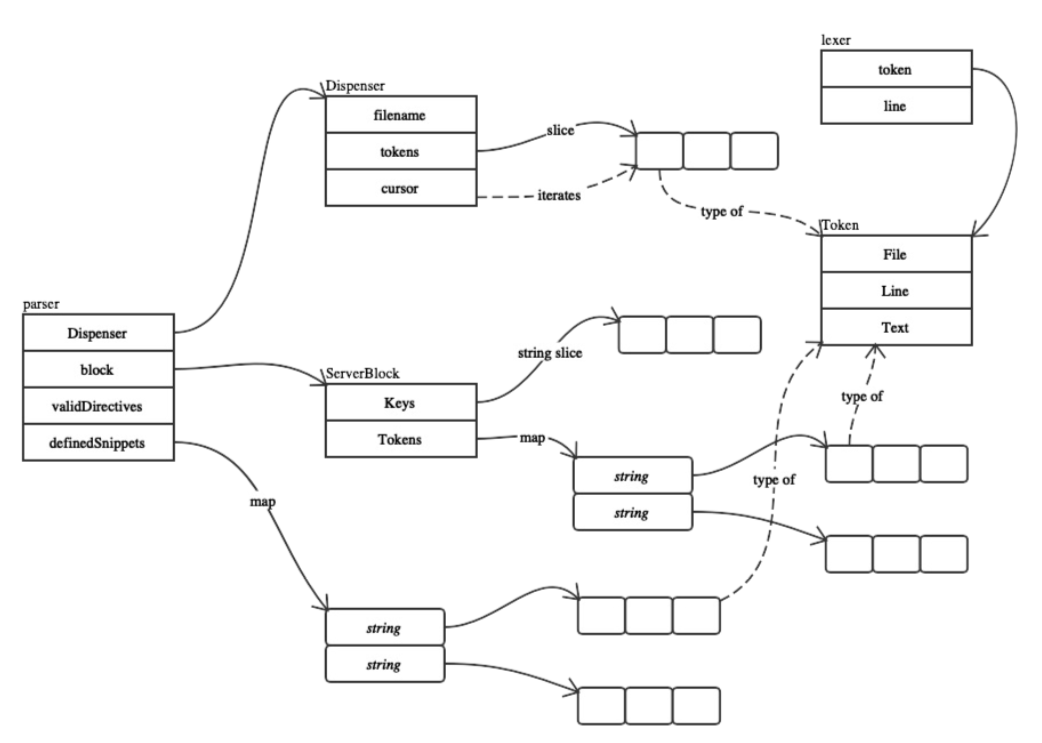
Dispenser
allTokens 会在 新建 Dispenser 的时候调用
// NewDispenser returns a Dispenser, ready to use for parsing the given input.func NewDispenser(filename string, input io.Reader) Dispenser {tokens, _ := allTokens(input) // ignoring error because nothing to do with itreturn Dispenser{filename: filename,tokens: tokens,cursor: -1,}}
如此,整个解析流程就串起来了, lexer 负责词法分析,Parse 用于将一组 tokens 分类(因为很多的插件的设置稍微复杂一些),Dispenser 负责分析去的 tokens 令牌消费
Dispenser 的关键是 把不同的 tokens 转换成 Directives 命令来执行
dispenser 中由 cursor 来进行 Token 数组中的迭代
关键在于移动 cursor 索引的函数
需要注意到的是 Dispenser 中的函数实际上都是 获取 tokens 的函数,意思是,在 Dispenser 中不会做任何配置,而是在相应的 controller.go ,caddy.go 中使用
请看下集,Plugin 的逻辑和相应的配置如何更改