引言:
变量表示存储位置。每个变量都具有一个类型。
C# 定义了 7 类变量:类的字段(静态变量、实例变量)、方法的形参:数组元素、值参数、引用参数、输出参数和方法体的局部变量。
class A{public static int x;int y;void F(int[] v, int a, ref int b, out int c) {int i = 1;c = a + b++;}}
x 是静态变量,yy 是实例变量,v[0] 是数组元素,a 是值参数,b 是引用参数,c 是输出参数,i 是局部变量。
方法有四种形参:
- 值形参,声明时不带任何修饰符
- 引用形参,用 ref 修饰符声明
- 输出形参,用 out 修饰符声明
- 形参数组,用params 修饰符声明
形参补充三种特殊参数
- 具名参数
- 可选参数:参数有默认值
- 扩展方法(this参数)

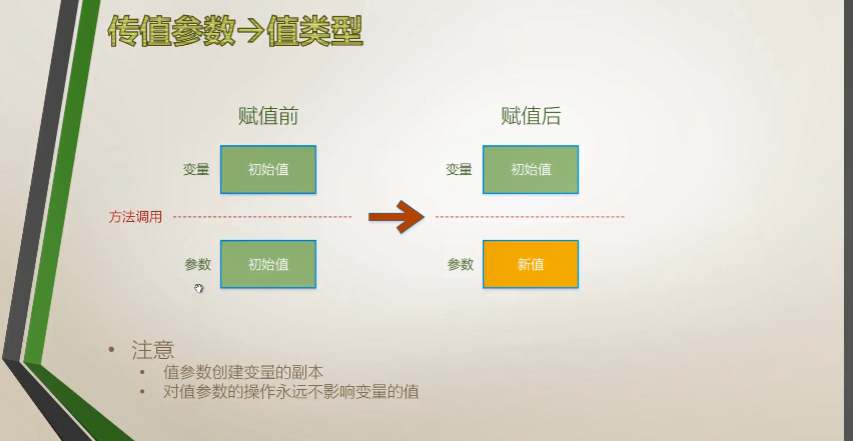
1、传值参数
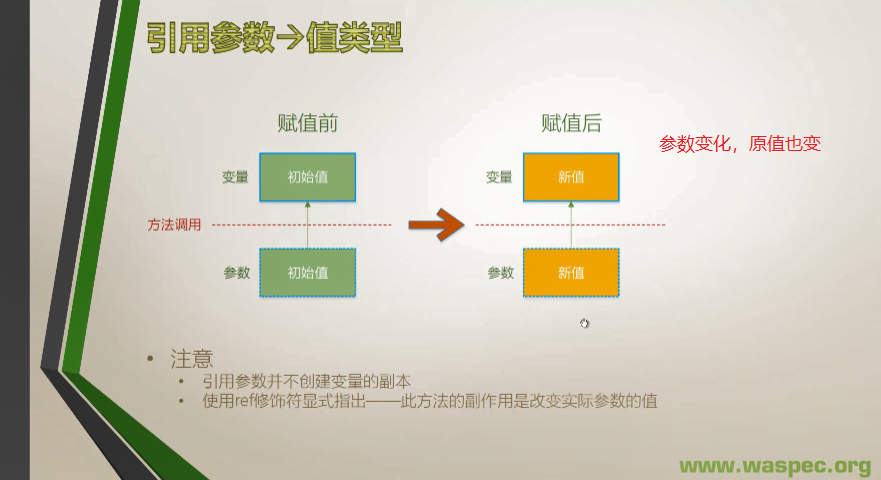
特点:分身术,一式两份。值参数创建变量的副本,对值参数的操作永远不影响变量的值
值类型
引用类型
创建新对象:少用
- 在栈中为形参分配空间。
- 复制实参到形参。
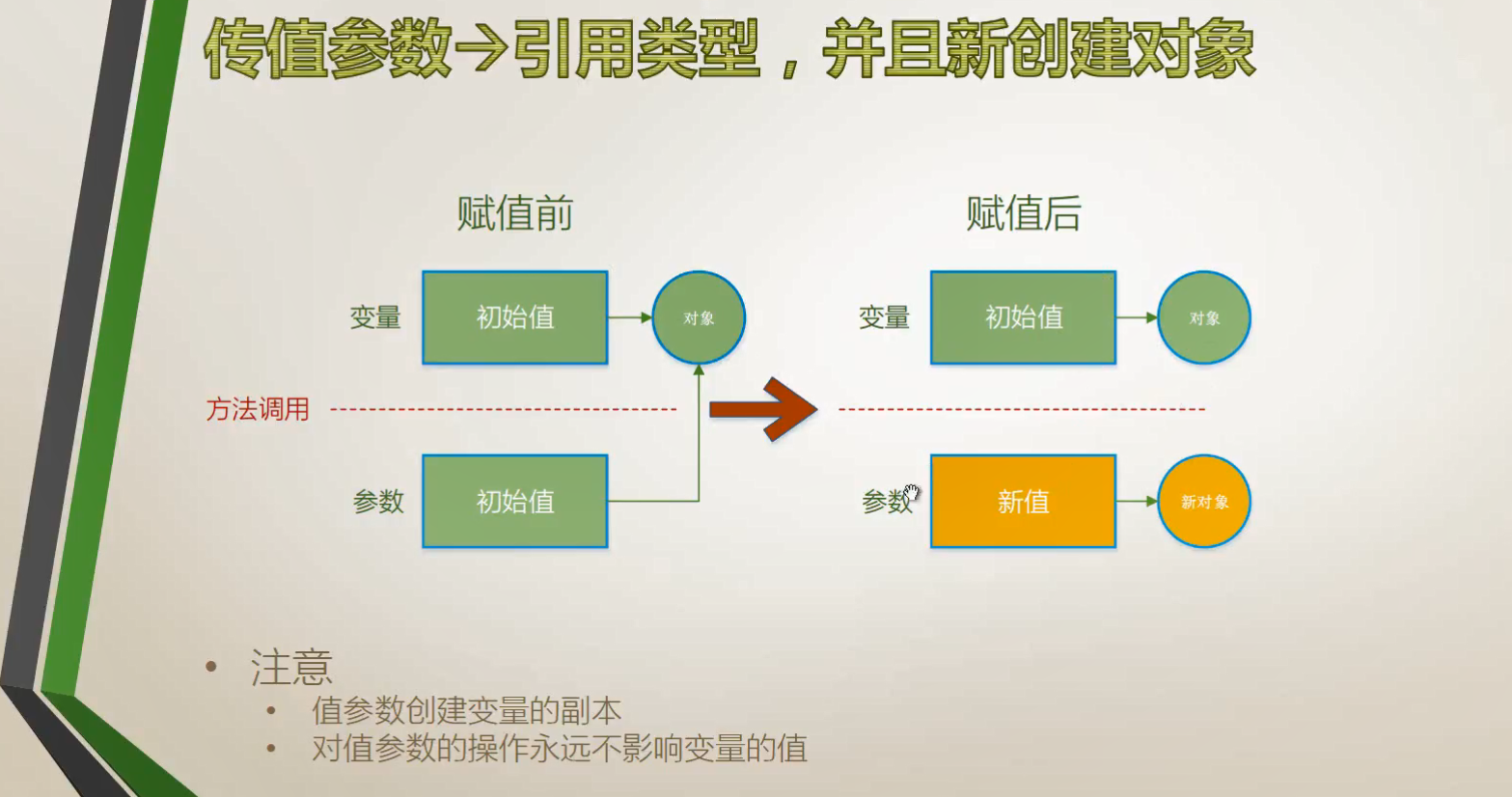
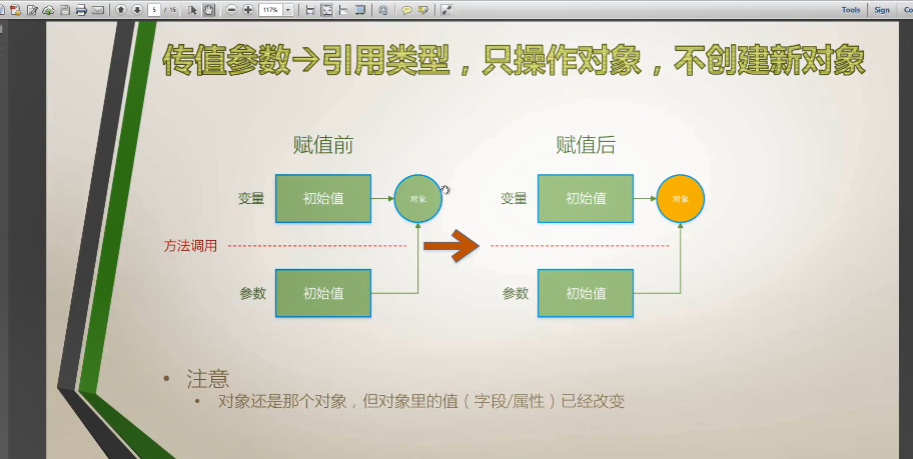
操作对象:对象的值(字段、属性)会变化
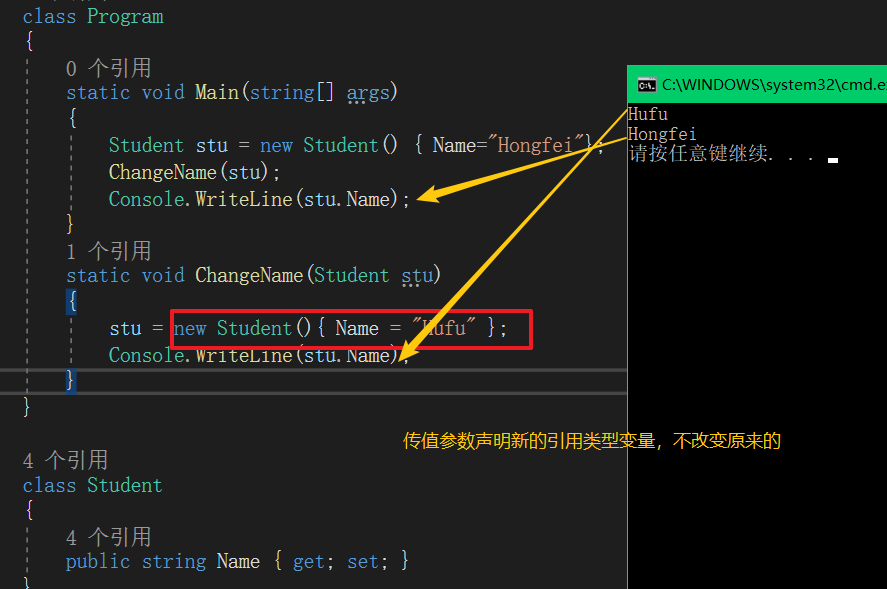
