1、Math类
- Math类概述:Math包含执行基本数学运算的方法
- 没有构造方法,该如何使用类中成员?
- 看类的成员是否都是静态(static修饰),如果是,可以直接通过类名进行直接调用
- Math类的常用方法 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public static int abs(int a) | 返回参数的绝对值 | | public static double ceil(double a) | 返回大于或等于参数的最小double值,等于一个整数,上取整 | | public static double floor(double a) | 返回小于等于参数的最大double值,等于一个整数,下取整 | | public static int round(float a) | 按照四舍五入返回最接近参数的int | | public static int max(int a,int b) | 返回两个int值中的较大值 | | public static int min(int a,int b) | 返回两个int值中的较小值 | | public static double pow(double a,double b) | 返回a的b次幂的值,即a的b次方 | | public static double random() | 返回值为double的正值,[0.0,1.0) |
2、System类
- System类概述:System包含几个有用的类字段和方法,它不能被实例化
- System类的常用方法 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public static void exit(int status) | 终止当前运行的Java虚拟机,非零表示异常终止 | | public static long currentTimeMillis() | 返回当前时间(以毫秒为单位) |
3、Object类
- Object是类层次结构的根,每个类都可以将Object类作为超类(父类、基类)。所有类都直接或间接的继承该类
- 构造方法:public Object()
- 回想面向对象中,为什么子类的构造方法默认访问的是父类的无参构造方法?
- 因为它们的顶级父类只有无参构造方法
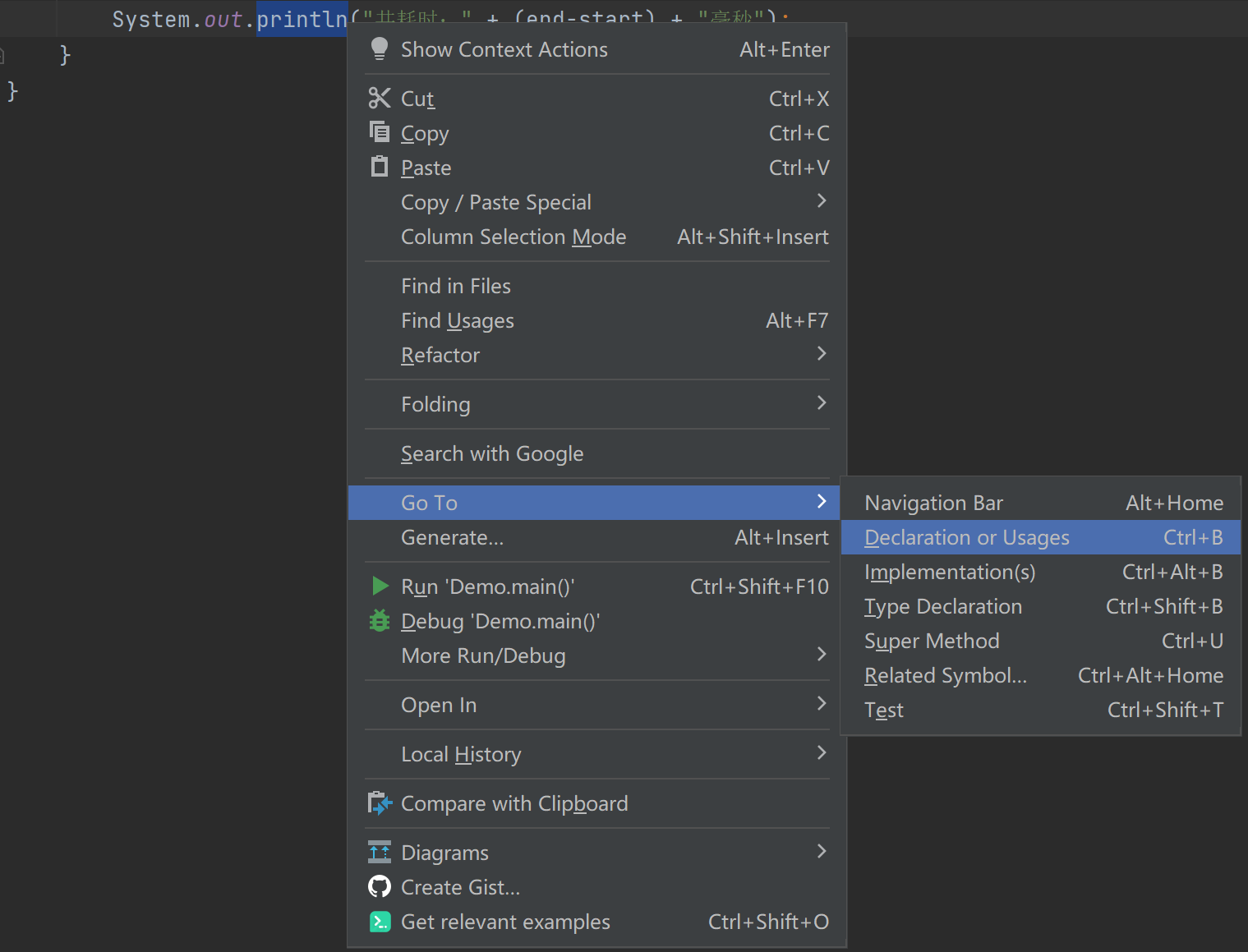
- 看方法的源码 右键->Go To->Declaration or Usages 或者 Ctrl + B
- 重写toString()方法 一般自动生成与构造函数类似
- Object类的常用方法 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public String toString() | 返回对象的字符串表示形式。建议所有子类重写该方法,自动生成 | | public boolean equals(Object obj) | 比较对象是否相等。默认比较地址,重写可以比较内容,自动生成 |
4、Arrays
冒泡排序
- 排序:将一组数据按照固定的规则进行排序
- 冒泡排序:一种排序的方式,对要进行排序的数据中相邻的数据进行两两比较,将较大的数据放在后面,依次对所有的数据进行操作,直至所有数据按要求完成排序
- 如果有n个数据进行排序,总共需要比较n-1次
- 每一次比较完毕,下一次的比较就会少一个数据参与
public class ArrayDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = {24, 69, 80, 57, 13};System.out.println("排序前:" + arrayToString(arr));//若元素个数为n,则总共比较次数为n-1 体现在外层循环的5-1次循环//每次比较后都会有一个元素不参与比较// 第一次比较 0-1 1-2 2-3 3-4// 第二次比较 0-1 1-2 2-3// 第三次比较 0-1 1-2// 第四次比较 0-1for(int i=0; i< arr.length-1; i++) {for(int j=0; j< arr.length-1-i; j++) {if(arr[j] > arr[j+1]) {int temp = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j+1];arr[j+1] = temp;}}}System.out.println("排序后:" + arrayToString(arr));}public static String arrayToString(int[] array) {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.append("{");for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {if(i == array.length-1) {sb.append(array[i] + "}");} else {sb.append(array[i] + ", ");}}return sb.toString();}}
