1、原地移除元素
数组原地移除元素,且空间复杂度为O(1) ,可以直接使用快慢指针
- 快慢指针都以0 开始增加
- 快指针直接递增,慢指针在nums[slow]!=nums[fast] 时递增,这样就可以保证慢指针的记录的值仅包含非目标值。
- 返回慢指针,可以看作返回长度为 slow的数组。
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {int slow = 0, fast;for (fast = 0; fast < nums.length; fast++) {if (nums[fast] != val) {nums[slow] = nums[fast];slow++;}}return slow;}
2、反转字符串中的单词
class Solution {public String reverseWords(String s) {//直接在字符串首位加空格,方便判断s = " " + s;int n = s.length();StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();int left, right;//left 一直在往左边走for (left = n - 1, right = n; left >= 0; left--) {char ch = s.charAt(left);//如果遇到空格if (ch == ' ') {//将截取的字符串加入到结果中if (left + 1 < right) {sb.append(s, left + 1, right).append(' ');}//移动右指针right = left;}}return sb.substring(0, sb.length() - 1);}}
3、环形链表
选取快慢指针,快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,如果有环,必定相遇 设链表非环部分长度为 a , 环中部分长度为 b ,f = 2s 且fast总比slow多走n个环,所以 f = s + nb 由上得:f = 2nb s = nb 此时将f 指向头节点,slow 与 fast 同时每轮向前走1 步 当 f 走到a 点时,s = nb+a 此时两指针重合,并指向入口
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode slow = head, fast = slow;while (slow.next != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;if (fast == slow) {ListNode index1 = head;ListNode index2 = fast;while (index2 != index1) {index2 = index2.next;index1 = index1.next;}return index1;}}return null;}
4、盛最多水的容器
从两个方向比较
class Solution {public int maxArea(int[] height) {int left = 0, right = height.length - 1;int max = 0, cur = 0;while (left < right) {cur = Math.min(height[left], height[right]) * (right - left);max = Math.max(cur, max);if (height[left]>height[right]) right--;else left++;}return max;}}
5、三数之和
主要思想就是先排序,再处理。 对于排序好的数组
- 如果nums[i] > 0,后面不可能有三个数相加和等于 0 ,直接返回结果。
- 重复元素跳过,避免出现重复解。
- 令左指针 L = i+1,右指针R = n-1,当 L < R时,执行循环。
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();Arrays.sort(nums);int n = nums.length;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {if (nums[i]>0) break;//去除重复解if (i>0&& nums[i]==nums[i-1]) continue;int left = i + 1, right = n - 1;while (left < right) {if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] == 0) {res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]));//去除重复解,并且移动下标while (left<right && nums[left]==nums[left+1]) left++;while (left<right && nums[right]==nums[right-1]) right--;left++;right--;}// nums[right] 太大,right左移else if (nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right] > 0) right--;//nums[left] 太小,right 右移else left++;}}return res;}
6、反转链表
双指针法: 定义三个指针:pre:存储前一个节点,cur:当前节点,temp:暂存下一个节点
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode cur = head;ListNode pre = null, temp= null;while (cur != null) {temp = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = temp;}return pre;}
递归:
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {return reverse(null, head);}private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {if (cur == null) {return prev;}ListNode temp = null;temp = cur.next;// 先保存下一个节点cur.next = prev;// 反转// 更新prev、cur位置// prev = cur;// cur = temp;return reverse(cur, temp);}
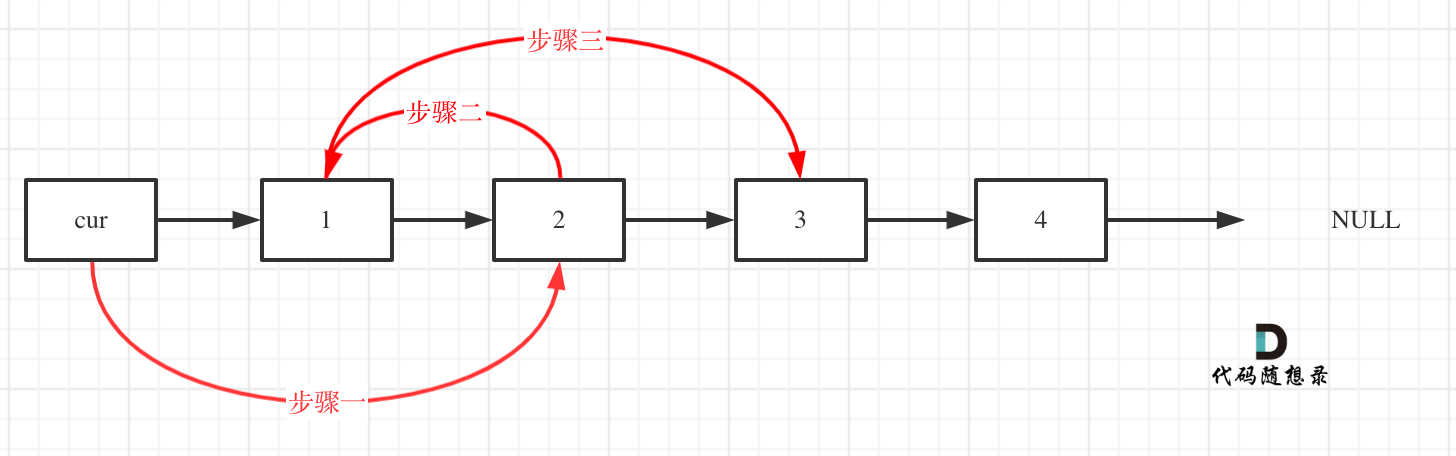
7、两两交换链表中的节点
双指针: 引入虚拟头节点 prehead,将cur = prehead ,分解为以下几个动作:
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}ListNode preHead = new ListNode(-1);preHead.next = head;ListNode cur = preHead;//first 存储两两中第一个节点//secode 存储第二个节点//temp 存储下一个两两节点中第一个节点ListNode first, second,temp;while (cur.next != null && cur.next != null) {temp = cur.next.next.next;first = cur.next;second = first.next;cur.next = second; //步骤 1second.next = first; // 步骤 2first.next = temp; //步骤 3cur = first;}return preHead.next;}
递归:
···java