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student() { Name="Hongfei"};
ChangeName(stu);
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", stu.GetHashCode(), stu.Name);
}
static void ChangeName(Student stu1)
{
// stu = new Student(){ Name = "Hufu" };
stu1.Name = "Hufu";//副作用,side-effect
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}",stu1.GetHashCode(),stu1.Name);
}
}
输出:
46104728,Hufu
46104728,Hufu//完全一样就意味着,
stu.GetHashCode() 获得当前对象的身份证号。gethashcode的类为object类
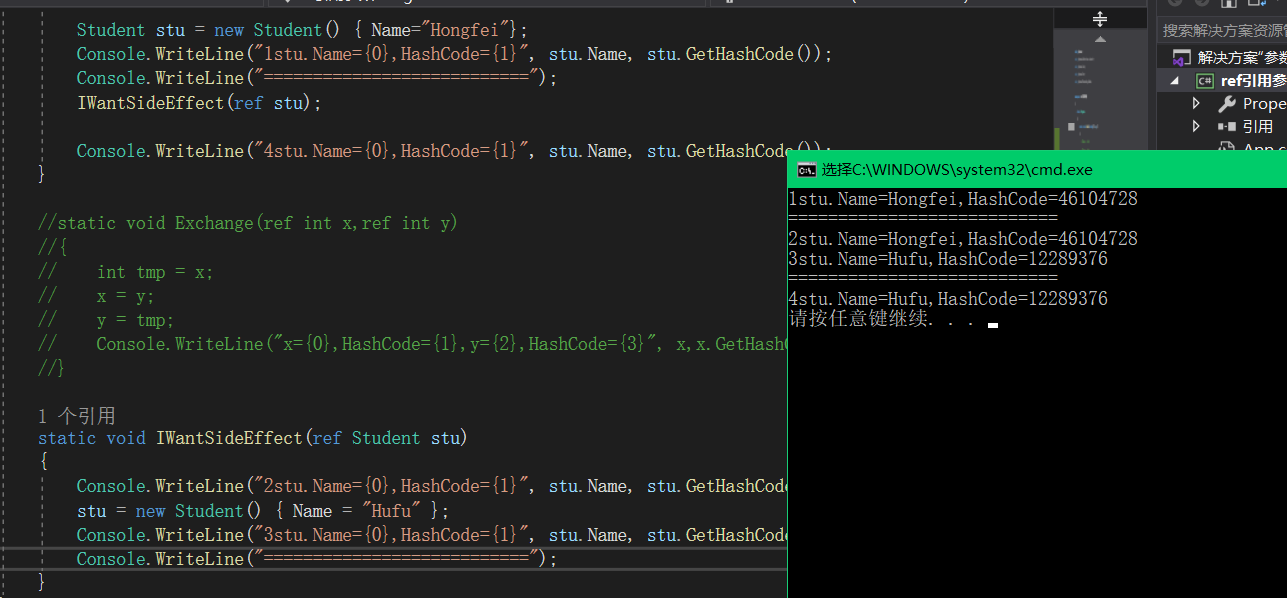
2、引用参数 ref
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
Exchange(ref x,ref y);
Console.WriteLine("x={0},HashCode={1},y={2},HashCode={3}", x, x.GetHashCode(), y, y.GetHashCode());
