1. 基本原理
- LinkedList 底层是基于双向链表实现的,一个节点挂着另一个节点
- 第一个节点的 prev 指向 null
- 最后一个节点的 next 指向 null
- first、last 会一直保持指向第一个和最后一个节点

public class LinkedList<E> ... {transient int size = 0; // list中元素个数/*** Pointer to first node.* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)*/transient Node<E> first;/*** Pointer to last node.* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||* (last.next == null && last.item != null)*/transient Node<E> last;/*** Constructs an empty list. 默认构造函数*/public LinkedList() {}}private static class Node<E> {E item;Node<E> next;Node<E> prev;Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}}
2. 优缺点
- 缺点:
- 由于底层链表的特点,不适合在随机位置,获取某个随机位置的元素,比如 LinkedList.get(10) 这个操作需要从头开始遍历这个链表,直到找到 index=10 的这个元素为止,不像 ArrayList 不需要遍历,直接根据内存的地址,根据指定的 index 直接定位那个元素;
- 优点:
- 向 LinkedList 不断插入元素,不需要像 ArrayList 那样还需要扩容+挪动元素,它是基于链表实现的,就是不断把新的节点挂到链表上就可以了;
- 非常适合频繁插入元素;
3. 使用场景
- LinkedList 由于基于链表的实现,非常适合频繁的在 list 中插入和删除某个元素;
- LinkedList 非常适合当作队列来用,队列的先进先出的特点,非常适合使用 LinkedList 对尾部插入一个元素,头部删除一个元素,性能还是不错的;
4. 核心方法的原理
4.1 插入元素的方法
(1) add(element)
- 来自 List
接口的方法 - 作用:在双向链表的尾部插入一个元素,返回 boolean
- 逻辑:
- last 节点保存在临时节点 l;
- 新元素放到 newNode = Node(l, e, null) 新节点;
- 将 newNode 设置为 last 节点;
- 如果链表是空链表(原尾节点 last == null),first 和 last 指向同一个节点 newNode;
- 如果链表是非空的,则将原尾节点的next(l.next)指向 newNode;
- 链表元素个数 size+1; ```java public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; }
//在链表的尾部插入一个元素节点
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node
// 插入的新节点的next指向null,作为最后一个节点
// 插入的新节点的prev指向原来的最后节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
<a name="lFOY1"></a>
#### (2) add(index, element)
- 来自 List<E> 接口的方法
- 作用:在链表的指定位置插入一个元素,如果之前这个位置有元素,则将这个元素及后续元素往后移一位,此位置插入新元素,无返回;
- 逻辑:
- 检查插入位置是否在 [0, size] 内,否则抛出索引越界异常;(size 可以作为尾部新元素的位置)
- 插入位置是链表尾部,则执行链表尾部插入元素的操作;
- 否则,先找到原 index 位置的节点(经典算法:遍历链表读取某位置元素),在此节点的前面插入新节点(双向链表指针交换 + 判断是否首节点);
- 链表元素个数 size+1;
```java
public void add(int index, E element) {
// 检查是否索引越界