Arrays类的概述和常用方法
- Arrays类包含用于操作数组的各种方法 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public static String toString(int[] a) | 返回指定数组的内容的字符串表示形式 | | public static void sort(int[] a) | 按照数字顺序排序指定的数组 |
工具类的设计思想:(Math类、Arrays类、System类等)
- 构造方法用private修饰
- 成员用public static修饰
5、基本类型包装类
基本类型包装类概述
- 将基本数据类型封装成对象的好处在于可以在对象中定义更多的功能方法操作该数据
- 常用的操作之一:用于基本数据类型与字符串之间的转换 | 基本数据类型 | 包装类 | | —- | —- | | byte | Byte | | short | Short | | int | Integer | | long | Long | | float | Float | | double | Double | | char | Character | | boolean | Boolean |
Integer类的概述和使用
- Integer:包装一个对象中的原始类型int的值 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public Integer(int value) | 根据int值创建Integer对象(过时) | | public Integer(String s) | 根据String值创建Integer对象(过时) | | public static Integer valueOf(int i) | 返回表示指定的int值的Integer实例 | | public static Integer valueOf(String s) | 返回一个保存指定值的Integer对象String |
int和String的相互转换
- 基本类型包装类最常见操作就是:用于基本类型和字符串之间的相互转换
- 1、int转换为String
- public static String valueOf(int i):返回int参数的字符串表示形式。该方法是String类中的方法。
2、String转换为int
public static int parseInt(String s):将字符串解析为int类型。该方法时Integer类中的方法。 ```java public class IntToString { public static void main(String[] args) { //int —-> String //方式1 利用String字符串的拼接 int num = 100; String s = “” + num; System.out.println(s);
//方式2 public static String valueOf(int i)返回int参数的字符串int形式。 //该表示恰好是一个参数的Integer.toString方法返回的表示。 int num2 = 200; String s2 = String.valueOf(num2); System.out.println(s2);
//String —-> int //先 String —-> Integer 再 Integer —-> int //方式1 public static Integer valueOf(String s) //public int intValue()将 Integer的值作为 int 。 String s3 = “300”; Integer num3 = Integer.valueOf(s3); num3.intValue(); System.out.println(num3);
//方式2 public static int parseInt(String s) 将字符串参数解析为带符号的十进制整数。 Integer类中方法 String s4 = “400”; int num4 = Integer.parseInt(s4); System.out.println(s4);
} } ```
自动装箱和拆箱
- 装箱:把基本数据类型转换为对应的包装类类型
- 拆箱:把包装类类型转换为对应的基本数据类型
Integer i = 100; // 自动装箱i += 200; // i = i + 200; i + 200 自动拆箱;i = i + 200 自动装箱;
注意:在使用包装类类型的时候,如果做操作,最好先判读是否为null
- 只要是对象,在使用前就必须进行不为null的判断
6、日期类
Date类概述和构造方法
- Date代表了一个特定的时间,精确到毫秒 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public Date() | 分配一个Date对象,并初始化,以便它代表它被分配的时间,精确到毫秒 | | public Date(long date) | 分配一个Date对象,并将其初始化为表示从标准基准时间起指定的毫秒数 |
