到目前为止,如果要把数据从服务端发送到设备端,只能使用指令下发的方式,这种方式相当于是”Push”的模式,服务端主动推数据到设备端。这一课,我们来实现服务端到设备数据传输的另一种方式——“Pull”模式:设备数据请求。
设备数据请求
想较于之前的 Push 模式,数据的传输是由服务端触发的,Pull 模式是指由设备端主动向服务端请求数据(这个服务端包括业务系统和 IotHub)。
我在这里举一个很有意义的例子,比如:业务系统通过 Push 的方式把一些本地数据同步到设备了,过了一段时间以后设备的存储坏掉了,经过维修,换了一块新的存储,但是原有的本地数据已经丢失,这时候设备可以用 Pull 方式再把本地数据从业务系统主动同步过来。
可以看到,数据同步这个功能需要提供 Push 和 Pull 这两种语义的操作才完整。
在 IotHub 里,一次设备主动数据请求的流程如下: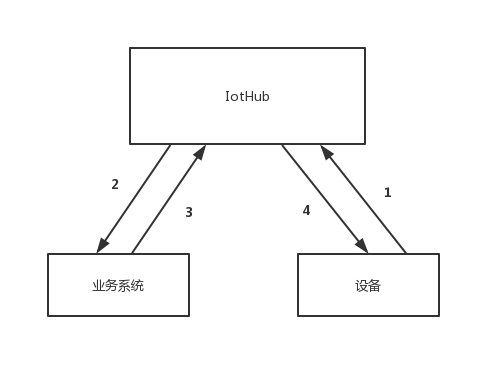
- 设备发送数据请求到特定的主题:get/:ProductName/:DeviceName/:Resource/:MessageID,其中 Resource 代表要请求的资源名称。
- IotHub 将请求的内容,包括 DeviceName 和 Resource 已经请求的 Payload 通过 RabbmitMQ 发送给业务系统。
- 业务系统调用指令下发接口,请求 IotHub 将相应的数据下发给设备。
- IotHub 将数据用指令的方式下发给设备,指令名称以及设备是否需要回复这个指令,由设备和业务系统约定,IotHub 不做强制要求。
我们可以把这个流程看是一次类似于 HTTP Get 操作,主题中的 Resource 相当于是 Query 的 URL,DeviceName 和消息的 Payload 相当于是查询参数,而 ProductName 相当于 Host,指示 IotHub 把请求路由到对应的业务系统。
设备端实现
设备端只需要实现向对应的主题发送消息,对业务系统下发的数据使用之前处理指令的流程就可以了:
//IotHub_Device/sdk/iot_device.jssendDataRequest(resource, payload = "") {if (this.client != null) {var topic = `get/${this.productName}/${this.deviceName}/${resource}/${new ObjectId().toHexString()}`this.client.publish(topic, payload, {qos: 1})}}
然后将新的主题加入设备的 ACL 列表:
//IotHub_Server/models/device.jsdeviceSchema.methods.getACLRule = function () {const publish = [`upload_data/${this.product_name}/${this.device_name}/+/+`,`update_status/${this.product_name}/${this.device_name}/+`,`cmd_resp/${this.product_name}/${this.device_name}/+/+/+`,`rpc_resp/${this.product_name}/${this.device_name}/+/+/+`,`get/${this.product_name}/${this.device_name}/+/+`]...}
你需要重新注册一个设备或者手动更新已注册设备存储在 MongoDB 的 ACL 列表。
服务端实现
服务端需要解析新的主题名并将相应的数据转发到业务系统就可以了:
//IotHub_Server/services/message_service.jsstatic dispatchMessage({topic, payload, ts} = {}) {...var dataRequestTopicRule = "get/:productName/:deviceName/:resource/:messageId"const dataRequestRegx = pathToRegexp(dataRequestTopicRule)var result = null;...} else if((result = dataRequestRegx.exec(topic)) != null){this.checkMessageDuplication(result[4], function (isDup) {if(!isDup){MessageService.handleDataRequest({productName: result[1],deviceName: result[2],resource: result[3],payload: payload})}})}}
Data Request 相关的数据将会被发送到名为”iothub.events.data_request”的 RabbitMQ Exchange 中,Exchange 的类型为 Direct,Routing key 为ProductName:
//IotHub_Server/services/message_service.jsstatic handleDataRequest({productName, deviceName, resource, payload}) {NotifyService.notifyDataRequest({productName: productName,deviceName: deviceName,resource: resource,payload: payload})}
//IotHub_Server/services/notify_service.jsstatic notifyDataRequest({productName, deviceName, resource, payload}){var data = bson.serialize({device_name: deviceName,resource: resource,payload: payload})if(currentChannel != null){currentChannel.publish(dataRequestRespExchange, productName, data)}}
这样设备端和服务端的代码就都完成了,接下来我们写一点代码来验证一下。
代码联调
这里我们模拟一个设备向业务系统请求当前天气数据的场景,首先需要实现业务系统的代码。当收到设备 Resource 为”weather”的数据请求时,会下发名为”weather”的指令,指令数据为{temp: 25, wind: 4}:
//IotHub_Server/samples/resp_to_data_request.jsrequire('dotenv').config({path: "../.env"})const bson = require('bson')const request = require("request")var amqp = require('amqplib/callback_api');var exchange = "iothub.events.data_request"amqp.connect(process.env.RABBITMQ_URL, function (error0, connection) {if (error0) {console.log(error0);} else {connection.createChannel(function (error1, channel) {if (error1) {console.log(error1)} else {channel.assertExchange(exchange, 'direct', {durable: true})var queue = "iotapp_data_request";channel.assertQueue(queue, {durable: true})channel.bindQueue(queue, exchange, process.env.TARGET_PRODUCT_NAME)channel.consume(queue, function (msg) {var data = bson.deserialize(msg.content)if (data.resource == "weather") {console.log(`received request for weather from ${data.device_name}`)request.post(`http://127.0.0.1:3000/devices/${process.env.TARGET_PRODUCT_NAME}/${data.device_name}/command`, {form: {command: "weather",data: JSON.stringify({temp: 25, wind: 4}),}}, function (error, response, body) {if (error) {console.log(error)} else {console.log('statusCode:', response && response.statusCode);console.log('body:', body);}})}channel.ack(msg)})}});}});
在设备端发起对应的数据请求,并处理来自业务系统的相应指令:
//IotHub_Device/samples/send_data_request.js
var IotDevice = require("../sdk/iot_device")
require('dotenv').config()
var path = require('path');
var device = new IotDevice({
productName: process.env.PRODUCT_NAME,
deviceName: process.env.DEVICE_NAME,
secret: process.env.SECRET,
clientID: path.basename(__filename, ".js"),
storePath: `../tmp/${path.basename(__filename, ".js")}`
})
device.on("online", function () {
console.log("device is online")
})
device.on("command", function (command, data) {
if (command == "weather") {
console.log(`weather: ${data.toString()}`)
device.disconnect()
}
})
device.connect()
device.sendDataRequest("weather")
首先运行 resp_to_data_request.js,再运行 send_data_request.js,我们可以观察到以下输出:
## resp_to_data_request.js
received request for weather from yUNNHoQzv
## send_data_request.js
device is online
weather: {"temp":25,"wind":4}
这样,IotHub 的设备主动数据请求功能能就实现了。
这一节我们实现了 IotHub 的设备数据请求功能,接下来,我们基于这个功能实现 IotHub 的 NTP 服务。