}
static void Exchange(ref int x,ref int y)
{
int tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
Console.WriteLine("x={0},HashCode={1},y={2},HashCode={3}", x,x.GetHashCode(), y,y.GetHashCode());
}
exchange方法的副作用(side-effect)就是交换值
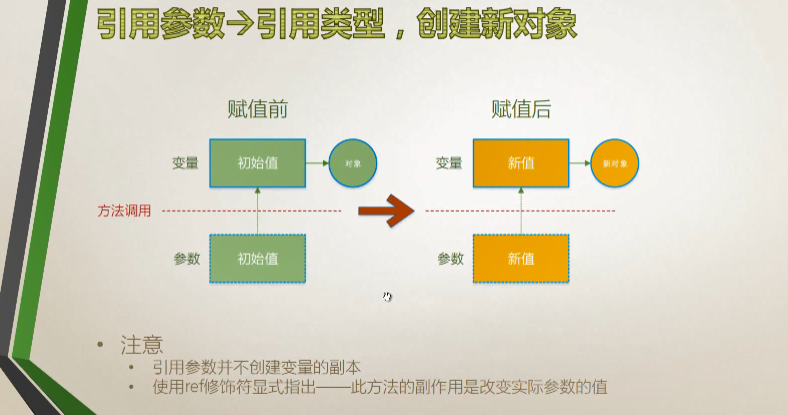
引用类型
创建新对象
操作对象:改变对象的值
功能上:和传值参数引用类型变量操作值(1.2.2)是一样的,只是原理不同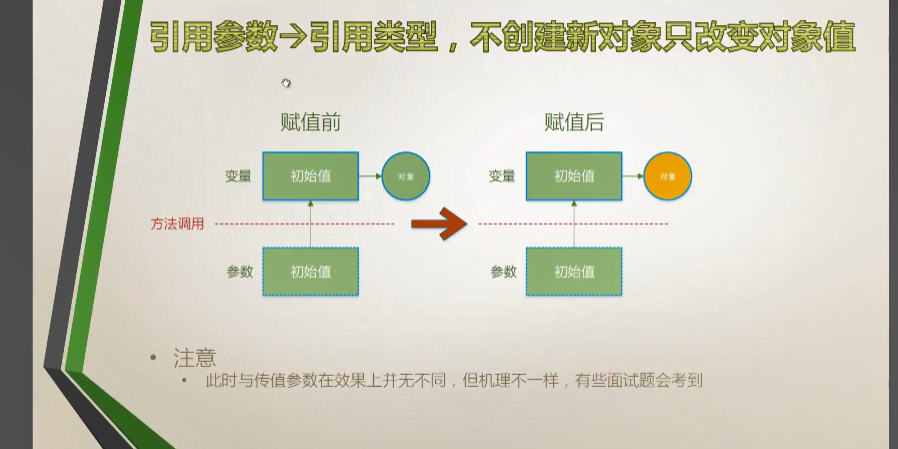
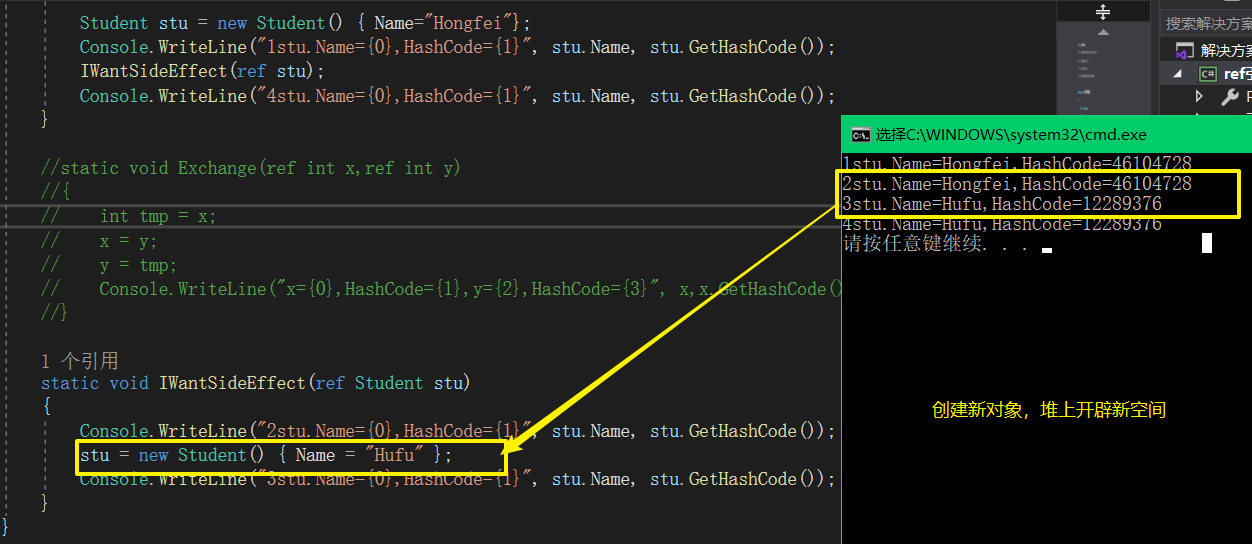
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student() { Name="Hongfei"};
SomeSideEffect(ref stu);
Console.WriteLine("4stu.Name={0},HashCode={1}", stu.Name, stu.GetHashCode());
}
static void SomeSideEffect(ref Student stu)
