242. 有效的字母异位词
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-anagram/
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {char[] schar = s.toCharArray();char[] tchar = t.toCharArray();if (s.length() != t.length()) return false;int[] count = new int[26];for (int i = 0; i < schar.length; i++) {count[schar[i] - 'a']++;}for (int i = 0; i < tchar.length; i++) {if (--count[tchar[i] - 'a'] < 0) {return false;}}return true;}
383. 赎金信
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ransom-note/
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {char[] str1 = ransomNote.toCharArray();char[] str2 = magazine.toCharArray();int[] count = new int[26];for (int i = 0; i < str2.length; i++) {count[str2[i] - 'a']++;}for (int i = 0; i < str1.length; i++) {count[str1[i] - 'a']--;}for (int i : count) {if (i < 0) {return false;}}return true;}
49. 字母异位词分组
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/group-anagrams/
- 排序
由于互为字母异位词的两个字符串包含的字母相同,因此对两个字符串分别进行排序之后得到的字符串一定是相同的,故可以将排序之后的字符串作为哈希表的键
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();for (String str : strs) {char[] chs = str.toCharArray();Arrays.sort(chs);String key = String.valueOf(chs);if (!map.containsKey(key)) {map.put(key, new ArrayList<>());}map.get(key).add(str);}List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();for (List<String> list : map.values()) {res.add(list);}return res;}
438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/
- 滑动窗口 + 欠帐表 + 总账目
https://www.yuque.com/docs/share/38e3c359-548d-4304-be67-dab91724041a?#
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s, String p) {List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();if (s == null || p == null || s.length() < p.length()) {return ans;}char[] str = s.toCharArray();char[] ptr = p.toCharArray();int N = str.length;int M = ptr.length;// 欠帐表Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();// 总账目int all = M;// 欠帐表初始化for (char c : ptr) {if (map.containsKey(c)) {map.put(c, map.get(c) + 1);} else {map.put(c, 1);}}for (int i = 0; i < M - 1; i++) {if (map.containsKey(str[i])) {int count = map.get(str[i]);map.put(str[i], count - 1);if (count > 0) {all--;}}}for (int end = M - 1, start = 0; end < N; end++, start++) {if (map.containsKey(str[end])) {int count = map.get(str[end]);map.put(str[end], count - 1);if (count > 0) {all--;}}if (all == 0) {ans.add(start);}if (map.containsKey(str[start])) {int count = map.get(str[start]);map.put(str[start], count + 1);if (count >= 0) {all++;}}}return ans;}
349. 两个数组的交集
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {Set<Integer> set = new HashSet();Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet();for (int i : nums1) {set.add(i);}for (int i : nums2) {if (set.contains(i)) {set1.add(i);}}int[] ans = new int[set1.size()];int index = 0;for (int i : set1) {ans[index++] = i;}return ans;}
350. 两个数组的交集Ⅱ
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays-ii/
public int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for (int i : nums1) {if (!map.containsKey(i)) {map.put(i, 1);} else {map.put(i, map.get(i) + 1);}}List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i : nums2) {if (map.containsKey(i) && map.get(i) >= 1) {list.add(i);map.put(i, map.get(i) - 1);} else {continue;}}int[] ans = new int[list.size()];int index = 0;for (int i : list) {ans[index++] = i;}return ans;}
202. 快乐数
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/happy-number/
题目中说了会 无限循环,那么也就是说求和的过程中,sum会重复出现,这对解题很重要!
