class UF {// 连通分量个数private int count;// 存储一棵树private int[] parent;// 记录树的“重量”private int[] size;public UF(int n) {this.count = n;parent = new int[n];size = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {parent[i] = i;size[i] = 1;}}public void union(int p, int q) {int rootP = find(p);int rootQ = find(q);if (rootP == rootQ)return;// 小树接到大树下面,较平衡if (size[rootP] > size[rootQ]) {parent[rootQ] = rootP;size[rootP] += size[rootQ];} else {parent[rootP] = rootQ;size[rootQ] += size[rootP];}count--;}public boolean connected(int p, int q) {int rootP = find(p);int rootQ = find(q);return rootP == rootQ;}private int find(int x) {//通过find来更新value值,进行路径压缩if(x!=parent[x]){int p = parent[x]parent[x] = find(p);}return parent[x];}public int count() {return count;}}
被环绕的区域
[130]被围绕的区域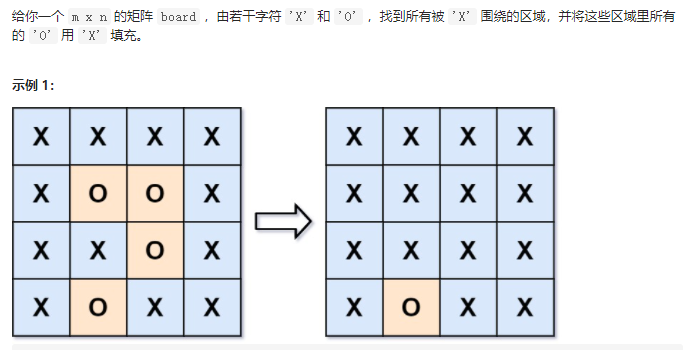
可以用dfs也可以用并查集
使用并查集
参数太多,什么xyij的混杂在一起,容易写错,使用dfs方法更清晰,效率也更高。
序列化二位矩阵[m,n] index=nx+y,index范围[0,mn-1]
给一个矩阵外的点dummy,dummy的index设置为m*n
首先把边界为’O’的点都与dummy相连接
再遍历非边界点,把值为’O’的点与周边为’O’的点相连
最后找到与dummy没有连接路径的点,标记为’X’
public void solve(char[][] board) {int m = board.length;if (m == 0) return;int n = board[0].length;UF uf = new UF(m * n + 1);int dummy = m * n;for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {if (board[i][0] == 'O') uf.union(dummy, n * i);if (board[i][n - 1] == 'O') uf.union(dummy, n * i + n - 1);}for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (board[0][j] == 'O') uf.union(dummy, j);if (board[m - 1][j] == 'O') uf.union(dummy, n * (m - 1) + j);}int[][] directions = new int[][]{{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; i++) {for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {if (board[i][j] == 'O') {for (int[] dir : directions) {int x = i + dir[0];int y = j + dir[1];if (board[x][y] == 'O') uf.union(x * n + y, i * n + j);}}}}for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; i++) {for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {if (!uf.connected(dummy, n * i + j)) board[i][j] = 'X';}}}
使用dfs
找到边界为’O’的位置,并将与其相连的点都标记为’#’
那么余下的’O’就是被’X’包围的,最后循环的时候,把’O’改为’X’,把’#’改回’O’
class Solution {public void solve(char[][] board) {int m = board.length;if (m == 0) return;int n = board[0].length;for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {if (board[i][0] == 'O') dfs(i,0,board);if (board[i][n - 1] == 'O') dfs(i,n-1,board);}for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (board[0][j] == 'O') dfs(0,j,board);if (board[m - 1][j] == 'O') dfs(m-1,j,board);}for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {if (board[i][j] == 'O') board[i][j]='X';if (board[i][j] == '#') board[i][j]='O';}}}public void dfs(int x,int y,char[][] board){if(board.length==0) return;if(x<0||y<0||x>=board.length||y>=board[0].length||board[x][y]!='O') return;board[x][y]='#';dfs(x-1,y,board);dfs(x+1,y,board);dfs(x,y-1,board);dfs(x,y+1,board);}}
990. 等式方程的可满足性
[990]等式方程的可满足性
一个非常适合用并查集的例子
public boolean equationsPossible(String[] equations) {int len = equations.length;if (len == 0) return true;UF uf = new UF(128);for (String equation:equations) {if (equation.charAt(1)=='!') continue;char c1 = equation.charAt(0);char c2 = equation.charAt(3);uf.union(c1, c2);}for (String equation:equations) {if (equation.charAt(1)=='=') continue;char c1 = equation.charAt(0);char c2 = equation.charAt(3);if(uf.connected(c1,c2)) return false;}return true;}
399. 除法求值
题目:399.除法求值
做了一个半小时,救命
class Solution {public double[] calcEquation(List<List<String>> equations, double[] values, List<List<String>> queries) {Map<String,Integer> stringToIndex=new HashMap<>();int k=0;for(int i=0;i<equations.size();i++){for(int j=0;j<2;j++){String s=equations.get(i).get(j);if(!stringToIndex.containsKey(s)){stringToIndex.put(s,k++);}}}UnionFind uf=new UnionFind(k);for(int i=0;i<equations.size();i++){int i1=stringToIndex.get(equations.get(i).get(0));int i2=stringToIndex.get(equations.get(i).get(1));uf.union(i1,i2,values[i]);}int n=queries.size();double[] res=new double[n];for(int i=0;i<n;i++){int i1=stringToIndex.getOrDefault(queries.get(i).get(0),-1);int i2=stringToIndex.getOrDefault(queries.get(i).get(1),-1);if(i1==-1||i2==-1) res[i]=-1.0;else res[i]=uf.isConnected(i1,i2);}return res;}class UnionFind{int[] parent;double[] value;//index=i的节点到parent的值public UnionFind(int n){parent=new int[n];value=new double[n];for(int i=0;i<n;i++){parent[i]=i;value[i]=1.0;}}public void union(int p,int q,double val){//p/q=valint rootp=find(p);int rootq=find(q);if(rootp==rootq) return;parent[rootp]=rootq;//注意这里value[rootp]=val*value[q]/value[p];}public int find(int x){//通过find来更新value值if(x!=parent[x]){//当还有parent的时候int p=parent[x];parent[x]=find(p);value[x]=value[x]*value[p];}return parent[x];}public double isConnected(int p,int q){int rootp=find(p);int rootq=find(q);if(rootp==rootq){return value[p]/value[q];}else{return -1.0;}}}}