{
Console.WriteLine("=======================");
Console.WriteLine("2stu.Name={0},HashCode={1}", stu.Name, stu.GetHashCode());
stu.Name = "Hufu";
Console.WriteLine("2stu.Name={0},HashCode={1}", stu.Name, stu.GetHashCode());
Console.WriteLine("=======================");
}
}
result:
=======================
2stu.Name=Hongfei,HashCode=46104728
2stu.Name=Hufu,HashCode=46104728
=======================
4stu.Name=Hufu,HashCode=46104728
hashcode never change
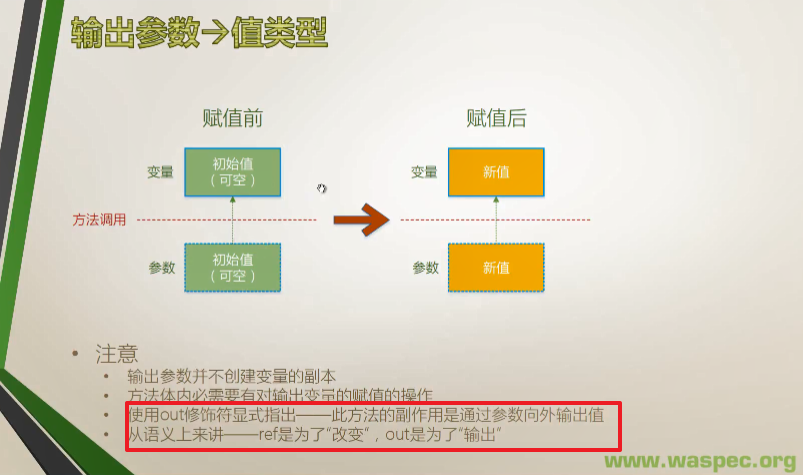
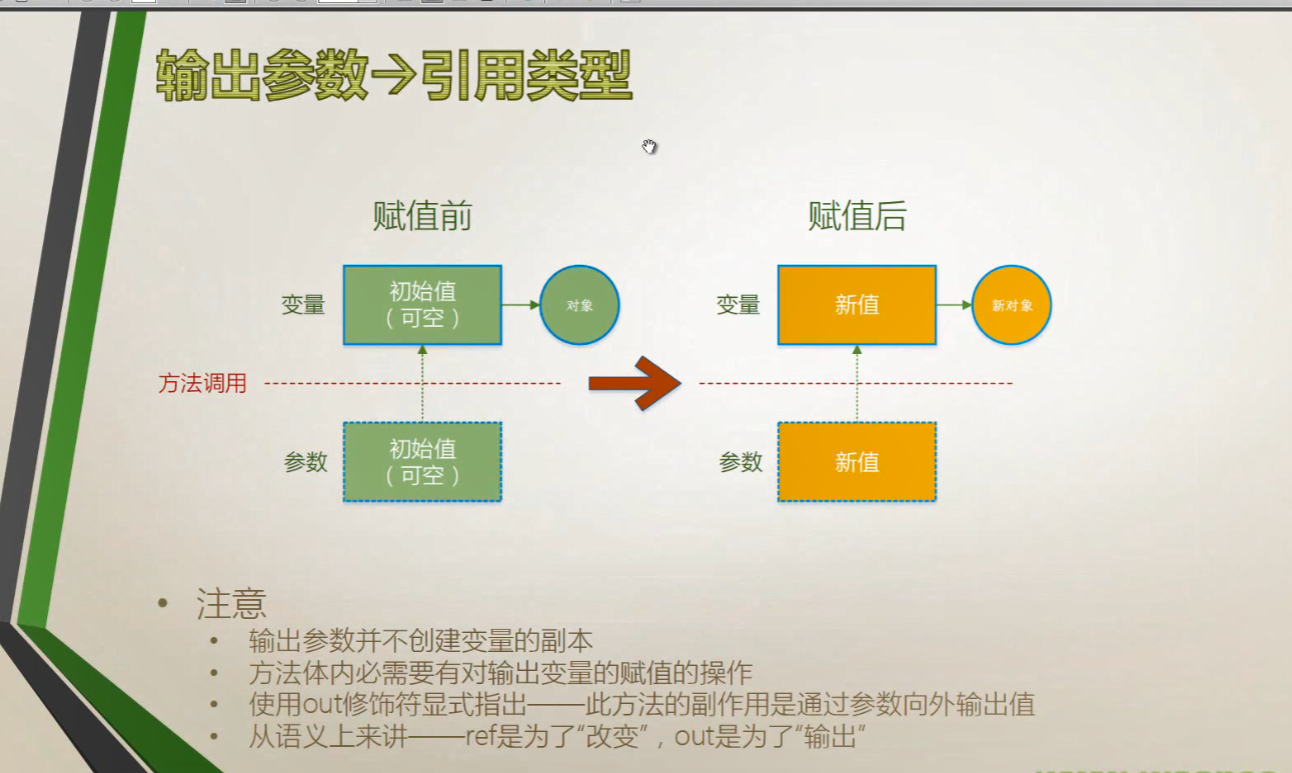
3、输出参数 out
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("input first number:");
string str1= Console.ReadLine();
double x = 0;