checkPositionIndex(index);
// 在链表的尾部放入新元素
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index)); // 在index位置原节点的前面插入新元素
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
// 经典遍历链表读取元素的算法:
// index在前半部分,从first开始往后遍历
// index在后半部分,从last开始往前遍历
// 返回index位置的 Node 节点
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
// 在链表尾部插入元素
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 在某个节点的前面插入新的节点
// 如果原节点的node.prev==null,说明原节点是第一个节点,将newNode设置为first作为首节点
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
(3) addFirst(element)
- 来自 Deque
接口的队列方法 - 作用:在队列的头部插入一个元素,无返回
- 逻辑:
- 在链表首部插入元素
- 双向链表的指针交换
- 判断是否空链表,空链表还需要设置 first last 同时指向插入的新节点 ```java public void addFirst(E e) { linkFirst(e); }
- 在链表首部插入元素
// 在链表首部插入元素
// 双向链表的指针交换
// 判断是否空链表,空链表还需要设置 first last 同时指向插入的新节点
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node
<a name="aI5YJ"></a>
#### (4) addLast(element)
- 来自 Deque<E> 接口的队列方法
- 作用:在队列的尾部插入一个元素,无返回
- 逻辑:
- 与 add(element) 方法是一样的,都是在尾部插入元素,只是这个无返回,而 add(element) 返回 boolean;
```java
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
4.2 获取元素的方法
(1) getFirst()
- 来自 Deque
接口的队列方法 - 作用:返回链表的首节点中的元素内容,如果空链表,则返回 NoSuchElementException 异常
逻辑:
来自 Deque
接口的队列方法 - 作用:返回链表的首节点中的元素内容,如果空链表,则返回 null
逻辑:
来自 List
接口的方法 - 作用:返回链表中指定位置的元素内容
- 逻辑:
- 检查 index 是否在 [0, size) 范围内,否则抛出索引越界异常
- 经典算法:判断index在链表的前半部分还是后半部分,从头部或尾部开始遍历链表,找到 index 位置节点的元素 ```java public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; }
private void checkElementIndex(int index) { if (!isElementIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index < size; }
<a name="mhSkn"></a>
### 4.3 删除元素的方法
<a name="bWItq"></a>
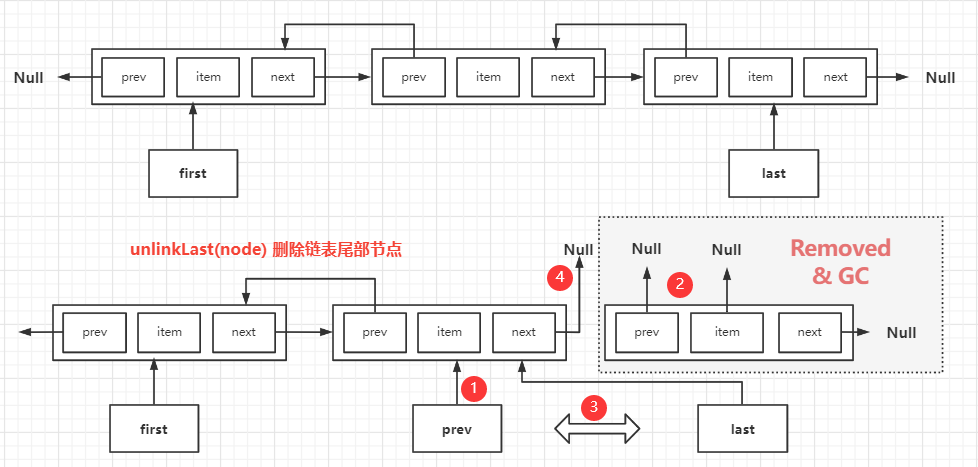
#### (1) removeLast()
- 来自 Deque<E> 接口的队列方法
- 作用:移除链表尾部的节点,并返回移除节点中的元素内容
- 逻辑:
- 先获取 last 指向的节点,如果是空链表(如 last 指向 null),则抛出异常
- 将 last 指向的节点从链表中移除
- 先将 last 指向的节点中元素内容保存到临时变量中,并最终返回这个变量中的元素内容;
- 用一个临时指针 prev 保存 last 的前一个节点;
- 然后将 last 指向的尾部节点中的 item 元素、prev 对象都设置 null,便于 GC 回收;
