import java.util.Scanner;public class ScannerDemo {public static viod main(String[] arg){//创建对象Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);//接受数据int x = sc.nextInt();//输出数据System.out.println("x:" + x);}}
import java.util.Scanner;public class ScannerDemo {public static void main(String[] arg){Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("依次输入三个和尚的身高:");int height1 = sc.nextInt();int height2 = sc.nextInt();int height3 = sc.nextInt();int tempHeight = height1 > height2 ? height1 : height2;int maxHeight = tempHeight > height3 ? tempHeight : height3;System.out.println("这三个和尚中身高最高的是:" + maxHeight + "cm");}
import java.util.Scanner;public class IsEven {public static void main(String[] arg){Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int num = sc.nextInt();if(num % 2 == 0){System.out.println("该数为偶数!");}else{System.out.println("该数为奇数!");}}}
import java.util.Scanner;public class JudgeSeason {public static void main(String[] arg){Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int num = sc.nextInt();switch(num){case 3:case 4:case 5:System.out.println("该季节为春季!");break;case 6:case 7:case 8:System.out.println("该季节为夏季!");break;case 9:case 10:case 11:System.out.println("该季节为秋季!");break;case 12:case 1:case 2:System.out.println("该季节为冬季!");break;default:System.out.println("输入有误!");}}}
public class LoopOutput{public static void main(String[] arg){for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){System.out.println(i);}for(int i=5;i>0;i--){System.out.println(i);}}}
public class EvenSum{public static void main(String[] arg){int sum = 0;for(int i=0;i<=100;i+=2){sum += i;}System.out.println(sum);}}
- 三位数的个位数字如何求:
- 371 1就是原始数字对10进行取余运算的结果 371 % 10 = 1
- 三位数的百位数字如何求:
- 371 3就是原始数字除以100的结果(整除) 371 / 100 = 3
三位数的十位数字如何求:
- 371 371通过除以10,可以将7移动到个位上(整除) 371 / 10 = 37
37通过对10进行取余运算可以得到最后一位的值7
public class DaffNum{public static void main(String[] arg){int singleDig,tenDig,hundredDig,sum;for(int i=100;i<1000;i++){singleDig = i % 10;tenDig =(i/10)%10;hundredDig = i/100;sum=singleDig*singleDig*singleDig + tenDig*tenDig*tenDig + hundredDig*hundredDig*hundredDig;if(sum == i)System.out.println(i);}}}
Random 的作用和使用步骤
- 作用:用于产生一个随机数
- 使用步骤:
- 导包
- import java.util.Random;
- 创建对象
- Random r = new Random();
- 获取随机数
- int number = r.nextInt(10); //获取数据的范围:[0,10) 包括0,不包括10 ```java import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Random;