bool result1= double.TryParse(str1, out x);
if (result1 == false)
{
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("input second number:");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
double y = 0;
bool result2 = double.TryParse(str2, out y);
if (result2 == false)
{
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}",x,y,x+y);
}
自定义out参数的函数
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("input first number:");
string str1 = Console.ReadLine();
double x = 0;
bool result1 =DoubleParse.TryParse(str1, out x);
if (result1 == false)
{
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("input second number:");
string str2 = Console.ReadLine();
double y = 0;
bool result2 = DoubleParse.TryParse(str2, out y);
if (result2 == false)
{
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}", x, y, x + y);
double sum;
double sub;
DoubleParse.AddReduce(x, y, out sum, out sub);
Console.WriteLine("和:{0},差:{1}", sum, sub);
}
//static bool DoublePrase(string str, out double x)
//{
// try
// {
// x = double.Parse(str);
// return true;
// }
// catch
// {
// x = 0;
// return false;
// }
//}
}
class DoubleParse
{
public static bool TryParse(string str,out double x)
{
try
{
x = double.Parse(str);
return true;
}
catch
{
x = 0;
return false;
}
}
public static void AddReduce(double a,double b,out double sum,out double sub)
{
sum = a + b;
sub = a - b;
}
}
引用类型
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x= Sum(1,2,3);
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
static int Sum(params int[] intArray)
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var item in intArray)
{
sum += item;
}
return sum;
}
4、数组参数params
- 只能有一个,且是形参列表最后一个
- 过程为:自动创建一个数组,并将变量赋值,最后传递给方法
string str = "Hufu,luofei;laobao.zhu";
string[] str1=str.Split(';', '.', ',');//先创建char[],char[0]=';',char[1]='.',char[2]=','
foreach (var result in str1)
{
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
定义一维数组
//没有初始值
int[] a1=new int[4];
//给定初始值
int[] s2=new int[]{1,2,3};
//静态初始化
int[] a2={1,2,3,4}
交错数组
int[][] a = new int[3][];
a[0] = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 };
