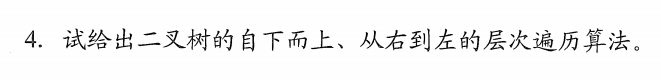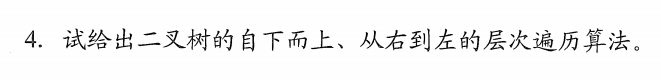
/* 试给出二叉树的自下而上、从右到左的层次遍历算法 分析: 我们只需要在层次遍历的基础上加入栈的使用,我们每次出队后的数据将其入栈,队列空了时,再去依次访问栈中元素,即可达到要求*/struct biTree { char data; struct biTree *lchild; struct biTree *rchild;};struct Squeue { biTree *arr; int front, rear;};struct Stack { biTree *arr; int len; int top;};#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>void levelOrder2(biTree *T, Squeue *sq, int maxSize) { struct Stack *s = (struct Stack *)malloc(sizeof(struct Stack)); struct biTree *p = T; struct biTree *r = (struct biTree *)malloc(sizeof(struct biTree)); bool enQueue(Squeue *, biTree *, int); bool isEmpty(Squeue *); bool deQueue(Squeue *, biTree **, int); Stack *createStack(int); bool push(Stack *,biTree *); bool empty(Stack *); biTree *top(Stack *); bool pop(Stack *); s = createStack(maxSize); enQueue(sq, p, maxSize); while (!isEmpty(sq)) { deQueue(sq, &r, maxSize); push(s,r); if (r->lchild)enQueue(sq, r->lchild, maxSize); if (r->rchild)enQueue(sq, r->rchild, maxSize); } while (!empty(s)) { r = top(s); printf("%c ",r->data); pop(s); }}int main() { int count = 0; struct biTree *T = (struct biTree *)malloc(sizeof(struct biTree)); struct Squeue *sq = (struct Squeue *)malloc(sizeof(struct Squeue)); biTree *create(biTree *); void nodeNum(biTree *, int *); Squeue *createQueue(int); T = create(T);//创建一颗二叉树 nodeNum(T, &count);//统计二叉树节点个数 sq = createQueue(count); levelOrder2(T, sq, count); return 0;}