所以这道题目使用哈希法,来判断这个sum是否重复出现,如果重复了就是return false, 否则一直找到sum为1为止。
public boolean isHappy(int n) {HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();while (n != 1) {int sum = 0;while (n != 0) {sum += Math.pow(n % 10, 2);n /= 10;}n = sum;if (set.contains(n)) {break;}set.add(n);}return n == 1;}
5. 两数之和
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/two-sum/
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {if (map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {return new int[]{map.get(target - nums[i]), i};}map.put(nums[i], i);}return new int[]{-1, -1};}
454. 四数相加Ⅱ
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum-ii/
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();int ans = 0;for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < nums2.length; j++) {int sum = nums1[i] + nums2[j];if (map.containsKey(sum)) {map.put(sum, map.get(sum) + 1);} else {map.put(sum, 1);}}}for (int i = 0; i < nums3.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < nums4.length; j++) {int sum = nums3[i] + nums4[j];if (map.containsKey(-sum) && map.get(-sum) > 0) {ans += map.get(-sum);}}}return ans;}
15. 三数之和
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum/
排序+ 双指针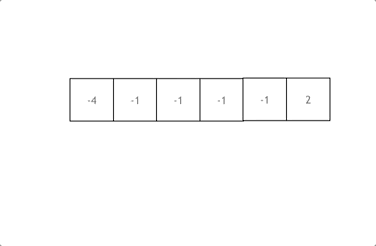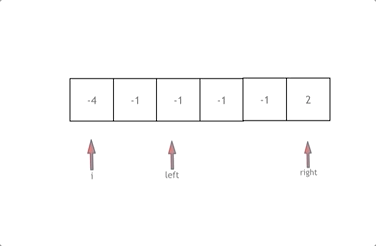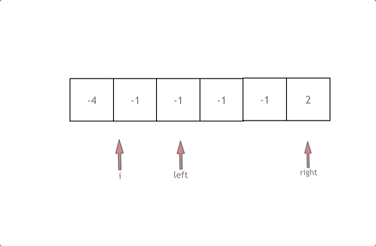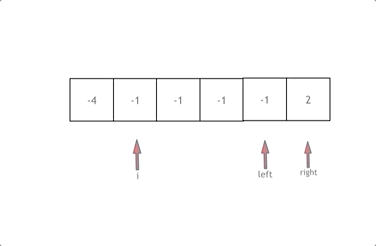
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {// 排序Arrays.sort(nums);List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {if (i == 0 || nums[i] != nums[i - 1]) { // 去重List<LinkedList<Integer>> nexts = twoSum(nums, i + 1, -nums[i]);for (LinkedList<Integer> next : nexts) {next.addFirst(nums[i]);ans.add(next);}}}return ans;}// nums是排好序的private List<LinkedList<Integer>> twoSum(int[] nums, int begin, int target) {List<LinkedList<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();int L = begin;int R = nums.length - 1;while (L < R) {if (nums[L] + nums[R] > target) {R--;} else if (nums[L] + nums[R] < target) {L++;} else {if (L == begin || nums[L - 1] != nums[L]) { // 去重LinkedList<Integer> cur = new LinkedList<>();cur.add(nums[L]);cur.add(nums[R]);ans.add(cur);}L++;}}return ans;}
18. 四数之和
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/4sum/
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {// 排序Arrays.sort(nums);List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i <= nums.length - 4; i++) {if (i == 0 || nums[i] != nums[i - 1]) { //去重List<LinkedList<Integer>> nexts = threeSum(nums, i + 1, target - nums[i]);for (LinkedList<Integer> next : nexts) {next.addFirst(nums[i]);ans.add(next);}}}return ans;}private List<LinkedList<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums, int begin, int target) {List<LinkedList<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = begin; i <= nums.length - 3; i++) {if (i == begin || nums[i] != nums[i - 1]) {List<LinkedList<Integer>> nexts = twoSum(nums, i + 1, target - nums[i]);for (LinkedList<Integer> next : nexts) {next.addFirst(nums[i]);ans.add(next);}}}return ans;}// nums是排好序的private List<LinkedList<Integer>> twoSum(int[] nums, int begin, int target) {List<LinkedList<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();int L = begin;int R = nums.length - 1;while (L < R) {if (nums[L] + nums[R] > target) {R--;} else if (nums[L] + nums[R] < target) {L++;} else {if (L == begin || nums[L] != nums[L - 1]) {LinkedList<Integer> cur = new LinkedList<>();cur.add(nums[L]);cur.add(nums[R]);ans.add(cur);}L++;}}return ans;}