a[1] = new int[] { 1, 2 };
a[2] = new int[] { 1 };
foreach (var item in a[0])
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
5、具名参数

static void Main(string[] args)
{
OutPut(age: 22,name:"hufu");
}
static void OutPut(string name,int age)
{
Console.WriteLine("name:{0},age:{1}", name, age);
}
6、可选参数
可写可不写
static void Main(string[] args)
{
OutPut();
}
static void OutPut(string name="Hufu",int age=22)
{
Console.WriteLine("name:{0},age:{1}", name, age);
}
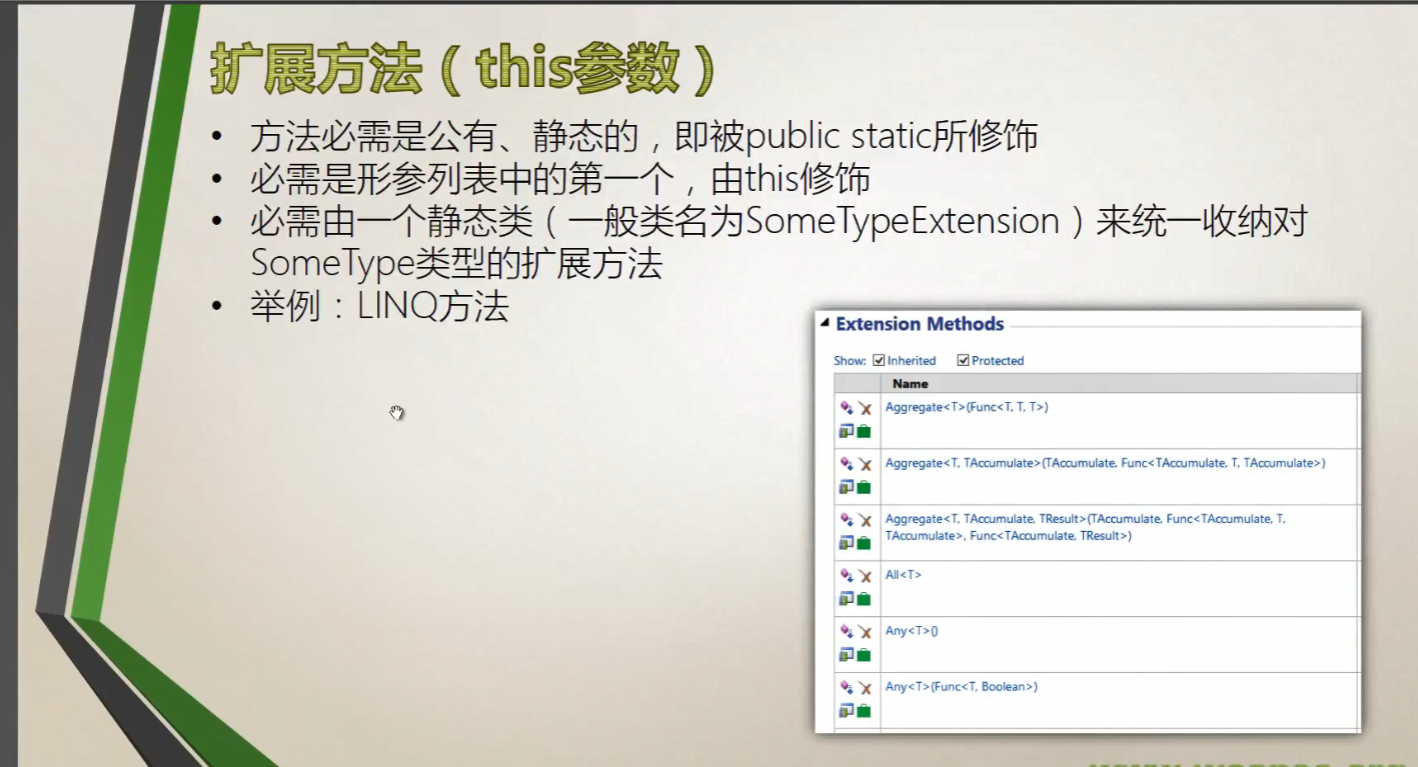
7、扩展方法(this参数)
静态类:
静态类不能实例化,不能用作类型,而且仅可以包含静态成员。只有静态类才能包含扩展方法的声明(第 10.6.9 节)。静态类的行为就好像既是密封的又是抽象的。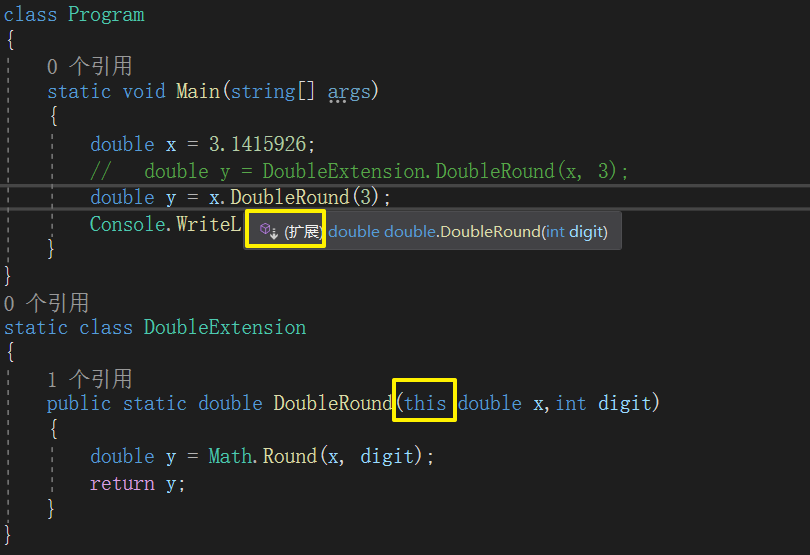
linq enumerable类中可多扩展方法了