- 导包
public class GuassNum{
public static void main(String[] arg)
{
Random r = new Random();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int randomNum = r.nextInt(100) + 1;
int scannerNum;
while(true)
{
System.out.println(“请输入你猜的数字:”);
scannerNum = sc.nextInt();
if(scannerNum < randomNum)
{
System.out.println(“你猜的数小了!”);
}
else if(scannerNum > randomNum)
{
System.out.println(“你猜的数大了!”);
}
else
{
System.out.println(“恭喜你猜中了!”);
break;
}
}
}
}
<a name="um2Mf"></a>### IDEA概述IDEA全程IntelliJ IDEA,适用于开发Java语言的集成环境- 集成环境:把代码编写,编译,执行,调试等多种功能综合到一起的开发工具。IDEA项目结构:- HelloWorld 项目步骤- 创建一个空项目(javaSE_Code)- 创建一个新模块(idea_test)- 在idea_test模块下的src下创建一个包(com.itheima)- 在com.itheima包下新建一个类(HelloWord)- 在Helloworld类中编写代码- 在idea中执行程序- 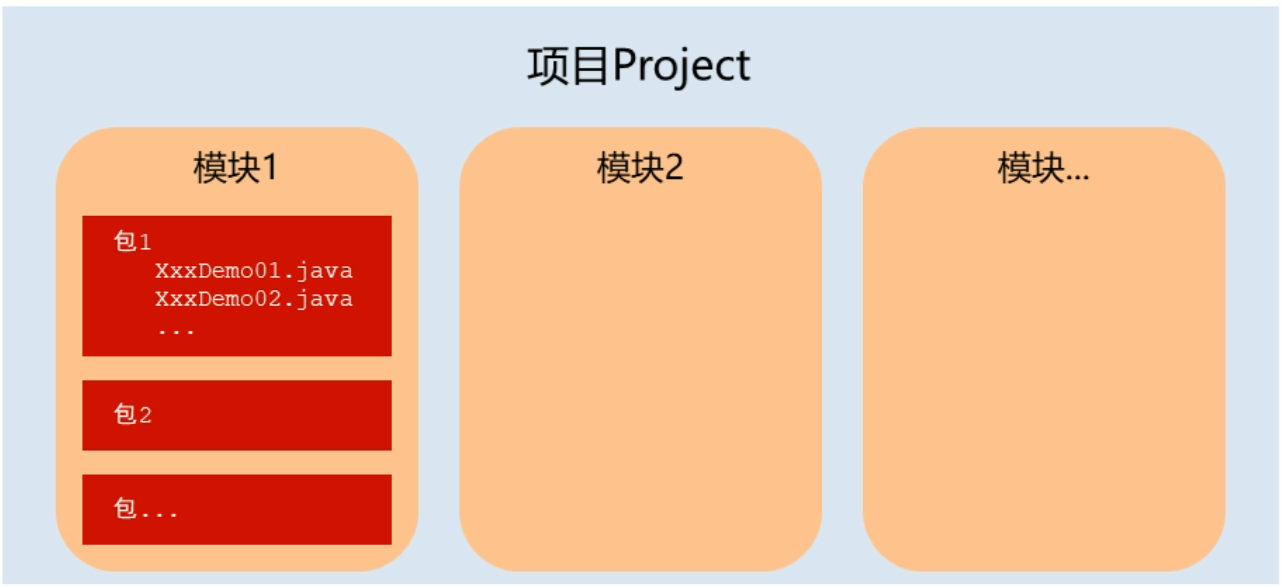IDEA中内容辅助键和快捷键:- 内容辅助键:- 快速生成语句:- 快速生成main()方法:psvm,回车- 快速生成输出语句:sout,回车- 内容辅助键:- Ctrl + Alt + Space(内容提示,代码补全等)- 快捷键:- 注释:- 单行:选中代码,Ctrl + /,再来一次,就是取消- 多行:选中代码,Ctrl + Shift + /,再来一次,就是取消- 格式化:- Ctrl + Alt + L<a name="HzgM6"></a>### 数组数组定义格式:- 数据类型[] 变量名 int[] arr 定义了一个int类型的数组,数组名是arr- 数据类型 变量名[] int arr[] 定义了一个int类型的变量,变量名是arr数组```javapublic class Array {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = new int[3];/*左边:int:说明数组中的元素类型是int类型[]:这是一个数组arr:数组的名称右边:new:为数组申请内存空间int:数组中的元素是int类型[]:这是一个数组3:数组长度,数组中的元素个数*/}}
JAVA中内存分配
java程序在运行时,需要在内存中分配空间,为了提高运算效率,就对空间进行了不同区域的划分,因为每一片区域都有特定的处理数据方式和内存管理方式。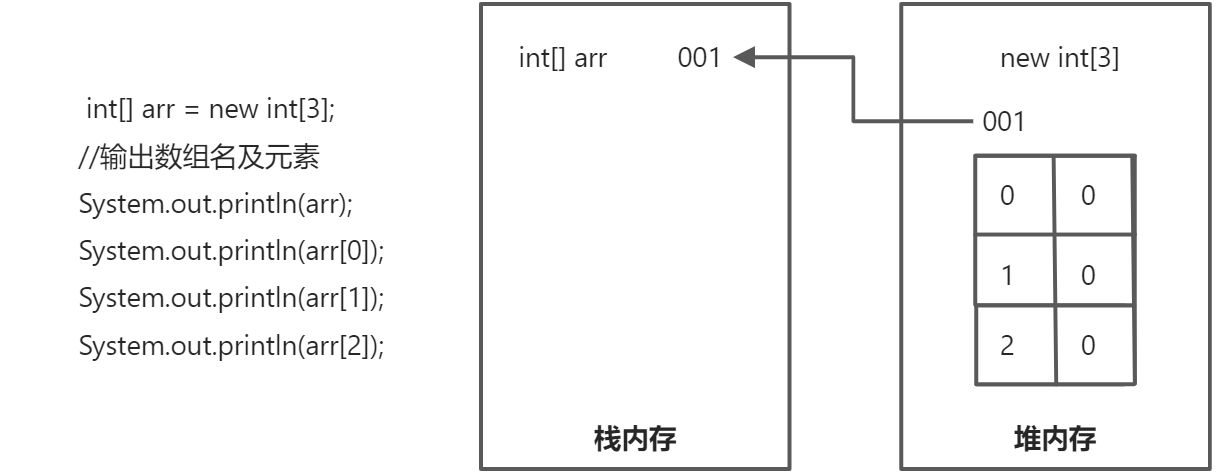
- 栈内存:存储局部变量
- 定义在方法中的变量,例如:arr
- 使用完毕,立即消失
- 堆内存:存储new出来的内容(实体,对象)
- 数组在初始化时,会为存储空间添加默认值
- 整数:0
- 浮点数:0.0
- 布尔:false
- 字符:空字符
- 引用数据类型:null
- 每一个new出来的东西都有一个地址值,使用完毕,会在垃圾回收器空闲时被回收
- 数组在初始化时,会为存储空间添加默认值
public class Array {public static void main(String[] args) {//省略了new int 实际上系统仍执行int[] arr2 = {1, 2, 3};System.out.println(arr2);System.out.println(arr2[0]);System.out.println(arr2[1]);System.out.println(arr2[2]);}}
获取数组元素个数:
- 格式:数组名.length
public class CompareValue {public static void main(String[] args) {boolean result;short number1 = 12;short number2 = 15;result = compare(number1,number2);System.out.println(result);}public static boolean compare(byte a, byte b){return a == b ? true : false;}public static boolean compare(short a, short b){return a == b ? true : false;}public static boolean compare(int a, int b){return a == b ? true : false;}public static boolean compare(long a, long b){return a == b ? true : false;}}