- 将 last 指针指向和 prev 指向相同的节点,即 last 指向链表原尾部节点的前一个节点;
- 如果移除节点后变成空链表(prev==null),要将 first 也设置 null;
- 如果移除节点后链表非空,将现在的尾部节点 last 的 next 指向 null;
```java
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
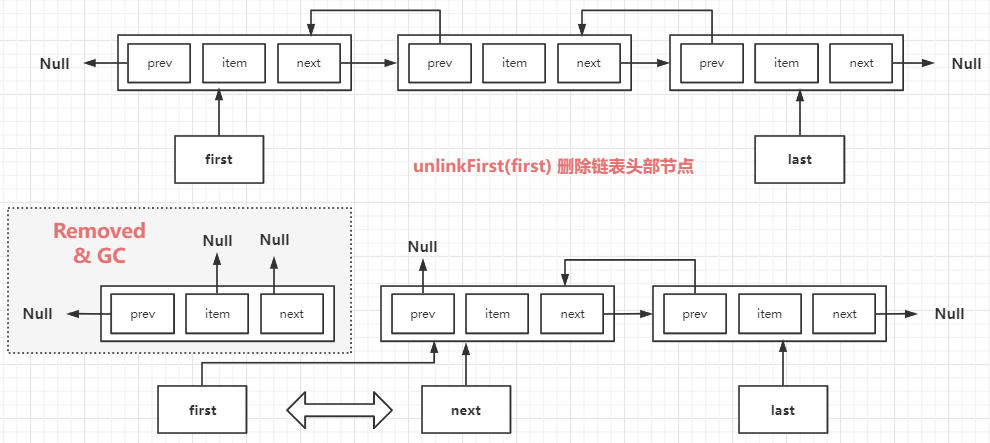
(2) removeFirst()
- 来自 Deque
接口的队列方法 - 作用:移除链表头部的节点,并返回移除节点中的元素内容
- 逻辑:
- 先获取 first 指向的节点,如果是空链表(如 first 指向 null),则抛出异常
- 将 first 指向的节点从链表中移除
- 先将 first 指向的节点中元素内容保存到临时变量中,并最终返回这个变量中的元素内容;
- 用一个临时指针 next 保存 first 的后一个节点;
- 然后将 first 指向的头部节点中的 item 元素、next 对象都设置 null,便于 GC 回收;
- 将 first 指针指向和 next 指向相同的节点,即 first 指向链表原头部节点的后一个节点;
- 如果移除节点后变成空链表(next==null),要将 last 也设置 null;
- 如果移除节点后链表非空,将现在的头部节点 first 的 prev 指向 null;
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
(3) remove(index)
- 来自 List
接口的方法 - 作用:移除指定位置的节点,并返回该节点中的元素内容;
- 逻辑:
- 先检查 index 是否在 [0, size) 内,否则抛出索引越界的异常
- 先获取 index 位置的节点(经典的算法:链表遍历,寻找 index 位置的节点)
- 将 index 位置的节点 x 从链表中移除
- 先将index 位置的节点中元素内容保存到临时变量中,并最终返回这个变量中的元素内容;
- 用一个临时指针 next 保存 index 位置节点的后一个节点;
- 用一个临时指针 prev 保存 index 位置节点的前一个节点;
- 如果删除的是首节点(临时指针 prev==null),那么将后一个节点作为 first 节点;否则将前一个节点的 next 指向 x 的后一个节点;且 x 的 prev 指针设置 null;
- 如果删除的是尾节点(临时指针 next==null),那么将前一个节点作为 last 节点;否则将后一个节点的 prev 指向 x 的前一个节点;且 x 的 next 指针设置 null;
- 将 x 节点中 item 元素内容设置成 null;
- 链表的元素个数 size-1;

public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
5. 源码分析总结
- 插入元素的方法的时间复杂度
- add(element):添加到末尾,时间复杂度 O(1)
- add(index, element):添加第几个元素后,需要先查找到第几个元素,直接指针指向操作,复杂度 O(n/2) = O(n)
- addFirst(element):添加到头部,时间复杂度 O(1)
- addLast(element):等同 add(element),时间复杂度 O(1)
- 获取元素的方法的时间复杂度
- getFirst():获取头部元素,O(1)
- peek():等同 getFirst(),O(1)
- get(index):获取指定位置的元素,O(n/2) = O(n)
- 删除元素的方法的时间复杂度
- removeLast():移除尾部的元素,O(1)
- removeFirst():移除头部的元素,O(1)
- remove(index):先查找到指定位置的元素,然后删除该元素,O(n/2) = O(n)
- 总结:
- 很适合大量的插入数据,往头部、尾部、中间插入的性能都不错,哪怕是中间插入元素,由于基于双向链表底层实现,不会出现大量元素的挪动和扩容情况,只是没有头部和尾部插入的性能那么好,但也不错;
- LinkedList 很适合做队列,头部和尾部的操作性能很高;
- 对指定位置的元素进行操作的性能比较差,因为需要先遍历一下链表,随机读的性能是要比 ArrayList 差;