Date类的常用方法 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public long getTime() | 获取的是日期对象从1970年1月1日00:00:00到现在的毫秒值 | | public void setTime(long time) | 设置时间,给的是毫秒值 |
SimpleDateFormat类概述
- SimpleDateFormat是一个具体类,用于以区域设置敏感的方式格式化和解析日期。
- 日期和时间格式由日期和时间模式字符串指定,在日期和时间模式字符串中,从’A’ 到 ‘Z’ 以及从 ‘a’ 到 ‘z’ 的字母被解释为表示日期或时间字符串的组件的模式字母
- y 年
- M 月
- d 日
- H 时
- m 分
- s 秒
- SimpleDateFormat构造方法 | 方法名 | 说明 | | —- | —- | | public SimpleDateFormat() | 构造一个SimpleDateFormat,使用默认模式和日期格式 | | public SimpleDateFormat(String pattern) | 构造一个SimpleDateFormat使用给定的模式和默认的日期格式 |
SimpleDateFormat格式化和解析日期
- 格式化(从Data到String)
- public final String format(Date date):将日期格式化成日期/时间字符串
解析(从String到Date)
public Date parse(String source):从给定字符串的开始解析文本以生成日期
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {//格式化:将Date类转换为StringDate d = new Date();// SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();// String s = sdf.format(d);SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");String s = sdf.format(d);System.out.println(s);//解析:将String转换为DateString s2 = "2022-02-20 20:20:20";SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");Date d2 = sdf2.parse(s2);System.out.println(d2);}}
- 格式化(从Data到String)
Calendar类概述
- Calendar为某一时刻和一组日历字段之间的转换提供了一些方法,并为操作日历字段提供了一些方法
- Calendar提供了一个类方法getInstance用于获取Calendar对象,其日历字段已使用当前日期和时间初始化
- Calendar rightNow = Calendar.getInstance(); ```java public class CalendarDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建对象 Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); int year = c.get(Calendar.YEAR); int month = c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1; int day = c.get(Calendar.DATE); System.out.println(year + “年” + month + “月” + day + “日”); } }
```javapublic class TwoMonthDay {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入年份:");int year = sc.nextInt();Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();// c.set(Calendar.YEAR, year);// c.set(Calendar.MONTH, 2);// c.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 1);c.set(year, 2, 1);c.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, -1); //DATE 等同于 DAY_OF_MONTHint count = c.get(Calendar.DATE);System.out.println(year + "年的2月份有" + count + "天");}}