寻找重复的子树
通过序列化树结构,结合HashSet,来判断是否重复
(1)如果能加入set说明是第一次出现,如果不能加入set但是能加入resSet说明是第二次出现,无法加入set和resSet说明出现两次以上。返回结果不重复。
(2)还有序列化的顺序:注意,不能使用中序遍历
测试用例:[0,0,0,0,null,null,0,null,null,null,0]
如果采用中序遍历,那么左子树是#0#0#,右子树的右子树也是#0#0#
采用前序遍历,那么左子树是00###,右子树是0#0##
采用后序遍历,那么左子树是#0##0,右子树是##0#0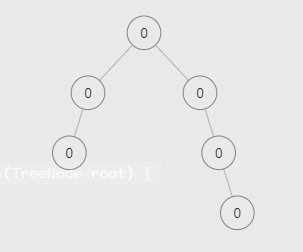
class Solution {HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();List<TreeNode> res = new ArrayList<>();HashSet<String> resSet = new HashSet<>();public List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) {findHelper(root);return res;}public String findHelper(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) return "#";String left = findHelper(root.left);String right = findHelper(root.right);StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();//注意这里的顺序sb.append(root.val).append(",").append(left).append(",").append(right);if(!set.add(sb.toString())&&resSet.add(sb.toString())){res.add(root);}return sb.toString();}}
二叉搜索树
判断BST的合法性
不可以仅仅判断每个节点的左子节点小于该节点,右子节点大于该节点。因为以根为界,右子树的左子树也不能小于根节点的数值,每个节点都有一个范围。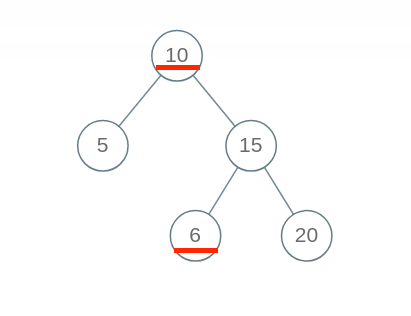
boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {return isValidBST(root, null, null);}/* 限定以 root 为根的子树节点必须满足 max.val > root.val > min.val */boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root, TreeNode min, TreeNode max) {// base caseif (root == null) return true;// 若 root.val 不符合 max 和 min 的限制,说明不是合法 BSTif (min != null && root.val <= min.val) return false;if (max != null && root.val >= max.val) return false;// 限定左子树的最大值是 root.val,右子树的最小值是 root.valreturn isValidBST(root.left, min, root)&& isValidBST(root.right, root, max);}
在二叉树中插入一个值
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root==null) return new TreeNode(val);
if(root.val>val){
root.left=insertIntoBST(root.left,val);
}else{
root.right=insertIntoBST(root.right,val);
}
return root;
}
}
在二叉搜索树中搜索一个值
返回以它为根节点的子树
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root==null) return null;
if(root.val==val) return root;
else if(root.val<val) return searchBST(root.right, val);
else return searchBST(root.left,val);
}
}
在二叉树中删除一个值
需要注意如何处理左右子树都不为空的情况
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root==null) return null;
if(root.val==key){
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) return null;
if(root.left==null&&root.right!=null) return root.right;
if(root.left!=null&&root.right==null) return root.left;
if(root.left!=null&&root.right!=null){
//找到右边最小的节点或左边最大的节点
TreeNode min=findMin(root.right);
root.val=min.val;
root.right=deleteNode(root.right, min.val);
}
}else if(root.val>key){
root.left=deleteNode(root.left, key);
}else{
root.right=deleteNode(root.right, key);
}
return root;
}
private TreeNode findMin(TreeNode node){
if(node.left!=null) node=findMin(node.left);
return node;
}
}
【困难】 二叉搜索子树的最大键值和
class Solution {
int sum=0;
public int maxSumBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
maxSumBSTHelper(root);
return sum;
}
public int[] maxSumBSTHelper(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
//isBST,min,max,sum
return new int[]{1,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MIN_VALUE,0};
}
int[] left=maxSumBSTHelper(root.left);
int[] right=maxSumBSTHelper(root.right);
int[] res=new int[4];
if(left[0]==1&&right[0]==1&&root.val>left[2]&&root.val<right[1]){
res[0]=1;
res[1]=Math.min(left[1],root.val);
res[2]=Math.max(right[2],root.val);
res[3]=left[3]+right[3]+root.val;
sum=Math.max(res[3],sum);
}else{
res[0]=0;
}
return res;
}
}
【困难】二叉树的序列化和反序列化
使用递归
这里用的先序遍历,也可以用后序遍历,但是不可以用中序遍历,原因和寻找重复子树里出现的问题相似。
public class Codec {
private int index=0;
private static final String ISNULL="#";
private static final String SEP=",";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
serializeHelper(root,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
private void serializeHelper(TreeNode root,StringBuffer sb){
if(root==null){
sb.append(ISNULL).append(SEP);
return;
}
sb.append(root.val).append(SEP);
serializeHelper(root.left,sb);
serializeHelper(root.right,sb);
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] datas=data.split(SEP);
return deserializeHelper(datas);
}
private TreeNode deserializeHelper(String[] datas){
if(index==datas.length) return null;
String str=datas[index++];
if(str.equals(ISNULL)) return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str));
root.left=deserializeHelper(datas);
root.right=deserializeHelper(datas);
return root;
}
}
使用栈
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if (root == null) {
return sb.toString();
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (sb.length() != 0) {
sb.append(",");
}
if (node != null) {
sb.append(node.val);
queue.offer(node.left);
queue.offer(node.right);
} else {
sb.append("null");
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if (data.length() == 0) return null;
String[] strings = data.split(",");
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(strings[0]));
TreeNode node = root;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(node);
for (int i = 1; i < strings.length;) {
node=queue.poll();
String leftVal = strings[i++];
if(leftVal.equalsIgnoreCase("null")){
node.left=null;
}else{
TreeNode leftNode=new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(leftVal));
queue.offer(leftNode);
node.left=leftNode;
}
String rightVal = strings[i++];
if(rightVal.equalsIgnoreCase("null")){
node.right=null;
}else{
TreeNode rightNode=new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(rightVal));
queue.offer(rightNode);
node.right=rightNode;
}
}
return root;
}
}
二叉树的最近公共祖先
lowestCommonAncestor(root,p,q)这个函数,如果以root为根节点的树里面既没有p也没有q返回null。
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null||p==root||q==root) return root;
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left!=null&&right!=null) return root;
if(left!=null) return left;
if(right!=null) return right;
return null;
}
}
完全二叉树的节点个数
计算二叉树的节点个数可以用下面代码,时间复杂度O(N)
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
return 1+countNodes(root.left)+countNodes(root.right);
}
完全二叉树的话需要利用完全二叉树的性质,时间复杂度O(logN*logN)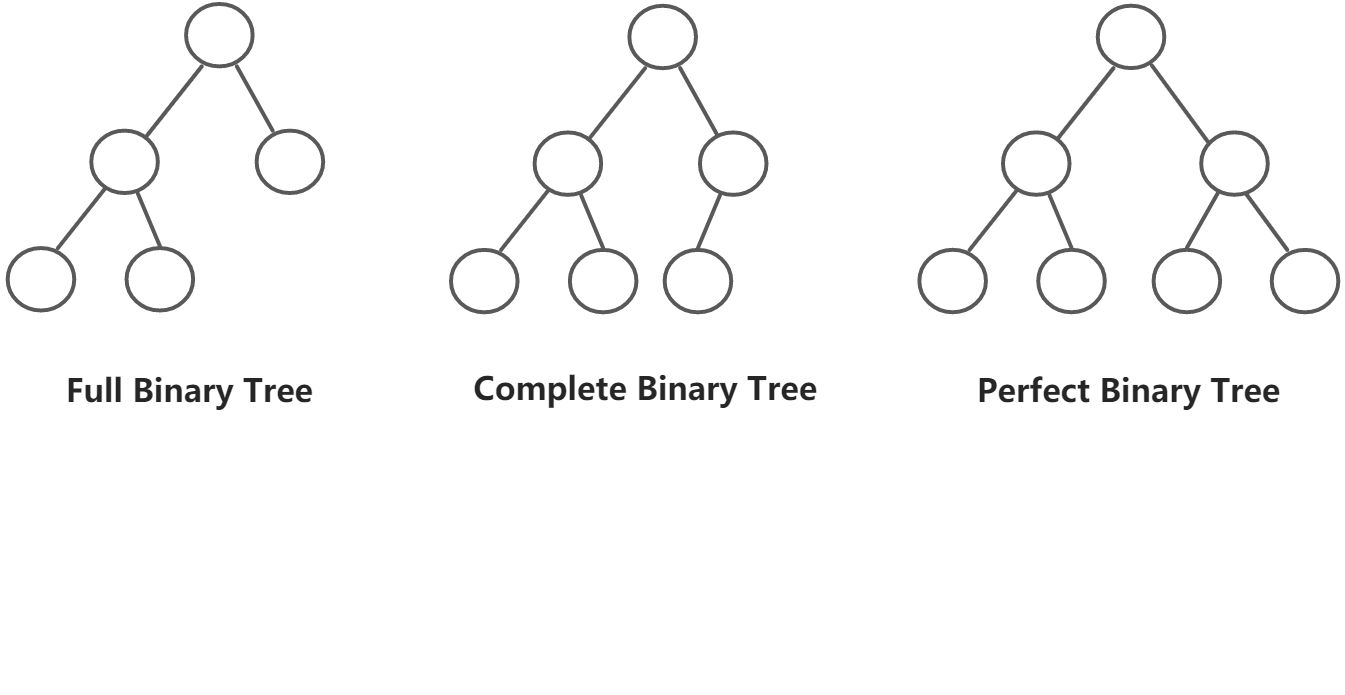
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
int left=0,right=0;
TreeNode node=root;
while(node!=null){
left++;
node=node.left;
}
node=root;
while(node!=null){
right++;
node=node.right;
}
if(left==right) return (int)Math.pow(2,left)-1;
else return 1+countNodes(root.left)+countNodes(root.right);
}
}

